Model

A model is an informative representation of an object, person, or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin modulus, a measure.[1]
Models can be divided into physical models (e.g. a ship model or a fashion model) and abstract models (e.g. a set of mathematical equations describing the workings of the atmosphere for the purpose of weather forecasting). Abstract or conceptual models are central to philosophy of science.[2][3]
In scholarly research and applied science, a model should not be confused with a theory: while a model seeks only to represent reality with the purpose of better understanding or predicting the world, a theory is more ambitious in that it claims to be an explanation of reality.[4]
Model in specific contexts
[edit]As a noun, model has specific meanings in certain fields, derived from its original meaning of "structural design or layout":
- Model (art), a person posing for an artist, e.g. a 15th-century criminal representing the biblical Judas in Leonardo da Vinci's painting The Last Supper
- Model (person), a person who serves as a template for others to copy, as in a role model, often in the context of advertising commercial products; e.g. the first fashion model, Marie Vernet Worth in 1853, wife of designer Charles Frederick Worth.[5][6]
- Model (product), a particular design of a product as displayed in a catalogue or show room (e.g. Ford Model T, an early car model)
- Model (organism) a non-human species that is studied to understand biological phenomena in other organisms, e.g. a guinea pig starved of vitamin C to study scurvy, an experiment that would be immoral to conduct on a person
- Model (mimicry), a species that is mimicked by another species
- Model (logic), a structure (a set of items, such as natural numbers 1, 2, 3,..., along with mathematical operations such as addition and multiplication, and relations, such as ) that satisfies a given system of axioms (basic truisms), i.e. that satisfies the statements of a given theory[7]
- Model (CGI), a mathematical representation of any surface of an object in three dimensions via specialized software
- Model (MVC), the information-representing internal component of a software, as distinct from its user interface
Physical model
[edit]
A physical model (most commonly referred to simply as a model but in this context distinguished from a conceptual model) is a smaller or larger physical representation of an object, person or system. The object being modelled may be small (e.g., an atom) or large (e.g., the Solar System) or life-size (e.g., a fashion model displaying clothes for similarly-built potential customers).
The geometry of the model and the object it represents are often similar in the sense that one is a rescaling of the other. However, in many cases the similarity is only approximate or even intentionally distorted. Sometimes the distortion is systematic, e.g., a fixed scale horizontally and a larger fixed scale vertically when modelling topography to enhance a region's mountains.
An architectural model permits visualization of internal relationships within the structure or external relationships of the structure to the environment. Another use is as a toy.
Instrumented physical models are an effective way of investigating fluid flows for engineering design. Physical models are often coupled with computational fluid dynamics models to optimize the design of equipment and processes. This includes external flow such as around buildings, vehicles, people, or hydraulic structures. Wind tunnel and water tunnel testing is often used for these design efforts. Instrumented physical models can also examine internal flows, for the design of ductwork systems, pollution control equipment, food processing machines, and mixing vessels. Transparent flow models are used in this case to observe the detailed flow phenomenon. These models are scaled in terms of both geometry and important forces, for example, using Froude number or Reynolds number scaling (see Similitude). In the pre-computer era, the UK economy was modelled with the hydraulic model MONIAC, to predict for example the effect of tax rises on employment.
-
Water-powered model of the UK economy – MONIAC in the Science Museum, London
-
Female model demonstrating brassiere for similarly-built potential buyers
-
Model of a war scene — Australian War Memorial, Canberra
-
Guinea pig used as animal model for studying human leptospirosis
-
NASA wind tunnel with the scale model of an aeroplane
Conceptual model
[edit]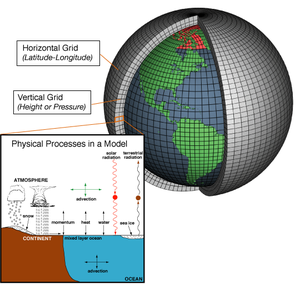
A conceptual model is a theoretical representation of a system, e.g. a set of mathematical equations attempting to describe the workings of the atmosphere for the purpose of weather forecasting.[8] It consists of concepts used to help understand or simulate a subject the model represents.
Abstract or conceptual models are central to philosophy of science,[2][3] as almost every scientific theory effectively embeds some kind of model of the physical or human sphere. In some sense, a physical model "is always the reification of some conceptual model; the conceptual model is conceived ahead as the blueprint of the physical one", which is then constructed as conceived.[9] Thus, the term refers to models that are formed after a conceptualization or generalization process.[2][3]
Examples
[edit]- Conceptual model (computer science), an agreed representation of entities and their relationships, to assist in developing software
- Economic model, a theoretical construct representing economic processes
- Language model a probabilistic model of a natural language, used for speech recognition, language generation, and information retrieval
- Large language models are artificial neural networks used for generative artificial intelligence (AI), e.g. ChatGPT
- Mathematical model, a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language
- Statistical model, a mathematical model that usually specifies the relationship between one or more random variables and other non-random variables
- Model (CGI), a mathematical representation of any surface of an object in three dimensions via specialized software
- Medical model, a proposed "set of procedures in which all doctors are trained"
- Mental model, in psychology, an internal representation of external reality
- Model (logic), a set along with a collection of finitary operations, and relations that are defined on it, satisfying a given collection of axioms
- Model (MVC), information-representing component of a software, distinct from the user interface (the "view"), both linked by the "controller" component, in the context of the model–view–controller software design
- Model act, a law drafted centrally to be disseminated and proposed for enactment in multiple independent legislatures
- Standard model (disambiguation)
Properties of models, according to general model theory
[edit]According to Herbert Stachowiak, a model is characterized by at least three properties:[10]
- 1. Mapping
- A model always is a model of something—it is an image or representation of some natural or artificial, existing or imagined original,[11] where this original itself could be a model.
- 2. Reduction
- In general, a model will not include all attributes that describe the original but only those that appear relevant to the model's creator or user.
- 3. Pragmatism
- A model does not relate unambiguously to its original. It is intended to work as a replacement for the original
- a) for certain subjects (for whom?)
- b) within a certain time range (when?)
- c) restricted to certain conceptual or physical actions (what for?).
For example, a street map is a model of the actual streets in a city (mapping), showing the course of the streets while leaving out, say, traffic signs and road markings (reduction), made for pedestrians and vehicle drivers for the purpose of finding one's way in the city (pragmatism).
Additional properties have been proposed, like extension and distortion[12] as well as validity.[13] The American philosopher Michael Weisberg differentiates between concrete and mathematical models and proposes computer simulations (computational models) as their own class of models.[14]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Oxford English Dictionary, Oxford University Press, doi:10.1093/OED/3984201854, retrieved 1 July 2023
- ^ a b c Merriam-Webster, Merriam-Webster's Collegiate Dictionary, Merriam-Webster.
- ^ a b c Tatomir, A.; et al. (2018). "Conceptual model development using a generic Features, Events, and Processes (FEP) database for assessing the potential impact of hydraulic fracturing on groundwater aquifers". Advances in Geosciences. 45: 185–192. Bibcode:2018AdG....45..185T. doi:10.5194/adgeo-45-185-2018. hdl:20.500.11820/b83437b4-6791-4c4c-8f45-744a116c6ead.
- ^ Wunsch, G. (1994). "Theories, models, and data". Demografie. 36 (1): 20–29. PMID 12346076.
- ^ "modelworker.com". Archived from the original on 2007-10-17.
- ^ Walker, Harriet (4 May 2009). "Fabulous faces of fashion: A century of modelling". The Independent. Archived from the original on 2011-05-28. Retrieved 2017-09-05.
- ^ Chang and Keisler, p. 1
- ^ Forecast models, Met Office.
- ^ Ibrahim A. Halloun, Modeling Theory in Science Education (2007), p. 36.
- ^ Herbert Stachowiak: Allgemeine Modelltheorie, 1973, S. 131–133.
- ^ "TRICK: An Easy Acronym to Conceptualize Digital Twin". automation.com. Retrieved 2024-11-05.
- ^ Thalheim: Towards a Theory of Conceptual Modelling. In: Journal of Universal Computer Science, vol. 16, 2010, no. 20, S. 3120
- ^ Dietrich Dörner: Thought and Design – Research Strategies, Single-case Approach and Methods of Validation. In: E. Frankenberger et al. (eds.): Designers. The Key to Successful Product Development. Springer-Verlag, Berlin et al. 1998, S. 3–11.
- ^ M. Weisberg: Simulation and Similarity - using models to understand the world. Oxford University Press, New York 2013
External links
[edit] Media related to Physical models at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Physical models at Wikimedia Commons






