Soma (biology)
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2008) |
In cellular neuroscience, the soma (pl.: somata or somas; from Greek σῶμα (sôma) 'body'), neurocyton, or cell body is the bulbous, non-process portion of a neuron or other brain cell type, containing the cell nucleus. Although it is often used to refer to neurons, it can also refer to other cell types as well, including astrocytes,[1] oligodendrocytes,[2] and microglia.[3] The part of the soma without the nucleus is called perikaryon (pl.: perikarya).[4]
There are many different specialized types of neurons, and their sizes vary from as small as about 5 micrometres to over 10 millimetres for some of the smallest and largest neurons of invertebrates, respectively.
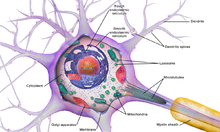
The soma of a neuron (i.e., the main part of the neuron in which the dendrites branch off of) contains many organelles, including granules called Nissl granules, which are composed largely of rough endoplasmic reticulum and free polyribosomes.[5] The cell nucleus is a key feature of the soma. The nucleus is the source of most of the RNA that is produced in neurons. In general, most proteins are produced from mRNAs that do not travel far from the cell nucleus. This creates a challenge for supplying new proteins to axon endings that can be a meter or more away from the soma. Axons contain microtubule-associated motor proteins that transport protein-containing vesicles between the soma and the synapses at the axon terminals. Such transport of molecules towards and away from the soma maintains critical cell functions. In case of neurons, the soma receives a large number of inhibitory synapses,[6] which can regulate the activity of these cells. It has also been shown that microglial processes constantly monitor neuronal functions through somatic junctions, and exert neuroprotection when needed.[7]
The axon hillock is a specialized domain of the neuronal cell body from which the axon originates. A high amount of protein synthesis occurs in this region, as it contains many Nissl granules (which are ribosomes wrapped in RER) and polyribosomes. Within the axon hillock, materials are sorted as either items that will enter the axon (like the components of the cytoskeletal architecture of the axon, mitochondria, etc.) or will remain in the soma. In addition, the axon hillock also has a specialized plasma membrane that contains large numbers of voltage-gated ion channels, since this is most often the site of action potential initiation and triggering.[5]
The survival of some sensory neurons depends on axon terminals making contact with sources of survival factors that prevent apoptosis. The survival factors are neurotrophic factors, including molecules such as nerve growth factor (NGF). NGF interacts with receptors at axon terminals, and this produces a signal that must be transported up the length of the axon to the nucleus. A current theory of how such survival signals are sent from axon endings to the soma includes the idea that NGF receptors are endocytosed from the surface of axon tips and that such endocytotic vesicles are transported up the axon.[8]
Intermediate filaments are abundant in both perikarya and axonal and dendritic processes and are called neurofilaments. The neurofilaments become cross linked with certain fixatives and when impregnated with silver, they form neuro fibrils visible with the light microscope. [9]
References
[edit]- ^ Bazargani, N; Attwell, D (February 2016). "Astrocyte calcium signaling: the third wave". Nature Neuroscience. 19 (2): 182–9. doi:10.1038/nn.4201. PMID 26814587. S2CID 205438341.
- ^ Baumann, N; Pham-Dinh, D (April 2001). "Biology of oligodendrocyte and myelin in the mammalian central nervous system". Physiological Reviews. 81 (2): 871–927. doi:10.1152/physrev.2001.81.2.871. PMID 11274346.
- ^ Kozlowski, C; Weimer, RM (2012). "An automated method to quantify microglia morphology and application to monitor activation state longitudinally in vivo". PLOS ONE. 7 (2): e31814. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...731814K. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0031814. PMC 3294422. PMID 22457705.
- ^ "Perykarion". Gene Ontology (GO). Retrieved 29 October 2024.
- ^ a b Squire, Larry; Berg, Darwin; Bloom, Floyd; du Lac, Sascha; Ghosh, Anirvan; Spitzer, Nicholas, eds. (2008). Fundamental Neuroscience (3rd ed.). Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-374019-9.
- ^ Freund and Katona, Neuron, Volume 56, Issue 1, 4 October 2007, Pages 33-42, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2007.09.012
- ^ Cserép C, Pósfai B, Lénárt N, Fekete R, László ZI, Lele Z, et al. (January 2020). "Microglia monitor and protect neuronal function through specialized somatic purinergic junctions" (PDF). Science. 367 (6477): 528–537. Bibcode:2020Sci...367..528C. doi:10.1126/science.aax6752. PMID 31831638. S2CID 209343260.
- ^ Delcroix JD, Valletta J, Wu C, et al. (2004). "Trafficking the NGF signal: implications for normal and degenerating neurons". NGF and Related Molecules in Health and Disease. Progress in Brain Research. Vol. 146. pp. 3–23. doi:10.1016/s0079-6123(03)46001-9. ISBN 9780444514721. PMID 14699953.
- ^ Junqueira 12th edition.
External links
[edit]- Histology image: 3_09 at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center - "Slide 3 Spinal cord"

