Supraventricular tachycardia
| Supraventricular tachycardia | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Supraventricular arrhythmia |
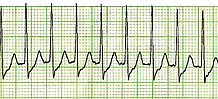 | |
| Lead II electrocardiogram strip showing PSVT with a heart rate of about 180 | |
| Specialty | Cardiology |
| Symptoms | Palpitations, feeling faint, sweating, shortness of breath, chest pain.[1] |
| Types | Atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT), Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome,[2] AVRT, AVNRT, PJRT, Sinus Tachycardia, MAT, JET, Atrial tachycardia, SA Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia (SANRT) |
| Causes | Re-entry or increased cardiac muscle automaticity[3] |
| Diagnostic method | Electrocardiogram (ECG), Holter monitor, event monitor[4] |
| Treatment | Medications, medical procedures, surgery[5] |
| Frequency | ~3%[6][7][8] |
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is an umbrella term for fast heart rhythms arising from the upper part of the heart.[2] This is in contrast to the other group of fast heart rhythms – ventricular tachycardia, which start within the lower chambers of the heart.[2] There are four main types of SVT: atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT), and Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome.[2] The symptoms of SVT include palpitations, feeling of faintness, sweating, shortness of breath, and/or chest pain.[1]
These abnormal rhythms start from either the atria or atrioventricular node.[2] They are generally due to one of two mechanisms: re-entry or increased automaticity.[3] Diagnosis is typically by electrocardiogram (ECG), Holter monitor, or event monitor.[4] Blood tests may be done to rule out specific underlying causes such as hyperthyroidism, pheochromocytomas, or electrolyte abnormalities.[4]
A normal resting heart rate is 60 to 100 beats per minute. A resting heart rate of more than 100 beats per minute is defined as a tachycardia. During an episode of SVT, the heart beats about 150 to 220 times per minute.[9]
Specific treatment depends on the type of SVT[5] and can include medications, medical procedures, or surgery.[5] Vagal maneuvers, or a procedure known as catheter ablation, may be effective in certain types.[5] For atrial fibrillation, calcium channel blockers or beta blockers may be used for rate control, and selected patients benefit from blood thinners (anticoagulants) such as warfarin or novel anticoagulants.[5] Atrial fibrillation affects about 25 per 1000 people,[7] paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia 2.3 per 1000,[6] Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome 2 per 1000,[8] and atrial flutter 0.8 per 1000.[10]
Signs and symptoms
[edit]Signs and symptoms can arise suddenly and may resolve without treatment. Stress, exercise, and emotion can all result in a normal or physiological increase in heart rate, but they can precipitate SVT in rare cases. Episodes can last from a few minutes to one or two days. They sometimes persist until treated. The rapid heart rate, if fast enough, reduces the opportunity for the "pump" to fill between beats decreasing cardiac output and consequently blood pressure. The following symptoms are typical with a rate of 150–270 or more beats per minute:[11]
- Pounding heart
- Rapid heart beat
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Rapid breathing
- Dizziness
- Sweating
- Loss of consciousness
Symptoms of heart arrhythmias, such as SVT, are more difficult to assess in infants and toddlers because of their limited ability to communicate. Caregivers should watch for lack of interest in feeding, shallow breathing, and lethargy. These symptoms may be subtle and may be accompanied by vomiting and/or a decrease in responsiveness.[12]
Pathophysiology
[edit]
The main pumping chamber, the ventricle, is protected (to a certain extent) against excessively high rates arising from the supraventricular areas by a "gating mechanism" at the atrioventricular node,[13] which allows only a proportion of the fast impulses to pass through to the ventricles. An accessory "bypass tract" can avoid the AV node and its protection so that the fast rate may be directly transmitted to the ventricles. This situation has characteristic findings on ECG.[14] A congenital heart lesion, Ebstein's anomaly, is most commonly associated with supraventricular tachycardia.
Diagnosis
[edit]

Subtypes of SVT can often be distinguished by their electrocardiogram (ECG) characteristics. Most have a narrow QRS complex, although, occasionally, electrical conduction abnormalities may produce a wide QRS complex that may mimic ventricular tachycardia (VT). In the clinical setting, the distinction between narrow and wide complex tachycardia (supraventricular vs. ventricular) is fundamental since they are treated differently. In addition, ventricular tachycardia can quickly degenerate into ventricular fibrillation and death and merits different consideration. In the less common situation in which a wide-complex tachycardia may be supraventricular, a number of algorithms have been devised to assist in distinguishing between them.[15] In general, a history of structural heart disease markedly increases the likelihood that the tachycardia is ventricular in origin.[16]
- Sinus tachycardia is physiologic when a reasonable stimulus, such as the catecholamine surge associated with fright, stress, or physical activity, provokes the tachycardia. It is identical to a normal sinus rhythm, except for its faster rate (>100 beats per minute in adults). However, sinus tachycardia is considered part of the diagnoses included in SVT by most sources.[17]
- Sinoatrial node reentrant tachycardia (SANRT) is caused by a reentry circuit localised to the SA node, resulting in a P-wave of normal shape and size (morphology) that falls before a regular, narrow QRS complex. It cannot be distinguished electrocardiographically from sinus tachycardia unless the sudden onset is observed (or recorded on a continuous monitoring device). It may sometimes be distinguished by its prompt response to vagal maneuvers.[18]
- Ectopic (unifocal) atrial tachycardia arises from an independent focus within the atria, distinguished by a consistent P-wave of abnormal shape and/or size that falls before a narrow, regular QRS complex. It can be caused by automaticity, which means that some cardiac muscle cells, which have the primordial (primitive, inborn, inherent) ability to generate electrical impulses that are common to all cardiac muscle cells, have established themselves as a 'rhythm center' with a natural rate of electrical discharge that is faster than the normal SA node. Some atrial tachycardias, rather than being a result of increased automaticity may be a result of a micro-reentrant circuit (defined by some as less than 2 cm in longest diameter to distinguish it from macro-reentrant atrial flutter). Still other atrial tachycardias may be due to triggered activity caused by after-depolarizations.[19]
- Multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT) is tachycardia arising from at least three ectopic foci within the atria, distinguished by P-waves of at least three different morphologies that all fall before irregular, narrow QRS complexes. This rhythm is most commonly seen in elderly people with COPD.[20]

- Atrial fibrillation meets the definition of SVT when associated with a ventricular response greater than 100 beats per minute. It is characterized as an "irregularly, irregular rhythm" both in its atrial and ventricular depolarizations and is distinguished by its fibrillatory atrial waves that, at some point in their chaos, stimulate a response from the ventricles in the form of irregular, narrow QRS complexes.
- Atrial flutter, is caused by a re-entry rhythm in the atria, with a regular atrial rate often of about 300 beats per minute. On the ECG this appears as a line of "sawtooth" waves preceding the QRS complex. The AV node will not usually conduct 300 beats per minute so the P:QRS ratio is usually 2:1 or 4:1 pattern, (though rarely 3:1, and sometimes 1:1 where class IC antiarrhythmic drug are in use). Because the ratio of P to QRS is usually consistent, A-flutter is often regular in comparison to its irregular counterpart, atrial fibrillation. Atrial flutter is also not necessarily a tachycardia by definition unless the AV node permits a ventricular response greater than 100 beats per minute.
- AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) involves a reentry circuit forming next to, or within, the AV node. The circuit most often involves two tiny pathways one faster than the other. Because the node is immediately between the atria and ventricle, the re-entry circuit often stimulates both, appearing as a backward (retrograde) conducted P-wave buried within or occurring just after the regular, narrow QRS complexes.
- Atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia (AVRT), also results from a reentry circuit, although one physically much larger than AVNRT. One portion of the circuit is usually the AV node, and the other, an abnormal accessory pathway (muscular connection) from the atria to the ventricle. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) is a relatively common abnormality with an accessory pathway, the bundle of Kent crossing the AV valvular ring.[21]
- In orthodromic AVRT, atrial impulses are conducted down through the AV node and retrogradely re-enter the atrium via the accessory pathway. A distinguishing characteristic of orthodromic AVRT can therefore be an inverted P-wave (relative to a sinus P wave) that follows each of its regular, narrow QRS complexes, due to retrograde conduction.
- In antidromic AVRT, atrial impulses are conducted down through the accessory pathway and re-enter the atrium retrogradely via the AV node. Because the accessory pathway initiates conduction in the ventricles outside of the bundle of His, the QRS complex in antidromic AVRT is wider than usual. A delta wave is an initial slurred deflection seen in the initial part of an otherwise narrow QRS of a patient at risk for WPW and is an indicator of the presence of an accessory pathway. These beats are a fusion between the conduction down the accessory pathway and the slightly delayed but then-dominant conduction via the AV node. Once an antidromic AVRT tachycardia is initiated, it is no longer delta waves but rather a wide complex (>120 ms) tachycardia that is seen.
- Junctional ectopic tachycardia (JET) is a rare tachycardia caused by increased automaticity of the AV node itself initiating frequent heartbeats. On the ECG, junctional tachycardia often presents with abnormal morphology P-waves that may fall anywhere in relation to a regular, narrow QRS complex. It is often due to drug toxicity.[22]
Classification
[edit]

The following types of supraventricular tachycardias are more precisely classified by their specific site of origin. While each belongs to the broad classification of SVT, the specific term/diagnosis is preferred when possible:
Sinoatrial origin:[23]
- Sinoatrial nodal reentrant tachycardia (SNRT)
Atrial origin:
- Ectopic (unifocal) atrial tachycardia (EAT)
- Multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT)
- Atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response
- Atrial flutter with rapid ventricular response
- (Without rapid ventricular response, fibrillation and flutter are usually not classified as SVT)
Atrioventricular origin:[22]
- AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) or junctional reciprocating tachycardia (JRT)
- AV reciprocating tachycardia (AVRT) – visible or concealed (including Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome)
- Permanent (or persistent) junctional reciprocating tachycardia (PJRT), a form of SVT that involves a slow retrograde conduction over accessory pathway – occurs predominantly in infants and children but can occasionally occur in adults
- Junctional ectopic tachycardia (JET)
Prevention
[edit]Once an acute arrhythmia has been terminated, ongoing treatment may be indicated to prevent recurrence. However, those that have an isolated episode, or infrequent and minimally symptomatic episodes, usually do not warrant treatment other than observation and explanation.
In general, patients with more frequent or disabling symptoms warrant some form of prevention. A variety of drugs including simple AV nodal blocking agents such as beta blockers and verapamil, as well as antiarrhythmic drugs may be used, usually with good effect, although the adverse effects of these therapies need to be weighed against potential benefits.[24]
Radiofrequency ablation has revolutionized the treatment of tachycardia caused by a re-entrant pathway. This is a low-risk procedure that uses a catheter inside the heart to deliver radiofrequency energy to locate and destroy the abnormal electrical pathways. Ablation has been shown to be highly effective: around 90% in the case of AVNRT. Similar high rates of success are achieved with AVRT and typical atrial flutter.[25]
Cryoablation is a newer treatment involving the AV node directly. SVT involving the AV node is often a contraindication to using radiofrequency ablation due to the small (1%) incidence of injuring the AV node, then requiring a permanent pacemaker. Cryoablation uses a catheter supercooled by nitrous oxide gas freezing the tissue to −10 °C (+14.0 °F). This provides the same result as radiofrequency ablation but does not carry the same risk. If it is found that the wrong tissue is being frozen, the freezing process can be quickly stopped with the tissue returning to normal temperature and function in a short time. If after freezing the tissue to −10 °C the desired result is obtained, the tissue can be further cooled to a temperature of −73 °C (-99.4 °F) and it will be permanently ablated.[26]
This therapy has further improved the treatment options for AVNRT (and other SVTs with pathways close to the AV node), widening the application of curative ablation to young patients with relatively mild but still troublesome symptoms who might not have accepted the risk of requiring a pacemaker.
Treatment
[edit]Most SVTs are unpleasant rather than life-threatening, although very fast heart rates can be problematic for those with underlying ischemic heart disease, or the elderly. Episodes can be treated when they occur by Valsalva maneuver, adenosine injection or taking a AV node blocking agent as pill-in-pocket, but regular medication may also be used to prevent or reduce recurrence. While some treatment modalities can be applied to all SVTs, there are specific therapies available to treat some sub-types. Effective treatment consequently requires knowledge of how and where the arrhythmia is initiated and its mode of spread.[27]
Lifestyle changes, medication and heart procedures may be needed to control or eliminate the rapid heartbeats and related symptoms.[9]
SVTs can be categorised by whether the AV node is involved in maintaining the rhythm. If it is, manoeuvres slowing conduction through the AV node will terminate it. If it is not, AV nodal blocking maneuvers will not terminate it, but resulting temporary suppression of the AV node is still useful to unmask the underlying abnormal rhythm.[28]
Acute attacks of supraventricular tachycardia are treated with Esmolol (i.v.).
Society and culture
[edit]Notable cases of SVT:
- Bobby Julich, American professional road cyclist, third-place finisher in the 1998 Tour de France, bronze medalist in the 2004 Summer Olympics[29]
- Tayyiba Haneef-Park, American volleyball competitor in the 2008 Summer Olympics[30]
- Tony Blair, former Prime Minister of the United Kingdom[31]
- Anastacia, American singer-songwriter.[32]
- Rebecca Soni, American Gold Medal Olympic swimmer[33]
- Dana Vollmer, American Gold Medal Olympic swimmer[34]
- Neville Fields, Australian football player[citation needed]
- Paul Bearer, wrestling manager[35]
- Nathan Cohen, New Zealand's two-time world champion and Olympic champion rower, was diagnosed with SVT in 2013 when he was 27 years old.[36][37][38]
- Miley Cyrus, American singer and actress[39]
- George Plimpton, notable author, sportswriter, and literary personality[40]
References
[edit]- ^ a b "What Are the Signs and Symptoms of an Arrhythmia?". NHLBI. July 1, 2011. Archived from the original on 19 February 2015. Retrieved 27 September 2016.
- ^ a b c d e "Types of Arrhythmia". NHLBI. July 1, 2011. Archived from the original on June 7, 2015.
- ^ a b Al-Zaiti, SS; Magdic, KS (September 2016). "Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management". Critical Care Nursing Clinics of North America. 28 (3): 309–316. doi:10.1016/j.cnc.2016.04.005. PMID 27484659.
- ^ a b c "How Are Arrhythmias Diagnosed?". NHLBI. July 1, 2011. Archived from the original on February 18, 2015.
- ^ a b c d e "How Are Arrhythmias Treated?". NHLBI. July 1, 2011. Retrieved 27 September 2016.
- ^ a b Katritsis, Demosthenes G.; Camm, A. John; Gersh, Bernard J. (2016). Clinical Cardiology: Current Practice Guidelines. Oxford University Press. p. 538. ISBN 9780198733324. Archived from the original on 2016-10-02.
- ^ a b Zoni-Berisso, M; Lercari, F; Carazza, T; Domenicucci, S (2014). "Epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: European perspective". Clinical Epidemiology. 6: 213–220. doi:10.2147/CLEP.S47385. PMC 4064952. PMID 24966695.
- ^ a b Ferri, Fred F. (2016). Ferri's Clinical Advisor 2017. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 1372. ISBN 9780323448383. Archived from the original on 2016-10-02.
- ^ a b "Supraventricular tachycardia – Symptoms and causes". Mayo Clinic. Retrieved 2022-03-18.
- ^ Bennett, David H. (2012). Bennett's Cardiac Arrhythmias: Practical Notes on Interpretation and Treatment. John Wiley & Sons. p. 49. ISBN 9781118432402. Archived from the original on 2016-10-02.
- ^ Mahtani AU, Nair DG. Supraventricular Tachycardia. Med Clin North Am. 2019 Sep;103(5):863–879. doi:10.1016/j.mcna.2019.05.007. PMID 31378331.
- ^ Iyer, V. Ramesh, MD, MRCP (2014-03-26). "Supraventricular Tachycardia". Children's Hospital of Philadelphia. Archived from the original on September 11, 2014. Retrieved June 8, 2014.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Aumüller G. Die Entdeckung des AV-Knotens des Herzens durch Sunao Tawara und Ludwig Aschoff [The Discovery of the Cardiac Atrioventricular Node by Sunao Tawara and Ludwig Aschoff]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2019 Dec;144(25):1771–1777. German. doi:10.1055/a-0819-7328. Epub 2019 Dec 17. PMID 31847012
- ^ Bibas L, Levi M, Essebag V. Diagnosis and management of supraventricular tachycardias. CMAJ. 2016 Dec 6;188(17–18):E466–E473. doi:10.1503/cmaj.160079. Epub 2016 Oct 24. PMID 27777258; PMC PMC5135523.
- ^ Lau EW, Ng GA (2002). "Comparison of the performance of three diagnostic algorithms for regular broad complex tachycardia in practical application". Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology. 25 (5): 822–827. doi:10.1046/j.1460-9592.2002.00822.x. PMID 12049375. S2CID 42297040.
- ^ Hadid C. Sustained ventricular tachycardia in structural heart disease. Cardiol J. 2015;22(1):12–24. doi:10.5603/CJ.a2014.0069. Epub 2014 Oct 9. PMID 25299497.
- ^ Hafeez Y, Quintanilla Rodriguez BS, Ahmed I, et al. Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia. [Updated 2021 Apr 7]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507699/
- ^ Hadid C. Sustained ventricular tachycardia in structural heart disease. Cardiol J. 2015;22(1):12-24. doi: 10.5603/CJ.a2014.0069. Epub 2014 Oct 9. PMID 25299497.
- ^ Rosen MR, Moak JP, Damiano B. The clinical relevance of afterdepolarizations. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;427:84-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1984.tb20776.x. PMID 6378020.
- ^ Custer AM, Yelamanchili VS, Lappin SL. Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia. 2020 Jul 19. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan–. PMID 29083603.
- ^ Electrocardiograms of the months. Wolff-Parkinson-White pattern with alternating conduction between the A-V node and the aberrant pathway (bundle of Kent). N Y State J Med. 1982 Dec;82(13):1847-8. PMID 6961308.
- ^ a b Alasti M, Mirzaee S, Machado C, et al. Junctional ectopic tachycardia (JET). J Arrhythm. 2020;36(5):837-844. Published 2020 Jul 27. doi:10.1002/joa3.12410
- ^ "Supraventricular Tachycardias". The Lecturio Medical Concept Library. 9 September 2020. Retrieved 3 July 2021.
- ^ Kotadia ID, Williams SE, O'Neill M. Supraventricular tachycardia: An overview of diagnosis and management. Clin Med (Lond). 2020;20(1):43-47. doi:10.7861/clinmed.cme.20.1.3
- ^ Bhaskaran A, Chik W, Thomas S, Kovoor P, Thiagalingam A. A review of the safety aspects of radio frequency ablation. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2015;8:147-153. Published 2015 Jun 9. doi:10.1016/j.ijcha.2015.04.011
- ^ Schwagten, Bruno et al. "Long-term follow-up after catheter ablation for atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia: a comparison of cryothermal and radiofrequency energy in a large series of patients." Journal of interventional cardiac electrophysiology : an international journal of arrhythmias and pacing vol. 30,1 (2011): 55-61. doi:10.1007/s10840-010-9530-4
- ^ "What Is Supraventricular Tachycardia?". WebMD. Retrieved 3 July 2021.
- ^ "What Is Supraventricular Tachycardia?". WebMD. Retrieved 3 July 2021.
- ^ Re-entrant Supraventricular Tachycardia (RSVT) Archived June 19, 2006, at the Wayback Machine, at BobbyJulich.com Archived 2007-07-03 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "USA Volleyball 2008 Olympic Games Press Kit" (PDF). Usavolleyball.org. Retrieved 2013-11-02.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Abnormal coronary condition where the heart falls out of synch". The Guardian. UK. 20 October 2003. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ "Anastacia delays heart surgery". News of the World. 3 Nov 2008. Archived from the original on 2012-03-14. Retrieved 30 Apr 2010.
- ^ "Finding Her Rhythm: Swimmer Adjusts to a Heart Procedure and a New Coach". The New York Times. Los Angeles. 20 March 2008. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ "Olympic gold medalist Dana Vollmer has overcome two heart conditions". USA: The Mercury News. 30 May 2012. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ "Paul Bearer Cause of Death – Heart Attack". TMZ.com. 2013-03-23. Archived from the original on 2013-11-02. Retrieved 2013-11-02.
- ^ Ian Anderson (27 August 2013). "Rowing | Bad day for New Zealand crews". Stuff.co.nz. Retrieved 30 October 2013.
- ^ "Heart problems force Olympic champion out of world champs". Radio New Zealand. 26 August 2013. Archived from the original on 2 November 2013. Retrieved 30 October 2013.
- ^ "Heart trouble rules Cohen out of rowing World Champs". TVNZ. 26 August 2013. Archived from the original on 1 November 2013. Retrieved 30 October 2013. Scott Brady of punk band Brave The Wild ("Archived copy". Facebook. Archived from the original on 2017-09-08. Retrieved 2014-04-17.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)) has this. He had his first attack on April 9, 2012 while golfing and was hospitalized over night. He was diagnosed April 17, 2014 in Hamilton ON after having an attack walking home from dinner on March 16, 2014. - ^ "Miley Cyrus Opens Up About Heart Condition". mtv.com. MTV. Archived from the original on March 4, 2017. Retrieved March 4, 2017.
- ^ Severo, Richard (September 26, 2003). "George Plimpton, Urbane and Witty Writer, Dies at 76". The New York Times. Retrieved May 25, 2010.
External links
[edit]- Cardiac Disorders – Open Directory Project Archived 2017-03-16 at the Wayback Machine

