Saltoro Mountains
| Saltoro Mountains | |
|---|---|
| Saltoro Muztagh | |
 | |
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Saltoro Kangri |
| Elevation | 7,742 m (25,400 ft) |
| Coordinates | 35°24′01″N 76°50′55″E / 35.40028°N 76.84861°E |
| Geography | |
 | |
| Location | Actual Ground Position Line, on the border between Indian and Pakistani controlled territories |
| Borders on | Masherbrum Mountains |
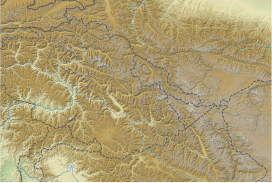
The Saltoro Mountains form a subrange within the Karakoram Range[1] and are situated in the southeastern part of the Karakoram. They lie on the southwest side of the Siachen Glacier, which is one of the two longest glaciers in the world outside the polar regions.[citation needed] The name "Saltoro" is also associated with the Saltoro Valley, located west of this range and descending on the Pakistani side of the Saltoro Range, which generally follows the Actual Ground Position Line (AGPL).
Saltoro Kangri peak, Saltoro River, and Saltoro Valley are features within the Saltoro Mountains range. The Actual Ground Position Line (AGPL) demarcates the boundary between the areas held by India and Pakistan in this region. In the Siachen area, India controls the high peaks and passes, while Pakistan occupies the lower peaks and valleys to the west.[2]
The Saltoro Mountains are part of the Lesser Karakorams and are situated on the southwestern side of the major Karakoram glaciers, including the Siachen, Baltoro, Biafo and Hispar Glacier, which run from east to west. The primary ridge of the Karakoram Range is located to the northeast of these glaciers.
The subranges of the main ridge are generally referred to as "Muztagh," while the mountain groups within the Lesser Karakorams are often designated as individual mountains, ranges or groups.[3]
The Saltoro Range is claimed by India as part of the Ladakh region and as part of the Gilgit–Baltistan region by Pakistan. Between 1984 and 1987, India assumed military control of the main peaks and passes of the range, with Pakistani forces holding the glacial valleys just to the west.[citation needed] Hence, despite high peaks and dramatic climbing opportunities, they are rarely visited except by military forces due to the ongoing Siachen Conflict.
On the southwest side, the Saltoro Mountains drop steeply to the valleys of the Kondus and Dansam Rivers, which join to form the Saltoro River, a tributary of the Shyok River. This in turn flows into the Indus River. To the northwest, the Kondus Glacier separates the range from the neighboring Masherbrum Mountains, while on the southeast, the Gyong River, Glacier, and Pass (Gyong La) separate the northern Saltoro Mountains from the southern Saltoro Mountains or "Kailas Mountains" (not to be confused with Tibet's sacred Mount Kailash).
Background
[edit]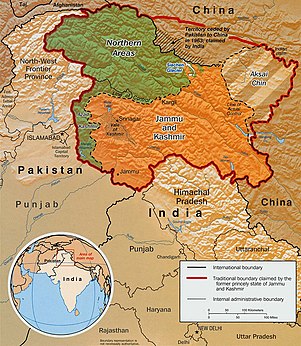

Indo-Pakistan borders: SC, IB, LOC, AGPL
[edit]The actual India-Pakistan boundary is divided into 4 types of borders: disputed Sir Creek (SC) riverine border, mutually agreed India–Pakistan International Border (IB) from north of Sir Creek to north of Dhalan near Jammu, Line of Control (LoC) across disputed Kashmir and Ladakh regions from north of Dhalan in India and west of Chicken's Neck in Pakistan to Point NJ9842, and Actual Ground Position Line (AGPL) across Siachen from Point NJ9842 to Indira Col West. Siachen lies south of the Shaksgam ceded by Pakistan to China via the 1963 Sino-Pakistan Agreement but also claimed by India[4] and Aksai Chin held by China since 1962 but also claimed by India. The Shaksgam Tract controlled by China is located north of the Saltoro mountain range from the Apsarasas Kangri Range to 90 km northwest of K2.[5]
AGPL
[edit]The AGPL runs roughly along the Saltoro Mountains from Point NJ9842 on the India-Pakistan LoC to near La Yongma Ri, Gyong La, Gyong Kangri, Chumik Kangri, Bilafond La (pass) and nearby Bana Post, Saltoro Kangri, Ghent Kangri, and Sia La to the India–Pakistan–China trijunction northwest of Indira Col West on the Sino-Indian LAC.[6][5] The peaks and passes under Pakistan's control such as Gayari Camp, Chogolisa, Baltoro Glacier, Conway Saddle,[5] Baltoro Muztagh, and Gasherbrum lie west of the AGPL.
Selected peaks
[edit]The following is a table of the peaks in the Saltoro Mountains which are over 7,200 metres (23,622 ft) in elevation and have over 500 metres (1,640 ft) of topographic prominence. (This is a common criterion for peaks of this stature to be independent.)
| Mountain | Height (m) | Height (ft) | Coordinates | Prominence (m) | Parent mountain | First ascent | Ascents (attempts) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saltoro Kangri | 7,742 | 25,400 | 35°23′57″N 76°50′51″E / 35.39917°N 76.84750°E | 2,160 | Gasherbrum I | 1962 | 2 (1) |
| K12 | 7,428 | 24,370 | 35°17′42″N 77°01′18″E / 35.29500°N 77.02167°E | 1,978 | Saltoro Kangri | 1974 | 4 (2) |
| Ghent Kangri (Mount Ghent) | 7,401 | 24,281 | 35°31′03″N 76°48′01″E / 35.51750°N 76.80028°E | 1,493 | Saltoro Kangri | 1961 | 4 (0) |
| Sherpi Kangri | 7,380 | 24,213 | 35°27′58″N 76°46′53″E / 35.46611°N 76.78139°E | 900 | Ghent Kangri | 1976 | 1 (1) |
See also
[edit]- Borders
- Actual Ground Position Line (AGPL)
- India–Pakistan International Border (IB)
- Line of Control (LoC)
- Line of Actual Control (LAC)
- Sir Creek (SC)
- Borders of China
- Borders of India
- Borders of Pakistan
- Conflicts
- Kashmir conflict
- Siachen conflict
- Sino-Indian conflict
- List of disputed territories of China
- List of disputed territories of India
- List of disputed territories of Pakistan
- Northern Areas
- Trans-Karakoram Tract
- Operations
- Operation Meghdoot 1984 in Siachen, by India
- Operation Rajiv 1987 in Siachen, by India
- Operation Safed Sagar 1999 in Kargil War, by India
- Other related topics
- Awards and decorations of the Indian Armed Forces
- Bana Singh, after whom Quaid Post was renamed to Bana Top
- Dafdar, westernmost town in Trans-Karakoram Tract
- India-China Border Roads
- Sino-Pakistan Agreement for transfer of Trans-Karakoram Tract to China
References
[edit]- ^ "Tryst With Deceit?". outlookindia.com/.
- ^ How India realised it was at risk of losing the Siachen glacier to Pakistan, The Print, 12 April 2018.
- ^ Mason, Kenneth (1938). "Karakoram Nomenclature". Himalayan Journal 10. Retrieved 10 February 2014.
- ^ "Pakistan: Signing with the Red Chinese". Time (magazine). 15 March 1963. Retrieved 11 January 2020.
- ^ a b c R Baghela and M Nüsserab, 2015, Securing the heights: The vertical dimension of the Siachen conflict between India and Pakistan in the Eastern Karakoram, Political Geography (journal), Volume 48, Pages 24–36.
- ^ "Manning the Siachen Glacier". Bharat Rakshak Monitor. 2003. Archived from the original on 14 June 2012. Retrieved 27 January 2011.
Sources
[edit]- Jerzy Wala, Geographical Sketch Map of the Karakoram, Swiss Foundation for Alpine Research, Zurich, 1990.