Oral cancer
| Oral cancer | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Cancer of the lip, oral cavity and pharynx, mouth cancer, tongue cancer, cancer of the lips, oral cavity and pharynx[1] |
 | |
| Oral cancer on the side of the tongue, a common site along with the floor of the mouth | |
| Specialty | Oncology, oral and maxillofacial surgery, ENT surgery |
| Symptoms | Persistent rough white or red patch in the mouth lasting longer than 2 weeks, ulceration, lumps/bumps in the neck, pain, loose teeth, difficulty swallowing |
| Risk factors | Smoking, alcohol, HPV infection, sun exposure, chewing tobacco |
| Diagnostic method | Tissue biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Non-squamous cell carcinoma oral cancer, salivary gland tumors, benign mucosal disease |
| Prevention | Avoiding risk factors,[2] HPV vaccination[3] |
| Treatment | Surgery, radiation, chemotherapy |
| Prognosis | Five-year survival ~ 65% (US 2015)[4] |
| Frequency | 355,000 new cases (2018)[5] |
| Deaths | 177,000 (2018)[5] |
Oral cancer, also known as oral cavity cancer, tongue cancer or mouth cancer, is a cancer of the lining of the lips, mouth, or upper throat.[6] In the mouth, it most commonly starts as a painless red or white patch, that thickens, gets ulcerated and continues to grow. When on the lips, it commonly looks like a persistent crusting ulcer that does not heal, and slowly grows.[7] Other symptoms may include difficult or painful swallowing, new lumps or bumps in the neck, a swelling in the mouth, or a feeling of numbness in the mouth or lips.[8]
Risk factors include tobacco and alcohol use.[9][10] Those who use both alcohol and tobacco have a 15 times greater risk of oral cancer than those who use neither.[11] Other risk factors include betel nut chewing[12] and sun exposure on the lip.[13] HPV infection may play a limited role in some oral cavity cancers.[14] Oral cancer is a subgroup of head and neck cancers.[6] Diagnosis is made by sampling (biopsy) of the lesion, followed by an imaging workup (called staging) which can include CT scan, MRI, PET scan to determine the local extension of the tumor, and if the disease has spread to distant parts of the body.
Oral cancer can be prevented by avoiding tobacco products, limiting alcohol use, sun protection on the lip, HPV vaccination, and avoidance of betel nut chewing. Treatments used for oral cancer can include a combination of surgery (to remove the tumor and regional lymph nodes), radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or targeted therapy. The types of treatments will depend on the size, locations, and spread of the cancer taken into consideration with the general health of the person.[7]
In 2018, oral cancer occurred globally in about 355,000 people, and resulted in 177,000 deaths.[5] Between 1999 and 2015 in the United States, the rate of oral cancer increased 6% (from 10.9 to 11.6 per 100,000). Deaths from oral cancer during this time decreased 7% (from 2.7 to 2.5 per 100,000).[15] Oral cancer has an overall 5 year survival rate of 65% in the United States as of 2015.[4] This varies from 84% if diagnosed when localized, compared to 66% if it has spread to the lymph nodes in the neck, and 39% if it has spread to distant parts of the body.[4] Survival rates also are dependent on the location of the disease in the mouth.[16]
Signs and symptoms
[edit]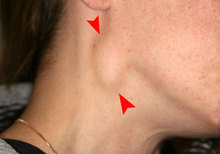

The signs and symptoms of oral cancer depend on the location of the tumor but are generally thin, irregular, red and/or white patches in the mouth. The classic warning sign is a persistent rough patch with ulceration, and a raised border that is minimally painful. On the lip, the ulcer is more commonly crusting and dry, and in the pharynx it is more commonly a mass. It can also be associated with loose teeth, bleeding gums, persistent ear ache, a feeling of numbness in the lip and chin, or swelling.[17] When the cancer extends to the oropharynx (back of the throat), there can also be difficulty swallowing.
Typically, the lesions cause very little pain until they become larger and then are associated with a local pain, burning sensation or ear ache (referred otalgia).[18] As the lesion spreads to the lymph nodes of the neck, a painless, hard mass will develop. If it spreads elsewhere in the body, general aches can develop, most often due to bone metastasis.[18]
Causes
[edit]The main causes of oral cancer are alcohol and tobacco (smoked or chewed). The risk is especially high when a person regularly uses both. The more is consumed of either the higher the risk of developing oral cancer. Like all environmental factors, the rate at which cancer will develop is dependent on the dose, frequency and method of application of the carcinogen (the substance that is causing the cancer).[19][20] Aside from tobacco and alcohol, other carcinogens for oral cancer include viruses (particularly HPV 16 and 18), radiation, and UV light.[7]
Tobacco
[edit]Tobacco is the greatest single cause of oral and pharyngeal cancer. Using tobacco increases the risk of oral cancer by 3 to 6 times[20][9] and is responsible for around 40% of all oral cancers.[21] Smokeless tobacco (including chewing tobacco, snuff, snus) also causes oral cancer.[22][23][24] Cigar and pipe smoking are also important risk factors.[25]
The use of electronic cigarettes may also lead to the development of head and neck cancers due to the substances like propylene glycol, glycerol, nitrosamines, and metals contained therein, which can cause damage to the airways.[26]
Use of marijuana has currently not been shown to be associated with head and neck cancer risk.[27]
Alcohol
[edit]Drinking alcohol is a major cause of oral cancer.[28][29] It was responsible for 20% of global oral cancer cases in 2020.[30] The more alcohol is consumed regularly the higher the risk, but light to moderate drinking still somewhat increases the chances of getting oral cancer.[31] The risk is especially high when both alcohol and tobacco are used.[32]
It has been controversial if the use of alcohol-based mouthwashes increases oral cancer risk.[33] As of 2024, there is some limited evidence supporting that the use of mouthwashes containing alcohol can increase the occurrence of oral cancer in some cases.[34] There are complex interactions between alcohol content, usage patterns, reduction of oral pathogens, poor oral hygiene, smoking, and drinking which make any broad conclusion very tenuous in the absence of rigorously controlled studies.[35][34] In subgroup analyses, various combinations of smoking, drinking alcohol, poor oral hygiene, and using mouthwash several times a day for 35 years or more significantly increased risk.[36] Although alcohol is necessary to dissolve some active antimicrobial agents, Rao et al. advise reducing the alcohol content of mouthwashes if possible.[34]
Human papillomavirus
[edit]Infection with human papillomavirus (HPV), particularly type 16, is a cause of oropharyngeal cancer (tonsils, base of tongue).[37] However, its role in the genesis of oral cavity cancers is a matter of debate.[14] A 2023 meta-analysis observed that the HPV was present 6% of all oral cavity cancer cases, however without establishing a role of this virus in the oncogenesis of these tumors. The authors even reported that some base of tongue tumors may have been misclassified as oral cavity tumors, therefore mistakenly increasing the rate of HPV-positive oral cavity cancers.[38]
Betel nut
[edit]
Chewing betel quid (paan) and Areca nut-based products is known to be a strong risk factor for developing oral cancer even in the absence of tobacco. It doubles the risk of oral cancer 2.1 times[20] and when chewed with additional tobacco in its preparation (like in gutka), there is an even higher risk.[39]
In India where such practices are common, oral cancer represents up to 40% of all cancers, compared to just 4% in the UK.
Stem cell transplantation
[edit]People after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) are at a higher risk for oral cancer. Post-HSCT oral cancer may have more aggressive behavior with poorer prognosis, when compared to oral cancer in people not treated with HSCT.[40] This effect is supposed to be owing to the continuous lifelong immune suppression and chronic oral graft-versus-host disease.[40]
This HPV16 (along with HPV18) is the same virus responsible for the vast majority of all cervical cancers and is the most common sexually transmitted infection. Risk factors for developing HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancer include multiple sexual partners, anal and oral sex and a weak immune system.[41]
Premalignant lesions
[edit]
A premalignant (or precancerous) lesion is defined as "a benign, morphologically altered tissue that has a greater than normal risk of malignant transformation." There are several different types of premalignant lesion that occur in the mouth. Some oral cancers begin as white patches (leukoplakia), red patches (erythroplakia) or mixed red and white patches (erythroleukoplakia or "speckled leukoplakia"). Other common premalignant lesions include oral submucous fibrosis and actinic cheilitis.[42] In the Indian subcontinent oral submucous fibrosis is very common due to betel nut chewing. This condition is characterized by limited opening of mouth and burning sensation on eating of spicy food. This is a progressive lesion in which the opening of the mouth becomes progressively limited, and later on even normal eating becomes difficult.
Pathophysiology
[edit]Oral squamous cell carcinoma is the end product of an unregulated proliferation of mucous basal cells. A single precursor cell is transformed into a clone consisting of many daughter cells with an accumulation of altered genes called oncogenes. What characterizes a malignant tumor over a benign one is its ability to metastasize. This ability is independent of the size or grade of the tumor (often seemingly slow growing cancers like the adenoid cystic carcinoma can metastasis widely). It is not just rapid growth that characterizes a cancer, but their ability to secrete enzymes, angiogeneic factors, invasion factors, growth factors and many other factors that allow it to spread.[7]
The full causal relation between alcohol consumption and the elevated risk of cancer remains unclear, but acetaldehyde plays a major role.[43] Immediately after alcohol consumption, there are elevated levels of acetaldehyde in saliva, peaking after about 2 minutes. Acetaldehyde is produced by the oral microbiome, and also by enzymes in the oral mucosa, saliva glands, and liver. It is also naturally present in alcoholic beverages. Of these, the microbiome is the major contributor, accounting for at least half of the acetaldehyde present. Poor oral hygiene, smoking, and heavy drinking induce an increase in acetaldehyde-producing bacteria in the mouth. Many species of bacteria contribute to acetaldehyde production and their epidemiological significance is not known. The acetaldehyde reacts with oral epithelial cells, inducing DNA modifications, which can lead to mutations and cancer development. The ability to metabolize acetaldehyde in the mouth is limited, so it may remain in the saliva for hours. L-cysteine tablets may be used to decrease acetaldehyde exposure in the oral cavity.[44]
Diagnosis
[edit]

Diagnosis of oral cancer is completed for (1) initial diagnosis, (2) staging, and (3) treatment planning. A complete history, and clinical examination is first completed, then a wedge of tissue is cut from the suspicious lesion for tissue diagnosis. This might be done with scalpel biopsy, punch biopsy, fine or core needle biopsy. In this procedure, the surgeon cuts all, or a piece of the tissue, to have it examined under a microscope by a pathologist.[45] Brush biopsies are not considered accurate for the diagnosis of oral cancer.[46] Salivary biomarkers are also being under investigation with emerging outcomes and could potentially be used as a non-invasive diagnostic tool in the future.[47]
With the first biopsy, the pathologist will provide a tissue diagnosis (e.g. squamous cell carcinoma), and classify the cell structure. They may add additional information that can be used in staging, and treatment planning, such as the mitotic rate, the depth of invasion, and the HPV status of the tissue.
After the tissue is confirmed cancerous, other tests will be completed to:
- better assess the size of the lesion (CT scan, MRI or PET scan with 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)),[45]: 143
- look for other cancers in the upper aerodigestive tract (which may include endoscopy of the nasal cavity/pharynx, larynx, bronchus, and esophagus called panendoscopy or quadoscopy),
- spread to the lymph nodes (CT scan) or
- spread to other parts of the body (chest X-ray, nuclear medicine).
Other, more invasive tests, may also be completed such as fine needle aspiration, biopsy of lymph nodes, and sentinel node biopsy. When the cancer has spread to lymph nodes, their exact location, size, and spread beyond the capsule (of the lymph nodes) needs to be determined, as each can have a significant impact on treatment and prognosis. Small differences in the pattern of lymph node spread, can have a significant impact on treatment and prognosis. Panendoscopy may be recommended, because the tissues of the entire upper aerodigestive tract are generally affected by the same carcinogens, so other primary cancers are a common occurrence.[48][49]
From these collective findings, taken in consideration with the health and desires of the person, the cancer team develops a plan for treatment. Since most oral cancers require surgical removal, a second set of histopathologic tests will be completed on any tumor removed to determine the prognosis, need for additional surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, immunotherapy, or other interventions.
Classification
[edit]Oral cancer is a subgroup of head and neck cancers which includes those of the oropharynx, larynx, nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses, salivary glands, and thyroid gland. Oral melanoma, while part of head and neck cancers is considered separately.[6] Other cancers can occur in the mouth (such as bone cancer, lymphoma, or metastatic cancers from distant sites) but are also considered separately from oral cancers.[6]
Staging
[edit]Oral cancer staging is an assessment of the degree of spread of the cancer from its original source.[50] It is one of the factors affecting both the prognosis and the potential treatment of oral cancer.[50]
The evaluation of squamous cell carcinoma of the mouth and pharynx staging uses the TNM classification (tumor, node, metastasis). This is based on the size of the primary tumor, lymph node involvement, and distant metastasis.[51]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

TMN evaluation allows the person to be classified into a prognostic staging group;[51]
| When T is... | And N is... | And M is... | Then the stage group is... |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tis | N0 | M0 | 0 |
| T1 | N0 | M0 | I |
| T2 | N0 | M0 | II |
| T3 | N0 | M0 | III |
| T1,T2,T3 | N1 | M0 | III |
| T4a | N0,N1 | M0 | IVA |
| T1,T2,T3,T4a | N2 | M0 | IVA |
| Any T | N3 | M0 | IVB |
| T4b | Any N | M0 | IVB |
| Any T | Any N | M1 | IVC |
Screening
[edit]The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) in 2013 stated evidence was insufficient to determine the balance of benefits and harms of screening for oral cancer in adults without symptoms by primary care providers.[52] The American Academy of Family Physicians comes to similar conclusions while the American Cancer Society recommends that adults over 20 years who have periodic health examinations should have the oral cavity examined for cancer.[52] The American Dental Association recommends that providers remain alert for signs of cancer during routine examinations.[52]
There are a variety of screening devices such as toluidine blue, brush biopsy, or fluorescence imaging, however, there is no evidence that routine use of these devices in general dental practice is helpful.[53] Potential risks of using screening devices include false positives, unnecessary surgical biopsies, and a financial burden.[53] Micronuclei assays can help in early detection of pre-malignant and malignant lesions, thereby improving survival and reducing morbidity associated with treatment.[medical citation needed]
There has also been research showing potential in using oral cytology as a diagnostic test for oral cancer instead of traditional biopsy techniques. In oral cytology, a brush is used to take some cells from the suspected lesion/area and these are sent to a laboratory for examination.[54] This can be much less invasive and painful than a scalpel biopsy for the patient, however, there needs to be further research before oral cytology can be considered as an effective routine screening tool when compared to biopsies.[54]
Management
[edit]
Oral cancer (squamous cell carcinoma) is usually treated with surgery alone, or in combination with adjunctive therapy, including radiation, with or without chemotherapy.[45]: 602 With small lesions (T1), surgery or radiation have similar control rates, so the decision about which to use is based on functional outcome, and complication rates.[45]
Surgery
[edit]In most centres, removal of squamous cell carcinoma from the oral cavity and neck is achieved primarily through surgery. This also allows a detailed examination of the tissue for histopathologic characteristics, such as depth, and spread to lymph nodes that might require radiation or chemotherapy. For small lesions (T1–2), access to the oral cavity is through the mouth. When the lesion is larger, involves the bone of the maxilla or mandible, or access is limited due to mouth opening, the upper or lower lip is split, and the cheek pulled back to give greater access to the mouth.[45] When the tumor involves the jaw bone, or when surgery or radiation will cause severe limited mouth opening, part of the bone is also removed with the tumor.
Management of the neck
[edit]
Spread of cancer from the oral cavity to the lymph nodes of the neck has a significant effect on survival. Between 60 and 70% of people with early stage oral cancer will have no lymph node involvement of the neck clinically, but 20–30% of those people (or up to 20% of all those affected) will have clinically undetectable spread of cancer to the lymph nodes of the neck (called occult disease).
The management of the neck is crucial, since spread to it reduces the chance of survival by 50%.[55] If there is evidence of lymph node involvement of the neck, during the diagnostic phase, then a modified radical neck dissection is generally performed. Where the neck lymph nodes have no evidence of involvement clinically, but the oral cavity lesion is high risk for spread (e.g. T2 or above lesions), then a neck dissection of the lymph nodes above the level of the omohyoid muscle may be completed. T1 lesions that are 4 mm or greater in thickness have a significant risk of spread to neck nodes. When disease if found in the nodes after removal (but not seen clinically) the recurrence rates is 10–24%. If post-operative radiation is added, the failure rate is 0–15%. When lymph nodes are clinically found during the diagnosis phase, and radiation is added post-operative, disease control is >80%.[56]
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy
[edit]
Chemotherapy and radiotherapy are most often used, as an adjunct to surgery, to control oral cancer that is greater than stage 1, or has spread to either regional lymph nodes or other parts of the body.[45] Radiotherapy alone can be used instead of surgery, for very small lesions, but is generally used as an adjunct when lesions are large, cannot be completely removed, or have spread to the lymph nodes of the neck. Chemotherapy is useful in oral cancers when used in combination with other treatment modalities such as radiation therapy but it is not used alone as a monotherapy. When a cure is unlikely, it can also be used to extend life and can be considered palliative but not curative care.[57]
Monoclonal antibody therapy (with agents such as cetuximab) have been shown to be effective in the treatment of squamous cell head and neck cancers, and are likely to have an increasing role in the future management of this condition when used in conjunction with other established treatment modalities, although it is not a replacement for chemotherapy in head and neck cancers.[58][57] Likewise, molecularly targeted therapies and immunotherapies may be effective for the treatment of oral and oropharyngeal cancers. Adding epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody (EGFR mAb) to standard treatment may increase survival, keeping the cancer limited to that area of the body and may decrease reappearance of the cancer.[58]
Rehabilitation
[edit]Following treatment, rehabilitation may be necessary to improve movement, chewing, swallowing, and speech. Speech and language pathologists may be involved at this stage. Treatment of oral cancer will usually be by a multidisciplinary team, with treatment professionals from the realms of radiation, surgery, chemotherapy, nutrition, dentistry, and even psychology all possibly involved with diagnosis, treatment, rehabilitation, and care. Due to the location of oral cancer, there may be a period where the person requires a tracheotomy and feeding tube.
Prognosis
[edit]Survival rates for oral cancer depend on the precise site and the stage of the cancer at diagnosis. Overall, 2011 data from the SEER database shows that survival is around 57% at five years when all stages of initial diagnosis, all genders, all ethnicities, all age groups, and all treatment modalities are considered. Survival rates for stage 1 cancers are approximately 90%, hence the emphasis on early detection to increase survival outcome for people. Similar survival rates are reported from other countries, such as Germany.[59]
Epidemiology
[edit]
Globally, it newly occurred in about 355,000 people and resulted in 177,000 deaths in 2018.[5] Of these 355,000, about 246,000 are males and 108,000 are females.[5]
In 2013, oral cancer resulted in 135,000 deaths, up from 84,000 deaths in 1990.[60] Oral cancer occurs more often in people from lower and middle income countries.[61]
Europe
[edit]Europe places second-highest after Southeast Asia among all continents for age-standardised rate (ASR) specific to oral and oropharyngeal cancer. It is estimated that there were 61,400 cases of oral and lip cancer within Europe in 2012. Hungary recorded the highest number of mortality and morbidity due to oral and pharyngeal cancer among all European countries while Cyprus reported the lowest numbers [62]
United Kingdom
[edit]British Cancer Research found 2,386 deaths due to oral cancer in 2014; while most oral cancer cases are diagnosed in older adults between 50 and 74 years old, this condition can affect the young as well;[63] 6% of people affected by oral cancer are under 45 years of age.[64] The United Kingdom is 16th-lowest for males and 11th-highest for females for oral cancer incidence among Europe. Additionally, there is a regional variability within the United Kingdom, with Scotland and northern England having higher rates than southern England. The same analysis applies to lifetime risk of developing oral cancer, as in Scotland it is 1.84% in males and 0.74% in females, higher than the rest of the UK, being 1.06% and 0.48%, respectively.
Oral cancer is the sixteenth most-common cancer in the United Kingdom (around 6,800 people were diagnosed with oral cancer in the United Kingdom in 2011), and it is the 19th most-common cause of cancer death (around 2,100 people died from the disease in 2012).[64]
Northern Europe
[edit]The highest incidence of oral and pharyngeal cancer was recorded in Denmark, with age-standardised rates per 100,000 of 13.0, followed by Lithuania (9.9) and the United Kingdom (9.8).[62] Lithuania reported the highest incidence in men while Denmark reported the highest in women. The highest rates for mortality in 2012 were reported in Lithuania (7.5), Estonia (6.0), and Latvia (5.4).[62] Incidence of oral cancer in young adults (ages 20–39 years old) in Scandinavia has reportedly risen approximately 6-fold between 1960 and 1994[65] The high incidence rate of oral and pharyngeal cancer in Denmark could be attributed to their higher alcohol intake than citizens of other Scandinavian countries and low intake of fruits and vegetables in general.
Eastern Europe
[edit]Hungary (23.3), Slovakia (16.4), and Romania (15.5) reported the highest incidences of oral and pharyngeal cancer.[62] Hungary also recorded the highest incidence in both genders as well as the highest mortality rates in Europe.[62] It is ranked third globally for cancer mortality rates.[66] Cigarette smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, inequalities in the care received by people with cancer, and gender-specific systemic risk factors have been determined as the leading causes for the high morbidity and mortality rates in Hungary.[67][68][69][70]
Western Europe
[edit]The incidence rates of oral cancer in western Europe found France, Germany and Belgium to be highest. The ASRs (per 100,000) were 15.0, 14.6, and 14.1, respectively. When filtered by gender category, the same countries rank top 3 for male, however, in different order of Belgium (21.9), Germany (23.1), and France (23.1). France, Belgium, and the Netherlands rank highest for females, with ASRs 7.6, 7.0, and 7.0, respectively.[62]
Southern Europe
[edit]Incidence of oral and oropharyngeal cancers were recorded, finding Portugal, Croatia and Serbia to have highest rates (ASR per 100,000). These values are 15.4, 12, and 11.7, respectively.
North America
[edit]It is the eleventh-most-common cancer in the United States among males while in Canada and Mexico it is the twelfth and thirteenth-most-common cancer respectively. The ASIR for lip and oral cavity cancer among men in Canada and Mexico is 4.2 and 3.1, respectively.[71]
Of all the cancers, oral cancer attributes to 3% in males, opposed to 2% in women. New cases of oral cancer in US as of 2013, approximated almost 66,000 with almost 14000 attributed from tongue cancer, and nearly 12000 from the mouth, and the remainder from the oral cavity and pharynx. In the previous year, 1.6% of lip and oral cavity cancers were diagnosed, where the age-standardised incidence rate (ASIR) across all geographic regions of United States of America estimates at 5.2 per 100,000 population.[71]
In 2022, close to 54,000 Americans are projected to be diagnosed with oral or oropharyngeal cancer. 66% of the time, these will be found as late stage three and four disease. It will cause over 8,000 deaths. Of those newly diagnosed, only slightly more than half will be alive in five years. Similar survival estimates are reported from other countries. For example, five-year relative survival for oral cavity cancer in Germany is about 55%.[59] In the US oral cancer accounts for about 8 percent of all malignant growths.
Oral cancers overall risk higher in black males opposed to white males, however specific oral cancers-such as of the lip, have a higher risk in white males opposed to black males. Overall, rates of oral cancer between gender groups (male and female) seem to be decreasing, according to data from 3 studies.[72]
South America
[edit]The ASIR across all geographic regions of South America as of 2012 sits at 3.8 per 100,000 population where approximately 6,046 deaths have occurred due to lip and oral cavity cancer, where the age-standardized mortality rate remains at 1.4.[73]
In Brazil, however, lip and oral cavity cancer is the 7th most common cancer, with an estimated 6,930 new cases diagnosed in the year 2012. This number is rising and has an overall higher ASIR at 7.2 per 100,000 population whereby an approx 3000 deaths have occurred [73]
Rates are increasing across both males and females. As of 2017, almost 50000 new cases of oropharyngeal cancers will be diagnosed, with incidence rates being more than twice as high in men than women.[73]
Asia
[edit]Oral cancer is one of the most-common types of cancer in Asia due to its association with smoking (tobacco, bidi), betel quid and alcohol consumption. Regionally incidence varies with highest rates in South Asia, particularly India, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, and Afghanistan.[74] In South East Asia and Arab countries, although the prevalence is not as high, estimated incidences of oral cancer ranged from 1.6 to 8.6/ 100,000 and 1.8 to 2.13/ 100,000 respectively.[75][76] According to GLOBOCAN 2012, the estimated age-standardised rates of cancer incidence and mortality was higher in males than females. However, in some areas, specifically South East Asia, similar rates were recorded for both genders.[75] The average age of those diagnosed with oral squamous cell carcinoma is approximately 51–55.[74] In 2012, there were 97,400 deaths recorded due to oral cancer.[77]
India
[edit]Oral cancer is the third-most-common form of cancer in India with over 77 000 new cases diagnosed in 2012 (2.3:1 male to female ratio).[78] Studies estimate over five deaths per hour.[79] One of the reasons behind such high incidence might be popularity of betel and areca nuts, which are considered to be risk factors for development of oral cavity cancers.[80]
Africa
[edit]There is limited data for the prevalence of oral cancer in Africa. The following rates describe the number of new cases (for incidence rates) or deaths (for mortality rates) per 100 000 individuals per year.[77]
The incidence rate of oral cancer is 2.6 for both sexes. The rate is higher in males at 3.3 and lower in females at 2.0.[77]
The mortality rate is lower than the incidence rate at 1.6 for both sexes. The rate is again higher for males at 2.1 and lower for females at 1.3.[77]
Australia
[edit]The following rates describe the number of new cases or deaths per 100 000 individuals per year. The incidence rate of oral cancer is 6.3 for both sexes; this is higher in males at 6.8–8.8 and lower in females at 3.7–3.9.[81] The mortality rate is significantly lower than the incidence rate at 1.0 for both sexes. The rate is higher in males at 1.4 and lower in females at 0.6.[82] Table 1 provides age-standardised incidence and mortality rates for oral cancer based on the location in the mouth. The location 'other mouth' refers to the buccal mucosa, the vestibule and other unspecified parts of the mouth. The data suggests lip cancer has the highest incidence rate while gingival cancer has the lowest rate overall. In terms of mortality rates, oropharyngeal cancer has the highest rate in males and tongue cancer has the highest rate in females. Lip, palatal and gingival cancer have the lowest mortality rates overall.[82]
| Location | Incidence per 100 000 individuals per year | Mortality per 100 000 individuals per year | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Both sexes | Males | Females | Both sexes | Males | Females | |
| Lip | 5.3 | 8.4 | 2.4 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 |
| Tongue | 2.4 | 3.3 | 1.4 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 0.4 |
| Gingivae | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 |
| Floor of mouth | 0.9 | 1.4 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.1 |
| Palate | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Other Mouth | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Major salivary glands | 1.2 | 1.6 | 0.9 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.2 |
| Oropharynx | 1.9 | 3.0 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 1.2 | 0.3 |
Other animals
[edit]
Oral cancers are the fourth most common type seen in other animals in veterinary medicine, with older animals having higher chances of developing it.[83]
Dogs that are a breed that is at higher risk of developing oral cancer are more susceptible. Tumors that are found early in development can be removed by surgery, however some cases involve removing a part of the jaw. Chemotherapy is used following surgeries or to remove a tumor that cannot be accessed. Tumors that are caught when the cancer has already spread to other places of the body will result in the dog living for only 6-12 more months.[84]
The most common type of oral cancer seen in cats is squamous cell carcinoma. Due to tumors developing in hidden spots such as beneath the tongue, when the tumors in the cats mouth are caught it is often untreatable.[85] Risk factors include secondhand smoke, as the smoke settles on the fur which is ingested when cats groom, and potentially the over consumption of canned food and use of flea collars.[86]
References
[edit]- ^ Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, et al. (December 2012). "Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010". Lancet. 380 (9859): 2095–128. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0. hdl:10536/DRO/DU:30050819. PMC 10790329. PMID 23245604. S2CID 1541253.
- ^ "Oral Cavity, Pharyngeal, and Laryngeal Cancer Prevention". National Cancer Institute. 1 January 1980. Retrieved 5 June 2019.
- ^ "HPV Vaccine May Prevent Oral HPV Infection". National Cancer Institute. 5 June 2017. Retrieved 5 June 2019.
- ^ a b c "Cancer Stat Facts: Oral Cavity and Pharynx Cancer". NCI. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ^ a b c d e "Cancer today". gco.iarc.fr. Retrieved 9 June 2019.
- ^ a b c d Edge SB, et al. (American Joint Committee on Cancer) (2010). AJCC cancer staging manual (7th ed.). New York: Springer. ISBN 9780387884400. OCLC 316431417.
- ^ a b c d Marx RE, Stern D (2003). Oral and maxillofacial pathology : a rationale for diagnosis and treatment. Stern, Diane. Chicago: Quintessence Pub. Co. ISBN 978-0867153903. OCLC 49566229.
- ^ "Head and Neck Cancers". CDC. 2019-01-17. Retrieved 2019-03-10.
- ^ a b Gandini S, Botteri E, Iodice S, Boniol M, Lowenfels AB, Maisonneuve P, et al. (January 2008). "Tobacco smoking and cancer: a meta-analysis". International Journal of Cancer. 122 (1): 155–64. doi:10.1002/ijc.23033. PMID 17893872. S2CID 27018547.
- ^ Goldstein BY, Chang SC, Hashibe M, La Vecchia C, Zhang ZF (November 2010). "Alcohol consumption and cancers of the oral cavity and pharynx from 1988 to 2009: an update". European Journal of Cancer Prevention. 19 (6): 431–65. doi:10.1097/CEJ.0b013e32833d936d. PMC 2954597. PMID 20679896.
- ^ "The Tobacco Connection". The Oral Cancer Foundation. 9 March 2016. Retrieved 2019-03-10.
- ^ Goldenberg D, Lee J, Koch WM, Kim MM, Trink B, Sidransky D, et al. (December 2004). "Habitual risk factors for head and neck cancer". Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery. 131 (6): 986–93. doi:10.1016/j.otohns.2004.02.035. PMID 15577802. S2CID 34356067.
- ^ Kerawala C, Roques T, Jeannon JP, Bisase B (May 2016). "Oral cavity and lip cancer: United Kingdom National Multidisciplinary Guidelines". The Journal of Laryngology and Otology. 130 (S2): S83–S89. doi:10.1017/S0022215116000499. PMC 4873943. PMID 27841120.
- ^ a b Katirachi SK, Grønlund MP, Jakobsen KK, Grønhøj C, von Buchwald C (February 2023). "The Prevalence of HPV in Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma". Viruses. 15 (2): 451. doi:10.3390/v15020451. PMC 9964223. PMID 36851665.
- ^ "USCS Data Visualizations". gis.cdc.gov. Archived from the original on 2019-01-25. Retrieved 2019-03-10.
- ^ "Survival Rates for Oral Cavity and Oropharyngeal Cancer". www.cancer.org. Retrieved 2019-03-10.
- ^ Ravikiran Ongole, Praveen B N, ed. (2014). Textbook of Oral Medicine, Oral Diagnosis and Oral Radiology. Elsevier India. p. 387. ISBN 978-8131230916.
- ^ a b Markopoulos AK (2012-08-10). "Current aspects on oral squamous cell carcinoma". The Open Dentistry Journal. 6 (1): 126–30. doi:10.2174/1874210601206010126. PMC 3428647. PMID 22930665.
- ^ Mello FW, Melo G, Pasetto JJ, Silva CA, Warnakulasuriya S, Rivero ER (July 2019). "The synergistic effect of tobacco and alcohol consumption on oral squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Clinical Oral Investigations. 23 (7): 2849–2859. doi:10.1007/s00784-019-02958-1. PMID 31111280.
- ^ a b c IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans (2012). "Personal habits and indoor combustions". IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. 100 (Pt E): 1–538. PMC 4781577. PMID 23193840.
- ^ Cancer Care Ontario (2014). "Cancer Risk Factors in Ontario: Tobacco" (PDF). www.cancercare.on.ca.
- ^ Aupérin A (May 2020). "Epidemiology of head and neck cancers: an update". Current Opinion in Oncology. 32 (3): 178–186. doi:10.1097/CCO.0000000000000629. PMID 32209823. S2CID 214644380.
- ^ Wyss AB, Hashibe M, Lee YA, Chuang SC, Muscat J, Chen C, et al. (November 2016). "Smokeless Tobacco Use and the Risk of Head and Neck Cancer: Pooled Analysis of US Studies in the INHANCE Consortium". American Journal of Epidemiology. 184 (10): 703–716. doi:10.1093/aje/kww075. PMC 5141945. PMID 27744388.
- ^ Hecht SS, Hatsukami DK (March 2022). "Smokeless tobacco and cigarette smoking: chemical mechanisms and cancer prevention". Nature Reviews. Cancer. 22 (3): 143–155. doi:10.1038/s41568-021-00423-4. PMC 9308447. PMID 34980891.
- ^ Wyss A, Hashibe M, Chuang SC, Lee YC, Zhang ZF, Yu GP, et al. (September 2013). "Cigarette, cigar, and pipe smoking and the risk of head and neck cancers: pooled analysis in the International Head and Neck Cancer Epidemiology Consortium". American Journal of Epidemiology. 178 (5): 679–690. doi:10.1093/aje/kwt029. PMC 3755640. PMID 23817919.
- ^ Ralho A, Coelho A, Ribeiro M, Paula A, Amaro I, Sousa J, et al. (December 2019). "Effects of Electronic Cigarettes on Oral Cavity: A Systematic Review". The Journal of Evidence-Based Dental Practice. 19 (4): 101318. doi:10.1016/j.jebdp.2019.04.002. PMID 31843181. S2CID 145920823.
- ^ Ghasemiesfe M, Barrow B, Leonard S, Keyhani S, Korenstein D (November 2019). "Association Between Marijuana Use and Risk of Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis". JAMA Network Open. 2 (11): e1916318. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.16318. PMC 6902836. PMID 31774524.
- ^ Gormley M, Creaney G, Schache A, Ingarfield K, Conway DI (November 2022). "Reviewing the epidemiology of head and neck cancer: definitions, trends and risk factors". British Dental Journal. 233 (9): 780–786. doi:10.1038/s41415-022-5166-x. PMC 9652141. PMID 36369568.
- ^ Tramacere I, Negri E, Bagnardi V, Garavello W, Rota M, Scotti L, et al. (July 2010). "A meta-analysis of alcohol drinking and oral and pharyngeal cancers. Part 1: overall results and dose-risk relation". Oral Oncology. 46 (7): 497–503. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2010.03.024. PMID 20444641.
- ^ Rumgay H, Shield K, Charvat H, Ferrari P, Sornpaisarn B, Obot I, et al. (August 2021). "Global burden of cancer in 2020 attributable to alcohol consumption: a population-based study". The Lancet. Oncology. 22 (8): 1071–1080. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00279-5. PMC 8324483. PMID 34270924.
- ^ Bagnardi V, Rota M, Botteri E, Tramacere I, Islami F, Fedirko V, et al. (February 2015). "Alcohol consumption and site-specific cancer risk: a comprehensive dose-response meta-analysis". British Journal of Cancer. 112 (3): 580–593. doi:10.1038/bjc.2014.579. PMC 4453639. PMID 25422909.
- ^ Hashibe M, Brennan P, Chuang SC, Boccia S, Castellsague X, Chen C, et al. (February 2009). "Interaction between tobacco and alcohol use and the risk of head and neck cancer: pooled analysis in the International Head and Neck Cancer Epidemiology Consortium". Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention. 18 (2): 541–550. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-08-0347. PMC 3051410. PMID 19190158.
- ^ Ustrell-Borràs M, Traboulsi-Garet B, Gay-Escoda C (January 2020). "Alcohol-based mouthwash as a risk factor of oral cancer: A systematic review". Medicina Oral, Patologia Oral y Cirugia Bucal. 25 (1): e1–e12. doi:10.4317/medoral.23085. PMC 6982979. PMID 31655832.
- ^ a b c Rao KN, Mehta R, Dange P, Nagarkar NM (2024-05-08). "Alcohol-Containing Mouthwash and the Risk of Oral Cancer: Exploring the Association". Indian Journal of Surgical Oncology. doi:10.1007/s13193-024-01948-4. ISSN 0975-7651.
- ^ Currie S, Farah CS (10 February 2014). "Alcohol-containing mouthwash and oral cancer risk: a review of current evidence". OA Alcohol. 2 (1). Open Access Publishing London: 4.1–4.9. ISSN 2053-0285.
- ^ Carr E, Aslam-Pervez B (March 2022). "Does the use of alcohol mouthwash increase the risk of developing oral cancer?". Evidence-Based Dentistry. 23 (1): 28–29. doi:10.1038/s41432-022-0236-0. PMID 35338325.
- ^ Gillison ML, Chaturvedi AK, Anderson WF, Fakhry C (October 2015). "Epidemiology of Human Papillomavirus-Positive Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 33 (29): 3235–42. doi:10.1200/JCO.2015.61.6995. PMC 4979086. PMID 26351338.
- ^ Katirachi SK, Grønlund MP, Jakobsen KK, Grønhøj C, von Buchwald C (February 2023). "The Prevalence of HPV in Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma". Viruses. 15 (2): 451. doi:10.3390/v15020451. PMC 9964223. PMID 36851665.
- ^ Gormley M, Creaney G, Schache A, Ingarfield K, Conway DI (November 2022). "Reviewing the epidemiology of head and neck cancer: definitions, trends and risk factors". British Dental Journal. 233 (9): 780–786. doi:10.1038/s41415-022-5166-x. PMC 9652141. PMID 36369568.
- ^ a b Elad S, Zadik Y, Zeevi I, Miyazaki A, de Figueiredo MA, Or R (December 2010). "Oral cancer in patients after hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation: long-term follow-up suggests an increased risk for recurrence". Transplantation. 90 (11): 1243–4. doi:10.1097/TP.0b013e3181f9caaa. PMID 21119507.
- ^ Barsouk A, Aluru JS, Rawla P, Saginala K, Barsouk A (June 2023). "Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Prevention of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma". Medical Sciences. 11 (2): 42. doi:10.3390/medsci11020042. PMC 10304137. PMID 37367741.
- ^ Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CM, Bouquot JE (2002). Oral & maxillofacial pathology (2nd ed.). Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders. pp. 337, 345, 349, 353. ISBN 978-0721690032.
- ^ Marziliano A, Teckie S, Diefenbach MA (April 2020). "Alcohol-related head and neck cancer: Summary of the literature". Head & Neck. 42 (4): 732–738. doi:10.1002/hed.26023. PMID 31777131.
- ^ Stornetta A, Guidolin V, Balbo S (January 2018). "Alcohol-Derived Acetaldehyde Exposure in the Oral Cavity". Cancers. 10 (1): 20. doi:10.3390/cancers10010020. PMC 5789370. PMID 29342885.
- ^ a b c d e f Gullane P (2016). Sataloff's Comprehensive Textbook of Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery: Head and Neck Surgery. Vol. 5. New Delhi, India: The Health Sciences Publisher. p. 600. ISBN 978-93-5152-458-8.
- ^ H Alsarraf A, Kujan O, Farah CS (February 2018). "The utility of oral brush cytology in the early detection of oral cancer and oral potentially malignant disorders: A systematic review". Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine. 47 (2): 104–116. doi:10.1111/jop.12660. PMID 29130527. S2CID 46832488.
- ^ AlAli AM, Walsh T, Maranzano M (August 2020). "CYFRA 21-1 and MMP-9 as salivary biomarkers for the detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review of diagnostic test accuracy" (PDF). International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. 49 (8): 973–983. doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2020.01.020. PMID 32035907. S2CID 211070749.
- ^ Levine B, Nielsen EW (August 1992). "The justifications and controversies of panendoscopy--a review". Ear, Nose, & Throat Journal. 71 (8): 335–40, 343. doi:10.1177/014556139207100802. PMID 1396181. S2CID 25921527.
- ^ Clayburgh DR, Brickman D (January 2017). "Is esophagoscopy necessary during panendoscopy?". The Laryngoscope. 127 (1): 2–3. doi:10.1002/lary.25532. PMID 27774605. S2CID 19124543.
- ^ a b Connolly JL, Goldsmith JD, Wang HH, et al. (2010). "37: Principles of Cancer Pathology". Holland-Frei Cancer Medicine (8th ed.). People's Medical Publishing House. ISBN 978-1-60795-014-1.
- ^ a b c d "AJCC Cancer Staging Form Supplement. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, eighth Edition Update 05 June 2018" (PDF). www.cancerstaging.org. 5 June 2018. Retrieved 7 April 2019.
- ^ a b c "Final Recommendation Statement: Oral Cancer: Screening—US Preventive Services Task Force". www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org. November 2013. Retrieved 23 November 2017.
- ^ a b Brocklehurst P, Kujan O, O'Malley LA, Ogden G, Shepherd S, Glenny AM (November 2013). "Screening programmes for the early detection and prevention of oral cancer". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2021 (11): CD004150. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004150.pub4. PMC 8078625. PMID 24254989.
- ^ a b Walsh T, Macey R, Kerr AR, Lingen MW, Ogden GR, Warnakulasuriya S (July 2021). "Diagnostic tests for oral cancer and potentially malignant disorders in patients presenting with clinically evident lesions". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 7 (7): CD010276. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010276.pub3. PMC 8407012. PMID 34282854.
- ^ Robbins KT, Ferlito A, Shah JP, Hamoir M, Takes RP, Strojan P, et al. (March 2013). "The evolving role of selective neck dissection for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma". European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology. 270 (4): 1195–202. doi:10.1007/s00405-012-2153-x. PMID 22903756. S2CID 22423135.
- ^ Zelefsky MJ, Harrison LB, Fass DE, Armstrong JG, Shah JP, Strong EW (January 1993). "Postoperative radiation therapy for squamous cell carcinomas of the oral cavity and oropharynx: impact of therapy on patients with positive surgical margins". International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics. 25 (1): 17–21. doi:10.1016/0360-3016(93)90139-m. PMID 8416876.
- ^ a b Petrelli F, Coinu A, Riboldi V, Borgonovo K, Ghilardi M, Cabiddu M, et al. (November 2014). "Concomitant platinum-based chemotherapy or cetuximab with radiotherapy for locally advanced head and neck cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of published studies". Oral Oncology. 50 (11): 1041–8. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2014.08.005. PMID 25176576.
- ^ a b Chan KK, Glenny AM, Weldon JC, Furness S, Worthington HV, Wakeford H (December 2015). "Interventions for the treatment of oral and oropharyngeal cancers: targeted therapy and immunotherapy". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2015 (12): CD010341. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010341.pub2. PMC 9465394. PMID 26625332.
- ^ a b Listl S, Jansen L, Stenzinger A, Freier K, Emrich K, Holleczek B, et al. (GEKID Cancer Survival Working Group) (2013). Scheurer M (ed.). "Survival of patients with oral cavity cancer in Germany". PLOS ONE. 8 (1): e53415. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...853415L. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0053415. PMC 3548847. PMID 23349710.
- ^ Naghavi M, Wang H, Lozano R, Davis A, Liang X, Zhou M, et al. (GBD 2013 Mortality Causes of Death Collaborators) (January 2015). "Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013". Lancet. 385 (9963): 117–71. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2. PMC 4340604. PMID 25530442.
- ^ Sacker A, Bartley M (2015). Social inequalities in oral health: from evidence to action (PDF). UCL Research Department of Epidemiology and Public Health. p. 9. ISBN 9780952737766.
- ^ a b c d e f "Cancer of lip, oral cavity and pharynx. [online]". EUCAN. Archived from the original on 23 December 2017. Retrieved 14 November 2017.
- ^ "Mouth cancer". www.nhsinform.scot. Retrieved 2021-04-23.
- ^ a b "oral cancer statistics". CancerresearchUK. Retrieved 28 October 2014.
- ^ Annertz K, Anderson H, Biörklund A, Möller T, Kantola S, Mork J, et al. (September 2002). "Incidence and survival of squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue in Scandinavia, with special reference to young adults". International Journal of Cancer. 101 (1): 95–99. doi:10.1002/ijc.10577. PMID 12209594. S2CID 23069745.
- ^ "World Life Expectancy". 2014.
- ^ Diz P, Meleti M, Diniz-Freitas M, Vescovi P, Warnakulasuriya S, Johnson N, et al. (2017). "Oral and pharyngeal cancer in Europe". Translational Research in Oral Oncology. 2: 2057178X1770151. doi:10.1177/2057178X17701517. hdl:10072/347247.
- ^ Nemes JA, Redl P, Boda R, Kiss C, Márton IJ (March 2008). "Oral cancer report from Northeastern Hungary". Pathology & Oncology Research. 14 (1): 85–92. doi:10.1007/s12253-008-9021-4. PMID 18351444. S2CID 1187249.
- ^ Suba Z, Mihályi S, Takács D, Gyulai-Gaál S (2009). "Oral cancer: Morbus hungaricus in the 21st century". Fogorv Sz. 102 (2): 63–68. PMID 19514245.
- ^ Endre A (February 2006). "Hungarian national cancer control programme" (PDF).
- ^ a b Gupta N, Gupta R, Acharya AK, Patthi B, Goud V, Reddy S, et al. (December 2016). "Changing Trends in oral cancer - a global scenario". Nepal Journal of Epidemiology. 6 (4): 613–619. doi:10.3126/nje.v6i4.17255. PMC 5506386. PMID 28804673.
- ^ Moore SR, Johnson NW, Pierce AM, Wilson DF (March 2000). "The epidemiology of mouth cancer: a review of global incidence". Oral Diseases. 6 (2): 65–74. doi:10.1111/j.1601-0825.2000.tb00104.x. PMID 10702782.
- ^ a b c "Cancer Facts & Figures 2017". America cancer society.
- ^ a b Krishna Rao SV, Mejia G, Roberts-Thomson K, Logan R (30 October 2013). "Epidemiology of oral cancer in Asia in the past decade--an update (2000-2012)". Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention. 14 (10). Asian Pacific Organization for Cancer Prevention: 5567–5577. doi:10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.10.5567. PMID 24289546.
- ^ a b Cheong SC, Vatanasapt P, Yi-Hsin Y, Zain RB, Kerr AR, Johnson NW (2017). "Oral cancer in South East Asia". Translational Research in Oral Oncology. 2: 2057178X1770292. doi:10.1177/2057178X17702921. hdl:10072/389476. ISSN 2057-178X.
- ^ Al-Jaber A, Al-Nasser L, El-Metwally A (March 2016). "Epidemiology of oral cancer in Arab countries". Saudi Medical Journal. 37 (3): 249–255. doi:10.15537/smj.2016.3.11388. PMC 4800887. PMID 26905345.
- ^ a b c d "All Cancers (excluding non-melanoma skin cancer) Estimated Incidence, Mortality and Prevalence Worldwide in 2012". International Agency for Research on Cancer. 2012.
- ^ Mallath MK, Taylor DG, Badwe RA, Rath GK, Shanta V, Pramesh CS, et al. (May 2014). "The growing burden of cancer in India: epidemiology and social context". The Lancet. Oncology. 15 (6): e205-12. doi:10.1016/s1470-2045(14)70115-9. PMID 24731885.
- ^ Varshitha A (2015). "Prevalence of Oral Cancer in India". Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research. 7 (10): e845-48.
- ^ Chapman DH, Garsa A (2018). "Cancer of the Lip and Oral Cavity". In Hansen E, Roach III M (eds.). Handbook of Evidence-Based Radiation Oncology. Springer International Publishing. pp. 193–207. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-62642-0_8. ISBN 9783319626413.
- ^ Chaturvedi AK, Anderson WF, Lortet-Tieulent J, Curado MP, Ferlay J, Franceschi S, et al. (December 2013). "Worldwide trends in incidence rates for oral cavity and oropharyngeal cancers". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 31 (36): 4550–9. doi:10.1200/jco.2013.50.3870. PMC 3865341. PMID 24248688.
- ^ a b c Farah CS, Simanovic B, Dost F (September 2014). "Oral cancer in Australia 1982-2008: a growing need for opportunistic screening and prevention". Australian Dental Journal. 59 (3): 349–59. doi:10.1111/adj.12198. PMID 24889757.
- ^ Foale RD, Demetriou J (2010). Saunders Solutions in Veterinary Practice: Small Animal Oncology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 49. ISBN 978-0-7020-4989-7.
- ^ "Mouth Cancer (Oral Cancer) in Dogs | Oakland Vets". East Bay Veterinary Clinic. Retrieved 2023-07-21.
- ^ Balas M, Colleran E (2015-06-17). "Pet Talk: Feline oral cancer a silent but deadly disease in cats". oregonlive. Archived from the original on 2023-07-21. Retrieved 2023-07-21.
- ^ Bertone ER, Snyder LA, Moore AS (2003). "Environmental and lifestyle risk factors for oral squamous cell carcinoma in domestic cats". Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine. 17 (4): 557–562. doi:10.1111/j.1939-1676.2003.tb02478.x. PMID 12892308.
