Théâtre Optique

The Théâtre Optique (Optical Theatre) is an animated moving picture system invented by Émile Reynaud and patented in 1888. From 28 October 1892 to March 1900 Reynaud gave over 12,800 shows to a total of over 500,000 visitors at the Musée Grévin in Paris. His Pantomimes Lumineuses series of animated films include Pauvre Pierrot and Autour d'une cabine.[1][2] Reynaud's Théâtre Optique predated Auguste and Louis Lumière's first commercial, public screening of the cinematograph on 28 December 1895, which has long been seen as the birth of film.
Technology
[edit]
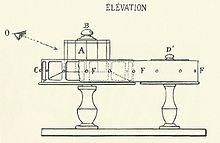
The realized films had 300 to 700 transparent pictures of successive phases of moving figures with black backgrounds. The pictures were hand painted by Reynaud in aniline inks directly on 6 x 6 cm gelatin plates.[1] The plates were coated with shellac and framed in a cardboard strip of which the sides were clad in fabric bands attached with split pins. The horizontal film strip could be up to 50 meters long, with black leader tape at the beginning. Central perforations in the cardboard between the images engaged with metal notches protruding from a large central turning wheel. The wheel transferred the strip between two copper 25 cm spools. The film was guided further by pinch rollers at the corners of the table and passed in front of a magic lantern. The magic lantern projected each image in turn towards one of the 36 rectangular mirrors at the center of the turning wheel. Each image was in turn reflected to another mirror, which reflected it through a focusing lens towards a movable mirror. The movable mirror could be adjusted to project the moving characters at the desired place within an immobile background image on the screen. The background was projected with a second magic lantern from a painted glass plate. Reynaud would manipulate the speed of the film by hand and repeat movements to produce a visual story that could last longer than 10 minutes.[1] The projectionist operated the machine behind the screen, with only the projection visible to the audience.[3][4][5]
Some synchronized sound effects were automated at key moments marked with silver tabs on the flexible band to activate an electromagnet. The magnet in turn triggered a buzzer, small drums or other acoustic devices.[1][6]
The 1888 patent covered the film band to be of indefinite length and of any material, opaque or transparent (the reflection of a brightly lit opaque picture could also be projected). The band could be fully flexible or only between the pictures. The pictures could be hand-drawn, printed or "obtained by photography from nature". The amount of praxinoscope mirrors could differ per model. Either a spool or the central wheel could be rotated by hand or a mechanical motor to move the film. illumination and optical arrangements could be made for either direct-viewing or for projection on a screen.[7]
In a prospectus Reynaud offered the Théâtre Optique in different versions and with separately available parts; one version came installed on an 80 x 100 cm mahogany table and another on a two part iron frame that could be stored inside two wooden boxes (85 x 85 x 25 cm). Copies of the three available films were offered in "special printing in color" (quote translated from French).[3]
History
[edit]
The Théâtre Optique was not the first occurrence of projected animation. Mechanical animation projections and other more primitive moving picture techniques had already been featured long before in visual storytelling in magic lantern shows, especially in phantasmagoria. However, this was not yet animation as we now know it: a rapid successive substitution of sequential images to create a lifelike moving picture. A few animation projectors had been available for a few decades using the stroboscopic effect invented with the phénakisticope, but these projected very short animation loops.
The Théâtre Optique was a further development of the projection version of Reynaud's praxinoscope animation toy, which had already been covered in the first praxinoscope patent as registered on 30 August 1877. Reynaud in the 1888 patent: "The aim of the apparatus is to obtain the illusion of motion, which is no longer limited to the repetition of the same poses at each turn of the instrument, as is necessary in all known apparatus (Zootropes, Praxinoscopes, etc.), but Having, on the contrary, an indefinite variety and duration, and thus producing real scenes animated by unlimited development. Hence the name of Optical Theater given by the inventor to this apparatus" (translated from French).[7]
The term had been used occasionally for a theatrical variation of peep shows or dioramas with moving figures since at least the 18th century.[8]
In 1877 Reynaud had created the praxinoscope, an improvement of the zoetrope. The praxinoscope replaced the narrow viewing slits of the zoetrope with an inner circle of 12 mirrors (equal to the number of images), allowing a brighter and clearer view of the moving image. After Reynaud licensed his invention in 1877, it sold well in a number of the large Paris department stores.
Reynaud applied for a French patent (Brevet d'invention N° 194 482) for the Théâtre Optique on 1 December 1888.
On January 14, 1889, Reynaud received a French patent for the Théâtre Optique. He also received a British patent for the system on February 8. The system was displayed at the world's fair Exposition Universelle (May-October, 1889) in Paris. [9][10][11]
Reynaud tried to sell the system with his films between 1889 and 1892 and offered demonstrations at his address in Paris. When it didn't sell, he decided to exploit it with theatrical screenings in 1892. [3]
La Nature No. 999 of 23 July 1892 featured an enthusiastic article about the Théâtre Optique. Gaston Tissandier described how it enabled uninterrupted projection of a considerable series of actions and wrote that Reynaud had composed very amusing scenes with characters "who engage in lively scenes and execute rapid movements of a charming effect" (translated from French). He sensed that the system provided new possibilities and thought it would undoubtedly have a future with photographed series of poses, when it would become technically and economically more feasible to produce photographic strips.[12]

On October 28, 1892, Reynaud debuted his Pantomimes Lumineuses animation films at the Cabinet Fantastique of the Musée Grévin in Paris. The show included three Pantomimes Illumineuses films, Pauvre Pierrot!, Un bon bock, and Le Clown et ses chiens. Reynaud acted as the projectionist and the show was accompanied by Gaston Paulin on the piano. Paulin had written the music especially for the shows, including a song that he sung as Pierrot's serenade to Colombine in Pauvre Pierrot!. Occasionally two assistants would provide dialogue for the characters. The show was immediately successful with hundreds of visitors for the five daily shows.[2] Although the films shown by the Lumière Brothers in 1895 eclipsed it, the show stayed at the Musée Grévin until March 1900. Over 500,000 people had seen it.
The entrance fee was 50 centimes, currently roughly equivalent to U.S. $5. According to his unfortunate contract with Musée Grevin, signed on 8 October 1892, Reynaud received 500 francs per month plus 10% of the box office. Reynaud was required to direct each performance and was responsible for the maintenance of the strips, which did not endure the heavy usage very well. He reinforced the strips with metal rods, but eventually had to remake one of the films entirely.[2]
Émile Reynayd also presented his Pantomimes Lumineuses in Rouen in December 1892.[3]
Reynaud ended up ruined, forgotten and disillusioned. Around 1913 Reynaud destroyed his last Théâtre Optique machine with a hammer and threw five of his seven films into the Seine.[13] A few days later he would be visited by a French inventor and producer Léon Gaumont, to buy the invention and donate it to the Conservatoire des Arts et Métiers.[citation needed]
The moving picture shows of Émile Reynaud have been inscribed in Memory of the World Register of UNESCO in 2015.[14]
Legacy
[edit]The Pantomimes Lumineuses premiere on 28 October 1892 marks the first occurrence of public theatrical exhibition of motion pictures on film. The films have often been ignored in summaries of the history of film, presumably because the pictures were painted (rather than photographed) and the materials and technique differed from what would be film standards. However, the cinematographic films that are often seen as the first films lack several qualities that Reynaud's films had: the duration of the Pantomimes Lumineuses exceeds the early cinematographic films (they contained up to 700 frames, but were used with repetition of movements for up to 15 minutes), they were in color, had some synchronized sound effects and a specially composed score with a song (performed live), and some dialogue (performed live). It would take years before cinematographic films began to approach the narrative and aesthetic quality of the Pantomimes Lumineuses.[15]
The Théâtre Optique patent of 1 December 1888 introduced the idea of film perforations.[7] It has been suggested that Thomas Edison may have picked up this idea for the development of the Kinetoscope when he visited the Paris Exposition Universelle of 1889, where Reynaud won a bronze medal for all his works and purportedly exhibited his Théâtre Optique.[2] According to Émile Reynaud's son, Auguste and Louis Lumière visited the Pantomimes Lumineuses and later were allowed to see the machine at Reynaud's workshop. One day, he would have complained to his family that the Lumières came to visit the apparatus a bit too often.[16]
Reynaud covered the use of photographic pictures in the 1888 patent.[7] The July 1892 article in La Nature saw its future especially in the combination with photography.[12] In 1895 Reynaud worked on a Photo-Scenographe and from 1896 he included two Photo-Peinture Animée films in his Pantomimes Lumineuses programs,[17] but these only premiered after cinematographic films had been introduced.
Reynaud not only had a piano score composed for his films, but also used some synchronized sound effects. Most early film screenings, including that of Lumière's cinematograph introduction, only had (improvised) piano accompaniment.
Using a separate image for a motionless background - rather than drawing the background into each frame together with the moving characters - became a standard technique in cel animation, dominant for many decades from soon after it was patented in 1914 until it was surpassed by digital techniques.
After the introduction of the cinématographe, it took over 10 years before animated films returned to the theatres (with Humorous Phases of Funny Faces (1906) by J. Stuart Blackton).
The animated segment in Winsor McCay's Little Nemo (1911) was probably the first animation to use more hand-drawn images than the 700 images of Reynaud's Un Bon Bock. While most early animations were black and white, a version of Little Nemo was hand-colored by McCay. Winsor McCay also used short loops of repeated images in several films, which is quite similar to Reynaud's technique of moving the film back and forth during projection.
A rêve au coin du feu made use of a flashback for the first time as a narrative element to explain the past of the protagonist when his house was devoured by the flames. [citation needed]
Filmography
[edit]

Dates given are for the Pantomimes Illumineuses performances at Musée Grevin.
- 28-10-1892 - 12-1894 Un bon bock (created 1888) 700 images, 50 meters, circa 15 minutes (lost)
- 28-10-1892 - 02-1894 Le Clown et ses chiens (created 1890) 300 images, 22 meters, circa 10 minutes (lost)
- 28-10-1892 - 02-1894 Pauvre Pierrot! (created 1891) 500 images, 36 meters, circa 14 minutes
- 12-1894 - 03-1900 Autour d'une cabine (created 1893) 636 images, 45 meters, circa 15 minutes
- 12-1894 - 07-1897 A rêve au coin du feu 400 images, 29 meters, circa 12 minutes (lost)
Photo-Peintures animée:
- 08-1896 - 03-1900 Guillaume Tell (created 04–1896)
- 07-1897 - 12-1898 Le Premier cigare (created 1896)
- unreleased Les Clowns Price (created 1898)
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d "Le Théâtre optique - Émile Reynaud". www.emilereynaud.fr. Archived from the original on 11 November 2008. Retrieved 6 June 2022.
- ^ a b c d Myrent, Glenn (1989). "Emile Reynaud: First Motion Picture Cartoonist". Film History. 3 (3): 191–202. JSTOR 3814977.
- ^ a b c d "Théâtre optique (Reconstitution) (AP-95-1724) - Collection - Catalogue des appareils cinématographiques - la Cinémathèque française".
- ^ "Théâtre optique (Bande peinte pour le) (AP-12-2770) - Collection - Catalogue des appareils cinématographiques - la Cinémathèque française".
- ^ Laurent Mannoni i, Donata Pesenti Campagnoni (2009). Lanterne magique et film peint : 400 ans de Cinéma. Paris: La Martinière/La Cinématèque française.
- ^ "Cinémathèque française and Museo Nazionale del Cinema: Zoom on… the Optical Theatre of Émile Reynaud".
- ^ a b c d Reynaud, Émile (1888-12-01). Brevet d'invention N° 194 482.
- ^ "Gazette du commerce". 13 June 1769.
- ^ Myrent 1989, p. 193; 195-198.
- ^ Bendazzi 1994, p. 5.
- ^ Rossell 1995, p. 119.
- ^ a b Tissandier, Gaston (1892-07-23). Le Théâtre optique de M. Reynaud.
- ^ Laurent Mannoni Le grand art de la lumiere" 1995 p. 358
- ^ "The moving picture shows of Émile Reynaud | United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization".
- ^ Laurent Mannoni Le grand art de la lumiere" 1995 p. 356
- ^ M. Noverre, Emile Reynaud, sa vie et ses travaux, Brest, 1926, p. 46
- ^ "Les Photo-Peintures animées".
Sources
[edit]- Sylvie Saerens (October 1997). "Emile Reynaud". Retrieved 8 December 2006.
- "Animation Notes #3 A Short History (part II)". RMIT University. Retrieved 8 December 2006.
- Bendazzi, Giannalberto (1994). Cartoons: One hundred years of cinema animation. Indiana University Press. ISBN 0253209374.
- Chardère, B.; Borgé, G. and M. (1985). Les Lumière, Paris: Bibliothèque des Arts. ISBN 2-85047-068-6 (Language: French)
- Rossell, Deac (1995). "A Chronology of Cinema, 1889-1896". Film History. 7 (2). Indiana University Press: 115–236. JSTOR 3815166.
