Sukhoi Su-11
| Su-11 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| General information | |
| Type | Interceptor aircraft |
| National origin | Soviet Union |
| Manufacturer | Sukhoi |
| Primary user | Soviet Air Forces |
| Number built | 108 |
| History | |
| Manufactured | 1962–1965 |
| Introduction date | 1964 |
| First flight | 25 December 1958 |
| Retired | 1983 |
| Developed from | Sukhoi Su-9 |
| Variants | Sukhoi T-49 |
The Sukhoi Su-11 (NATO reporting name: Fishpot-C) is an interceptor aircraft used by the Soviet Union during the Cold War.
Design and development
[edit]The Su-11 was an upgraded version of the Sukhoi Su-9 ('Fishpot') interceptor, which had been developed in parallel with the OKB's swept wing Su-7 fighter bomber. Recognizing the Su-9's fundamental limitations, Sukhoi began work on the Su-11, which first flew in 1961 as the T-47 prototype.
The Su-11 shared the Su-9's delta wing, swept tailplanes and cigar-shaped fuselage, as well as the circular nose intake, but had a longer nose to accommodate the more powerful 'Oryol' (Eagle; NATO reporting name 'Skip Spin') radar set. A more powerful Lyulka AL-7F-1 turbojet was installed, providing 9.8 kN (2,210 lbf) more afterburning thrust for improved climb rate and high-altitude performance (and to compensate for increased weight). The Su-11 can be distinguished from the Su-9 by the external fuel pipes atop the fuselage, aft of the cockpit.
The Su-9's beam-riding K-5 missiles were replaced by a pair of R-98 (AA-3 'Anab') weapons, usually one R-98MR semi-active radar homing and one R-98MT infrared guided. Like many interceptors of the period, it had no cannon.
Production of the definitive Su-11-8M began in 1962, ended in 1965, after about 108 aircraft had been delivered, although it is believed that at least some Su-9s were upgraded to Su-11 form.
A conversion trainer version, the Su-11U 'Maiden,' was also developed ; Similar to the Su-9U, it had full armament and radar systems for training purposes, but the second seat reduced its already marginal fuel capacity and was not intended for combat use.
Operational history
[edit]Development problems and accidents delayed squadron introduction with the Soviet Air Force (VVS)/ Soviet Air Defence Forces (PVO) until 1964 and only small number of aircraft were delivered.
Even with the superior radar, the Su-11 remained heavily dependent on ground control interception (GCI) to vector its pilot onto targets. It had no capability against low-flying aircraft either, and Sukhoi OKB considered the Su-11 to be a misfire, much inferior to the far more formidable Su-15 ('Flagon'). Nevertheless, a few examples remained operational until the early 1980s. The last Su-11s left front-line service around 1983.
Operators
[edit]Specifications (Su-11)
[edit]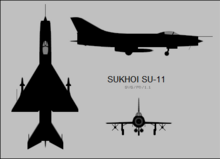
Data from OKB Sukhoi : a history of the design bureau and its aircraft[1]
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 18.225 m (59 ft 10 in)
- Wingspan: 8.536 m (28 ft 0 in)
- Height: 4.7 m (15 ft 5 in)
- Wing area: 34 m2 (370 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 8,562 kg (18,876 lb)
- Gross weight: 12,674 kg (27,941 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 13,986 kg (30,834 lb)
- Fuel capacity: 3,440 kg (7,580 lb) internal : 4,620 kg (10,190 lb) with external tanks
- Powerplant: 1 × Lyulka AL-7F-2 afterburning turbojet engine, 99.1 kN (22,270 lbf) thrust
Performance
- Maximum speed: 2,340 km/h (1,450 mph, 1,260 kn) at 1,100 m (3,600 ft) [citation needed]
- Maximum speed: Mach 2.2
- Combat range: 500 km (310 mi, 270 nmi) [citation needed]
- Ferry range: 1,125 km (699 mi, 607 nmi) [citation needed]
- Endurance: 1 hour 28 minutes internal fuel; 1 hour 59 minutes with external fuel
- Service ceiling: 18,000 m (59,000 ft)
- Rate of climb: 136.7 m/s (26,910 ft/min)
- Wing loading: 76.09 kg/m2 (15.58 lb/sq ft) [citation needed]
- Thrust/weight: 0.71
- Take-off speed (internal fuel): 330–340 km/h (210–210 mph; 180–180 kn)
- Take-off speed (with external fuel): 360–380 km/h (220–240 mph; 190–210 kn)
- Landing speed (internal fuel): 280–290 km/h (170–180 mph; 150–160 kn)
- Landing roll: 1,000–1,200 m (3,300–3,900 ft)
Armament
- Missiles: 2 × K-8 air-to-air missiles
See also
[edit]Related development
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
References
[edit]- ^ Antonov, Vladimir; Gordon, Yefim; Gordyukov, Nikolai; Yakovlev, Vladimir; Zenkin, Vyacheslav; Carruth, Lenox; Miller, Jay (1996). OKB Sukhoi : a history of the design bureau and its aircraft (1st ed.). Earl Shilton: Midland Publishing. ISBN 9781857800128.
