Portal:Spain
Portal maintenance status: (June 2018)
|
The Spain Portal (Bienvenido al portal español)

Spain, formally the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southwestern Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the southernmost point of continental Europe, It is the largest country in Southern Europe and the fourth-most populous European Union member state. Spanning across the majority of the Iberian Peninsula, its territory also includes the Canary Islands, in the Atlantic Ocean, the Balearic Islands, in the Mediterranean Sea, and the autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla, in Africa. Peninsular Spain is bordered to the north by France, Andorra, and the Bay of Biscay; to the east and south by the Mediterranean Sea and Gibraltar; and to the west by Portugal and the Atlantic Ocean. Spain's capital and largest city is Madrid, and other major urban areas include Barcelona, Valencia, Seville, Zaragoza, Málaga, Murcia and Palma de Mallorca.
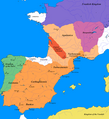
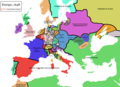
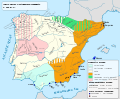
In early antiquity, the Iberian Peninsula was inhabited by Celts, Iberians, and other pre-Roman peoples. With the Roman conquest of the Iberian Peninsula, the province of Hispania was established. Following the Romanization and Christianization of Hispania, the fall of the Western Roman Empire ushered in the inward migration of tribes from Central Europe, including the Visigoths, who formed the Visigothic Kingdom centred on Toledo. In the early eighth century, most of the peninsula was invaded by the Umayyad Caliphate, and during early Islamic rule, Al-Andalus became a dominant peninsular power centred on Córdoba. Several Christian kingdoms emerged in Northern Iberia, chief among them Asturias, León, Castile, Aragon, Navarre, and Portugal; made an intermittent southward military expansion and repopulation, known as the Reconquista, repelling Islamic rule in Iberia, which culminated with the Christian seizure of the Nasrid Kingdom of Granada in 1492. The dynastic union of the Crown of Castile and the Crown of Aragon in 1479 under the Catholic Monarchs is often considered the de facto unification of Spain as a nation-state. (Full article...)
 Featured article – show another
Featured article – show another
-
Image 1Dinar minted in Yusuf I's name
Abu al-Hajjaj Yusuf ibn Ismail (Arabic: أبو الحجاج يوسف بن إسماعيل; 29 June 1318 – 19 October 1354), known by the regnal name al-Muayyad billah (المؤيد بالله, "He who is aided by God"), was the seventh Nasrid ruler of the Emirate of Granada on the Iberian Peninsula. The third son of Ismail I (r. 1314–1322), he was Sultan between 1333 and 1354, after his brother Muhammad IV (r. 1325–1333) was assassinated. (Full article...) -
Image 2The Colossus of Rhodes is a 1954 oil painting by the Spanish surrealist Salvador Dalí. It is one of a series of seven paintings he created for the 1956 film Seven Wonders of the World, each depicting one of the wonders. The work shows the Colossus of Rhodes, the ancient statue of the Greek titan-god of the sun, Helios. The painting was not used for the film and was donated to the Kunstmuseum Bern in 1981, where it remains. (Full article...)
-
Image 3Portrait of a Man (presumed self-portrait of El Greco, c. 1595–1600) in Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York City
Doménikos Theotokópoulos (Greek: Δομήνικος Θεοτοκόπουλος, IPA: [ðoˈminikos θeotoˈkopulos]; 1 October 1541 – 7 April 1614), most widely known as El Greco (Spanish pronunciation: [el ˈgɾeko]; "The Greek"), was a Greek painter, sculptor and architect of the Spanish Renaissance. El Greco was a nickname, and the artist normally signed his paintings with his full birth name in Greek letters often adding the word Κρής (Krḗs), which means "Cretan" in Ancient Greek. (Full article...) -
Image 4Muhammad I (red tunic and shield) depicted leading his troops during the Mudéjar revolt of 1264–1266 in the Cantigas de Santa Maria
Abu Abdullah Muhammad ibn Yusuf ibn Nasr (Arabic: أبو عبد الله محمد بن يوسف بن نصر, romanized: Muḥammad ibn Yūsuf ibn Naṣr; c. 1195 – 22 January 1273), also known as Ibn al-Ahmar (ابن الأحمر, lit. 'Son of the Red') and by his honorific al-Ghalib billah (الغالب بالله, lit. 'The Victor by the Grace of God'), was the first ruler of the Emirate of Granada, the last independent Muslim state on the Iberian Peninsula, and the founder of its ruling Nasrid dynasty. He lived during a time when Iberia's Christian kingdoms—especially Portugal, Castile and Aragon—were expanding at the expense of the Islamic territory in Iberia, called Al-Andalus. Muhammad ibn Yusuf took power in his native Arjona in 1232 when he rebelled against the de facto leader of Al-Andalus, Ibn Hud. During this rebellion, he was able to take control of Córdoba and Seville briefly, before he lost both cities to Ibn Hud. Forced to acknowledge Ibn Hud's suzerainty, Muhammad was able to retain Arjona and Jaén. In 1236, he betrayed Ibn Hud by helping Ferdinand III of Castile take Córdoba. In the years that followed, Muhammad was able to gain control over southern cities, including Granada (1237), Almería (1238), and Málaga (1239). In 1244, he lost Arjona to Castile. Two years later, in 1246, he agreed to surrender Jaén and accept Ferdinand's overlordship in exchange for a 20-year truce. (Full article...) -
Image 5

North View of Gibraltar from Spanish Lines by John Mace (1782)
The history of Gibraltar, a small peninsula on the southern Iberian coast near the entrance of the Mediterranean Sea, spans over 2,900 years. The peninsula has evolved from a place of reverence in ancient times into "one of the most densely fortified and fought-over places in Europe", as one historian has put it. Gibraltar's location has given it an outsized significance in the history of Europe and its fortified town, established in the Middle Ages, has hosted garrisons that sustained numerous sieges and battles over the centuries. (Full article...) -
Image 6
The Andalusian, also known as the Pure Spanish Horse or PRE (pura raza española), is a horse breed from the Iberian Peninsula, where its ancestors have lived for thousands of years. The Andalusian has been recognized as a distinct breed since the 15th century, and its conformation has changed very little over the centuries. Throughout its history, it has been known for its prowess as a war horse, and was prized by the nobility. The breed was used as a tool of diplomacy by the Spanish government, and kings across Europe rode and owned Spanish horses. During the 19th century, warfare, disease and crossbreeding reduced herd numbers dramatically, and despite some recovery in the late 19th century, the trend continued into the early 20th century. Exports of Andalusians from Spain were restricted until the 1960s, but the breed has since spread throughout the world, despite their low population. In 2010, there were more than 185,000 registered Andalusians worldwide. (Full article...) -
Image 7Hurricane Leslie near peak intensity southwest of the Azores on 11 October
Hurricane Leslie (known as Storm Leslie or Cyclone Leslie while extratropical) was the strongest cyclone of tropical origin to strike the Iberian Peninsula since 1842. A large, long-lived, and very erratic tropical cyclone, Leslie was the twelfth named storm and sixth hurricane of the 2018 Atlantic hurricane season.[1] The storm had a non-tropical origin, developing from an extratropical cyclone that was situated over the northern Atlantic on 22 September. The low quickly acquired subtropical characteristics and was classified as Subtropical Storm Leslie on the following day. The cyclone meandered over the northern Atlantic and gradually weakened, before merging with a frontal system on 25 September, which later intensified into a powerful hurricane-force extratropical low over the northern Atlantic. (Full article...) -
Image 8Muhammad III (Arabic: محمد الثالث; 15 August 1257 – 21 January 1314) was the ruler of the Emirate of Granada in Al-Andalus on the Iberian Peninsula from 8 April 1302 until 14 March 1309, and a member of the Nasrid dynasty. He ascended the Granadan throne after the death of his father Muhammad II, which according to rumours, was caused by Muhammad III poisoning him. He had the reputation of being both cultured and cruel. Later in his life, he became visually impaired—which caused him to be absent from many government activities and to rely on high officials, especially the powerful Vizier Ibn al-Hakim al-Rundi. (Full article...)
-
Image 9
The AMX-30E (E stands for España, Spanish for Spain) is a Spanish main battle tank based on France's AMX-30. Although originally the Spanish government sought to procure the German Leopard 1, the AMX-30 was ultimately awarded the contract due to its lower price and the ability to manufacture it in Spain. 280 units were manufactured by Santa Bárbara Sistemas for the Spanish Army, between 1974 and 1983. (Full article...) -
Image 10
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Italy and Iberia, but also on the islands of Sicily and Sardinia and, towards the end of the war, in North Africa. After immense materiel and human losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were once again defeated. Macedonia, Syracuse and several Numidian kingdoms were drawn into the fighting, and Iberian and Gallic forces fought on both sides. There were three main military theatres during the war: Italy, where Hannibal defeated the Roman legions repeatedly, with occasional subsidiary campaigns in Sicily, Sardinia and Greece; Iberia, where Hasdrubal, a younger brother of Hannibal, defended the Carthaginian colonial cities with mixed success before moving into Italy; and Africa, where Rome finally won the war. (Full article...) -
Image 11

Boletus aereus, commonly known as the dark cep, bronze bolete, or queen bolete, is a highly prized and much sought-after edible mushroom in the family Boletaceae. The bolete is widely consumed in Spain (Basque Country and Navarre), France, Italy, Greece, and generally throughout the Mediterranean. Described in 1789 by French mycologist Pierre Bulliard, it is closely related to several other European boletes, including B. reticulatus, B. pinophilus, and the popular B. edulis. Some populations in North Africa have in the past been classified as a separate species, B. mamorensis, but have been shown to be phylogenetically conspecific to B. aereus and this taxon is now regarded as a synonym. (Full article...) -
Image 12The Nyon Conference was a diplomatic conference held in Nyon, Switzerland, in September 1937 to address attacks on international shipping in the Mediterranean Sea during the Spanish Civil War. The conference was convened in part because Italy had been carrying out unrestricted submarine warfare, although the final conference agreement did not accuse Italy directly; instead, the attacks were referred to as "piracy" by an unidentified body. Italy was not officially at war, nor did any submarine identify itself. The conference was designed to strengthen non-intervention in the Spanish Civil War. The United Kingdom and France led the conference, which was also attended by Bulgaria, Egypt, Greece, Romania, Turkey, the Soviet Union and Yugoslavia. (Full article...)
-
Image 13The Lince (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈlinθe], meaning "Lynx") was a Spanish development programme for a proposed main battle tank that unfolded during the late 1980s and early 1990s. The intention was to replace the M47 and M48 Patton tanks that the Spanish Army had received under the U.S. Mutual Defense Assistance Act between 1954 and 1975, and to complement the AMX-30E tanks manufactured for the army during the 1970s. Companies from several nations, such as German Krauss-Maffei, Spanish Santa Bárbara, and French GIAT, made bids for the development contract. The main priorities were mobility and firepower, with secondary priority placed on protection; the Lince tank was to have been lighter and faster than its competitors. To achieve a sufficient level of firepower and protection, the Lince was to use Rheinmetall's 120 mm L/44 tank-gun and German composite armour from the Leopard 2A4. (Full article...)
-
Image 14Nasr (1 November 1287 – 16 November 1322), full name Abu al-Juyush Nasr ibn Muhammad (Arabic: أبو الجيوش نصر بن محمد), was the fourth Nasrid ruler of the Emirate of Granada from 14 March 1309 until his abdication on 8 February 1314. He was the son of Muhammad II al-Faqih and Shams al-Duha. He ascended the throne after his brother Muhammad III was dethroned in a palace revolution. At the time of his accession, Granada faced a three-front war against Castile, Aragon and the Marinid Sultanate, triggered by his predecessor's foreign policy. He made peace with the Marinids in September 1309, ceding to them the African port of Ceuta, which had already been captured, as well as Algeciras and Ronda in Europe. Granada lost Gibraltar to a Castilian siege in September, but successfully defended Algeciras until it was given to the Marinids, who continued its defense until the siege was abandoned in January 1310. James II of Aragon sued for peace after Granadan defenders defeated the Aragonese siege of Almería in December 1309, withdrawing his forces and leaving the Emirate's territories by January. In the ensuing treaty, Nasr agreed to pay tributes and indemnities to Ferdinand IV of Castile and yield some border towns in exchange for seven years of peace. (Full article...)
-
Image 15Conquistador Pedro de Alvarado led the initial efforts to conquer Guatemala.
In a protracted conflict during the Spanish colonization of the Americas, Spanish colonisers gradually incorporated the territory that became the modern country of Guatemala into the colonial Viceroyalty of New Spain. Before the conquest, this territory contained a number of competing Mesoamerican kingdoms, the majority of which were Maya. Many conquistadors viewed the Maya as "infidels" who needed to be forcefully converted and pacified, disregarding the achievements of their civilization. The first contact between the Maya and European explorers came in the early 16th century when a Spanish ship sailing from Panama to Santo Domingo was wrecked on the east coast of the Yucatán Peninsula in 1511. Several Spanish expeditions followed in 1517 and 1519, making landfall on various parts of the Yucatán coast. The Spanish conquest of the Maya was a prolonged affair; the Maya kingdoms resisted integration into the Spanish Empire with such tenacity that their defeat took almost two centuries. (Full article...) -
Image 16Spanish Leopard 2E in Zaragoza, June 2008
The Leopardo 2E or Leopard 2A6E (E stands for España (Spanish for 'Spain')) is a variant of the German Leopard 2 main battle tank (specifically the Leopard 2A6 variant), tailored to the requirements of the Spanish army, which acquired it as part of an armament modernization program named Programa Coraza, or Program Cuirass. The acquisition program for the Leopard 2E began in 1994, five years after the cancellation of the Lince tank program that culminated in an agreement to transfer 108 Leopard 2A4s to the Spanish army in 1998 and started the local production of the Leopard 2E in December 2002. Despite postponement of production owing to the 2003 merger between Santa Bárbara Sistemas and General Dynamics, and continued manufacturing issues between 2006 and 2007, 219 Leopard 2Es have been delivered to the Spanish army. (Full article...) -
Image 17Muhammad II (Arabic: محمد الثاني) (also known by the epithet al-Faqih, "the canon-lawyer", c. 1235 – 8 April 1302; reigned from 1273 until his death) was the second Nasrid ruler of the Emirate of Granada in Al-Andalus on the Iberian Peninsula, succeeding his father, Muhammad I. Already experienced in matters of state when he ascended the throne, he continued his father's policy of maintaining independence in the face of Granada's larger neighbours, the Christian kingdom of Castile and the Muslim Marinid state of Morocco, as well as an internal rebellion by his family's former allies, the Banu Ashqilula. (Full article...)
-
Image 18The siege of Nice by a Franco-Ottoman fleet in 1543 (drawing by Toselli, after an engraving by Aeneas Vico)
The Italian War of 1542–1546 was a conflict late in the Italian Wars, pitting Francis I of France and Suleiman I of the Ottoman Empire against the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V and Henry VIII of England. The course of the war saw extensive fighting in Italy, France, and the Low Countries, as well as attempted invasions of Spain and England. The conflict was inconclusive and ruinously expensive for the major participants. (Full article...) -
Image 19Battle of Chiclana, 5 March 1811, Louis-François Lejeune
The Battle of Barrosa (Chiclana, 5 March 1811, also known as the Battle of Chiclana or Battle of Cerro del Puerco) was part of an unsuccessful manoeuvre by an Anglo-Iberian force to break the French siege of Cádiz during the Peninsular War. During the battle, a single British division defeated two French divisions and captured a regimental eagle. (Full article...) -
Image 20The ruins of Santa María de Óvila in Spain, shown more than 75 years after the most striking architectural features were removed by agents of William Randolph Hearst
Santa María de Óvila is a former Cistercian monastery built in Spain beginning in 1181 on the Tagus River near Trillo, Guadalajara, about 90 miles (140 km) northeast of Madrid. During prosperous times over the next four centuries, construction projects expanded and improved the small monastery. Its fortunes declined significantly in the 18th century, and in 1835 it was confiscated by the Spanish government and sold to private owners who used its buildings to shelter farm animals. (Full article...) -
Image 21

A carillonneur plays the 56-bell carillon of the Plummer Building, Rochester, Minnesota, US
A carillon is a pitched percussion instrument that is played with a keyboard and consists of at least 23 bells. The bells are cast in bronze, hung in fixed suspension, and tuned in chromatic order so that they can be sounded harmoniously together. They are struck with clappers connected to a keyboard of wooden batons played with the hands and pedals played with the feet. Often housed in bell towers, carillons are usually owned by churches, universities, or municipalities. They can include an automatic system through which the time is announced and simple tunes are played throughout the day. (Full article...) -
Image 22
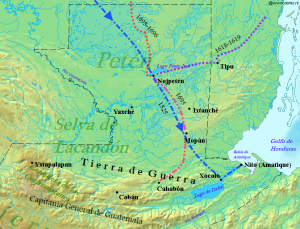
The Spanish conquest of Petén was the last stage of the conquest of Guatemala, a prolonged conflict during the Spanish colonisation of the Americas. A wide lowland plain covered with dense rainforest, Petén contains a central drainage basin with a series of lakes and areas of savannah. It is crossed by several ranges of low karstic hills and rises to the south as it nears the Guatemalan Highlands. The conquest of Petén, a region now incorporated into the modern republic of Guatemala, climaxed in 1697 with the capture of Nojpetén, the island capital of the Itza kingdom, by Martín de Ursúa y Arizmendi. With the defeat of the Itza, the last independent and unconquered native kingdom in the Americas fell to European colonisers. (Full article...) -
Image 23
The black stork (Ciconia nigra) is a large bird in the stork family Ciconiidae. It was first described by Carl Linnaeus in the 10th edition of his Systema Naturae. Measuring on average 95 to 100 cm (37 to 39 in) from beak tip to end of tail with a 145-to-155 cm (57-to-61 in) wingspan, the adult black stork has mainly black plumage, with white underparts, long red legs and a long pointed red beak. A widespread but uncommon species, it breeds in scattered locations across Europe (predominantly in Portugal and Spain, and central and eastern parts), and east across the Palearctic to the Pacific Ocean. It is a long-distance migrant, with European populations wintering in tropical Sub-Saharan Africa, and Asian populations in the Indian subcontinent. When migrating between Europe and Africa, it avoids crossing broad expanses of the Mediterranean Sea and detours via the Levant in the east, the Strait of Sicily in the center, or the Strait of Gibraltar in the west. An isolated non-migratory population lives in Southern Africa. (Full article...) -
Image 24

Rokeby Venus, c. 1647–1651. 122 cm × 177 cm (48 in × 70 in). National Gallery, London.
The Rokeby Venus (/ˈroʊkbi/ ROHK-bee; also known as The Toilet of Venus, Venus at her Mirror, Venus and Cupid; Whose original title was "The Mirror's Venus" Spanish: La Venus del espejo) is a painting by Diego Velázquez, the leading artist of the Spanish Golden Age. Completed between 1647 and 1651, and probably painted during the artist's visit to Italy, the work depicts the goddess Venus in a sensual pose, lying on a bed with her back facing the viewer, and looking into a mirror held by the Roman god of physical love, her son Cupid. The painting is in the National Gallery, London. (Full article...) -
Image 25The Oran fatwa was a responsum fatwa, or an Islamic legal opinion, issued in 1502 to address the crisis that occurred when Muslims in the Crown of Castile, in present-day Spain, were forced to convert to Christianity in 1500–1502. It was authored by mufti Ahmad ibn Abi Jum'ah, an Algerian scholar of Islamic law of the Maliki school; the term "Oran fatwa" was applied by modern scholars, due to the word "Al-Wahrani" ("of Oran") that appears in the text as part of the author's name. (Full article...)
Selected biography

Luis Carrero Blanco, 1st Duke of Carrero-Blanco (March 4, 1903, Santoña, Cantabria – December 20, 1973, Madrid) was a Spanish admiral and statesman. In July 1936, when the Spanish Civil War erupted, Carrero Blanco found himself behind the coalescing Republican line. Taking refuge in the embassy of Mexico and later that of France, he was able to sneak across the front and reach the Nationalist side in June of 1937. Carrero Blanco then served in the Nationalist navy. After the Nationalist victory and subsequent installation of Generalísimo Francisco Franco as military dictator (Caudillo) of Spain, Carrero Blanco became one of his closest collaborators as well a chief of naval operations.
He was said to be in opposition to Spain entering World War II on the side of the Axis powers, a notably different political position compared to some other Falangists. Carrero Blanco himself was a monarchist. Devoted to the Roman Catholic Church, he was close to Opus Dei. After as political career of many positions, he reached its zenith in June 1973 upon being named Prime Minister of Spain and made a top deputy to Franco. It seemed as though it was only a matter of time before he would succeed the ailing dictator. Blanco was assassinated in 1973 in Madrid by four members of the ETA.
Selected picture
-
Image 1Photo: David IliffThe Giralda is a 104.5 m (343 ft) tall bell tower for the Seville Cathedral in Seville, Andalusia, Spain. It was originally constructed as a minaret in 1198, when Seville was ruled by the Almohad Caliphate. After the city was taken by the Christians in the Reconquista, the city's mosque was converted to a church. The upper third of the structure was completed during the Spanish Renaissance.
-
Image 3Painting credit: Francisco GoyaCharles IV of Spain and His Family is a portrait of the royal family of Spain painted by Francisco Goya in 1800 and 1801. King Charles IV, his wife Maria Luisa of Parma, and his children and relatives are dressed in the height of contemporary fashion, lavishly adorned with jewelry and the sashes of the order of Charles III. The artist does not attempt to flatter the family; instead the group portrait is unflinchingly realist, both in detail and tone. The artist, seated at his easel, is visible in the background. The painting is in the collection of the Museo del Prado in Madrid.
-
Image 4Photograph credit: Biblioteca Nacional de EspañaAna Santos Aramburo (born 1957) has been the director of the National Library of Spain since February 2013. Having received a degree in geography and history from the University of Zaragoza in Spain, she has spent much of her career working at the Complutense University of Madrid, first at the library of the Faculty of Economics and Business Sciences, and later serving as deputy director of the university library. Later she served as Director of the Historical Library Marquis of Valdecilla, General Director of Libraries and Archives of the City of Madrid, and Director of Cultural Action at the National Library. This photograph of Santos shows her at the headquarters of the National Library of Spain in Madrid.
-
Image 5
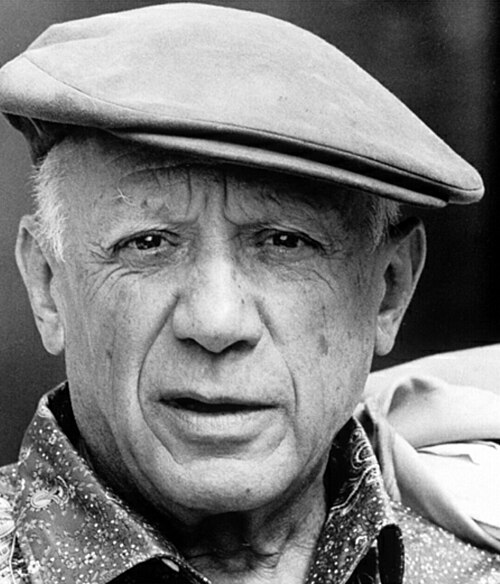

Pablo Picasso Credit: TyreniusPablo Picasso (October 25, 1881 — April 8, 1973) was an artist and sculptor. Picasso was born in Málaga, Spain. This image was taken of him in 1962, eleven years before his death. -
Image 6

A statue showing Christopher Columbus Credit: Luis GarcíaA statue showing Christopher Columbus and Queen Isabella, the statue was made in 1885. -
Image 7
The Temple of Debod. Credit: OsvaldoGagoThe Temple of Debod is an ancient Egyptian temple which has been rebuilt in Madrid, Spain. The temple was built in southern Egypt, very close to the first cataract of the Nile and to the great religious center dedicated to the goddess Isis, in Philae. -
Image 8The peaks of the Central Massif overlook the village of Sotres in Cabrales, located in the Picos de Europa, a mountain range in northern Spain forming part of the Cantabrian Mountains. The name (literally: "Peaks of Europe") is believed to derive from being the first European landforms visible to mariners arriving from the Americas.
-
Image 9Photograph: Benny TrappThe Spanish painted frog (Discoglossus jeanneae) is a species of frog in the family Alytidae. Endemic to Spain, it mostly lives in open areas, pine groves and shrublands. It feeds mostly on insects and worms.
-
Image 10
Aneto Peak Credit: BrugesFR
Aneto is a mountain located in Benasque municipality, Aragon, area of the Pyreenes. The mountain is the highest mountain in the Pyrenees, and Spain's third-highest mountain. -
Image 11Photo credit: David IliffThe Tagus River, seen here passing through the World Heritage listed city of Toledo, Spain. It is the longest river on the Iberian Peninsula at 1,038 kilometres (645 mi). It begins its journey in the Albarracín mountains in Spain, and follows a very constricted course for much of its length before reaching the Atlantic Ocean in Portugal.
-
Image 12Photo credit: DiliffThe Torre Agbar is a landmark skyscraper and the third tallest building in Barcelona, Spain. It was designed by French architect Jean Nouvel, who stated that the shape of the Torre Agbar was inspired by the mountains of Montserrat that surround Barcelona, and by the shape of a geyser of water rising into the air. Its design combines a number of different architectural concepts, resulting in a striking structure built with reinforced concrete, covered with a facade of glass, and over 4,500 window openings cut out of the structural concrete.
-
Image 13Photo credit: David IliffThe Queen Sofia Palace of the Arts (Valencian: Palau de les Arts Reina Sofía) is an opera house located in Valencia, Spain. The last to be completed of the City of Arts and Sciences complex, it was designed by architect Santiago Calatrava. The 14-story structure opened on 8 October 2005.
-
Image 14Image: Royal Household of Spain; Restoration: Lise BroerA Grant of Arms by Philip II of Spain to Alonso de Mesa and Hernando de Mesa, signed 25 November 1566. In Spanish heraldry, coats of arms were granted based almost entirely on military service, which made it possible for commoners to join the ranks of the Spanish nobility. Also unique to Spain was that titles could be inherited through females and via illegitimacy.
-
Image 15Smoke coming from Madrid Barajas International Airport after the 2006 Madrid Barajas International Airport bombing. The terrorist incident occurred on the morning of December 30, 2006, when an explosion took place in the carpark building attached to Terminal 4 of the airport.
-
Image 16Painting credit: Federico de Madrazo y KuntzAmalia de Llano (April 29, 1822 – July 6, 1874) was a Spanish countess and writer. This 1853 oil-on-canvas portrait by Federico de Madrazo y Kuntz shows her seated in a fine armchair wearing sumptuous clothes, with her youth and beauty accentuated by the dark background, and is quite unlike a traditional Spanish portrait of the period.
-
Image 17

A portrait of Francisco Martínez de la Rosa Credit: Petronas
Francisco de Paula Martinez de la Rosa (10 March 1789 — 1862) was a dramatist and statesman. Rosa was born in Granada, and educated at the University of Granada. Rosa became well known after epigrams he performed on celebrities. -
Image 18Painting: Marià FortunyThe Spanish Wedding is an oil on panel painting by Marià Fortuny completed over a two-year period ending in 1870. It depicts the signing of a wedding contract in 18th century Spain and was influenced heavily by the works of Francisco Goya, whom the artist admired. It is currently exhibited at the National Art Museum of Catalonia.
-
Image 19Gaspar de Guzmán, Count-Duke of Olivares (1587–1645) was a Spanish royal favourite of Philip IV and minister. As prime minister from 1621 to 1643, he over-exerted Spain in foreign affairs and unsuccessfully attempted domestic reform. His policies of committing Spain to recapture the Dutch Republic led to his major involvement in the Thirty Years War. This portrait was completed in 1634, with its composition referring to Olivares' military leadership in the service of King Philip.
-
Image 20Photograph: J.Ligero & I.BarriosA three-month old Spanish ibex (Capra pyrenaica) in Sierra de Gredos, Spain. These ibexes are strong mountain animals characterized by their large and flexible hooves and short legs.
The two sexes of adults form separate social groups; juveniles stay with the female groups from birth until the following birth season, when they leave. Yearling males then join male groups, while females eventually return to their mothers' groups and stay several years. -
Image 21Photo credit: David IliffThe Casa Milà, a 1912 work by Catalán architect Antoni Gaudi, in the Eixample district of Barcelona, Spain. Gaudí's fascination with trencadís-influenced decoration and curves (predating biomorphism by almost 20 years) can be seen here.
-
Image 22Architecture credit: José Grases Riera; photographed by Carlos DelgadoThe Monument to Alfonso XII is located in Buen Retiro Park (El Retiro) in Madrid, Spain. Measuring 30 m (98 ft) high, 86 m (282 ft) long, and 58 m (190 ft) wide, it has at its center an equestrian statue of King Alfonso XII, cast in bronze by the Spanish sculptor Mariano Benlliure in 1904. The monument is situated on the eastern edge of an artificial lake near the center of the park and was inaugurated on 6 June 1922.
Did you know...
- ... that in 1976, Carmen Valero became the first female track and field athlete to represent Spain at the Olympics?
- ... that some California schoolchildren build dioramas when learning about their state's Spanish missions?
- ... that Juan de Casas, the Spanish military governor of Venezuela, cried after the French demanded that he accept a Frenchman as king?
- ... that the Kitāb al-ṭabīẖ, a medieval Andalusian cookbook, contains an early version of Jewish challah bread, which traveled with Jews expelled from Spain and likely influenced Ashkenazi cuisine?
- ... that people of the Zenú culture built canals in the La Mojana wetland area of Colombia long before Spanish arrival?
- ... that the flag of La Guaira is based on the design of a banner from a 1797 conspiracy against Spanish rule in Venezuela?
 Good article – show another
Good article – show another
-
Image 1

Legislative elections were held in Spain on 16 February 1936. At stake were all 473 seats in the unicameral Cortes Generales. The winners of the 1936 elections were the Popular Front, a left-wing coalition of the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party (PSOE), Republican Left (Spain) (IR), Esquerra Republicana de Catalunya (ERC), Republican Union (UR), Communist Party of Spain (PCE), Acció Catalana (AC), and other parties. Their coalition commanded a narrow lead over the divided opposition in terms of the popular vote, but a significant lead over the main opposition party, Spanish Confederation of the Autonomous Right (CEDA), in terms of seats. The election had been prompted by a collapse of a government led by Alejandro Lerroux, and his Radical Republican Party. Manuel Azaña would replace Manuel Portela Valladares, caretaker, as prime minister. (Full article...) -
Image 2
The siege of the Salamanca forts (17–27 June 1812) saw an 800-man Imperial French garrison directed by Lieutenant Colonel Duchemin defend three fortified convents in the city of Salamanca against the 48,000-strong Allied army led by Arthur Wellesley, Lord Wellington. During this time, the French commander Marshal Auguste de Marmont led a 40,000-man French army in an unsuccessful attempt to relieve the garrison. An Allied failure to bring sufficient artillery ammunition caused the siege to be prolonged. The garrison repulsed a premature British attempt to storm the fortified convents on 23 June, but finally surrendered four days later after an artillery bombardment breached one fort and set another one on fire. During his maneuvering, Marmont formed the idea that Wellington was only willing to act on the defensive. This mistaken notion would contribute to Marmont's defeat at the Battle of Salamanca a month later. (Full article...) -
Image 3The Es Pontàs sea arch in Mallorca; the climb goes along the inside right-hand side of the arch to its landward apex
Es Pontàs is a 20-metre (66 ft) long limestone deep-water soloing (DWS) climbing route on the Es Pontàs sea-arch in Mallorca, Spain. After it was first free soloed in September 2006 by American climber Chris Sharma, it became graded at 9a+ (5.15a) – the world's first-ever DWS route at that grade, and one of the earliest 9a+ graded rock climbs of any type in history. Es Pontàs was credited with promoting the emerging sport of DWS, and further enhancing Sharma's reputation and legacy as a pioneer in rock climbing. Sharma's first ascent was featured in the award-winning 2007 climbing film, King Lines. (Full article...) -
Image 4
The Jiloca (Spanish pronunciation: [xiˈloka]) is a river in Aragón, Spain, a tributary of the river Jalón, and part of the watershed of the Ebro basin. The course of the river runs through the provinces of Teruel and Zaragoza. It has a length of 126 kilometres (78 mi) and an average flow rate of 2.1 cubic metres per second (74 cu ft/s), although this varies between the seasons. The river flows in a generally north easterly direction from its source near Monreal del Campo. (Full article...) -
Image 5

The 2014 Spanish Grand Prix (officially the Formula 1 Gran Premio de España Pirelli 2014) was a Formula One motor race held on 11 May 2014 at the Circuit de Barcelona-Catalunya in Montmeló, Catalonia, Spain. The race was the fifth round of the 2014 Formula One World Championship, the 44th Spanish Grand Prix held as part of the championship, and the 24th in Barcelona. Mercedes driver Lewis Hamilton won the 66-lap race from pole position. His teammate Nico Rosberg finished second and Red Bull's Daniel Ricciardo took third. (Full article...) -
Image 6
Mariano Rodríguez Vázquez (1909 – 18 June 1939), popularly known by his nickname Marianet, was a Spanish anarcho-syndicalist politician who served as General Secretary of the Confederación Nacional del Trabajo (CNT) during the Spanish Civil War. (Full article...) -
Image 7

Illustration of the dreadnought España in 1912
In the latter half of the 19th century, the Spanish Navy had built a series of ironclad warships that culminated in the barbette ship Pelayo in the 1880s. Following the destruction of much of the Spanish fleet in the Spanish–American War in 1898, Spain slowly began to rebuild its navy. In the early 20th century, the Spanish Navy built three battleships and planned several more; the three ships that were completed were the vessels of the España class. These ships were the smallest dreadnought-type battleships ever built. A further three ships of the Reina Victoria Eugenia class were authorized by the Navy Law of 1913, but the outbreak of World War I prevented these ships from being built, as Spain was heavily dependent on Great Britain for material and technical expertise. The three completed battleships all served in the Rif War in North Africa, where the lead ship, España, ran aground and was wrecked. (Full article...) -
Image 8Gómez de Alvarado y Contreras (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈɡomeθ ðe alβaˈɾaðoj konˈtɾeɾas]; 1482 – September 1542) was a Spanish conquistador and explorer. He was a member of the Alvarado family and the older brother of the famous conquistador Pedro de Alvarado. (Full article...)
-
Image 9
Abel David Azcona Marcos (born 1 April 1988) is a Spanish artist, specializing in performance art. His work includes installations, sculptures, and video art. He is known as the "enfant terrible" of Spanish contemporary art. His first works dealt with personal identity, violence and the limits of pain; his later works are of a more critical, political and social nature. (Full article...) -
Image 10Near the Saaler Bodden, Germany
The grey heron (Ardea cinerea) is a long-legged wading bird of the heron family, Ardeidae, native throughout temperate Europe and Asia, and also parts of Africa. It is resident in much of its range, but some populations from the more northern parts migrate southwards in autumn. A bird of wetland areas, it can be seen around lakes, rivers, ponds, marshes and on the sea coast. It feeds mostly on aquatic creatures which it catches after standing stationary beside or in the water, or stalking its prey through the shallows. (Full article...) -
Image 11Pablo playing for Atlético Madrid in 2007
Pablo Ibáñez Tébar (born 3 August 1981), sometimes known as just Pablo, is a Spanish former professional footballer who played as a centre back. (Full article...) -
Image 12

José María Gil Tamayo (born 5 June 1957) is a Spanish prelate of the Roman Catholic Church. He has been serving as archbishop of Granada since his installation on 1 February 2023. He previously served as coadjutor archbishop of that archdiocese and as bishop of Ávila. (Full article...) -
Image 13
Clara Thalmann (née Ensner; 24 September 1908 – 27 January 1987) was a Swiss journalist, athlete and militiawoman, who fought during the Spanish Civil War. (Full article...) -
Image 14
Anarkopenya, the squatted building where the initial events took place, photographed in 2005
The 4F case concerns the events of 4 February 2006 in Barcelona, in which a policeman patrolling outside a rave was paralyzed after being hit by a falling object and nine people were arrested in consequence. At a trial two years later, seven people were convicted, one of whom was then pardoned. On appeal to the Supreme Court, the sentences were lengthened and one person committed suicide. (Full article...) -
Image 15The blockade of Orbetello, engraving by Matthäus Merian.
The Battle of Orbetello, also known as the Battle of Isola del Giglio, was a major naval engagement of the Franco-Spanish War of 1635. It was fought on 14 June 1646 off the Spanish-ruled town of Orbetello, on the coast of Tuscany, Italy, between a French fleet led by Admiral Armand de Maillé, Marquis of Brézé, and a Spanish fleet commanded by Miguel de Noronha, 4th Count of Linhares sent to break the blockade of Orbetello and relieve the town, besieged since 12 May by a French army under the command of Prince Thomas of Savoy. The Battle of Orbetello was tactically very unusual, since it was fought by sailing ships towed by galleys in a light breeze. (Full article...) -
Image 16Gasol with FC Barcelona in 2021
Pau Gasol Sáez[a] (Catalan: [ˈpaw ɣəˈzɔl], Spanish: [ˈpaw ɣaˈsol]; born July 6, 1980) is a Spanish former professional basketball player. He was a six-time NBA All-Star and a four-time All-NBA team selection, twice on the second team and twice on the third team. Gasol won two NBA championships, both with the Los Angeles Lakers back-to-back in 2009 and 2010. He was the NBA Rookie of the Year in 2002 with the Memphis Grizzlies, being the first non-American player to have won that award. He is regarded as one of the greatest power forwards of all time and is also considered as one of the greatest European players of all time. He is the older brother of former NBA player Marc Gasol. (Full article...) -
Image 17

The 2008 Spanish Grand Prix (formally the Formula 1 Gran Premio de España Telefónica 2008) was a Formula One motor race held on 27 April 2008 at the Circuit de Catalunya, Montmeló, Spain. It was the fourth race of the 2008 Formula One World Championship. Kimi Räikkönen for the Ferrari team won the 66-lap race starting from pole position. Felipe Massa finished second in the other Ferrari, and Lewis Hamilton was third in a McLaren. (Full article...) -
Image 18"Te Lo Agradezco, Pero No" (English: "I thank you, but no") is a song recorded by Spanish singer Alejandro Sanz and Colombian singer Shakira, for Sanz's eighth studio album El Tren de los Momentos (2006). It was released as the second single from the record in December 2006 by Warner Music Latina. The track was written by Sanz, while production was handled by him along with Lulo Pérez. "Te Lo Agradezco, Pero No" is the second duet recorded by the two singers, following "La Tortura" for Shakira's album Fijación Oral Vol. 1 (2005). The song came about after she approached Sanz, telling him that she wanted to collaborate on something different from her own material. (Full article...)
-
Image 19The action of 26 April 1797 was a minor naval engagement during the French Revolutionary Wars in which a Spanish convoy of two frigates was trapped and defeated off the Spanish town of Conil de la Frontera by British ships of the Cadiz blockade. The British vessels, the ship of the line HMS Irresistible and the Fifth-rate frigate HMS Emerald, were significantly more powerful than the Spanish frigates, which were on the last stage of a voyage carrying treasure from Havana, Cuba, to the Spanish fleet base of Cadiz. (Full article...)
-
Image 20
Jaime I was a Spanish dreadnought battleship, the third and final member of the España class, which included two other ships: España and Alfonso XIII. Named after King James I of Aragon, Jaime I was built in the early 1910s, though her completion was delayed until 1921 owing to a shortage of materials that resulted from the start of World War I in 1914. The class was ordered as part of a naval construction program to rebuild the fleet after the losses of the Spanish–American War in the context of closer Spanish relations with Britain and France. The ships were armed with a main battery of eight 305 mm (12 in) guns and were intended to support the French Navy in the event of a major European war. (Full article...) -
Image 21
Ramón Iribarren Cavanilles Ing.D (15 April 1900 – 21 February 1967) was a Spanish civil engineer and professor of ports at the School of Civil Engineering (Spanish: Escuela Técnica Superior de Ingenieros de Caminos, Canales y Puertos, ETSICCP) in Madrid. He was chairman of the Spanish delegation to the Permanent International Association of Navigation Congresses (PIANC) and was elected as an academic at the Spanish Royal Academy of Sciences, although he did not take up the latter position. He made notable contributions in the field of coastal engineering, including methods for the calculation of breakwater stability and research which led to the development of the Iribarren number. (Full article...) -
Image 22
Queen Anne's War (1702–1713) was the second in a series of French and Indian Wars fought in North America involving the colonial empires of Great Britain, France, and Spain; it took place during the reign of Anne, Queen of Great Britain. In the United States, it is regarded as a standalone conflict under this name. Elsewhere it is usually viewed as the American theater of the War of the Spanish Succession. It is also known as the Third Indian War. In France it was known as the Second Intercolonial War. (Full article...) -
Image 23

The Spanish conquest of Honduras was a 16th-century conflict during the Spanish colonization of the Americas in which the territory that now comprises the Republic of Honduras, one of the seven states of Central America, was incorporated into the Spanish Empire. In 1502, the territory was claimed for the king of Spain by Christopher Columbus on his fourth and final trip to the New World. The territory that now comprises Honduras was inhabited by a mix of indigenous peoples straddling a transitional cultural zone between Mesoamerica to the northwest, and the Intermediate Area to the southeast. Indigenous groups included Maya, Lenca, Pech, Miskitu, Mayangna (Sumu), Jicaque, Pipil and Chorotega. Two indigenous leaders are particularly notable for their resistance against the Spanish; the Maya leader Sicumba, and the Lenca ruler referred to as Lempira (a title meaning "Lord of the Mountain"). (Full article...) -
Image 24The moonlight Battle off Cape St Vincent, 16 January 1780, Francis Holman
The Battle of Cape St. Vincent (Spanish: Batalla del Cabo de San Vicente) was a naval battle that took place off the southern coast of Portugal on 16 January 1780 during the American Revolutionary War. A British fleet under Admiral Sir George Rodney defeated a Spanish squadron under Don Juan de Lángara. The battle is sometimes referred to as the Moonlight Battle (batalla a la luz de la luna) because it was unusual for naval battles in the Age of Sail to take place at night. It was also the first major naval victory for the British over their European enemies in the war and proved the value of copper-sheathing the hulls of warships. (Full article...) -
Image 25Patricio Arabolaza in front of Eduardo Teus' goal during the match
The 1918 Copa del Rey Final was an association football match between Real Unión and Madrid FC on 12 May 1918, at the O'Donnell Stadium in Madrid. It was the deciding match of the Spanish cup competition, the Copa del Rey. Real Unión beat Madrid FC 2–0 to win their first title. Unión's captain, forward Juan Legarreta, scored both goals. The final was attended by approximately 10,000 spectators. (Full article...)
General images
-
Image 1The Conquest of Tenochtitlán (from History of Spain)
-
Image 2Plaza Mayor with the Casa de la Panadería to the left (from Spanish Golden Age)
-
Image 4The Port of Seville in the late 16th century. Seville became one of the most populous and cosmopolitan European cities after the expeditions to the New World. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 8Ethnology of the Iberian Peninsula c. 200 BC (from History of Spain)
-
Image 9Francisco Franco and his appointed successor Prince Juan Carlos de Borbón. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 101894 satirical cartoon depicting the tacit accord for seamless government change (turnismo) between the leaders of two dynastic parties (Sagasta and Cánovas del Castillo), with the country being lied in an allegorical fashion. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 14Episode of the 1854 Spanish Revolution in the Puerta del Sol, by Eugenio Lucas Velázquez. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 16Cabeza de Luis Buñuel, sculptor's work by Iñaki, in the center Buñuel Calanda. (from Culture of Spain)
-
Image 20In ictu oculi ("In the blink of an eye"), a vanitas by Juan de Valdés Leal (from Spanish Golden Age)
-
Image 21Recognition of the Duke of Anjou as King of Spain, under the name of Philip V, November 16, 1700 (from History of Spain)
-
Image 23Visigothic church, San Pedro de la Nave. Zamora. Spain (from History of Spain)
-
Image 24Visigothic King Roderic haranguing his troops before the Battle of Guadalete (from History of Spain)
-
Image 25The promulgation of the Constitution of 1812, oil painting by Salvador Viniegra. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 27Two women and a man during the siege of the Alcázar (from History of Spain)
-
Image 29Wedding portrait of the Catholic Monarchs (from History of Spain)
-
Image 30Visigothic Hispania and its regional divisions in 700, prior to the Muslim conquest (from History of Spain)
-
Image 31Map of territories that were once part of the Spanish Empire (from History of Spain)
-
Image 32Illustration depicting the (now lost) Luzaga's Bronze, an example of the Celtiberian script. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 36The title page of the Gramática de la lengua castellana (1492), the first grammar of a modern European language to be published. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 37Las Meninas (1656, English: The Maids of Honour) by Diego Velázquez (from Spanish Golden Age)
-
Image 38Execution of Torrijos and his men in 1831. Ferdinand VII took repressive measures against the liberal forces in his country. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 39Charles I of Spain (better known in the English-speaking world as the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V) was the most powerful European monarch of his day. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 43People's militias attacking on a Rebel position in Somosierra in the early stages of the war. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 44Detail of the votive crown of Recceswinth from the Treasure of Guarrazar, (Toledo-Spain) hanging in Madrid. The hanging letters spell [R]ECCESVINTHVS REX OFFERET [King R. offers this]. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 45The pro-independence forces delivered a crushing defeat to the royalists and secured the independence of Peru in the 1824 battle of Ayacucho. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 48The realms of Philip II of SpainTerritories administered by the Council of CastileTerritories administered by the Council of AragonTerritories administered by the Council of PortugalTerritories administered by the Council of ItalyTerritories administered by the Council of the IndiesTerritories appointed to the Council of Flanders(from Spanish Golden Age)
-
Image 49Felipe González signing the treaty of accession to the European Economic Community on 12 June 1985. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 50The explosion of the USS Maine launched the Spanish–American War in April 1898 (from History of Spain)
-
Image 51The greatest extent of the Visigothic Kingdom of Toulouse, c. 500, showing Territory lost after Vouillé in light orange (from History of Spain)
-
Image 52The Christian kingdoms of Hispania and the Islamic Almohad empire c. 1210
-
Image 55Members of the provisional government after the 1868 Glorious Revolution, by Jean Laurent. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 56The Second of May 1808 was the beginning of the popular Spanish resistance against Napoleon. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 58Proclamation of the Spanish Republic in Madrid (from History of Spain)
-
Image 60El paseo de las Delicias, a 1784–1785 painting by Ramón Bayeu depicting a meeting of members of the aristocracy in the aforementioned location. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 61Panoramic view of the lower level patio of the Palace (from Spanish Golden Age)
-
Image 64Celebrations of the proclamation of the 2nd Republic in Barcelona. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 65The successful 1925 Alhucemas landing turned the luck in the Rif War towards Spain's favour. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 66The Iberian Peninsula in the 3rd century BC (from History of Spain)
-
Image 67Louis XIV of France and Philip IV of Spain at the Meeting on the Isle of Pheasants in June 1660, part of the process to put an end to the Franco-Spanish War (1635–59). (from History of Spain)
-
Image 70Christopher Columbus leads expedition to the New World, 1492, sponsored by Spanish crown (from History of Spain)
In the news
- 13 November 2024 – 2024 Spanish floods
- Thousands of Spaniards living near river banks are evacuated following the issuing of AEMET's maximum weather alert in the Province of Málaga, Costa del Sol, and the Valencian Community caused by a new cold drop system. (The Independent)
- 12 November 2024 –
- Spanish writer Álvaro Pombo wins the Miguel de Cervantes Prize. (El País)
- 11 November 2024 – 2024 European floods
- 2024 Spanish floods
- Prime Minister of Spain Pedro Sánchez announces an additional €3.76 billion (US$4 billion) aid package to the Valencian Community which was affected by deadly floods in October. (DW)
No recent news
Spain topics
Categories
WikiProjects
- Main project
- Related projects
WikiProject Basque • WikiProject Catalan-speaking Countries • WikiProject Galicia • Spanish Translation of the Week
Things you can do

- Add {{WikiProject Spain}} to article talk pages which have some relation to Spain
- Help write new Spain-related articles and improve and expand existent ones
- Assess: unassessed Spain-related articles
- Suggest: selected articles, biographies, pictures, did you knows? and quotes for this Portal
Related portals
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
- ^ In this Spanish name, the first or paternal surname is Gasol and the second or maternal family name is Sáez.
- ^ "Atlantic hurricane best track (HURDAT version 2)" (Database). United States National Hurricane Center. April 5, 2023. Retrieved November 14, 2024.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- Pages with Greek IPA
- Pages with Spanish IPA
- Pages with Catalan IPA
- Portals with triaged subpages from June 2018
- All portals with triaged subpages
- Portals with no named maintainer
- Automated article-slideshow portals with 41–50 articles in article list
- Random portal component with 6–10 available subpages
- Automated article-slideshow portals with 101–200 articles in article list







































































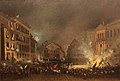



























![Image 44Detail of the votive crown of Recceswinth from the Treasure of Guarrazar, (Toledo-Spain) hanging in Madrid. The hanging letters spell [R]ECCESVINTHVS REX OFFERET [King R. offers this]. (from History of Spain)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/f2/Corona_de_%2829049230050%29.jpg/57px-Corona_de_%2829049230050%29.jpg)