Texas Blackland Prairies
| Texas Blackland Prairies | |
|---|---|
 | |
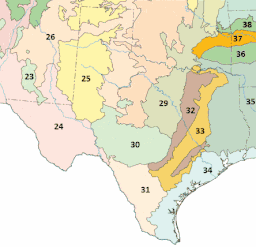 Texas blackland prairies (area 32 on the map) | |
| Ecology | |
| Realm | Nearctic |
| Biome | Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands |
| Borders |
|
| Bird species | 216[1] |
| Mammal species | 61[1] |
| Geography | |
| Area | 50,300 km2 (19,400 sq mi) |
| Country | United States |
| State | Texas |
| Climate type | Humid subtropical (Cfa) |
| Conservation | |
| Habitat loss | 76.458%[1] |
| Protected | 0.64%[1] |
The Texas Blackland Prairies are a temperate grassland ecoregion located in Texas that runs roughly 300 miles (480 km) from the Red River in North Texas to San Antonio in the south. The prairie was named after its rich, dark soil.[3] Less than 1% of the original Blackland prairie vegetation remains, scattered across Texas in parcels.[4]
Setting
[edit]The Texas Blackland Prairies ecoregion covers an area of 50,300 km2 (19,400 sq mi), consisting of a main belt of 43,000 km2 (17,000 sq mi) and two islands of tallgrass prairie grasslands southeast of the main Blackland Prairie belt; both the main belt and the islands extend northeast–southwest.
The main belt consists of oaklands and savannas and runs from just south of the Red River on the Texas-Oklahoma border through the Dallas–Fort Worth metropolitan area and southward to the vicinity of San Antonio, Bexar County. The central forest-grasslands transition lies to the north and northwest, and the Edwards Plateau savanna and the Tamaulipan mezquital lie to the southwest.
The larger of the two islands is the Fayette Prairie, encompassing 17,000 km2 (6,600 sq mi), and the smaller is the San Antonio Prairie, with an area of 7,000 km2 (2,700 sq mi). The two islands are separated from the main belt by the oak woodlands of the East Central Texas forests, which surround the islands on all sides but the northeast, where the Fayette Prairie meets the East Texas Piney Woods.
Texas counties that once supported blackland prairies include all or most of Collin, Dallas, Delta, Ellis, Hunt, Kaufman, Navarro, and Rockwall counties, as well as portions of Bastrop, Bell, Bexar, Caldwell, Denton, Falls, Fannin, Franklin, Freestone, Grayson, Guadalupe, Henderson, Hill, Hopkins, Johnson, Lamar, Limestone, McLennan, Milam, Rains, Red River, Tarrant, Titus, Travis, Van Zandt, and Williamson counties, all in the northwestern band of the region. The smaller southeastern band includes much of Grimes and Washington counties as well as portions of Austin, Colorado, Fayette, and the northwestern half of Lavaca county.[5]: 311 p. Sources and maps vary on the exact boundaries of the Blackland Prairie, and some may include or exclude different portions of peripheral counties.
History
[edit]Native American hunter-gatherers contributed to the maintenance of the prairie through controlled burns to make more land suitable for hunting bison and other game. Hunter-gatherers continually inhabited the prairie since pre-Clovis times over 15,000 years ago. In historic times, they included the Wichita, Waco, Tonkawa, and Comanche, each of whom were gradually replaced by settled agrarian society. The advent of large-scale irrigated farming and ranching in the area quickly led to widespread habitat loss.

Early Czechoslovakian and German immigrants arrived in the region around 1825 to 1845 and found the rich black soil excellent for farming. By the end of the 19th century 98% of the blackland prairies were cultivated and it was the leading cotton region of the state, also producing sorghum, corn, wheat, and hay. The land was so valuable, crops were planted abruptly up to the roadsides, seldom fenced, and riparian areas were cleared right to the creek banks. Several of the larger cities in the state, such as Austin, Dallas, Fort Worth, San Antonio, Temple, and Waco, are located in the region and the agricultural activity in the area was a significant factor in their growth in the 19th century.[5]: 393–394 p. [6]
The U. S. Bureau of Biological Survey [now the United States Fish and Wildlife Service], led by chief field naturalist Vernon Bailey with a crew of 12 federal field agents conducted a 17-year (1889–1905), statewide survey of the natural history of Texas.[7] The survey collected detailed data on the topography, land use, climate, as well as plant, bird, and mammal specimens, and extensive photographs of the landscape.[5]: 3 p. However, because the natural state of the Blackland Prairie region was so altered, even at that time, that little wildlife remained and the biological survey crew spent little time there, ca. 4% of the total fieldwork.[5]: 311 & 369 p. The human population of Texas in 1900 was less than 3,000,000 (ca. 11 people per square mile), in 2001 it was over 20,000,000 (ca. 78 people per square mile),[5]: 3 p. in 2019 it was nearly 29,000,000 (96 people per square mile).[8] Although 98% of the land was cultivated around 1900, after 1950 a shift in land use occurred, with about 50% in cultivation and a significant increase in pasture for livestock production, ca. 25% tame pasture and 25% rangeland. "As a result of cultivation, overgrazing, and other imprudent land-use practices, there are few if any remnants of climax vegetation in the region."[5]: 394 p.
Ecology
[edit]The Blackland Prairie was a disturbance maintained ecosystem prior to the arrival of Europeans. Fires ignited by lightning occasionally swept the area, clearing or reducing the encroachment of trees and shrubs on the prairie, while stimulating the native herbaceous prairie species of forbs and grasses which are pyrophytic, adapted and resistant to wildfires. The exact frequency of fires is unknown but estimated to have occurred at intervals of 5 to 10 years. Herds of bison, and to a lesser extent pronghorn and deer, grazed on the grasses and trampled and fertilized the soil, stimulating the growth of the tallgrass ecosystem. Bison were extirpated from the area by the 1850s.[9][6]
The soil of the Blackland Prairies, from which the "blackland" gets its name, contains black or dark-gray, alkaline clay in both upland and bottomland areas.[4] Some western areas have shallow soils over chalk, while some soils in eastern areas are slightly acidic to neutral, grayish clays and loams over mottled clay subsoils (occasionally referred to as graylands). "Black gumbo" and "black velvet" are local names for this soil. The soils have vertisols properties, shrinking and swelling with moisture content. In dry weather, deep cracks form in the clay, which can cause damage to buildings and infrastructure. Soil management problems also include water erosion, cotton root rot, soil tilth, and brush control.[10]
The rich black 'waxland' soil of these prairies is almost proof against burrowing rodents, which penetrate the region only along some sandy stream bottoms, while the open country tempts jack rabbits, coyotes, and other plains species eastward slightly beyond their usual bounds. Few, if any, species are restricted to these prairie, however, and the effect on distribution is mainly negative." [7]: 19 p.
The negative effect on distribution is evident in the Texas distribution of many wide-ranging species of both eastern and western North American fauna reaching their respective distributional limits in the region of the Texas Blackland Prairies and East Central Texas forests [e.g. eastern: American alligator (Alligator mississippiensis), eastern gray squirrel (Sciurus carolinensis), southern flying squirrel (Glaucomys volans),; western: American badger (Taxidea taxus), western diamondback rattlesnake (Crotalus atrox); and other fauna listed below].
Flora
[edit]Important prairie plants included little bluestem, yellow indiangrass, big bluestem, tall dropseed, and a variety of wildflowers including gayfeathers, asters, Maximilian sunflower, wild indigos and compass plant.
Fauna
[edit]
Mammals: Some species found in the region include Virginia opossum (Didelphis virginiana), nine-banded armadillo (Dasypus novemcinctus), Eastern red bat (Lasiurus borealis), Brazilian free-tailed bat (Tadarida brasiliensis), fulvous harvest mouse (Reithrodontomys fulvescens), white-footed mouse (Peromyscus leucopus), hispid cotton rat (Sigmodon hispidus)), eastern fox squirrel (Sciurus niger), American beaver (Castor canadensis), white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus), northern raccoon (Procyon lotor), striped skunk (Mephitis mephitis), bobcat (Lynx rufus), gray fox (Urocyon cinereoargenteus), and coyotes (Canis latrans).[11][12]
The large, keystone species that once inhabited the Blackland Prairies, before the arrival of Europeans and the destruction of the tallgrass ecosystem, are now extirpated, including American bison (Bos bison), gray wolf (Canis lupus), red wolf (Canis rufus), mountain lion (Puma concolor), black bear (Ursus americanus), and pronghorn (Antilocapra americana) which once ranged into the western areas, and even jaguar (Panthera onca) and ocelot (Leopardus pardalis) that once occurred in the southern regions. Invasive species include nutria or coypu (Myocastor coypus), house mouse (Mus musculus), roof rat (Rattus rattus), and Norway rat (Rattus norvegicus). Feral house cats (Felis catus) and feral pigs (Sus scrofa), are of conservation concerns and pose serious threats to native fauna.[11][12]

Birds: With spring and fall migrants, wintering species, breading and summer species, well over 325 species of birds occur in the region. Various seasonal and migratory species appearing in the region include Bufflehead (Bucephala albeola), Hooded Merganser (Lophodytes cucullatus), Little Blue Heron (Egretta caerulea), Yellow-crowned Night Heron (Nyctanassa violacea), Northern Harrier (Circus hudsonius), Inca Dove (Columbina inca), Yellow-billed Cuckoo (Coccyzus americanus), Ruby-throated Hummingbird (Archilochus colubris), Scissor-tailed Flycatcher (Tyrannus forficatus), American Pipit (Anthus rubescens), Orange-crowned Warbler (Leiothlypis celata), Blue Grosbeak (Passerina caerulea), Indigo Bunting (Passerina cyanea), Painted Bunting (Passerina ciris), Harris's Sparrow (Zonotrichia querula), and Dickcissel (Spiza americana).[13][14]
A few of the year round resident species include wood duck (Aix sponsa), blue-winged teal (Anas discors), black vulture (Coragyps atratus), cooper's hawk (Accipiter cooperii), red-shouldered hawk (Buteo lineatus), American kestrel (Falco sparverius), great horned owl (Bubo virginianus), barred owl (Strix varia), greater roadrunner (Geococcyx californianus), belted kingfisher (Megaceryle alcyon), red-bellied woodpecker (Melanerpes carolinus), hairy woodpecker (Leuconotopicus villosus), loggerhead shrike (Lanius ludovicianus), red-winged blackbird (Agelaius phoeniceus), eastern meadowlark (Sturnella magna), eastern bluebird (Sialia sialis), tufted titmouse (Baeolophus bicolor), Carolina wren (Thryothorus ludovicianus), chipping sparrow (Spizella passerina), lark sparrow (Chondestes grammacus), and grasshopper sparrow (Ammodramus savannarum).[14][13]

Reptiles: Although not particularly abundant, the American alligator (Alligator mississippiensis) ranges into the Blackland Prairies. The ubiquitous red-eared slider (Trachemys scripta) is found throughout the region, the river cooter (Pseudemys concinna) in the northeast, the Texas cooter (Pseudemys texana) in the southwest, the Mississippi map turtle (Graptemys pseudogeographica) in the larger rivers, and several records of the rare chicken turtle (Deirochelys reticularia). Others include eastern snapping turtle (Chelydra serpentina), three-toed box turtle (Terrapene triunguis), ornate box turtle (Terrapene ornata), Mississippi mud turtle (Kinosternon subrubrum), eastern musk turtle (Sternotherus odoratus), spiny softshellturtle (Apalone spinifera). Lizards include Green Anole (Anolis carolinensis), Six-lined Racerunner (Aspidoscelis sexlineatus), Prairie Lizard (Sceloporus conssbrinus), Western Slender Glass Lizard (Ophisaurus attenuatus), Five-lined Skink (Plestiodon fasciatus), Broad-headed Skink (Plestiodon laticeps), Prairie Skink (Plestiodon septentrionalis), and Ground Skink (Scincella lateralis).[15][16]
Snakes are the most diverse group of reptiles in the region, species include the North American racer (Coluber constrictor), eastern hog-nosed snake (Heterodon platirhinos), prairie kingsnake (Lampropeltis calligaster), speckled kingsnake (Lampropeltis holbrooki), coachwhip (Masticophis flagellum), yellow-bellied watersnake (Nerodia erythrogaster), diamond-backed watersnake (Nerodia rhombifer), rough greensnake (Opheodrys aestivus), western ratsnake (Pantherophis obsoletus), Graham's crayfishsnake (Regina grahamii), flat-headed snake (Tantilla gracilis), western ribbonsnake (Thamnophis proximus), and several others. Venomous species include the copperhead (Agkistrodon contortrix), cottonmouth (Agkistrodon piscivorus), timber rattlesnake (Crotalus horridus), and the Texas coralsnake (Micrurus tener).[15][16]
Amphibians: Frogs and toads in the region include the American bullfrog (Lithobates catesbeianus), southern leopard frog (Lithobates sphenocephalus), Woodhouse's toad (Anaxyrus woodhousii), Hurter's spadefoot toad (Scaphiopus hurterii), Great Plains narrow-mouthed toad (Gastrophryne olivacea), Blanchard's cricket frog (Acris blanchardi), Cope's gray treefrog (Hyla chrysoscelis), green treefrog (Hyla cinerea), spotted chorus frog (Pseudacris clarkii), Strecker's chorus frog (Pseudacris streckeri), and another ten species recorded from limited areas or marginal counties of the Blackland Prairie. Salamanders include the small-mouthed salamander (Ambystoma texanum), central newt (Notophthalmus viridescens), and western lesser siren (Siren intermedia).[15][16]

Fish: Among the many fish of the region are spotted bass (Micropterus punctulatus), white bass (Morone chrysops), black crappie (Pomoxis nigromaculatus), white crappie (Pomoxis annularis), black bullhead (Ameiurus melas), blue catfish (Ictalurus furcatus), flathead catfish (Pylodictis olivaris), freckled madtom (Noturus nocturnus), warmouth (Lepomis gulosus), orangespotted sundfish (Lepomis humilis), longear sunfish (Lepomis megalotis), freshwater drum (Aplodinotus grunniens).[17][18][19]
Just a few of the smaller species include threadfin shad (Dorosoma petenense), red shiner (Cyprinella lutrensis), blacktail shiner (Cyprinella venusta), shoal chub (Macrhybopsis hyostoma), ghost shiner (Notropis buchanani), pugnose minnow (Opsopoeodus emiliae), fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas), bullhead minnow (Pimephales vigilax), river carpsucker (Carpiodes carpio), blackstripe topminnow (Fundulus notatus), slough darter (Etheostoma gracile), bigscale logperch (Percina macrolepida), and dusky darter (Percina sciera) and many others.[17][18][19]
Conservation
[edit]Because of the soil and climate, this ecoregion is ideally suited to crop agriculture. This has led to most of the Blackland Prairie ecosystem being converted to crop production, leaving less than one percent remaining.[4] Some groups estimate that less than 0.1% of the area is remaining.[4] Small remnants are conserved at sites such as The Nature Conservancy's 1,400-acre Clymer Meadow Preserve near Celeste, TX.
Protected areas
[edit]The U.S. Forest Service manages the Caddo National Grassland (17,784 acres (71.97 km2)) under the multiple-use concept, balancing resource extraction, preservation, and recreation.[20]
The State of Texas administers a number of state parks and wildlife management areas in the region, however they are mostly located around human-made lakes and riparian zones of rivers and creeks, focusing on recreation, fishing, and hunting, and not prairie conservation. Many of these areas are leased, not owned, by the state (* = leased).[21]

- Texas Blackland Prairies
- Bonham State Park (261 acres)
- Cedar Creek Islands Wildlife Management Area (160 acres)
- Cedar Hill State Park (1,826 acres)
- Cooper Lake State Park (3,026 acres) U.S. Army Corps of Engineers*
- Cooper Wildlife Management Area (14,480 acres) U.S. Army Corps of Engineers*
- Lake Tawakoni State Park (376 acres), Sabine River Authority of Texas*
- Tawakoni Wildlife Management Area (2,335 acres), Sabine River Authority of Texas (1,561 acres)*
- Lockhart State Park (? acres)
- Purtis Creek State Park (1,582 acres)
- Louis René Barrera Indiangrass Wildlife Sanctuary (281 acres)
- Peripheral areas

- Caddo National Grasslands Wildlife Management Area (16,174 acres), U.S. Forest Service*
- Eisenhower State Park (463 acres), U.S. Army Corps of Engineers*
- Fort Parker State Park (ca. 1500 acres)
- Lake Bob Sandlin State Park (640 acres)
- Lake Summerville State Park (? acres), U.S. Army Corps of Engineers*
- McKinney Falls State Park (641 acres)
- Mother Neff State Park (400 acres)
- Richland Creek Wildlife Management Area (13,783 acres)
Gallery
[edit]-
Ranchland seen from Highway 916 east of Grandview, Johnson County, Texas, USA (26 June 2021)
-
Ranch and pastureland seen from Highway 339, Limestone County Texas, USA USA (26 June 2021)
-
Ranchland in the Blackland Prairie eco-region of Texas with Texas bluebonnets (Lupinus texensis), Washington County, Texas, USA (30 March 2012).
-
Washington-on-the-Brazos State Historic Site, Washington County, Texas, USA (30 March 2012).
-
Farmland in the Blackland Prairie region seen from Highway 123, Guadalupe County, Texas, USA (9 July 2020)
-
Texas bluebonnets (Lupinus texensis) in the Blackland Prairie eco-region, Highway 532 east of Gonzales, Gonzales County, Texas, USA (19 April 2014).
-
Fox Glove (Penstemon cobaea) on ranchland in the Blackland Prairie eco-region. County Road 269, Lavaca County, Texas, USA (19 April 2014).
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c d Hoekstra, J. M.; Molnar, J. L.; Jennings, M.; Revenga, C.; Spalding, M. D.; Boucher, T. M.; Robertson, J. C.; Heibel, T. J.; Ellison, K. (2010). Molnar, J. L. (ed.). The Atlas of Global Conservation: Changes, Challenges, and Opportunities to Make a Difference. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-26256-0.
- ^ a b c "Ecoregions of Texas" (PDF). U.S. EPA. Retrieved 2016-02-06.
- ^ "Blackland Prairies". Invasives 101. Texas Invasives. Retrieved 2017-02-06.
- ^ a b c d D’Annunzio, Francesca (2021-12-28). "North America's Most Endangered Ecoregion is in North Texas' Backyard". Dallas News.
- ^ a b c d e f Schimidly, David J. (2002) Texas Natural History: A Century of Change. Texas Tech University Press. Lubbock, Texas. xv, 534 pp. ISBN 0-89672-469-7
- ^ a b World Wildlife Fund, Texas Blackland Prairies https://www.worldwildlife.org/ecoregions/na0814, accessed 29 June 2021
- ^ a b Bailey, Vernon and C. Hart Merriam (1905) Biological survey of Texas. North American Fauna No. 25: 1-222.
- ^ United States Census Bureau: QuickFacts, Texas, accessed 29 June 2021
- ^ "Post Oak Savannah and Blackland Prairie Wildlife Management: Historical Perspective". Texas Parks and Wildlife Department. Retrieved 2008-08-15.
- ^ "Soils of Texas". Texas Almanac. Texas Historical Society. Retrieved 2017-02-26.
- ^ a b Schmidly, D. J. 2004. The Mammals of Texas, 6th. Ed. University of Texas Press, Austin, Texas. xviii, 501 pp. ISBN 0-292-70241-8
- ^ a b Reid, Fiona A. 2006. Field Guide to Mammals of North America North of Mexico, 4th ed., Peterson Field Guide Series. Houghton Mifflin Company. New York. xx, 579 pp. ISBN 0-395-93596-2
- ^ a b Mulroy, Kevin (Editor-in-Chief). 2002. Field Guide to the Birds of North America, 4th edition. National Geographic, Washington, D. C. 480 pp. ISBN 0-7922-6877-6
- ^ a b Peterson, Roger Troy. 1980. A Field Guide to the Birds: a Completely New Guide to all the Birds of Eastern and Central North America. Houghton Mifflin Co., Boston, 384 pp. ISBN 0-395-26621-1
- ^ a b c Dixon, James R. (2013) Amphibians and Reptiles of Texas: with keys, taxonomic synopses, bibliography, and distribution maps. Texas A&M University Press, College Station. 447 pp. ISBN 978-160344-734-8
- ^ a b c Powell, R, R. Conant, and J. T. Collins. 2016. Peterson Field Guide to Reptiles and Amphibians of Eastern and Central North America, 4th ed. Houghton Mifflin Co., Boston, Massachusetts. xiii, 494 pp. ISBN 978-0-544-12997-9
- ^ a b Lee, D. S., C. R. Gilbert, C. H. Hocutt, R. E. Jenkins, D. E. McAllister, and J. R. Stauffer, Jr. 1980. Atlas of North American Freshwater Fishes. North Carolina State Museum of Natural History. x, 867 pp. ISBN 0-917134-03-6
- ^ a b Page, L. M. and B. M. Burr. 2011. Peterson Field Guide to Freshwater Fishes: North America North of Mexico, Second Edition. Peterson Field Guide Series. Houghton Mifflin Company. Boston, Massachusetts. xix, 663 pp. ISBN 978-0-547-24206-4
- ^ a b Thomas, Chad, Timothy H. Bonner, & Bobby G. Whiteside. 2007. Freshwater Fishes of Texas: A Field Guide. Texas A&M University Press. College Station, Texas. xiv, 202 pp. ISBN 1-58544-570-3
- ^ "National Forests and Grasslands in Texas: Management". US Forest Service.
- ^ "Texas Parks and Wildlife". Retrieved 4 July 2021.
- Ricketts, Taylor H., Eric Dinerstein, David M. Olson, Colby J. Loucks, et al. (1999). Terrestrial Ecoregions of North America: a Conservation Assessment. Island Press, Washington DC.
External links
[edit]- Native Prairies Association of Texas (NPAT)
- NPAT protected prairies
- The Nature Conservancy (TNC)
- Texas Parks and Wildlife
- "Texas blackland prairie". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund.
- Connemara Conservancy
- Soil Physics at Oklahoma State
- Weeds of the Blackland Prairie
- Prairie Time: A Blackland Portrait
- Texas counties map showing the ecoregion
- Weeds of the Blackland Prairie







