Roman–Gallic wars
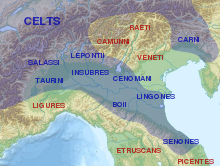

Over the course of nearly four centuries, the Roman Republic fought a series of wars against various Celtic tribes, whom they collectively described as Galli, or Gauls. Among the principal Gallic peoples described as antagonists by Greek and Roman writers were the Senones, Insubres, Boii, and Gaesatae.
The Romans first came into conflict with Gauls who entered Italy from the north. Some of these settled in the lands immediately south of the Alps, which became known as Cisalpine Gaul: "Gaul this side of the Alps". Gaulish armies, some perhaps fighting as mercenaries in the service of the cities of Magna Graecia, plundered territory in Etruria and Latium during the fourth century, famously sacking Rome circa 390 BC.[1]
Following the Samnite Wars and the Punic Wars, in which Gallic forces sometimes made common cause with Rome's enemies, the Romans found themselves in near-total control of Italy, including Cisalpine Gaul. As they consolidated their gains, they came into conflict with Gallic tribes on the borders of their growing empire, and subsequent conflicts occurred in and beyond the Alps. In the first century BC, Caesar's campaigns in Gaul brought most of the Gallic territory in western Europe under Roman control.[2]
Cisalpine conflicts
[edit]Major conflicts on the Italian side of the Alps include:
390[i] BC: Brennus leads the Senones to Clusium in Etruria. Rome sends an army to drive the Senones away, which the Senones defeat at the Battle of the Allia. Brennus leads his men on to Rome, entering the city without further opposition, and plundering it. They depart laden with booty, which according to varying traditions was recovered when the Gauls were defeated by a Caeretan army, or by Camillus.[4][5][6][7][1][8][9]
367 BC: A Gallic expedition is said to have been routed by Camillus, but the historicity of this episode is doubtful.[10][11][12][13]
361–358 BC: Gauls allied with Tibur attack Roman territory during that city's war with Rome. Titus Manlius Imperiosus wins the surname Torquatus after defeating a Gaulish champion in single combat, and taking his torque as a trophy.[14][15][13]
350–349 BC: The Gauls ravage Latium, and the Latin League refuses direct aid to Rome. Despite various hardships, the Romans defeat their attackers, and a young Marcus Valerius Corvus wins everlasting fame by slaying a giant Gaul in single combat, aided by a raven, from which he takes his surname.[16][17][18][19][20]
331 BC: The Romans conclude a peace with the Gauls, which holds for nearly thirty years.[21][22]
302 BC: Gauls cross the Alps into Cisalpine Gaul, where previously-settled Gallic tribes allow them to pass southward. Some of the latter join the march, as do some Etruscans. They pillage Roman territory and retire with the loot, but then fall to fighting among themselves.[23]
295 BC: During the Third Samnite War, an alliance of Samnites, Gauls, Etruscans and Umbrians fights Rome. After an initial defeat, the Romans win a major victory at the Battle of Sentinum under the consuls Quintus Fabius Maximus Rullianus and Publius Decius Mus, who devotes himself and perishes in the battle.[23][24][25]
284 BC:[26] The Gauls besiege Arretium. The Romans march to relieve the city, and the Gauls defeat them. Rome then sends a punitive expedition north which defeats the Senones and drives them out of their territory, which Rome occupies.[23] Then in 283 BC the Boii, with Etruscan allies, march on Rome.[27] Rome is victorious at the Battle of Lake Vadimo.[28][29][30][9]
225 BC: The Insubres and Boii hire Alpine Gauls, the Gaesatae, to join them and march on Rome. The Gauls defeated the Romans at Faesulae, but later the Romans defeated the Gauls at Telamon.[31][32][33]
223–193 BC: After this came a concerted Roman policy aimed at conquering Gallic territories south of the Alps. Rome invaded the territory of the Insubres in 223 BC, and took Clastidium, Acerrae and Mediolanum in 222 BC.[34][35][36] Rome fought Carthage in the Second Punic War (218–201 BC), and the Gauls typically sided with Carthage.[36] After the war, Rome took Bononia (196 BC),[37][38] Placentia (194 BC),[39][40][36] and Mutina (193 BC).[41][42] According to Strabo, many of the surviving Boii retreated north across the Alps to the land subsequently known as Boihaemum,[43] but in all probability the region was already inhabited by Boii prior to their subjugation in Italy.[44]
Transalpine conflicts
[edit]125–121 BC: Romans crossed the Alps and fought first the Salluvii and Vocontii,[45][46][47][48] and then Allobroges and Arveni. The Gauls were decisively defeated at the Battle of Vindalium and Battle of the Isère River in 121 BC.[49][50][51] The Allobrogian territory was subsequently annexed and incorporated the Roman province known as Gallia Transalpina, later Gallia Narbonensis.[52][53]
109 BC: During the Cimbrian War, the Cimbri defeat the consul Marcus Junius Silanus.[54][55] in 107 BC, the Cimbri and Ambrones, together with their allies Helvetii, defeat a Roman army near Agendicum in the Battle of Burdigala, in which the consul Lucius Cassius Longinus is killed.[56][54][57][58][59]
58–50 BC: Caesar leads a series of campaigns through Gaul, which he chronicles in detail. The result is the near-complete subjugation of the country between the Atlantic and the Rhine. After discovering that some of the Gauls are receiving aid from Britain, Caesar mounts the first Roman military expedition to that island.[60][61][2]
40–37 BC: Prompted by unrest in Gaul, Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa marches against the Aquitani, whom he defeats.[62][63]
28–27 BC: Marcus Valerius Messalla Corvinus suppresses a revolt in Aquitania, for which he celebrates a triumph.[64][65]
Notes
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Cornell, The Beginnings of Rome, pp. 313–318.
- ^ a b Oxford Classical Dictionary, 2nd Edition, pp. 455, 456 ("Gallic Wars").
- ^ Cornell, The Beginnings of Rome, p. 314.
- ^ Livy, v. 35–49.
- ^ Dionysius, xiii. 6 s. 7–12 s. 18.
- ^ Polybius, Histories, ii. 18.
- ^ Plutarch, "The Life of Camillus", 14–30.
- ^ Broughton, vol. I, pp. 94–96.
- ^ a b Oxford Classical Dictionary, 2nd Edition, p. 977 ("Senones").
- ^ Livy, vi. 42.
- ^ Plutarch, "The Life of Camillus", 40–42.
- ^ Broughton, vol. I, p. 113.
- ^ a b Cornell, The Beginnings of Rome, p. 324.
- ^ Livy, vii. 9–12, 15.
- ^ Broughton, vol. I, pp. 119–121.
- ^ Livy, vii. 23–26.
- ^ Dionysius, xv. 1.
- ^ Appian, Bella Celtica, 2, 10.
- ^ Broughton, vol. I, pp. 127–129.
- ^ Cornell, The Beginnings of Rome, pp. 324, 325.
- ^ Polybius, Histories, ii. 18.
- ^ Cornell, The Beginnings of Rome, p. 325.
- ^ a b c Polybius, Histories, ii. 19.
- ^ Livy, x. 21, 26–30.
- ^ Broughton, vol. I, pp. 177–179.
- ^ Gallic War (283 BC) http://www.keytoumbria.com/Umbria/Wars_with_Gauls_and_Etruscans_%28285_-_280_BC%29.html
- ^ Polybius, Histories, ii. 20.
- ^ Dionysius, xix. 12 s. 13.
- ^ Appian, Bella Celtica, 11.
- ^ Broughton, vol. I, pp. 188, 189.
- ^ Polybius, Histories, ii. 23, 25–31.
- ^ Appian, Bella Celtica, 2.
- ^ Broughton, vol. I, pp. 230, 231.
- ^ Polybius, Histories, ii. 34, 35.
- ^ Broughton, vol. I, pp. 231, 232.
- ^ a b c Oxford Classical Dictionary, 2nd Edition, p. 548 ("Insubres").
- ^ Livy, xxxiii. 36, 37.
- ^ Broughton, vol. I, p. 335.
- ^ Livy, xxxiv. 43.
- ^ Broughton, vol. I, pp. 342, 343.
- ^ Livy, xxxiv. 55, 56.
- ^ Broughton, vol. I, p. 346.
- ^ Strabo, Geographica, v. 6, 10.
- ^ Oxford Classical Dictionary, 2nd Edition, p. 171 ("Boii").
- ^ Livy, Epitome, lx, lxi.
- ^ Appian, Bellum Civile, i. 34; Bella Celtica, 12.
- ^ Diodorus, xxxiv. 23.
- ^ Broughton, vol. I, pp. 510–512, 514–516.
- ^ Cicero, Pro Fonteio, 36.
- ^ Caesar, De Bello Gallico, i. 45.
- ^ Broughton, vol. I, pp. 520–522.
- ^ Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography, vol. I, p. 954 ("Gallia Transalpina".
- ^ Oxford Classical Dictionary, 2nd Edition, p. 47 ("Allobroges").
- ^ a b Livy, Epitome, 65.
- ^ Broughton, vol. I, p, 545.
- ^ Caesar, De Bello Gallico, i. 7, xii. 5–7, xiii. 2, xiv. 3.
- ^ Appian, Bella Celtica, i. 3.
- ^ Tacitus, Germania, 37.
- ^ Broughton, vol. I, p. 550.
- ^ Caesar, De Bello Gallico, passim.
- ^ Plutarch, "The Life of Caesar", 15, 16, 18, 20, 22–27.
- ^ Appian, Bellum Civile, v. 75, 92.
- ^ Oxford Classical Dictionary, 2nd Edition, pp. 30 ("Agrippa"), 90 ("Aquitania").
- ^ Appian, Bellum Civile, iv. 38.
- ^ Oxford Classical Dictionary, 2nd Edition, pp. 90 ("Aquitania"), 674 ("Messalla Corvinus").
Bibliography
[edit]- Polybius, Historiae (The Histories).
- Marcus Tullius Cicero, Pro Fonteio.
- Gaius Julius Caesar, Commentarii de Bello Gallico (Commentaries on the Gallic War).
- Diodorus Siculus, Bibliotheca Historica (Library of History).
- Dionysius of Halicarnassus, Romaike Archaiologia (Roman Antiquities).
- Titus Livius (Livy), History of Rome.
- Strabo, Geographica.
- Publius Cornelius Tacitus, De Origine et Situ Germanorum (The Origin and Situation of the Germans, or "Germania").
- Appianus Alexandrinus (Appian), Bella Celtica (The Gallic Wars); Bellum Civile (The Civil War).
- Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography, William Smith, ed., Little, Brown and Company, Boston (1854).
- T. Robert S. Broughton, The Magistrates of the Roman Republic, American Philological Association (1952–1986).
- Oxford Classical Dictionary, Second Edition, N. G. L. Hammond and H. H. Scullard, eds., Clarendon Press, Oxford (1970).
- Timothy J. Cornell, The Beginnings of Rome: Italy and Rome from the Bronze Age to the Punic Wars (c. 1000–264 BC), Routledge, London (1995).
- 4th-century BC conflicts
- 3rd-century BC conflicts
- 2nd-century BC conflicts
- 1st-century BC conflicts
- 4th century BC in the Roman Republic
- 3rd century BC in the Roman Republic
- 2nd century BC in the Roman Republic
- 1st century BC in the Roman Republic
- Wars involving the Celts
- Pre-Roman Gaul
- Wars involving the Roman Republic
