Wolf Trap National Park for the Performing Arts
| Wolf Trap National Park for the Performing Arts | |
|---|---|
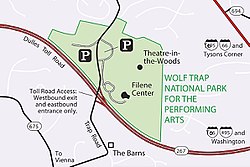 Map of the park | |
| Location | Wolf Trap, Virginia, U.S. |
| Nearest city | Vienna, Virginia, U.S. |
| Area | 130 acres (53 ha)[1] |
| Established | October 15, 1966 |
| Visitors | 424,364 (in 2017)[2] |
| Governing body | National Park Service Wolf Trap Foundation |
| Website | Wolf Trap National Park for the Performing Arts |
Wolf Trap National Park for the Performing Arts (originally known as the Wolf Trap Farm Park for the Performing Arts and simply known as Wolf Trap) is a performing arts center located on 117 acres (47 ha) of national park land in unincorporated Fairfax County, Virginia, near the town of Vienna. Through a partnership and collaboration of the National Park Service and the non-profit Wolf Trap Foundation for the Performing Arts, the park offers both natural and cultural resources.
Its land was donated to the United States government by Catherine Filene Shouse, who sought to preserve her former farm as parkland. In 1966, Congress accepted Shouse's gift and authorized Wolf Trap Farm Park as the first national park for the performing arts.[3] It was given its present name on August 21, 2002.
Wolf Trap Foundation for the Performing Arts
[edit]The Wolf Trap Foundation for the Performing Arts is a nonprofit organization founded by Catherine Filene Shouse when she donated her Wolf Trap Farm to the National Park Service.[3] The Park is operated as a public/private partnership between the Park Service, which staffs and operates the park grounds, and the Foundation, which produces and presents the performance and education programs.[4]
The Foundation presents performances in the Filene Center from May through September and year-round at The Barns at Wolf Trap, just outside the park proper. The Foundation also operates the Wolf Trap Opera Company, a resident company for young opera singers.[4]
The Foundation's education programs, also located next to the park proper, include the Wolf Trap Institute for Early Learning Through the Arts, a nationally recognized college internship program,[5] and the Children's Theatre-in-the-Woods, whose performance venue is in the park.[4]
Performing arts venues
[edit]Wolf Trap National Park for the Performing Arts organizes and runs several venues and facilities:
Filene Center
[edit] View of venue from lawn area (c. 2006) | |
 | |
| Address | 1551 Trap Rd, Vienna, Virginia 22182-1643 |
|---|---|
| Location | D.C. Area |
| Owner | Wolf Trap Foundation for the Performing Arts |
| Capacity | 7,028 |
| Construction | |
| Broke ground | May 22, 1968 |
| Opened | July 1, 1971 |
| Construction cost | $3.6 million ($31.5 million in 2023 dollars[6]) |
| Architect | MacFadyen and Knowles |
| Project manager | Eastern Service Center |
| Structural engineer | Lev Zetlin & Associates |
| Services engineer | Flack + Kurtz Inc. |
| General contractor | Coe Construction |
| Main contractors | Norair Engineering |
| Website | |
| www | |

The park's major indoor/outdoor performance venue is Filene Center, which can hold 7,028[7] in 3,800 seats under cover and space for another 3,200 to sit on the lawn. It is named for Shouse's parents, Abraham and Thérèse Lincoln Filene of the now-defunct department store chain[8] Performances are given nightly from May to early September and cover a wide range of musical styles from country music to opera.
The first Filene Center, constructed of Oregon redcedar, was a ten-story-high facility equipped with a computerized lighting system and sophisticated sound equipment. Just months before the theater was to open, it was partially destroyed by a fire on March 13, 1971.[9] On May 10, a benefit concert to cover the repair costs of around $650,000 was held at Constitution Hall in Washington, D.C.; it featured Pierre Boulez conducting the New York Philharmonic Orchestra.[10] The center opened on schedule on July 1, although the inaugural season opening was delayed one month.
That summer, 60 young musical performers were chosen for training in music, dance and acting, to culminate in a production at the center.
On April 14, 1982, the Filene Center was destroyed by fire. A temporary structure was built on the park to house performances for the upcoming season. [11] The second Filene Center, constructed between 1982 and 1984, is made of douglas-fir with a yellow pine ceiling. It includes a system to detect and suppress fire, as well as fire retardant wood, which all cost about a total of $1.7 million. The new amphitheater was also built with state-of-the-art sound and lighting equipment. It holds several hundred more patrons than the original Filene Center, provides better access for handicapped people, and adds backstage space for performers and crews.[12]
The main stage is 116 feet wide, 64 deep and 102 high.[13]
Children's Theatre in the Woods
[edit]
Set amid 117 rolling wooded acres,Children's Theatre in the Woods presents dozens of family-friendly shows each season from late June through early August. Shows have included music, dance, storytelling, puppetry, and theater, all recommended for children between kindergarten and 6th grade.[8]
Meadow Pavilion
[edit]
Until 2010, the Meadow Pavilion, a covered outdoor stage adjacent to Children's Theatre in the Woods, hosted events for the International Children's Festival at Wolf Trap (known as International Children's Day from 1971 to 1974). Today, the Meadow Pavilion can be rented through the Wolf Trap Foundation.
On March 6, 1980, a welder's torch ignited a fire at the Meadow Pavilion, causing around $10,000 in damage.[14]
The Barns at Wolf Trap
[edit]
Built from two restored 18th-century barns, this 382-seat theater holds performances between October and May. Shouse bought the barns in upstate New York and had them moved to the current site in 1981 using the 18th-century "block and tackle" method of construction. The theater barn was originally built in 1780 and seats 285 on the threshing floor and another 98 in the hayloft. The gathering barn is of the Scottish style and features a kitchen, bar and atrium.[15]
History
[edit]


Early records of Fairfax County, Virginia say that wolves would run wild in the area, and bounties were granted for trapping them. An August 1739 survey by J.M. Warner mentions "Wolf Trap Creek," a branch of the Difficult Run tributary stream.
During the 18th and 19th centuries, the land at Wolf Trap was frequently exchanged between wealthy families in the Fairfax area, including Bryan Fairfax, the 8th Lord Fairfax of Cameron and longtime friend of George Washington.[16]
20th century
[edit]In 1930, Catherine Filene Shouse acquired about 53 acres (21 ha) of land in the region and chose to preserve the name. By 1956, her holdings encompassed 168 acres (68 ha).[17]
Shouse bought Wolf Trap to offer her children a weekend retreat from their home in Georgetown, Washington, D.C. There they grew corn, wheat, alfalfa, and oats to feed their chickens, ducks, turkeys, and milk cows. They bred horses, built a stable and a hay barn, and opened a dog-breeding kennel, producing champion boxers, miniature pinschers, and Weimaraners. Shouse and her husband, Jouett Shouse, hosted large social gatherings for friends, family, and prominent public figures, including World War II Generals Omar Bradley and George C. Marshall and several members of the Dumbarton Oaks Conference in 1944.[8]
Donation of Wolf Trap to Congress, 1966–1970
[edit]In 1966, after several meetings with Secretary of the Interior Stewart Udall, Mrs. Shouse donated 60 acres (24 ha) of Wolf Trap land, in addition to 38 acres (15 ha) from the American Symphony Orchestra League, to the U.S. Government, a donation Congress subsequently accepted that year. In a letter to Congress that year, Udall argued that Wolf Trap would "augment the park and recreation opportunities in the National Capital region and involve the expenditure of only a minimum of Federal funds."[18] On May 28, 1966, Virginia Senator A. Willis Robertson introduced a bill to Congress to create and fund Wolf Trap, which passed with relative ease. Mrs. Shouse also offered over $2 million to construct the Filene Center for performances.
Around the same time, the Kennedy Center and Merriweather Post Pavilion, two other nearby concert venues, were also being constructed, so there were some questions in Congress about overloading the area with too many arts and music venues.[19] Rep. George H. Fallon of Maryland, for example, opposed the Wolf Trap bill on the basis that it would "only have the effect of dividing a small market" and would be in "direct conflict" with the Kennedy Center and Merriweather Post Pavilion.[20] Nevertheless, Wolf Trap became and remains the first and only U.S. National Park dedicated to the performance arts. With this collaboration, Mrs. Shouse became the first person to establish a partnership with the U.S. in bringing performing arts to the nation.
Ground was broken for the construction of the Filene Center in 1968, and the next year, Wolf Trap held its first concert. A ceremony was held for the topping out of the Filene Center in May 1970, attended by then-First Lady Pat Nixon.[8]
First performance seasons
[edit]
The inaugural performance at Wolf Trap occurred on June 1–2, 1971, and featured Van Cliburn, Julius Rudel and Norman Treigle conducting the New York City Opera. Follow-up performances were conducted by National Symphony Orchestra, Choral Arts Society of Washington, United States Marine Band and the Madison Madrigal Singers.[8]
For the first several performances at the Filene Center, Robert Lewis, founder of the Actors Studio and acclaimed Broadway director, was chosen to conduct the training program and direct the production called Musical Theatre Cavalcade. With a multimedia set by Leo Kerz, choreography by Gemeze de Lappe, and musical direction by Johnny Green, the Cavalcade was a history of musical theater from The Beggar's Opera to Hair. Pat Nixon, wife of President Richard Nixon, attended the opening night performance and invited the entire cast afterwards to the White House for a reception.[8]
The first 12 seasons saw many performances and events of historical significance. In 1971, the National Folk Festival was the first event at Wolf Trap to use the park grounds (versus Filene Center itself) for performances, and it set a precedent for other events at Wolf Trap to do the same. That same year, Richard Nixon became the first U.S. president to attend a Wolf Trap performance, viewing the Wolf Trap Company's performance of the "Musical Theater Cavacade" on August 12.[21] In 1976, the Scottish Military Tattoo, a Bicentennial gift from the United Kingdom, performed at the Filene Center for a capacity audience which included Britain's Prince Philip.[citation needed] Two years later, in 1978, the People's Republic of China's performing arts ensemble made its first performance outside China when it entertained Wolf Trap's audience with acrobatic troupes and dancers.[22] From 1971 until the early 1980s, the National Folk Festival was held annually at Wolf Trap. In the 1970s, WETA-TV produced the television series In Performance at Wolf Trap.[23]
Other highlights included Sarah Caldwell's production of Sergei Prokofiev's opera War and Peace, the Royal Ballet, Preservation Hall Jazz Band, the annual US National Symphony Orchestra's 1812 Overture concerts with live cannons and Beverly Sills' 1981 farewell appearance.[citation needed]
Composers' Cottage, 1971–1979
[edit]In May 1971, plans were developed to construct a series of composers' cottages across the park, where performing artists could stay for a temporary period and peacefully work on their respective works. Although five cottages were planned, only one was ever built. The two-bedroom house was donated by Edward R. Carr Jr., a metropolitan area realtor, and built by Fairfax County Public Schools high school students;[24] it was finished and dedicated in December 1973. During the next five years, the composers' cottage hosted several noteworthy composers, including Lester Trimble, Irwin Bazelon and Elie Siegmeister.
In 1979, however, a fire destroyed the composers' cottage, and it was never rebuilt.[8]
1982 Filene Center fire
[edit]As Wolf Trap was preparing for its 12th season, tragedy struck once again. On April 4, 1982, a fire of undetermined origin, intensified by high gusting winds, destroyed the Filene Center.
During the rebuilding of the Filene Center between 1982 and 1984, Wolf Trap received $29 million in contributions and pledges from over 16,000 donors in 47 states and five foreign countries, including a $9 million grant from Congress and support from then-President Ronald Reagan and former Presidents Richard Nixon and Jimmy Carter. WETA-TV also sponsored a star-studded, three-hour national telethon that raised more than $390,000 for the reconstruction of the Filene Center.[8]
Almost immediately, the Wolf Trap Foundation, the park's non-profit partner, announced that a 1982 season would still take place in the Meadow Center, a huge tent erected in the nearby meadow. The prefabricated structure, purchased with private and government funds, was disassembled from its previous site in the United Arab Emirates and transported to Wolf Trap by the government of Saudi Arabia. Volunteers provided much of the labor to erect the structure.
After the fire, the United States Postal Service issued a commemorative stamp honoring Wolf Trap on September 1, 1982. The stamp was the first in a series honoring Washington, D.C.'s cultural attractions, including the National Gallery of Art and the National Air and Space Museum.[25]
The first performance at the newly designed and constructed Filene Center, titled the "Filene Center Dedication," occurred on June 20, 1984.[8] The design work was accomplished by Dewberry and Davis, Joseph Boggs Studio, Architects. The new building featured state of the art fireproof design and acoustics. Attendees included opera star and frequent Wolf Trap performer Beverly Sills and then-Virginia Governor Charles Robb, as well as Mrs. Shouse herself.[26]
21st century
[edit]
In the years running up to 2009, Wolf Trap hosted an average of 96 shows during its performance season, which runs from late May to early September. However, because fewer artists toured in 2009, Wolf Trap only held 86 performances and reported a revenue decrease of about ten percent.[27]
On September 24, 2011, in conjunction with National Public Lands Day and First Lady Michelle Obama's Let's Move! campaign, Wolf Trap held its first annual "Let's Move with Music at Wolf Trap!" event.
After touring for sixteen years in North America, Riverdance had its final U.S. performance on July 17, 2012, at Wolf Trap.[28]
Free tickets to secretary of the interior
[edit]
The secretary of the interior has for decades been given eight free tickets for every event at Wolf Trap by the Wolf Trap Foundation.
This came to public light in a September 4, 2018, report by the Office of Inspector General for the Department of the Interior. The benefit was worth about $43,000 per year at the time of the report. The report raised ethics concerns about the tickets, since United States law generally prohibits government employees from receiving gifts. The inspector general's office recommended a review of the setup by ethics officials within the agency, and the department agreed to conduct the review.[29]
Despite the concerns, the National Park Service signed a new agreement with the Wolf Trap Foundation on May 3, 2019, that continued to provide the secretary's eight tickets for each performance for twenty more years. A Park Service spokesperson said the department conducted an ethical and legal review and "it was confirmed that the tickets are government property and may be used by the Department for authorized purposes."[30]
See also
[edit]- List of concert halls
- List of contemporary amphitheatres
- List of national parks of the United States
- International Children's Festival at Wolf Trap
Footnotes
[edit]- ^ "Listing of acreage – December 31, 2011" (XLSX). Land Resource Division, National Park Service. Retrieved May 13, 2012. (National Park Service Acreage Reports)
- ^ "NPS Annual Recreation Visits Report". National Park Service. Retrieved April 9, 2018.
- ^ a b Library of Congress Online Catalogue
- ^ a b c "Wolf Trap". Wolf Trap Foundation for the Performing Arts. Retrieved May 15, 2013.
- ^ "Best Internships of 2009". Bloomberg Businessweek. Archived from the original on December 14, 2009. Retrieved May 15, 2013.
- ^ 1634–1699: McCusker, J. J. (1997). How Much Is That in Real Money? A Historical Price Index for Use as a Deflator of Money Values in the Economy of the United States: Addenda et Corrigenda (PDF). American Antiquarian Society. 1700–1799: McCusker, J. J. (1992). How Much Is That in Real Money? A Historical Price Index for Use as a Deflator of Money Values in the Economy of the United States (PDF). American Antiquarian Society. 1800–present: Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis. "Consumer Price Index (estimate) 1800–". Retrieved February 29, 2024.
- ^ About the Filene Center https://www.wolftrap.org/about/venues/filene-center.aspx
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Wolf Trap National Park for the Performing Arts. Wolf Trap Interpretive Program Archives. Wolf Trap National Park for the Performing Arts. Vienna, VA: n.p., n.d. Print.
- ^ Ely, Eugene. "Wolf Trap Rebuilding Anticipated." Northern Virginia Sun Mar 15, 1971: 1+. Print.
- ^ "Fire-Stricken Filene Center Begins 'Recovering'." Northern Virginia Sun May 4, 1971: 3. Print.
- ^ https://www.wolftrap.org/about/venues/filene-center/filene-center-fire.aspx
- ^ Dills, Liz. "Wolf Trap Seeks $9 Million in Area." Faifax Connection Feb 29, 1984: 18. Print.
- ^ About the Filene Center." Wolf Trap Foundation, 2012. Aug 6, 2012.
- ^ Boselovic, Len. "In 11 Years of Life, It was the 3rd Fire". Fairfax Journal April 6, 1982: A7. Print.
- ^ The Barns at Wolf Trap https://www.wolftrap.org/about/venues/barns.aspx
- ^ Stuntz, Connie and Mayo. This Was Vienna, Virginia: Facts and Photos. N.p.: n.p., 1987. Print.
- ^ National Park Service, History of Wolf Trap NP
- ^ Asher, Robert L. "National Cultural Park Proposed for Fairfax Farm in Senate Bill." Washington Post May 28, 1966: B1. Print.
- ^ "Arts Center for Fairfax is Approved." Northern Virginia Sun July 16, 1966: 1. Print.
- ^ "Rep. Fallon Opposes Wolf Trap Cultural Park Bill." Washington Post July 25, 1966: C10. Print.
- ^ "Nixon Goes to Wolf Trap." Washington Post Aug 13, 1971: B1. Print.
- ^ Greenberg, Rudi (June 8, 2011). "Apart From the Pack: A Look Back at 40 Years of Wolf Trap". Washington Post.
- ^ "In Performance at Wolf Trap". Retrieved April 5, 2019.
- ^ Martin, Judith. "The Composer Vs. Blank Paper." Washington Post Aug 17, 1976: B1+. Print.
- ^ "A Stamp for Wolf Trap." Washington Post Aug 24, 1982: B3. Print.
- ^ Jordan, Mary. "New Filene Center Dedicated." Washington Post June 21, 1984: B3. Print.
- ^ Plumb, Tierney (October 22, 2009). "Wolf Trap Looks to Rebound with More Ticket Sales". Washington Business Journal. Retrieved August 11, 2012.
- ^ Traiger, Lisa (June 15, 2012). "Wolf Trap Ready for a Last Dance". Washington Post. Archived from the original on February 9, 2013. Retrieved August 11, 2012.
- ^ Watkins, Eli (September 6, 2018). "NPS orders ethics review of program giving Interior leader access to $43K in free concert tickets". CNN. Retrieved November 2, 2019.
- ^ Beitsch, Rebecca (May 3, 2019). "Free concert tickets flow to Interior secretary, despite ethics questions". The Hill. Retrieved November 2, 2019.
External links
[edit]- Parks in Fairfax County, Virginia
- Music venues in Virginia
- Performing arts centers in Virginia
- National parks in Virginia
- Theatre in Virginia
- Members of the Cultural Alliance of Greater Washington
- Protected areas established in 1966
- Tourist attractions in Fairfax County, Virginia
- Vienna, Virginia
- 1966 establishments in Virginia