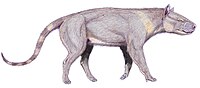
Sinonyx
| Sinonyx Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Skeleton cast of S. jiashanensis holotype (IVPP V10760), University of Michigan Museum of Natural History | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | †Mesonychia |
| Family: | †Mesonychidae |
| Genus: | †Sinonyx Zhou et al. 1995[1] |
| Species | |
|
S. jiashanensis | |
Sinonyx ("Chinese claw") is a genus of extinct, superficially wolf-like mesonychid mammals from the late Paleocene of China (about 56 million years ago). It is within the family Mesonychidae, and cladistic analysis of a skull of Sinonyx jiashanensis identifies its closest relative as Ankalagon.[1] S. jiashanensis was discovered in Anhui province, China (30°54′N 120°54′E / 30.9°N 120.9°E, paleocoordinates 33°54′N 113°36′E / 33.9°N 113.6°E), in the Tuijinshan formation.[2]
Description
[edit]
Sinonyx was about 1.5 m (5 ft) long, about the size of a modern grey wolf with a large elongated head, short legs, digitigrade feet adapted for running, and tiny hooves on all of its toes. The tooth count was 3.1.4.3=44, the primitive mammalian number. The canines were long and slender. Compressed teeth with shearing notches in the lower jaw operated against multiple-cusped molars in the upper.[1] The large skull had an extended occipital bone and large sagittal crest that contained the small brain typical of early mammals. The sagittal crest gave expanded attachment for the temporalis muscles; Sinonyx had a powerful bite.
Morphologic similarities between Sinonyx and cetaceans
[edit]
Morphologists long thought that Sinonyx was the direct ancestor of Cetacea (whales and dolphins), but the discovery of well-preserved hind limbs of archaic cetaceans as well as more recent DNA phylogenetic analyses[3][4][5] now indicates that cetaceans are more closely related to hippopotamids and other artiodactyls than they are to mesonychids, and this result is consistent with many molecular studies.[6] Some studies have found Andrewsarchus, once considered a mesonychid, to form the sister group to the clade composed of Cetacea and Hippopotamidae along with Entelodontidae.[7] Mesonychidae as defined by Szaly and Gould (1966) is probably paraphyletic or polyphyletic, with Hapalodectinae and Andrewsarchinae (represented by the lone skull of Andrewsarchus) wrongly assigned to the group.[1] The subfamily Mesonychinae, which includes Sinonyx, appears to be monophyletic: mesonychids proper.

Sinonyx is no longer considered ancestral to Cetacea,[7] but has convergent features to early land-dwelling whales that suggest it may have had some similar adaptations. Sinonyx' elongated, narrow muzzle is often seen in animals that snap at small, fast-moving prey (such as mice among small canids, or small fish among dolphins). The triangular cheek teeth have a prominent middle cusp or point and two relatively equal sized cusps on each side; this unusual feature for mammal teeth is similar in archeocetes and led early researchers to believe mesonychids were ancestral to them. However, both groups began with generalized basal ungulate-type cheek teeth adapted for eating soft plant foods, and readapted them for a carnivorous diet; they are the only known mammal groups to have done this. Other characters Sinonyx has in common with early whales include an ossified tympanic bulla, which improves sensitivity to high-frequency sounds and is often seen in predators that hunt small prey by sound, and an enlarged jugular foramen, which gives more room for the cranial nerves that control swallowing and the balance between athletic activity and digestion.[8]
Notes
[edit]- ^ a b c d e Zhou et al. 1995.
- ^ Tujinshan (Paleocene of China) in the Paleobiology Database. Retrieved 11 August 2013.
- ^ Geisler & Uhen 2003.
- ^ Geisler & Uhen 2005.
- ^ Boisserie, Lihoreau & Brunet 2005.
- ^ Gatesy et al. 1996.
- ^ a b Spaulding, O'Leary & Gatesy 2009.
- ^ Singh, Omesh; M Das, Joe (2020). "Anatomy, Head and Neck, Jugular Foramen". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. PMID 30860742. Retrieved 2020-02-15.
References
[edit]- Boisserie, J.−R.; Lihoreau, F.; Brunet, M. (2005). "The position of Hippopotamidae within Cetartiodactyla". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 102 (5): 1537–1541. Bibcode:2005PNAS..102.1537B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0409518102. PMC 547867. PMID 15677331.
- Carrol, Robert Lynn (1997). Patterns and Processes of Vertebrate Evolution. Cambridge Paleobiology Series. Vol. 2. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-47809-X.
- Gatesy, J.; Hayashi, C.; Cronin, A.; Arctander, P. (1996). "Evidence from milk casein genes that cetaceans are close relatives of hippopotamid artiodactyls". Molecular Biology and Evolution. 13 (7): 954–963. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a025663. PMID 8752004.
- Geisler, J. H.; Uhen, M. D. (2003). "Morphological support for a close relationship between hippos and whales" (PDF). Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 23 (4): 991–996. Bibcode:2003JVPal..23..991G. doi:10.1671/32. S2CID 59143599. Retrieved 2013-08-11.
- Geisler, J. H.; Uhen, M. D. (2005). "Phylogenetic relationships of extinct cetartiodactyls: results of simultaneous analyses of molecular, morphological, and stratigraphic data". Journal of Mammalian Evolution. 12 (1 and 2): 145–160. doi:10.1007/s10914-005-4963-8. S2CID 34683201.
- Nesbit, Joanne (25 March 1997). "Medical Illustrator Makes Puzzle Pieces Fit". The University Record Online, University of Michigan.
- Spaulding, M.; O'Leary, M. A.; Gatesy, J. (2009). Farke, Andrew Allen (ed.). "Relationships of Cetacea (Artiodactyla) Among Mammals: Increased Taxon Sampling Alters Interpretations of Key Fossils and Character Evolution". PLOS ONE. 4 (9): e7062. Bibcode:2009PLoSO...4.7062S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0007062. PMC 2740860. PMID 19774069.
- Zhou, Xiaoyuan; Zhai, Renjie; Gingerich, P. D.; Chen, Liezu (1995). "Skull of a New Mesonychid (Mammalia, Mesonychia) from the Late Paleocene of China" (PDF). Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 15 (2): 387–400. Bibcode:1995JVPal..15..387Z. doi:10.1080/02724634.1995.10011237. Retrieved 2013-08-11.