Ponte Vecchio, Bassano

The Ponte Vecchio (Old bridge) or Ponte degli Alpini (bridge of the Alpini, who rebuilt it in 1948) is the covered wooden designed by the architect Andrea Palladio in 1569. The bridge is located in Bassano del Grappa and was destroyed many times, the last time in World War II. The bridge spans the river Brenta.
The Brenta was an important means of communication in the 18th century from the mountains of Grappa to Venice.
History
[edit]The pre-existing bridge, existed from 1209 until 1569, was a wooden structure on pylons and covered by a roof and it constituted the fundamental road to guarantee the connection between Bassano and Vicenza.[citation needed]
In 1315, Bassano was involved in the war between Padua and Cangrande della Scala. When the latter occupied Marostica and Angarano, two towers were built to defend the bridge.[citation needed]
In 1402, the war between Gian Galeazzo and the Carraresi involved also Bassano: the lord of Milan tried to divert the Brenta to deprive Padua of its defences by building a bridge consisting of 94 stone arches equipped with wooden doors used as shutters. In the night between 6 and 7 August a flood overwhelmed the bridge, which was destroyed.[citation needed]
In 1511, French troops under General Jacques de La Palice set the bridge on fire to escape the Imperial army during the War of the League of Cambrai.[citation needed]
Project by Andrea Palladio
[edit]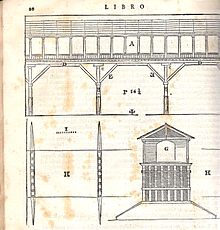
In October 1567, a vigorous flood of the river Brenta swept over the historic bridge. The architect Andrea Palladio was involved in the reconstruction from the months immediately following the collapse: he first designed a stone bridge completely different from the previous one, with three arches on the model of the ancient Roman bridges. However, the City Council rejected the project, requiring the architect not to deviate too much from the traditional structure.
In the summer of 1569, Palladio then presented a second final project of a wooden bridge that practically recalled the previous structure, although radically renewed in terms of technical and structural solutions[1] and of great visual impact. The only reference to an architectural language is the use of Tuscan columns as supports of the architrave that supports the two-pitched roof formed by a series of wooden trusses. The bridge has 5 bays about 13 meters long formed by large wooden beams with slanting breaker that are resting on the four intermediate pylons and on the two side shoulders. The 4 wooden pylons have a hydrodynamic shape compared to the current of the river and are formed by 8 poles about half a meter thick in the ground on the bed of the river and a series of poles at decreasing height that give an oblique profile to the intermediate pylons.
Demolitions and reconstructions
[edit]Confirming the technological efficiency of the Palladian structure, the bridge lasted for almost two hundred years, collapsing only because of the overwhelming flood of the Brenta on 19 August 1748. The bridge was rebuilt by Bartolomeo Ferracina faithfully following Palladio’s design.
In 1813, the bridge was then burnt down by Viceroy Eugène de Beauharnais and later rebuilt in 1821 by Angelo Casarotti, with the same previous apparences.
During the First World War the famous bridge was crossed by Italian troops to face the defence of the territories of the plateau of the Seven Municipalities.
The bridge was then razed to the ground for the third time on 17 February 1945: just after 7pm, when the curfew began, it was torn by a strong explosion. The sabotage action, which was part of a larger plan wanted by the Allies against the bridges of Pedemontana, was carried out by a group of 15 partisans all armed and cycling, two of which towed a cart each loaded with explosives. The attack unfortunately caused the death of a 50-year-old woman and a teenager. The commander of the group was Primo Visentin, a teacher of Loria (TV) who used the pseudonym of "Masaccio", as recalled by the plate still present today on the bridge.[2][3] During a retaliation, the Nazis took three partisans from the prisons, Federico Alberti, Cesare Lunardi and Antonio Zavagnin, and shot them on the bridge with the usual sign bearing the words "I am a bandit".[4] The bridge was rebuilt according to Palladio’s original design. It was inaugurated on 3 October 1948 with the presence of the Prime Minister Alcide De Gasperi. It was rebuilt by Giulio Tessarolo & Figli di Rosà. Since many workers of this firm were veterans of war belonging to the Alpini Corps and wore the typical cap with a pen during the work, the legend arose that it was the Alpini who put it back together. The bridge was severely damaged for the last time by the exceptional flood of 4 November 1966, following which a systematic structural restoration was carried out. Two extraordinary interventions followed: the one of 1990–93 for static consolidation of the foundations and the supporting structures of the four styled, and the one of 2003–6, which was a complex of works of restoration and extraordinary maintenance to counter the inevitable deterioration of the protection products and the connection of the various elements of the bridge.[5][6]
Recent works to check the stability of the structure and especially of the submerged parts, began at the end of 2015, but at the beginning of May 2018 the works were suspended. The work on the bridge was resumed in 2019 and on 12 February the bridge was raised about 45 cm in the collapsed area. The wooden foundations, completely degraded, have been completely replaced by lattice beams and pillars in stainless steel up to the lean level.
In June 2019, it was declared a National Monument (Law no. 65 of 5 July 2019).
References
[edit]- ^ "Structural analysis of palladios timber bridge in bassano del grappa".
- ^ "Tombstone on the bridge that recalls the event".
- ^ "Anpi Vicenza".
- ^ Enciclopedia dell'Antifascismo e della Resistenza Vol. I, Voce "Bassano, Ponte di", pag. 256, La Pietra, Milano, prima edizione, 1968
- ^ "Municipality of Bassano/Projects/Bridge of Alpini".
- ^ "Attraverso nove secoli di storia - Through nine centuries of history".
External links
[edit]- Palladio Museum - https://www.palladiomuseum.org/veneto/opera/29?lang=en
- Some images on postcards and calendars
- historical and artistic iconography
- Traditional song "Sul ponte di Bassano"
- Attualità di Andrea Palladio, [1] L'illustre Bassanese, spec. n. XXXIV, Editrice Artistica Bassano, published on May 23, 2018.

