Subdural hematoma
| Subdural hematoma | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Subdural haematoma, subdural haemorrhage |
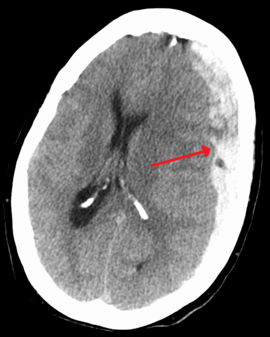 | |
| Subdural hematoma as marked by the arrow with significant midline shift | |
| Specialty | Neurosurgery, Neurology |
| Causes | Head injury, alcoholism, reduction in cerebrospinal fluid pressure[1][2] |
| Risk factors | Senescence, long-term excessive alcohol consumption, dementia, and cerebrospinal fluid leak[3][4] |
A subdural hematoma (SDH) is a type of bleeding in which a collection of blood—usually but not always associated with a traumatic brain injury—gathers between the inner layer of the dura mater and the arachnoid mater of the meninges surrounding the brain. It usually results from tears in bridging veins that cross the subdural space.
Subdural hematomas may cause an increase in the pressure inside the skull, which in turn can cause compression of and damage to delicate brain tissue. Acute subdural hematomas are often life-threatening. Chronic subdural hematomas have a better prognosis if properly managed.
In contrast, epidural hematomas are usually caused by tears in arteries, resulting in a build-up of blood between the dura mater and the skull. The third type of brain hemorrhage, known as a subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), causes bleeding into the subarachnoid space between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. SAH are often seen in trauma settings, or after rupture of intracranial aneurysms.[citation needed]
Signs and symptoms
[edit]The symptoms of a subdural hematoma have a slower onset than those of epidural hematomas because the lower-pressure veins involved bleed more slowly than arteries. Signs and symptoms of acute hematomas may appear in minutes, if not immediately,[5] but can also be delayed as much as two weeks.[6] Symptoms of chronic subdural hematomas are usually delayed more than three weeks after injury.[1]
If the bleeds are large enough to put pressure on the brain, signs of increased intracranial pressure or brain damage will be present.[3] Other symptoms of subdural hematoma can include any combination of the following:[7]
- Loss of consciousness or fluctuating levels of consciousness
- Irritability
- Seizures
- Pain
- Numbness
- Headache (either constant or fluctuating)
- Dizziness
- Disorientation
- Amnesia
- Weakness or lethargy
- Nausea or vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Personality changes
- Inability to speak or slurred speech
- Ataxia, or difficulty walking
- Loss of muscle control
- Altered breathing patterns
- Hearing loss or ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
- Blurred vision
- Deviated gaze, or abnormal movement of the eyes.[3]
Causes
[edit]Subdural hematomas are most often caused by head injury, in which rapidly changing velocities within the skull may stretch and tear small bridging veins. Much more common than epidural hemorrhages, subdural hemorrhages generally result from shearing injuries due to various rotational or linear forces.[3][2] There are claims that they can occur in cases of shaken baby syndrome, although there is no scientific evidence for this.[8]
They are also commonly seen in the elderly and in people with an alcohol use disorder who have evidence of cerebral atrophy.[1] Cerebral atrophy increases the length the bridging veins have to traverse between the two meningeal layers, thus increasing the likelihood of shearing forces causing a tear.[9] It is also more common in patients on anticoagulants or antiplatelet medications, such as warfarin and aspirin, respectively.[1] People on these medications can have a subdural hematoma after a relatively minor traumatic event. Another cause can be a reduction in cerebrospinal fluid pressure, which can reduce pressure in the subarachnoid space, pulling the arachnoid away from the dura mater and leading to a rupture of the blood vessels.[10]
Risk factors
[edit]Factors increasing the risk of a subdural hematoma include very young or very old age. As the brain shrinks with age, the subdural space enlarges and the veins that traverse the space must cover a wider distance, making them more vulnerable to tears. The elderly also have more brittle veins, making chronic subdural bleeds more common.[11] Infants, too, have larger subdural spaces and are more predisposed to subdural bleeds than are young adults.[3] It is often claimed that subdural hematoma is a common finding in shaken baby syndrome, although there is no science to support this.[8] In juveniles, an arachnoid cyst is a risk factor for subdural hematoma.[12]
Other risk factors include taking blood thinners (anticoagulants), long-term excessive alcohol consumption, dementia, and cerebrospinal fluid leaks.[4]
Pathophysiology
[edit]Acute
[edit]Acute subdural hematoma is usually caused by external trauma that creates tension in the wall of a bridging vein as it passes between the arachnoid and dural layers of the brain's lining—i.e., the subdural space. The circumferential arrangement of collagen surrounding the vein makes it susceptible to such tearing.[citation needed]
Intracerebral hemorrhage and ruptured cortical vessels (blood vessels on the surface of the brain) can also cause subdural hematoma. In these cases, blood usually accumulates between the two layers of the dura mater. This can cause ischemic brain damage by two mechanisms: one, pressure on the cortical blood vessels,[13] and two, vasoconstriction due to the substances released from the hematoma, which causes further ischemia by restricting blood flow to the brain.[14] When the brain is denied adequate blood flow, a biochemical cascade known as the ischemic cascade is unleashed, and may ultimately lead to brain cell death.[15]
Subdural hematomas grow continually larger as a result of the pressure they place on the brain: As intracranial pressure rises, blood is squeezed into the dural venous sinuses, raising the dural venous pressure and resulting in more bleeding from the ruptured bridging veins. They stop growing only when the pressure of the hematoma equalizes with the intracranial pressure, as the space for expansion shrinks.[13]
Chronic
[edit]
In chronic subdural hematomas, blood accumulates in the dural space as a result of damage to the dural border cells.[16] The resulting inflammation leads to new membrane formation through fibrosis and produces fragile and leaky blood vessels through angiogenesis, permitting the leakage of red blood cells, white blood cells, and plasma into the hematoma cavity. Traumatic tearing of the arachnoid mater also causes leakage of cerebrospinal fluid into the hematoma cavity, increasing the size of the hematoma over time. Excessive fibrinolysis also causes continuous bleeding.[citation needed]
Pro-inflammatory mediators active in the hematoma expansion process include Interleukin 1α (IL1A), Interleukin 6, and Interleukin 8, while the anti-inflammatory mediator is Interleukin 10. Mediators that promote angiogenesis are angiopoietin and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Prostaglandin E2 promotes the expression of VEGF. Matrix metalloproteinases remove surrounding collagen, providing space for new blood vessels to grow.[16]
Craniotomy for unruptured intracranial aneurysm is another risk factor for the development of chronic subdural hematoma. The incision in the arachnoid membrane during the operation causes cerebrospinal fluid to leak into the subdural space, leading to inflammation. This complication usually resolves on its own.[17]
Diagnosis
[edit]
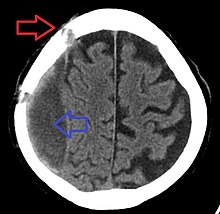
It is important that a person receive medical assessment, including a complete neurological examination, after any head trauma. A CT scan or MRI scan will usually detect significant subdural hematomas.[citation needed]
Subdural hematomas occur most often around the tops and sides of the frontal and parietal lobes.[3][2] They also occur in the posterior cranial fossa, and near the falx cerebri and tentorium cerebelli.[3] Unlike epidural hematomas, which cannot expand past the sutures of the skull, subdural hematomas can expand along the inside of the skull, creating a concave shape that follows the curve of the brain, stopping only at dural reflections like the tentorium cerebelli and falx cerebri.[citation needed]
On a CT scan, subdural hematomas are classically crescent-shaped, with a concave surface away from the skull. However, they can have a convex appearance, especially in the early stages of bleeding. This may cause difficulty in distinguishing between subdural and epidural hemorrhages. A more reliable indicator of subdural hemorrhage is its involvement of a larger portion of the cerebral hemisphere. Subdural blood can also be seen as a layering density along the tentorium cerebelli. This can be a chronic, stable process, since the feeding system is low-pressure. In such cases, subtle signs of bleeding—such as effacement of sulci or medial displacement of the junction between gray matter and white matter—may be apparent.[citation needed]
| Age | Attenuation (HU) |
|---|---|
| First hours | +75 to +100[18] |
| After 3 days | +65 to +85[18] |
| After 10–14 days | +35 to +40[19] |
Fresh subdural bleeding is hyperdense, but becomes more hypodense over time due to dissolution of cellular elements. After 3–14 days, the bleeding becomes isodense with brain tissue and may therefore be missed.[20] Subsequently, it will become more hypodense than brain tissue.[21]
Classification
[edit]Subdural hematomas are classified as acute, subacute, or chronic, depending on the speed of their onset.[22]
Acute bleeds often develop after high-speed acceleration or deceleration injuries. They are most severe if associated with cerebral contusions.[3] Though much faster than chronic subdural bleeds, acute subdural bleeding is usually venous and therefore slower than the arterial bleeding of an epidural hemorrhage. Acute subdural hematomas due to trauma are the most lethal of all head injuries and have a high mortality rate if they are not rapidly treated with surgical decompression.[23] The mortality rate is higher than that of epidural hematomas and diffuse brain injuries because the force required to cause subdural hematomas tends to cause other severe injuries as well.[24]
Chronic subdural bleeds develop over a period of days to weeks, often after minor head trauma, though a cause is not identifiable in 50% of patients.[11] They may not be discovered until they present clinically months or years after a head injury.[25] The bleeding from a chronic hematoma is slow and usually stops by itself.[2][26] Because these hematomas progress slowly, they can more often be stopped before they cause significant damage, especially if they are less than a centimeter wide. In one study, only 22% of patients with chronic subdural bleeds had outcomes worse than "good" or "complete recovery".[3] Chronic subdural hematomas are common in the elderly.[25]
Differential diagnosis
[edit]| Compared quality | Epidural | Subdural |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Between the skull and the inner meningeal layer of the dura mater or between outer endosteal and inner meningeal layer of dura mater | Between the meningeal layers of dura mater and the Arachnoid mater |
| Involved vessel | Temperoparietal locus (most likely) – Middle meningeal artery Frontal locus – anterior ethmoidal artery Occipital locus – transverse or sigmoid sinuses Vertex locus – superior sagittal sinus |
Bridging veins |
| Symptoms (depending on the severity)[27] | Lucid interval followed by unconsciousness | Gradually increasing headache and confusion |
| CT scan appearance | Biconvex lens | Crescent-shaped |
Treatment
[edit]Treatment of a subdural hematoma depends on its size and rate of growth. Some small subdural hematomas can be managed by careful monitoring as the blood clot is eventually resorbed naturally. Others can be treated by inserting a small catheter through a hole drilled through the skull and sucking out the hematoma.[citation needed]
Large or symptomatic hematomas require a craniotomy. A surgeon opens the skull and then the dura mater; removes the clot with suction or irrigation; and identifies and controls sites of bleeding.[28][29] The injured vessels must be repaired. Postoperative complications can include increased intracranial pressure, brain edema, new or recurrent bleeding, infection, and seizures. In patients with a chronic subdural hematoma but no history of seizures, it is unclear whether anticonvulsants are harmful or beneficial.[30]
Those with chronic subudural haematoma (CSDH) with few or no symptoms or have high risk of complication during surgery may be treated conservatively with medications such as atorvastatin, dexamethasone,[31] and mannitol, although supporting conservative treatment is still weak.[32] HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor such as Atorvastatin can reduce the haematoma volume and improving neurological function in eight weeks.[33] HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor may also reduce risk of recurrences in CSDH.[34] Dexamethasone, when used together with surgical drainage, may reduce the recurrence rate of subdural haematoma.[35] Even with surgical evacuation of chronic subdural haematoma, the recurrence rate is high, ranging from 7 to 20%.[32]
Prognosis
[edit]Acute subdural hematomas have one of the highest mortality rates of all head injuries, with 50 to 90 percent of cases resulting in death, depending on the underlying brain injury. About 20 to 30 percent of patients recover brain function.[36] Higher Glasgow Coma Scale score, younger age and responsive pupils are associated with better outcomes in acute subdural hematomas, while the time between the injury and the surgical evacuation, or the type of surgery, do not have a statistically significant impact on the outcomes.[37] Additionally, chronic subdural hematomas (CSDHs) have a relatively high mortality rate (up to 16.7% in patients over the age of 65); however, they have an even higher rate of recurrence (as mentioned in the previous section).[38] For the aforementioned reasons, researchers have developed predictive grading scales to identify patients at high risk of CSDH recurrence, one of which is the Puerto Rico Recurrence Scale developed by Mignucci-Jiménez et al.[38]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c d Ko BS, Lee JK, Seo BR, Moon SJ, Kim JH, Kim SH (January 2008). "Clinical analysis of risk factors related to recurrent chronic subdural hematoma". Journal of Korean Neurosurgical Society. 43 (1): 11–15. doi:10.3340/jkns.2008.43.1.11. PMC 2588154. PMID 19096538.
- ^ a b c d University of Vermont College of Medicine. "Neuropathology: Trauma to the CNS." Accessed through web archive on August 8, 2007.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Imaging in Subdural Hematoma at eMedicine
- ^ a b Beck J, Gralla J, Fung C, Ulrich CT, Schucht P, Fichtner J, et al. (December 2014). "Spinal cerebrospinal fluid leak as the cause of chronic subdural hematomas in nongeriatric patients". Journal of Neurosurgery. 121 (6): 1380–1387. doi:10.3171/2014.6.JNS14550. PMID 25036203. S2CID 207731566.
- ^ "Subdural hematoma : MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia". Nlm.nih.gov. 2012-06-28. Retrieved 2012-07-27.
- ^ Mezue WC, Ndubuisi CA, Chikani MC, Achebe DS, Ohaegbulam SC (July 2012). "Traumatic extradural hematoma in enugu, Nigeria". Nigerian Journal of Surgery. 18 (2): 80–84. doi:10.4103/1117-6806.103111. PMC 3762009. PMID 24027399.
- ^ "Subdural Hematoma: Types, Symptoms Treatments, Prevention". Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved 2022-03-10.
- ^ a b Lynøe N, Elinder G, Hallberg B, Rosén M, Sundgren P, Eriksson A (July 2017). "Insufficient evidence for 'shaken baby syndrome' – a systematic review". Acta Paediatrica. 106 (7): 1021–1027. doi:10.1111/apa.13760. PMID 28130787. S2CID 4435564.
- ^ Oishi M, Toyama M, Tamatani S, Kitazawa T, Saito M (August 2001). "Clinical factors of recurrent chronic subdural hematoma". Neurologia Medico-Chirurgica. 41 (8): 382–386. doi:10.2176/nmc.41.382. PMID 11561348.
- ^ Yamamoto H, Hirashima Y, Hamada H, Hayashi N, Origasa H, Endo S (June 2003). "Independent predictors of recurrence of chronic subdural hematoma: results of multivariate analysis performed using a logistic regression model". Journal of Neurosurgery. 98 (6): 1217–1221. doi:10.3171/jns.2003.98.6.1217. PMID 12816267.
- ^ a b Downie A. 2001. "Tutorial: CT in head trauma" Archived 2005-11-06 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved on August 7, 2007.
- ^ Mori K, Yamamoto T, Horinaka N, Maeda M (September 2002). "Arachnoid cyst is a risk factor for chronic subdural hematoma in juveniles: twelve cases of chronic subdural hematoma associated with arachnoid cyst". Journal of Neurotrauma. 19 (9): 1017–1027. doi:10.1089/089771502760341938. PMID 12482115.
- ^ a b Miller JD, Nader R (June 2014). "Acute subdural hematoma from bridging vein rupture: a potential mechanism for growth". Journal of Neurosurgery. 120 (6): 1378–1384. doi:10.3171/2013.10.JNS13272. PMID 24313607. S2CID 25404949.
- ^ Graham DI, Gennareli TA (2000). "Chapter 5: Pathology of brain damage after head injury". In Cooper P, Golfinos G (eds.). Head Injury (4th ed.). New York: Morgan Hill.
- ^ Tandon PN (March 2001). "Acute subdural haematoma : a reappraisal". Neurology India. 49 (1): 3–10. PMID 11303234. Retrieved 26 November 2017.
. The possibility of direct effect of some vasoactive substances released by the blood clot, being responsible for the ischaemia, seems attractive.
- ^ a b Edlmann E, Giorgi-Coll S, Whitfield PC, Carpenter KL, Hutchinson PJ (May 2017). "Pathophysiology of chronic subdural haematoma: inflammation, angiogenesis and implications for pharmacotherapy". Journal of Neuroinflammation. 14 (1): 108. doi:10.1186/s12974-017-0881-y. PMC 5450087. PMID 28558815.
- ^ Tanaka Y, Ohno K (June 2013). "Chronic subdural hematoma – an up-to-date concept" (PDF). Journal of Medical and Dental Sciences. 60 (2): 55–61. PMID 23918031. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 August 2017. Retrieved 26 November 2017.
- ^ a b Fig 3 in: Rao MG, Singh D, Khandelwal N, Sharma SK (April 2016). "Dating of Early Subdural Haematoma: A Correlative Clinico-Radiological Study". Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research. 10 (4): HC01–HC05. doi:10.7860/JCDR/2016/17207.7644. PMC 4866129. PMID 27190831.
- ^ Sharma R, Gaillard F. "Subdural haemorrhage". Radiopaedia. Retrieved 2018-08-14.
- ^ "Intracranial Hemorrhage – Subdural Hematomas (SDH)". Loyola University Chicago. Retrieved 2018-01-06.
- ^ Schweitzer AD, Niogi SN, Whitlow CT, Tsiouris AJ (October 2019). "Traumatic Brain Injury: Imaging Patterns and Complications". Radiographics. 39 (6): 1571–1595. doi:10.1148/rg.2019190076. PMID 31589576. S2CID 203926019.
- ^ Subdural Hematoma Surgery at eMedicine
- ^ "Acute Subdural Hematomas". UCLA Health. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- ^ Penetrating Head Trauma at eMedicine
- ^ a b Kushner D (1998). "Mild traumatic brain injury: toward understanding manifestations and treatment". Archives of Internal Medicine. 158 (15): 1617–1624. doi:10.1001/archinte.158.15.1617. PMID 9701095.
- ^ Faried A, Halim D, Widjaya IA, Badri RF, Sulaiman SF, Arifin MZ (October 2019). "Correlation between the skull base fracture and the incidence of intracranial hemorrhage in patients with traumatic brain injury". Chinese Journal of Traumatology = Zhonghua Chuang Shang Za Zhi. 22 (5): 286–289. doi:10.1016/j.cjtee.2019.05.006. PMC 6823676. PMID 31521457.
- ^ McDonough VT, King B. "What's the Difference Between a Subdural and Epidural Hematoma?" (PDF). BrainLine. WETA-TV. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 August 2010.
- ^ Koivisto T, Jääskeläinen JE (September 2009). "Chronic subdural haematoma – to drain or not to drain?". Lancet. 374 (9695): 1040–1041. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61682-2. PMID 19782854. S2CID 29932520.
- ^ Santarius T, Kirkpatrick PJ, Ganesan D, Chia HL, Jalloh I, Smielewski P, et al. (September 2009). "Use of drains versus no drains after burr-hole evacuation of chronic subdural haematoma: a randomised controlled trial". Lancet. 374 (9695): 1067–1073. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61115-6. PMID 19782872. S2CID 5206569.
- ^ Ratilal BO, Pappamikail L, Costa J, Sampaio C (June 2013). "Anticonvulsants for preventing seizures in patients with chronic subdural haematoma". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2013 (6): CD004893. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004893.pub3. PMC 7388908. PMID 23744552.
- ^ Thotakura AK, Marabathina NR (December 2015). "Nonsurgical Treatment of Chronic Subdural Hematoma with Steroids". World Neurosurgery. 84 (6): 1968–1972. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2015.08.044. PMID 26342776.
- ^ a b Soleman J, Nocera F, Mariani L (2017). "The conservative and pharmacological management of chronic subdural haematoma". Swiss Medical Weekly. 147: w14398. doi:10.4414/smw.2017.14398 (inactive 1 November 2024). PMID 28102879.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link) - ^ Jiang R, Zhao S, Wang R, Feng H, Zhang J, Li X, et al. (November 2018). "Safety and Efficacy of Atorvastatin for Chronic Subdural Hematoma in Chinese Patients: A Randomized ClinicalTrial". JAMA Neurology. 75 (11): 1338–1346. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.2030. PMC 6248109. PMID 30073290.
- ^ Yadav YR, Parihar V, Namdev H, Bajaj J (2016). "Chronic subdural hematoma". Asian Journal of Neurosurgery. 11 (4): 330–342. doi:10.4103/1793-5482.145102. PMC 4974954. PMID 27695533.
- ^ Chan DY, Sun TF, Poon WS (December 2015). "Steroid for chronic subdural hematoma? A prospective phase IIB pilot randomized controlled trial on the use of dexamethasone with surgical drainage for the reduction of recurrence with reoperation". Chinese Neurosurgical Journal. 1 (1): 2. doi:10.1186/s41016-015-0005-4. ISSN 2057-4967. S2CID 3934313.
- ^ "Acute Subdural Hematomas – UCLA Neurosurgery, Los Angeles, CA". neurosurgery.ucla.edu. Retrieved 2019-02-19.
- ^ Koç, R. Kemal; Akdemir, Hidayet; Oktem, I. Suat; Meral, Mehmet; Menkü, Ahmet (1997). "Acute subdural hematoma: Outcome and outcome prediction". Neurosurgical Review. 20 (4): 239–244. doi:10.1007/BF01105894. PMID 9457718. S2CID 29824615. Retrieved 16 February 2024.
- ^ a b Mignucci-Jiménez, Giancarlo; Matos-Cruz, Alejandro J.; Abramov, Irakliy; Hanalioglu, Sahin; Kovacs, Melissa S.; Preul, Mark C.; Feliciano-Valls, Caleb E. (3 June 2022). "Puerto Rico Recurrence Scale: Predicting chronic subdural hematoma recurrence risk after initial surgical drainage". Surgical Neurology International. 13: 230. doi:10.25259/SNI_240_2022. PMC 9282733. PMID 35855136. S2CID 249359877.
