International Organisation of Vine and Wine
Organisation Internationale de la vigne et du vin | |
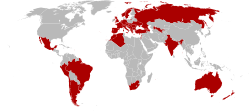 Member states as of 2011 | |
| Abbreviation | OIV |
|---|---|
| Predecessor | International Vine and Wine Office |
| Formation | January 1, 2004 |
| Type | Intergovernmental organisation |
| Headquarters | Hôtel Bouchu dit d'Esterno, 1 rue Monge, Dijon, France |
| Fields | Winemaking, viticulture |
Membership | 50 states |
Official languages |
|
Director General | Dr. John Barker |
Main organ | OIV General Assembly |
| Website | www |
The International Organisation of Vine and Wine (French: Organisation Internationale de la vigne et du vin; OIV) is an intergovernmental organization which deals with technical and scientific aspects of viticulture and winemaking.[1] The field of OIV includes grape production for all purposes, i.e. not just wine, but also table grapes and raisin production.
OIV is the compilation of global statistics within its field. One of the main responsibilities for OIV is to establish and maintain standards for the Vine and Wine industry.[2]
OIV is based in Dijon, and had 49 member states as of 2022.[3][4]
History
[edit]The earliest forerunners of the OIV are the international conferences held as a reaction to the 19th century phylloxera epidemic, with the five-nation Montpellier Congress held between 26 and 30 October 1874 being the foremost among these.[5] The idea of an international organization came up several times during the coming decades, and finally, on 29 November 1924, eight nations signed an agreement concerned with the creation of an International Wine Office (Office international du vin, OIV) in Paris. After that the agreement went back to nations for ratification. The first working session was held at Salon de l’Horloge on 3 December 1927. On 4 September 1958, the organization's name was changed to the International Vine and Wine Office (Office International de la Vigne et du Vin).
The current International Organisation of Vine and Wine was established following a 35-nation agreement on 3 April 2001, and replaced the International Vine and Wine Office. This agreement went into effect on 1 January 2004.[4]
Member states
[edit] Albania
Albania Algeria
Algeria Argentina
Argentina Armenia
Armenia Australia
Australia Austria
Austria Brazil
Brazil China
China Israel
Israel Italy
Italy Lebanon
Lebanon Luxemburg
Luxemburg North Macedonia
North Macedonia Malta
Malta Mexico
Mexico Moldova
Moldova Montenegro
Montenegro Morocco
Morocco Netherlands
Netherlands New Zealand
New Zealand Norway
Norway Peru
Peru Portugal
Portugal Romania
Romania Russia
Russia Serbia
Serbia Slovakia
Slovakia Slovenia
Slovenia South Africa
South Africa Spain
Spain Sweden
Sweden Switzerland
Switzerland Turkey
Turkey Ukraine[3][6]
Ukraine[3][6] Uruguay
Uruguay Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan United Kingdom
United Kingdom
Structure
[edit]The OIV organizational structure consists of a General Assembly, Executive Committee, Steering Committee, OIV Scientific and Technical Committee, Director General and General secretariat[7] The many committees of the OIV ensures a collaborative organization.
The General Assembly is established as a legislative body that is in charge of validating the procedures and policies of other committees. This is done by a consensus voting process. The representatives and observers of the General Assembly are chosen by the member states. The General Assembly meets twice a year[8]
The Executive Committee serves as an advising body to the General Assembly as well as observing the scientific and technical process and the policies thereof[8] This is meant to ensure that the OIV is being held to the established standards.
Establishment of Standards within the OIV
[edit]The main function of the OIV is to establish and maintain the standards of the Vine and Wine industry. The standards established serve as a recommendation for the organizations member countries and to ensure transparency to consumers. For the purpose of easing international trade of products multiple identifying factors must be present. These include, but are not limited to, geographical indication, alcohol strength, net content and country of origin[9]
Geographical Indication (GI) refers to factors that is identifiable to the specific area of which it is produced. In order to maintain a standard of authenticity there are regulations in place depending on which product is being produced. Wine needs to meet a goal of at least 85% grapes from the region classified on the label. Spirits must have all the production located in the area which is assigned on the label[10]
The International Organization of Vine and Wine also provides these standardized methods to assess the color of a wine using a spectrophotometer and the calculation of indices in the Lab color space.[11]
Resolutions
[edit]In 2013, the OIV took a resolution which "recommends obtaining and developing new cultivars which carry multiple resistance loci [...] to lower the risk of selection and of development of more aggressive pathogen strains", especially for downy and powdery mildew.[12]
References
[edit]- ^ OIV - Presentation Archived 2016-01-28 at the Wayback Machine, accessed on March 3, 2009
- ^ "International Organisation of Vine and Wine (OIV) – Ministero degli Affari Esteri e della Cooperazione Internazionale". www.esteri.it. Retrieved 2024-10-14.
- ^ a b "Ukraine, new OIV Member State". International Organisation of Vine and Wine. 2022-10-27. Retrieved 2022-10-29.
- ^ a b OIV members Archived 2015-09-24 at the Wayback Machine, accessed on December 1st, 2011
- ^ OIV - Background Archived 2016-01-29 at the Wayback Machine, accessed on March 3, 2009
- ^ "Після 14-річної перерви Україна повертається до Міжнародної організації виноробства". Економічна правда (in Ukrainian). 2022-10-27. Retrieved 2022-10-27.
- ^ "Structure | OIV". www.oiv.int. Retrieved 2024-10-31.
- ^ a b "Structure | OIV". www.oiv.int. Retrieved 2024-10-31.
- ^ "Standards and Technical Documents | OIV". www.oiv.int. Retrieved 2024-10-16.
- ^ "Standards and Technical Documents | OIV". www.oiv.int. Retrieved 2024-10-16.
- ^ CIELab Color Space Archived 2011-06-08 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Federico Castelluci, General Director of the OIV, Secretary of the General Assembly (2013-06-07). "Resolution OIV-VITI 515-2013: Stability of disease resistance in new cultivars by combining resistance loci" (PDF). oiv.int/. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-10-25. Retrieved 2014-10-25.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
