Thyronine
Appearance
(Redirected from Thyronines)
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
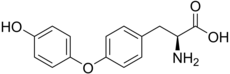
| IUPAC name
O-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-L-tyrosine
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2S)-2-Amino-3-[4-(4-hydroxyphenoxy)phenyl]propanoic acid | |
| Other names
4-(4-Hydroxyphenoxy)-L-phenylalanine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.986 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H15NO4 | |
| Molar mass | 273.28 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Thyronine is a metabolite derived from thyroxine and triiodothyronine via the peripheral enzymatic removal of iodines from the thyroxine nucleus. Thyronine is the thyroxine nucleus devoid of its four iodine atoms.[1]
References
[edit]
