Portal:Energy/Selected article/3
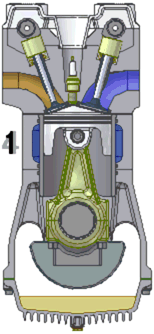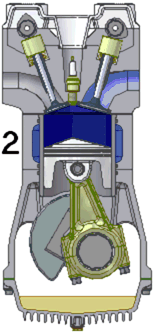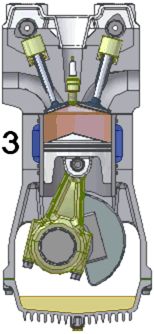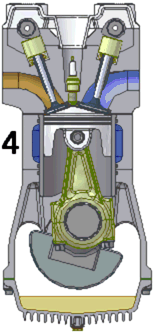
The internal combustion engine is widely used to power a great variety of vehicles and other devices. It is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an oxidizer creates gases of high temperature and pressure, which are permitted to expand.
The defining feature of an internal combustion engine is that useful work is performed by the expanding hot gases acting directly to cause movement, for example by acting on pistons, rotors, or even by pressing on and moving the entire engine itself.
Internal combustion engines are most commonly used for mobile propulsion systems, where their high power-to-weight ratios, together with excellent fuel energy-density, are advantageous. They have appeared in almost all automobiles, motorbikes, many boats, and in a wide variety of aircraft and locomotives. Where very high power is required, such as jet aircraft, helicopters and large ships, they appear mostly in the form of gas turbines. They are also used for electric generators and by industry.
The most common fuels in use today are hydrocarbons derived from petroleum including diesel, gasoline and liquified petroleum gas. Most internal combustion engines designed for gasoline can run on natural gas or liquified petroleum gases without modifications except for the fuel delivery components. Liquid and gaseous biofuels, including ethanol and biodiesel can also be used, and trials of hydrogen fuel have been in progress for some years.