Omanis
 | |
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| c. 2.67 million | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| 2,024[2] | |
| 390[2] | |
| 260[2] | |
| 149[3] | |
| 148[2] | |
| 24[2] | |
| Languages | |
| Omani Arabic (majority) · Standard Arabic · Mehri · Balochi · Swahili · Zadgali · Kumzari · Luri · Luwati · Persian · Urdu · Harsusi · Bathari · Dhofari Arabic · Shihhi Arabic · | |
| Religion | |
| Predominantly : Ibadi Islam, Sunni Islam | |
Omanis (Arabic: الشعب العماني) are the nationals of Sultanate of Oman, located in the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula. Omanis have inhabited the territory that is now Oman. In the eighteenth century, an alliance of traders and rulers transformed Muscat (Oman's capital) into the leading port of the Persian Gulf. Omani people are ethnically diverse; the Omani citizen population consists of many different ethnic groups. The majority of the population consists of Arabs, with many of these Arabs being Swahili language speakers and returnees from the Swahili Coast, particularly Zanzibar.
Additionally, there are ethnic Lurs, Persians and Mehri. There are also Omanis from South Asia like the Lawatis, Zadjalis and others.[4][5] Moreover, in Dhofar, Sur and Muscat, Afro-Omanis can be found. They are the descendants of the slaves who were brought from Africa centuries ago.[6]
Omani citizens make up the majority of Oman's total population. Over one and a half million other Omanis live in other areas of the Middle East and the Swahili Coast. In 2023, an estimated percentage of 47.2% of Omani Muslims were Sunni Muslims and 35.2% were Ibadi Muslims while only 6.5% were Shia Muslims.[7]
History
[edit]Omani presence in the Swahili Coast can be traced since the Nabhani dynasty.[8] In the late seventeenth century, Zanzibar became part of the overseas holdings of Oman after Saif bin Sultan, the imam of Oman, defeated the Portuguese in Mombasa, in what is now Kenya.[9]
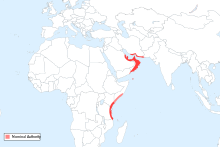
Large numbers of Omanis settled in the Swahili Coast — especially after 1832, when the Omani Sultan Said bin Sultan moved his court to Zanzibar. To the Omanis, the region became a land of economic opportunity.
Omanis who migrated to the Swahili Coast looked forward to a better life. The Omani community in the Swahili Coast grew and became financially successful.[10] Omanis stopped moving to Zanzibar after a revolution occurred in Zanzibar in 1964. The Omani descendant, sultan of Zanzibar, Sultan Jamshid bin Abdullah was overthrown, and thousands of Omanis were killed, among many other Arabs.[11] Soon after the revolution, many Omanis fled Zanzibar to avoid persecution and returned to their ancestral homeland in Oman, but others chose to remain on the Swahili Coast.
Gwadar, a region of Balochistan in Pakistan, was a Colony of Oman for more than a century and in the 1960s, Pakistan gained the land. Hence, many people in this region are Omani.[12] Around 20% of Omanis are of Baloch descent whose ancestors migrated to Oman centuries ago, and are now considered native.[13] With an additional 15% expatriate population,[14] the figure rises to 35%.[15]
Notable Omanis
[edit]
- Qaboos bin Said al Said, the Sultan of Oman from 1970 to 2020.
- Talal bin Suleiman Al Rahbi, economist and diplomat.
- Mohammed Al Rumhi, Oman's Minister of Oil and Gas.
- Haifa Al Khaifi, Interim CEO - Energy Development Oman SAOC & Finance Director - Petroleum Development Oman LLC.
- Ahmad Al Harthy, Oman's top racing driver and a leading international sportsman.
- Samira bint Mohamed Al-Moosa, Oman's ambassador and permanent delegate to UNESCO.
- Ali Al Habsi, Oman and Reading F.C. footballer
- Ahmed bin Hamad al-Khalili, grand mufti of Oman.
- Mohammed Al Barwani, billionaire and the richest man in Oman.
- Madeeha bint Ahmed bin Nassir al Shibaniyah, the Minister of Education Oman.
- Mubarak Al-Saadi, footballer
- Tariq Al Sadi, footballer
- Yusuf bin Alawi bin Abdullah, Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
- Rawya Saud Al Busaidi, Minister of Higher Education.
- Sultan bin Mohammed al Nu'amani, Minister of Royal Office.
- Ahmed Al-Harrasi, is an Omani scientist and a professor of organic chemistry at University of Nizwa.
- Jokha Al-Harthi, Omani writer
See also
[edit]References and notes
[edit]- ^ "Monthly Statistical Bulletin: October 2019" (PDF). www.ncsi.gov.om. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 October 2019. Retrieved 21 October 2019.
- ^ a b c d e "Country-of-birth database". Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. Archived from the original on 2009-06-17. Retrieved 2008-09-21.
- ^ Immigrants in Brazil (2024, in Portuguese)
- ^ "Oman's Diverse Society: Northern Oman" (PDF). JE Peterson.
- ^ "Oman's players of Pakistan origin caught in visa mix-up". 25 February 2016.
- ^ Valeri, Marc (2009). Oman: Politics and Society in the Qaboos State. Hurst. ISBN 978-1-85065-933-4.
- ^ "Oman - The World Factbook". www.cia.gov. Retrieved 2021-05-18.
- ^ Nabhan, Gary Paul (2008). Arab/American: Landscape, Culture, and Cuisine in Two Great Deserts. The University of Arizona Press. p. 78. ISBN 978-0-8165-2658-1. Retrieved 29 January 2015.
- ^ Thomas, Gavin (Nov 1, 2011). The Rough Guide to Oman. Penguin. ISBN 978-1-4053-8935-8.
- ^ "The Omani Ascendancy". britannica.com/. Retrieved 29 January 2015.
- ^ "Regime Banishes Sultan". The New York Times. 1964-01-14.
- ^ "Arab legacy lingers as Pakistan's Gwadar grows from tiny fishing town into port city | Arab News".
- ^ Long, Roger D.; Singh, Gurharpal; Samad, Yunas; Talbot, Ian (2015-10-08). State and Nation-Building in Pakistan: Beyond Islam and Security. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-317-44820-4.
- ^ "Oman". The Encyclopaedia Britannica.
- ^ "Harnessing the GCC's Baloch pedigree". The Express Tribune.
