Nationalisation of Northern Rock

In 2008 the Northern Rock bank was nationalised by the British government, due to financial problems caused by the subprime mortgage crisis. In 2010 the bank was split into two parts (assets and banking) to aid the eventual sale of the bank back to the private sector.
On 14 September 2007, the bank sought and received a liquidity support facility from the Bank of England,[1] as a result of its exposure in the credit markets, during the 2008 financial crisis.[2][3] On 22 February 2008 the bank was taken into state ownership. The nationalisation followed two unsuccessful bids to take over the bank, neither being able to fully commit to repayment of savers' and investors' money.[4][5]
In 2012 Virgin Money completed the purchase of Northern Rock from UK Financial Investments (UKFI) for approximately £1 billion and by October of that year the high street bank operated under the Virgin Money brand.[6][7][8]
2007 credit crisis
[edit]Emergence
[edit]
On 12 September 2007, Northern Rock asked the Bank of England, as lender of last resort in the United Kingdom, for a liquidity support facility due to problems in raising funds in the money market to replace maturing money market borrowings.[9] The problems arose from difficulties banks faced over the summer of 2007 in raising funds in the money market. Despite Northern Rock appearing to be in a stronger position than other UK banks on paper,[10] it faced a liquidity problem because institutional lenders became nervous about lending to mortgage banks following the US sub-prime crisis.[11] Bank of England figures suggest that Northern Rock borrowed £3 billion from the Bank of England in the first few days of this crisis.[12]
Government intervention
[edit]With shares in Northern Rock plummeting by nearly a third, the British Government moved to reassure investors with the bank, with account holders urged not to worry about the bank going bust. The Treasury select committee chairman John McFall MP said: "I don't think customers of Northern Rock should be worried about their current accounts or mortgages."[13]
Northern Rock was not the only British bank to have called on the Bank of England for funds since the sub-prime crisis began[14] but is the only one to have had emergency financial support from the Tripartite Authority (The Bank of England, the FSA and HM Treasury).[15] However, the bank was more vulnerable to a credit crunch as its 'high risk'[16] business model depended on funding from the wholesale credit markets, 75% of its funds coming from this source.[17] In his address to the Treasury Select Committee, Bank of England governor Mervyn King had stated emergency funds would be made available to any British bank that needed it, but at a penalty rate, to ensure that lenders who had made bad lending decisions would suffer relative to lenders who had made sensible lending decisions.[18]
In December, the EU regulators approved Britain's actions to provide aid to the bank by concluding that it was in line with European emergency aid rules.[19]
Run on the bank
[edit]
On Friday 14 September 2007, the first day branches opened following the news, many customers queued outside branches to withdraw their savings (a run on the bank).[20] This bank run was not the traditional form, where depositors withdraw money in a snowball effect, leading to a liquidity crisis; instead, it occurred in the aftermath of the liquidity crisis.[21] It was estimated that £1 billion was withdrawn by customers that day, about 5% of the total bank deposits held by Northern Rock.[22]
On Monday 17 September, as worried savers continued to flock to some Northern Rock bank branches to withdraw their savings, it was reported that an estimated £2 billion had been withdrawn since the bank applied to the Bank of England for emergency funds. By early afternoon in London, Northern Rock's shares, which had lost 32% on the previous Friday, fell a further 40% from 438 pence to 263 pence.[23]
Later that day, the Chancellor of the Exchequer, Alistair Darling, announced that the British Government and the Bank of England would guarantee all deposits held at Northern Rock.[24] Northern Rock shares rose by 16% after this was announced.
Stabilisation
[edit]The announcement by the chancellor showed its intended effects the next day, as the queues outside Northern Rock's branches gradually disappeared. In addition, Northern Rock had a series of advertisements published in major UK newspapers to reaffirm that their customers' money was safe.[25]
In an interview on BBC Radio 4, Bank of England governor Mervyn King revealed that they had anticipated emergency funding to be in the £20–30bn range.[26]
What we want to do is to give incentives for people to behave properly, so in judging the interest rate at which we lent to Northern Rock we asked ourselves the question: "At what interest rate would they have to pay in borrowing from us today that would make them regret not having taken out an insurance policy as Countrywide did before the 9th of August?"
— Bank of England governor, Mervyn King, BBC Radio 4 – File on 4
Boardroom changes
[edit]Matt Ridley was forced to resign as chairman in 2007, having been blamed in parliamentary committee hearings for not recognising the risks of the bank's financial strategy and thereby "harming the reputation of the British banking industry".[27]
John Devaney and Simon Laffin joined the board in November 2007, when Sir Derek Wanless, Nichola Pease, Adam Fenwick and Rosemary Radcliffe retired as non-executive directors. The chief executive, Adam Applegarth, stayed on in a caretaker role until December 2007. David Baker and Keith Currie left the board, but remained employed within the company. Currie later took early retirement with a bonus package reportedly worth £2.5 million, and in 2012, aged 56, was found dead at his home.[28]
The chief executive after the departure of Applegarth was Andy Kuipers, who joined the company in 1987, and later left on 31 August 2008.[29]
Growth of Bank of England loan
[edit]By January 2008, Northern Rock's loan from the Bank of England had grown to £26bn. On 11 January, Northern Rock announced that it had sold its portfolio of lifetime home equity release mortgages to JP Morgan for £2.2bn and that it would use this to pay off a piece of the Bank of England loan.[30][31]
On 6 February, the Office for National Statistics announced that it was treating Northern Rock as a public corporation, similar to the BBC and Royal Mail for accounting purposes, causing the loans (approximately £25 billion) and guarantees (approximately £30 billion) extended by the Bank of England and the value of the company's mortgage book (approximately £55 billion), provisionally estimated to total around £100 billion, to be added to the National Debt.[32] Although not technically a nationalisation, the decision effectively acknowledged that "In all but name, Northern Rock is now nationalised".[33]
The addition of this borrowing to the government's totals increased the National Debt from £537 billion, or 37.7% of GDP to around 45%,[32] breaking the so-called Golden Rule which sets the Public Sector Borrowing Requirement threshold at below 40%. The figure is the equivalent of £3,000 additional borrowing for every family in Britain.[34] In the 2008 Budget, the Chancellor of the Exchequer announced that the government would issue £14 billion of gilts in order to cover the Northern Rock debt.[35]
Handling of the crisis
[edit]On 26 March the Financial Services Authority released an internal report into the failings over handling the problems at Northern Rock. "They found that their supervision of the bank had not been carried out to a standard that is acceptable". The previous FSA review had taken place in February 2006.[36] In the light of these failings at Northern Rock, the FSA announced that they would overhaul their own staffing and systems.[37] The FSA internal report also concluded that ultimately the blame for the collapse of Northern Rock should sit at the feet of the bank's senior management. "The boards and managements of regulated firms carry the primary responsibility for ensuring their institutions' financial soundness," the FSA said. The British Bankers' Association (BBA), the UK banking body, agreed.[38]
In May 2009 the Financial Times reported that banking regulators had been examining "war games" as early as 2004, which dealt with possible turmoil in the mortgage markets. HBOS and Northern Rock are thought to have featured in these predictions.[39]
Commencing in October 2007, the All Party Commons Treasury Select Committee undertook a report into the failure of Northern Rock. The committee held several televised meetings, in which they called witnesses from the former Board of Northern Rock, the Bank of England, the Treasury, and the regulatory bodies. The report was detailed, and concluded:
"The [former] directors of Northern Rock were the principal authors of the difficulties that the company has faced since August 2007. It is right that members of the Board of Northern Rock have been replaced, though haphazardly, since the company became dependent on liquidity support from the Bank of England. The high-risk, reckless business strategy of Northern Rock, with its reliance on short- and medium-term wholesale funding and an absence of sufficient insurance and a failure to arrange standby facility or cover that risk, meant that it was unable to cope with the liquidity pressures placed upon it by the freezing of international capital markets in August 2007. Given that the formulation of that strategy was a fundamental role of the Board of Northern Rock, overseen by some directors who had been there since its demutualisation, the failure of that strategy must also be attributed to the Board. The non-executive members of the Board, and in particular the Chairman of the Board, the Chairman of the Risk Committee and the senior non-executive director, failed in the case of Northern Rock to ensure that it remained liquid as well as solvent, to provide against the risks that it was taking and to act as an effective restraining force on the strategy of the executive members."[40]
Financial performance
[edit]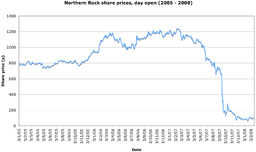
Prior to the subprime mortgage crisis the bank was part of the FTSE 100 Index, but was demoted back to the FTSE 250 in December 2007.[41] The shares were later delisted.
On 31 March the bank released its annual report for 2007, it showed a loss of £167 million. The former boss, Adam Applegarth received a £760,000 (£63,333 a month) payoff.[42] The report also outlined further details of their proposed business plan.[43]
On 5 August the bank announced that it had made a loss of £585.4m for the first 6 months of the year and that £9.4bn of a loan from the Bank of England had been paid back, reducing the amount owed to £17.5bn.[44]
Takeover offers
[edit]Virgin
[edit]On 12 October 2007, Virgin Group announced that it intended to bid for Northern Rock as the lead partner in a coalition including American giant AIG, turnaround specialist WL Ross and First Eastern Investment. Had the deal been successful, Northern Rock would have been integrated into Virgin Money as Virgin Bank.[45][46]
It is unclear what role partners would have had in the deal. This bid was later approved by HM Treasury and had been noted as the preferred option.[47] Virgin announced that Peter McNamara, a former Alliance & Leicester managing director, would be responsible for risk management at Northern Rock if its bid succeeds.[48]
Other bidders
[edit]The other front-runner was an investment company Olivant, headed by the former chief executive of Abbey, Luqman Arnold.[49] Olivant would have kept the Northern Rock brand.[50] By 17 November, a total of ten companies had put forward proposals for the bank. Among the other suitors for Northern Rock were private equity firm Cerberus,[51] JC Flowers[52] and Lloyds TSB.[53] In early December JC Flowers dropped out of the bidding.[54]
Bids rejection
[edit]Northern Rock announced that all offers had been "materially below" the previous trading value. Alistair Darling said on 19 November that the Government would have to approve or veto any sale, in the interests of taxpayers, depositors and wider financial stability.[55]
Possible nationalisation
[edit]In December the government prepared emergency legislation to nationalise the bank, in the event that the takeover bids fail.[56] On 12 January 2008, the Treasury recruited Ron Sandler, the former Lloyd's of London Chief Executive, to lead Northern Rock, in the event that the bank was nationalised.[57] If the bank was to be temporarily nationalised, the government would manage the bank at "arm's length" on a commercial basis, where services for savers and borrowers would not be affected and the company would continue to operate as normal. However nationalisation would also address the future of the Northern Rock Foundation.[58] Alistair Darling rejected the possibility of the bank being put into administration.
In-house proposal
[edit]On 15 December, Northern Rock hired the bank Goldman Sachs to put together a financing package, to assemble backers and present proposals to its board. This package would be available to any potential bidder for the bank.[59] The in-house bid was led by Paul Thompson and Andy Kuipers.
Final bids
[edit]The deadline for bids was 4 February 2008, where final bids were expected from Virgin, Olivant and the bank's management; other bidders could still have expressed interest. Goldman Sachs were likely to contact Cerberus and JC Flowers to see if they would like to rejoin the bidding, since the situation had materially changed.[60] Once a successful proposal had been chosen, it would be put to the European Commission by 17 March, which would consider whether it conformed to EU state aid rules.[61] Olivant pulled out of the bidding (but stated that they might still attempt a rescue bid if the Government changed their conditions)[62] on 4 February, leaving just the Virgin bid and the in-house bid.[63]
For repayment of the Government loans, there was a proposal to create an 'asset pool' at the bank, of a size greater than the loans. The bidder would have issued bonds against this asset pool, with maturities set inline with the repayment. Proceeds from the bond issue would have also gone to the Government and the bank would have paid for a government guarantee for the bonds to trade in the market at or near prices of similar gilt-edged stocks.[61] This would have replaced the original plan for the bidders to have to find their own investors to cover the first £15bn, which proved impossible, due to the credit crunch.[64] The government would also continue to guarantee the bank's liabilities, such as savers' deposits.[61]
Nationalisation
[edit]
On 17 February 2008, Alistair Darling, the Chancellor of the Exchequer, announced that Northern Rock was to be nationalised[4] claiming that the private bids did not offer "sufficient value for money to the taxpayer" and thus the bank was to be brought under a "temporary period of public ownership".[65][66]
The government is the sole shareholder through UK Financial Investments, and the bank is managed at "arm's length" on a commercial basis by an independent board under Ron Sandler. Customers are not affected by this change.
A Government-appointed arbitration panel will decide on a fair price for the compensation to be offered to investors for their shares.[67] Prior to the markets opening on 18 February, trading in Northern Rock's ordinary and preference shares on the London Stock Exchange was suspended.[68] The legal authorisation for the nationalisation is the Banking (Special Provisions) Act 2008, which also allows for the nationalisation of other banks if necessary.[69] At 00:01 on 22 February Northern Rock was formally nationalised.
In November 2008 the government set up a new company, UK Financial Investments, to manage their shareholdings in Northern Rock and Bradford & Bingley.[70] On 10 March 2009 the Office of Fair Trading published their report on the impacts of public support for Northern Rock on competition in financial services. The OFT concluded that "public support for Northern Rock did not, during that period, have a significantly adverse impact on competition."[71]
Boardroom changes
[edit]In February 2008, Ron Sandler was appointed executive chairman by the government. Bryan Sanderson, Sir Ian Gibson, David Jones and Paul Thompson resigned from the board at this time.[72] Gary Hoffman became chief executive of Northern Rock in October 2008. He has previously been the vice chairman of Barclays and a former managing director of Barclaycard.[73] With the appointment of Gary Hoffman, Ron Sandler changed to a non-executive chairman position.[74] On 4 November 2010 Hoffman left the bank to move to NBNK Investments; Sandler reverted to his executive chairman position.
In October 2008, the post-nationalisation management of Northern Rock decided not to bring legal action for negligence against the directors in charge during the crisis, including former chief executive Adam Applegarth, citing insufficient grounds to do so. There will be no action either against the auditors, PricewaterhouseCoopers.[75]
In January 2009 it was announced that Ann Godbehere would be leaving her post as chief financial officer at the end of February.[76]
Some former directors of the bank have been fined and banned by the FSA including former deputy chief executive David Baker £504,000 for misreporting mortgage arrears data and former credit director Richard Barclay was fined £140,000 for failing to ensure accurate financial information.[77] In April finance director David Jones quit the bank after reports that the FSA were to further investigate the activities at the bank prior to the nationalisation.[78] In July Jones was fined and banned by the FSA.[79]
Offshore mortgage book
[edit]It has subsequently become known that the best book of Northern Rock's mortgage business, comprising mortgages worth £47 billion – some 40% of the company's assets – had been transferred to a Channel Islands based company called Granite, together with an ongoing obligation to continue to supply business. Failure to maintain the arrangement could cost a reported £5 billion.[80] As is common practice in bank securitisations, Granite was set up as a charitable trust with any residue on winding-up to benefit a small charity, Down's Syndrome North East. Despite having assets worth an estimated £45 billion, Granite has never made a donation to the charity because it remains in business.[81]
At Northern Rock's heart is Granite, a £45bn securitisation vehicle though which mortgages are parcelled up and sold to investors. Under 'substitution clauses' in Granite, investors can call in their loans if maturing mortgages are not replaced with new ones.
Should the clauses be triggered, investors could demand their funding back – potentially leaving the Government with an immediate £45bn bill. At the moment, only £25bn of taxpayer's money has actually gone into Northern Rock, through Bank of England loans. The rest of the support is via state guarantees, which the Treasury would prefer are not drawn upon.
'Granite is the reason the Government opted for nationalisation and did not put it into administration,' one senior Northern Rock insider said. Administration would also have triggered the clause.
Granite matures in tranches, with roughly £5bn expected to come up this year and £10bn next. As the Government regains control of the vehicle, it can run it down or sell it off. Either way, the obligation will last almost five years. Hence, bankers' fervent belief that "temporary public ownership" will not be anything of the sort.[82]
In late 2008, Northern Rock, advised by Credit Suisse, decided to let Granite go into run-off, meaning that Northern Rock the bank will no longer supply it with fresh mortgages and bondholders will be repaid as old mortgages expire.[83]
Debt reduction strategy
[edit]On 18 March, Northern Rock announced the measures that it would be taking to reduce the government debt within three to four years.[84] The bank is to cut around a third of jobs (2,000) by 2011; on 1 May the bank confirmed that they would be initialising talks with the unions and that most of the job losses would be later in 2008.[85]
As of 30 September 2008 the bank is repaying the loan well ahead of target, owing a net balance of only £11.5 billion of the loan that stood at £26.9 billion at the end of 2007.[86]
On 21 October Standard & Poor's Ratings Services revised their outlook on Northern Rock to stable from positive; they also affirmed the bank's long and short-term 'A/A-1' counterparty credit ratings.[87] The Press Association noted on 22 October that Northern Rock may give their employees bonuses in the future, if certain targets in paying back the Government loan are met.[88]
On 21 January 2009 it was revealed that the bank's employees would receive a 10% bonus, due to the bank meeting its targets for repaying the Government loan. This caused some unrest from a number of media outlets and the Liberal Democrats' Vince Cable for example, but the decision to issue the bonus was defended by the Unite union, calling it a reward for their hard work and dedication.[89]
On 3 March 2009 Northern Rock noted that only £8.9 billion of the loan remained unpaid.[90]
On 1 October 2010 the bank announced that another £700 million had been paid off of the loan in the last three months.[91]
Job losses
[edit]
At the end of July 2008 Northern Rock announced the first set of redundancies; 800 staff were made compulsorily redundant and a further 500 staff left under a voluntary redundancy programme.[92] It is also aiming to halve its £100 billion loan book by either selling off mortgage assets to other lenders or by declining to offer new mortgages to existing customers.[93]
On 8 June 2010 as a part of the restructuring process it was announced that a further 650 jobs would be lost in the North East locations of the bank before the end of the year.[94]
In a report commissioned by development agency One North East it was detailed that the downfall of the bank cost the local region around £800 million, mainly in relation to the job losses. The report was kept confidential until 2010.[95]
On 28 March 2011 the bank announced that it was likely that around 680 more jobs would go during the restructuring prior to the bank's return to private sector.[96]
Danish operations
[edit]On 18 March, Northern Rock announced the termination of its Danish savings operation. All accounts in the Danish branch were closed on 18 April 2008.[97]
Lloyds TSB deal
[edit]On 5 June it was announced that Lloyds TSB, a former bidder for the bank, would assume a proportion of the Northern Rock mortgage book over 3 years; this would be achieved by Lloyds TSB offering new mortgages to Northern Rock customers who are nearing the end of their fixed-rate deals.[98]
Sponsorship
[edit]It was confirmed on 20 May 2008 that Northern Rock would continue to sponsor both Newcastle United and the Newcastle Falcons, the former due to the long-term agreement between them and the club. Chief Executive Ron Sandler was quoted as saying:
"We have already ended a number of sponsorships that I inherited... but we have chosen to continue the sponsorship of Newcastle United and Newcastle Falcons, partly because of commitments we have entered into there – sometimes sponsorships continue until they come to a contractual end – and partly because I believe it is in the commercial interest of the bank that we should continue with both of these."
In 2007, almost three weeks before the bank had to appeal to the Bank of England for an emergency loan, the bank bought the home ground of Newcastle Falcons Rugby Club, Kingston Park stadium for £15 million.[99] In February 2008, documents relating to the sale came to light, attracting much criticism that the purchase has been made at a time of impending crisis.[100] In late 2008 the bank sold Kingston Park stadium to Northumbria University for an undisclosed fee.[101]
On 18 January 2010 Northern Rock announced that they had signed a new 4-year sponsorship deal with Newcastle United, worth between £1.5 million and £10 million, starting from the 2010/11 season.[102] The sponsorship agreement with the Newcastle Falcons came to an end before the start of the 2010/11 season.[103]
Head office and The Tower
[edit]
At the time of its nationalisation, Northern Rock was developing two new offices. At its headquarters at the Regent Centre complex in Gosforth, Newcastle upon Tyne the bank was midway through construction of a 10-storey tower that would provide a focus for the whole site. As the redundancy programme has made the new space surplus to capacity, the bank sought to sell or lease the tower building to a third party.[104] The bank also developed a site at Rainton Bridge,[105] which was also surplus to capacity, and it sold the site to npower.[106]
In April 2009, the local council, Newcastle City Council, announced that they were to buy the building for £22 million, and lease it to a green support services company, Eaga.[107] By November the sale of the building was complete, and the council renamed it Partnership House.
Northern Rock Foundation
[edit]Prior to Nationalisation, the company donated substantial amounts annually to its own charity, the Northern Rock Foundation. Nationalisation ended the covenant requiring Northern Rock to remit a share of profits to the foundation. Instead, for the next three years the foundation will receive an annual £15 million payment from Northern Rock, whether it remains publicly owned or returns to the private sector. The foundation's shares were cancelled and compensated in the same way as those of other shareholders.[68]
Shareholders, hedge funds and legal action
[edit]Two hedge funds that owned 20% of the bank, SRM Global and RAB Capital, took legal action against the government, regulators and individuals whose nationalisation of the bank, they believed to have been inappropriate, and a contributory factor to the current crisis. On 15 January 2008, a meeting was held at the 11,000 seat Metro Radio Arena to discuss the situation which then existed, where all but one of the proposals put forward by the hedge funds were rejected. In May Legal & General joined the hedge funds, as an "interested party".[108] The hedge funds are to request that an independent valuer assesses the level of compensation and to argue that the bank's shares are worth more than the final price of their trading prior to nationalisation. This legal action is thought to have started on 8 May.[109] A number of Northern Rock shareholders have also taken action in an attempt to get some level of compensation for their shares. Three North Labour MPs have agreed to hand a series of petitions in, on behalf of shareholders who lost hundreds of thousands of pounds when their shares were confiscated.[110]
As of 6 July around about 10 firms had applied to value the bank.[111] The Times reported on 3 August that Houlihan Lokey, BDO Stoy Hayward and L.E.K. Consulting were the three companies short listed by the government to value the bank.[112] On 9 September The Times reported that Andrew Caldwell, a valuations partner at BDO Stoy Hayward had been chosen as the valuer, with a fee of £4.5 million.[113]
The legal action brought by investors against the Government started in the Royal Courts of Justice on 13 January 2009.[114] Shareholders were also staging a demonstration outside the court.[115] One of the points that was revealed about the case is that they were examining who 'leaked' the information about the bank receiving its emergency government bailout.[116] In order to give full consideration, Lord Justice Stanley Burnton and Mr Justice Silber reserved their decision, before they gave a written judgment of the case.[117] On 13 February it was announced that the shareholders had lost the case.[118][119] Roger Lawson of the UK Shareholders Association said that there was a 'good chance' that they would appeal the decision.[120]
In May 2009, it was reported that Sir Anthony Clarke and two other senior judges in the Court of Appeal would hear the next stage in the judicial review starting on 10 June for three days.[121][122] On 28 July it was revealed that the shareholders lost their appeal, but some shareholders said that they would now try to take the case to the House of Lords.[123] On 22 December it was reported that the shareholders had again lost their appeal, and now they will be going to the European Court of Human Rights in Strasbourg.[124][125]
On 8 December it was announced that the Northern Rock shareholders were to get no compensation, based on the findings of the valuer Andrew Caldwell.[126] This then went to a tribunal, Northern Rock v. Andrew Caldwell and HM Treasury, Upper Tribunal (Tax and Chancery Chamber), NR/001/2010, where the shareholders' appeal was rejected.
In 2011 Harbinger Capital Partners LLC, an entity which had held an interest in some £277 million preference shares in Northern Rock, and Chris Hulme, chairman of the Northern Rock Shareholders Action Group, lost their legal battle to overturn the valuation of the shares being worthless.[127] In January 2013 Harbinger's appeal is being heard in London.[128]
Repossession accusations
[edit]In October 2008 a small number of charities and media outlets accused Northern Rock of having an aggressive repossession policy.[129] These allegations were denied by the bank's spokesman Simon Hall.[130]
Restoration of confidence
[edit]By October customers appeared to be regaining confidence in the bank, when it emerged that there had been a surge in the number of new accounts which had been opened.[131] People appeared to see Northern Rock as a safe place to put their money, given the current status as a nationalised bank which cannot fail. The bank decided to remove some of their savings products from the market, as the bank has a commitment to take only a 1.5% share of total UK retail deposits.[132]
In January 2009 the media began to speculate about the Government having plans to use Northern Rock as a way of boosting lending.[133] On 19 January, it was announced that Northern Rock would change its business strategy by offering more retention deals to its existing mortgage borrowers as their products expire, hence taking longer to pay back the remainder of its Government loan.[134] Alistair Darling noted that it was "not appropriate for Northern Rock to continue to shrink its activities".[135] Reuters reported on 23 January, that the Government were considering injecting up to £10 billion into Northern Rock, as a new business plan at the bank.[136] However, the European Commission may object to changes in how the bank is run, and that it may break EU state aid rules, and are investigating the matter.[137][138]
In late February media sources began reporting that a section of the bank was to become a "good bank", issuing more mortgages, when it is injected with £10–14 billion by the Government.[139] On 23 February 2009 Northern Rock announced that they would be offering £14 billion worth of new mortgages, over the next two years, as a part of their new business plan.[140] This new lending was partly funded by an increase in the government loan, a reversal of previous strategy to pay the loan off as quickly as possible by actively encouraging mortgage customers to leave when their mortgage deal matures. The reason for this change being government policy to increase the availability of credit. This £14 billion was split into £5 billion in 2009 and £9 billion in 2010.[141]
In March 2009 mortgages issued by the bank rose by 70%, compared to the previous month.[142][143] In February 2010 The Times claimed that Northern Rock was interested in buying some of the branches of RBS and Lloyds.[144]
In February 2010 the government decided to remove the 100% guarantee of the deposits at Northern Rock.[145] Savers received 3 months notice before the removal of the guarantee at the end of May. This means that, like most banks, only the first £50,000 (or as of October 2011, £85,000) deposited is guaranteed.[146]
Eventual return to the private sector
[edit]
When the British Government nationalised the bank, they noted that it was to be a temporary measure, and one of their aims was to eventually return the bank back to the private sector. On 26 April 2009, The Times suggested that the Government would sell Northern Rock by the end of 2009. Potential buyers included Virgin Money, National Australia Bank, Santander, Blackstone and TowerBrook.[147] The Times noted that a British supermarket chain, Tesco, was interested in buying parts of the bank.[148] It is thought that adviser Credit Suisse examined the plans to split the bank into 2 parts, to separate the most toxic loans and assets into a "bad bank".[149] In May 2009 the EU demanded more information about the split.[150] Another possibility was a bond debt buyback.[151]
A spokesperson for the bank said that the sale of the bank was just one option, and there was currently no time scale. Reuters noted that there were considerations to sell the bank, but no formal discussions were taking place with potential buyers.[152] Alistair Darling has stated that he is in no hurry to return the bank back to the private sector.[153]
In January 2010 National Australia Bank were widely reported to have lined up potential advisers on the deal to buy the Northern Rock. NAB already owned two brands in the UK, Clydesdale and Yorkshire banks.[154] Also in January 2010 Virgin purchased a small bank, the Church House Trust, but according to the Times and other sources Virgin still had an interest in Northern Rock and had been contacting companies such as Blackstone.[155]
In July 2010 it was reported that a consortium of City executives were gathering to place a bid for Northern Rock using the vehicle NBNK Investments.[156] UKFI have been briefed on the proposals.[157] On 4 November Gary Hoffman left Northern Rock to become CEO at NBNK Investments. Hoffman was put on gardening leave by Northern Rock until he joins NBNK on 1 May 2011. Hoffman was to receive a package worth around £500,000 for his gardening leave, but decided to turn it down.[158] Due to Hoffman's previous position NBNK Investments would not be permitted to table a bid for Northern Rock for a period of 12 months from 1 November 2010.[159]
In January 2011 renewed speculation about the bank's sale was reported as it emerged that UKFI were beginning to search for both advisers and suitors for the potential sale.[160][161] On 11 March Deutsche Bank AG were appointed to be the advisers for Northern Rock's return to the private sector.[162]
On 28 March 2011 the bank announced that it was likely that around 680 more jobs would go during the restructuring prior to the bank's return to private sector.[96]
On 15 June 2011 it was announced that the bank was to be sold to a single buyer in the private sector by the end of the year.[163]
On 17 November 2011 the UK Government announced the sale of Northern Rock to Virgin Money for £747m.[6]
Banking and assets split
[edit]On 26 June 2009 the bank confirmed that it was to be split into two parts, an "assetco" and a "bankco". The plan was also to include that the remaining amount of the government loan was to be repaid by the end of 2010.[164][165] On 28 October the European Commission waived through plans to split the bank off and sell the "good" parts off.[166] On 8 December the Northern Rock plc Transfer Order 2009 was laid before Parliament and in this the Treasury announced that this restructuring would take place from 1 January 2010.[167]
There are two companies; the first being a new company, to be re-registered with the name "Northern Rock plc", which contains the bank's retail and wholesale deposit business, and the second being the current Northern Rock plc renamed to "Northern Rock (Asset Management) plc", which retains the balance of the bank's mortgage book, the Government loan, other borrowings, derivatives and certain wholesale deposits (held on behalf of Granite).[168] The bank, "Northern Rock plc", would be offering new savings and mortgage products, but the other company, "Northern Rock (Asset Management) plc", will not.[169]
The subsidiary in Guernsey, Northern Rock (Guernsey) Limited, and all Irish accounts are owned by the new Northern Rock plc.[170][171]
After the split there are two boards of directors; Ron Sandler is the chairman of the new Northern Rock plc and Richard Pym is chairman of the Asset Management company. Gary Hoffman is chief executive of both companies.[172]
On 10 March 2010 Northern Rock (Asset Management) plc announced that for the year 2009 the company made a better than expected loss of £257.4 million; this was a vast improvement on the previous year's losses of £1.36 billion.[173]
As a part of the restructuring the Guernsey business was shut down on 2 September 2010. Customers of the Guernsey business were given three months notice.[174]
The €650 million worth of Irish deposits were sold to Permanent TSB in 2011.[175]
On 23 July 2012 it was announced that Virgin would be acquiring £465 million worth of mortgage assets from Northern Rock (Asset Management) plc.[176] In July 2013, private equity firm JC Flowers agreed to buy $450 million of the bank's loans from the British Government.[177]
In December 2012 an administrative error was uncovered in the wording of the loan agreements made by the bank in 2008 for around 152,000 customers; the error may cost an estimated £270 million. As a result of the error the affected customers, who were borrowing £25,000 or less, may be entitled to a repayment of interest.[178][179]
Bradford & Bingley mortgage book merger
[edit]Around the time of the nationalisation of Bradford & Bingley's mortgage book the press suggested that merging it with Northern Rock was a possibility. In October 2008 the chairman Ron Sandler noted that there had been informal talks concerning the idea of the merger with the government, but there had been no subsequent discussion. Sandler did however add "It would not surprise me at some point if a closer look was taken at the method of managing loan books within government-owned banks".[180]
In March 2009 Alistair Darling said that he was keeping his options open during the "fast-moving" crisis in the banking industry, and thus not ruling out the possibility of a mortgage book merger between Northern Rock and Bradford & Bingley.[181]
On 24 March 2010 UKFI announced its intention to integrate Northern Rock (Asset Management) plc and Bradford & Bingley plc under a single holding company.[182] On 1 October it was announced that Bradford & Bingley plc and Northern Rock (Asset Management) plc had been merged under a single holding company UK Asset Resolution Ltd.[183] In 2014 the Northern Rock name disappeared from asset management company's name as it became NRAM plc.
In 2015 UKFI announced that it will seek expressions of interest for the divestment of mortgage servicing capabilities of the NRAM business as well as the Granite securitisation vehicle. UKFI have appointed Moelis & Company as advisers for the divestments.[184]
Remutualisation proposals
[edit]In September and October 2009 various groups of people, including the Building Societies Association, called for the Northern Rock to be remutualised. Treasury minister Sarah McCarthy-Fry said that the idea of mutualisation had not been ruled out. The Northern Rock Building Society had previously been de-mutualised in 1997, to become a bank.[185]
In the Labour Party's 2010 Manifesto there was a mention of a possible "mutual solution" for Northern Rock.[186] The Liberal Democrat's Manifesto noted that the party would have turned Northern Rock into a building society.[187]
On 1 February it was reported that Yorkshire Building Society were interested in Northern Rock.[188] It has also been reported that Nationwide Building Society are not interested in the bank.[188] On 31 March 2011 the Coventry Building Society expressed an interest in remutualising Northern Rock as a part of Coventry.[189]
Sale to Virgin Money
[edit]

During 2011 the government encouraged another round of bidding for the bank. By the first round deadline on 28 July Virgin Money and JC Flowers put forward their expressions of interest.[190] In late October Virgin Money submitted their 2nd round bid for the bank.[191] The following day NBNK rejoined the bidding process for the bank, leaving only NBNK and Virgin as contenders.[192] This came as the restriction on NBNK from Hoffman's appointment expired; at this time NBNK were also preparing a bid for 632 branches of Lloyds.[192] On 17 November 2011 it was announced that Virgin Money Holdings (UK) Limited were going to buy Northern Rock from UKFI for £747 million up front and other potential payments of up to £280 million over the next few years.[6] These additional payments which would take the value of the sale to over £1 billion could include a £150 million capital instrument and an additional cash consideration of £50–80 million would be paid upon a future profitable IPO or sale in the next five years. A £73 million deferred consideration was paid by Virgin by July 2012. In 2014 Virgin Money repaid a further £154.5 million that it had received as part of the refinancing package.[193]
The sale went through on 1 January 2012. The government said it had no plans to sell Northern Rock (Asset Management). There will be no further job losses for at least three years, except for the ones already announced previously. Virgin have also pledged to keep the headquarters of the new Virgin Money bank (savings and mortgages) in Newcastle upon Tyne.[194] The deal is pending regulatory and EU merger approval, and the combined business will operate under the Virgin Money brand.[195]
The deal with Virgin included jobs for 2,100 employees, around a million of Northern Rock's customers, 75 branches and around a £14bn mortgage book and a £16bn retail deposit book. Although the deal means that the British government are to lose hundreds of millions on the deal, they claim that this represented the best deal for the taxpayer. The purchase was funded by the Virgin Group and WL Ross & Co., and Virgin hope that the new enlarged Virgin Money with its 4 million customers will be "a significant new competitor in UK retail banking". WL Ross has a 44% stake in the enlarged Virgin Money – this is larger than his stake in Virgin Money after their purchase of Church House Trust in 2010.
The deals with the Northern Rock Foundation will be extended to at least 2013, giving Virgin and the foundation time to agree how they will work together. The new Virgin Money also aims lend £45bn in total to support its customers over the next five years. The enlarged Virgin Money is led by Sir David Clementi, as chairman, and Jayne-Anne Gadhia, as chief executive officer.
In December 2011 the National Audit Office announced an investigation into the splitting of assets within the bank and sale of the retail bank to Virgin Money.[196] They revealed their findings in May 2012 where they believe that the split was "reasonable at the time but the final net cost to the taxpayer could be some £2 billion".[197]
By October 2012 what remained of the retail operations of Northern Rock now operated under the Virgin Money brand. On 12 October 2012 Northern Rock plc was renamed Virgin Money plc, and Virgin Money Limited was renamed Northern Rock Limited. The Northern Rock website became a redirect to Virgin Money's website.
In October 2014, it was announced that Virgin Money Holdings (UK) plc would float shares on the London Stock Exchange in order to raise approximately £150 million which would go towards expanding and enabling it to continue to hire and maintain its existing base of top staff members.[198] The successful offer led to a final payment of £50 million to the UK Government with respect to the company's IPO following the purchase of Northern Rock.
Subsequently, in 2018, Virgin Money UK was itself was acquired by the larger CYBG plc, operator of Clydesdale Bank and Yorkshire Bank, for £1.7bn.[199] In 2024, the Nationwide Building Society announced its intent to acquire Virgin Money.[200]
See also
[edit]- Northern Rock (Asset Management)
- Partnership House
- Northern Rock
- UK Financial Investments
- Banking (Special Provisions) Act 2008
References
[edit]- ^ "Liquidity Support Facility for Northern Rock plc – Tripartite Statement by HM Treasury, Bank of England and Financial Services Authority". Bank of England. 14 September 2007. Archived from the original on 25 December 2018. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ "Northern Rock appoints new Chief Executive Officer". Northern Rock. 23 July 2008. Retrieved 25 July 2010.
- ^ "Northern Rock chairman Sandler says turnaround to take years". Forbes. 18 February 2008. Archived from the original on 20 September 2008. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ a b "Northern Rock to be nationalised". BBC News. 17 February 2008. Retrieved 8 April 2008.
- ^ Atkinson, Simon (18 February 2008). "Rock recovery is Sandler's goal". BBC News. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ a b c "Northern Rock sale announced by chancellor". BBC News. 17 November 2011. Retrieved 17 November 2011.
- ^ Falloon, Matt (1 January 2012). "UK sells Northern Rock to Virgin despite protest". Reuters. Archived from the original on 6 January 2016. Retrieved 1 January 2012.
- ^ "UKFI confirms completion of Northern Rock sale to Virgin Money" (PDF). UK Financial Investments. 1 January 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 January 2012. Retrieved 1 January 2012.
- ^ "Northern Rock gets bank bail out". BBC News. 13 September 2007. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ Larry Elliott; Jill Treanor (3 August 2017). "The day the credit crunch began, 10 years on: 'the world changed'". The Guardian. Retrieved 20 November 2023.
- ^ Adam Harcourt-Webster (9 November 2007). "Run on the Bank: Northern Crock". BBC News. Retrieved 20 November 2023.
Events in the American home loans market led to a global credit crunch, where banks stopped lending to each other, and so forced a desperate Northern Rock to appeal for help from the Bank of England.
- ^ "£3bn lent to Northern Rock". Financial Times. 22 September 2007. Archived from the original on 1 December 2008. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ Thal Larsen, Peter; Hume, Neil (13 September 2007). "Bank of England to bail out Northern Rock". Financial Times.
- ^ "Barclays again taps emergency facility". International Business Times. 31 August 2007. Archived from the original on 16 July 2012. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ "Tripartite Authority – Statement re Northern Rock". Reuters. 2008. Archived from the original on 14 October 2007. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ "Fifth Report". House of Commons. 24 January 2008. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ Aldrick, Philip (10 September 2007). "Weakened Northern Rock may face bid". The Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 14 October 2007. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ King, Mervyn (12 September 2007). "Treasury Committee" (PDF). Turmoil in Financial Markets: What Can Central Banks Do?. Retrieved 8 April 2008.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "EU regulators approve Northern Rock bailout". AFP (Google). 5 December 2007. Archived from the original on 2 October 2012. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ "Late Queues For Bank's Anxious Customers". Sky News Business. 14 September 2007. Archived from the original on 14 October 2007. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ Shin HS (2009). "Reflections on Northern Rock: the bank run that heralded the global financial crisis". J Econ Perspect. 23 (1): 101–19. doi:10.1257/jep.23.1.101.
- ^ "Rush on Northern Rock continues". BBC News. 15 September 2007. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ "Northern Rock besieged by savers". BBC News. 17 September 2007. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ "Northern Rock deposits guaranteed". BBC News. 17 September 2007. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ "Timeline: Northern Rock bank crisis". BBC News. 5 August 2008. Retrieved 21 April 2008.
- ^ "File on 4" (PDF). Mervyn King Interview. BBC Radio 4. 6 November 2007. Retrieved 15 October 2008.
- ^ "Northern Rock chairman quits after criticism from lawmakers". International Herald Tribune. 19 October 2007. Archived from the original on 21 October 2007. Retrieved 1 August 2021.
- ^ "Banker in charge of Northern Rock finance found dead". The Times. 27 November 2012. Retrieved 1 August 2021.
- ^ "Stock Exchange announcement – Northern Rock plc update". Northern Rock. 13 December 2007. Archived from the original on 20 December 2007. Retrieved 1 August 2021.
- ^ Wearden, Graeme (11 January 2008). "Northern Rock repays £2bn of £26bn Bank of England loan". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ "Sale of Lifetime Mortgage portfolio". Northern Rock. 11 January 2008. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ a b Porter, Andrew; Conway, Edmund (8 February 2008). "Nation hit with £100bn Northern Rock debts". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 9 February 2008. Retrieved 8 February 2008.
- ^ Conway, Edmund (10 February 2008). "Treasury suffers from Northern Rock debt". The Telegraph. London. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ "Northern Rock puts billions down the drain". The Telegraph. London. 8 February 2008. Archived from the original on 9 February 2008. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ Griffiths, Katherine (14 March 2008). "Budget 2008: Government to issue Rock gilts". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 14 March 2008.
- ^ "FSA admits failings over Northern Rock". Financial Times. 26 March 2008. Retrieved 27 March 2008.
- ^ Inman, Phillip (27 March 2008). "Northern Rock fiasco leads to FSA revamp". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 27 March 2008.
- ^ "Watchdog admits failure over Rock". BBC News. 26 March 2008. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ "Northern Rock risk revealed in 2004". Financial Times. 30 May 2009. Retrieved 30 May 2009.
- ^ "Treasury – Fifth Report". House of Commons. 24 January 2008. Retrieved 6 October 2010.
- ^ "Northern Rock drops from FTSE 100". BBC News. 12 December 2007. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ "Huge payoff for Northern Rock boss". Northumberland Gazette. 31 March 2008. Retrieved 31 March 2008.[dead link]
- ^ "Full year results for 2007 and further details of its proposed business plan". Northern Rock. 31 March 2008. Retrieved 31 March 2008.
- ^ "Northern Rock makes a £585m loss". BBC News. 5 August 2008. Retrieved 6 August 2008.
- ^ "Virgin pursues Northern Rock deal". BBC News. 12 October 2007. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ Webster, Philip; Hurst, Greg (21 January 2008). "Northern Rock's last chance– accept a deal or else". The Times. London. Archived from the original on 23 January 2008. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ "Virgin poised for Rock takeover". BBC News. 25 November 2007. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ "Virgin consortium strengthens Northern Rock bid – report". Forbes.com. 18 January 2008. Archived from the original on 21 January 2008. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ Waples, John (11 November 2007). "Abbey boss swoops on ailing Rock". The Times. London. Retrieved 20 February 2008.[dead link]
- ^ "Olivant Advisors Ltd – Statement re Northern Rock". Reuters. 7 December 2007. Archived from the original on 17 December 2007. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ Inman, Phillip (26 October 2007). "Virgin to name Northern Rock team". guardian.co.uk. London. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ Larner, Digby (26 October 2007). "J.C. Flowers Considers Bid For British Lender Northern Rock". Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ "Cameron criticises Rock 'failure'". BBC News. 13 January 2008. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ Slater, Steve (7 December 2007). "JC Flowers seen exiting N. Rock race". Reuters. Archived from the original on 13 December 2007. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ "Northern Rock sale faces Treasury veto". Accountancy Age. 20 November 2007. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ Elliott, Larry (14 December 2007). "Ministers prepare plan to nationalise Northern Rock". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ^ "Treasury lines up new Rock boss". BBC News. 12 January 2008. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ "Northern Rock". HM Treasury. 21 January 2008. Archived from the original on 16 October 2009. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ "Goldman hired to aid Northern Rock rescue". Reuters. 15 December 2007. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ Griffiths, Katherine (21 January 2008). "Northern Rock shares surge on bid hopes". The Telegraph. London. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ "Olivant not ruling out return to Northern Rock auction". Forbes. 5 February 2008. Archived from the original on 8 February 2008. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ Treanor, Jill (4 February 2008). "Private equity bidder Olivant pulls out of battle for Northern Rock". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ Hosking, Patrick (21 January 2008). "Q&A: The Northern Rock deal explained". The Times. London. Archived from the original on 5 July 2008. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ "Northern Rock to be nationalised". The Guardian. London. 17 February 2008. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ Walsh, Dominic (17 February 2008). "Chancellor to nationalise Northern Rock". The Times. London. Archived from the original on 23 September 2008. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ Hipwell, Deirdre (17 February 2008). "Q&A: what now for Northern Rock?". The Times. London. Archived from the original on 23 September 2008. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ a b "Northern Rock plc". HM Treasury. 17 February 2008. Archived from the original on 15 September 2008. Retrieved 26 September 2008.
- ^ "Banking (Special Provisions) Bill" (PDF). HM Treasury. 18 February 2008. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ "New company to manage Government's shareholding in banks". HM Treasury. 3 November 2008. Archived from the original on 4 December 2008. Retrieved 3 November 2008.
- ^ "OFT publishes report on Northern Rock". The Office of Fair Trading. 10 March 2009. Archived from the original on 8 May 2009. Retrieved 13 March 2009.
- ^ Slater, Steve (22 February 2008). "N.Rock Unveils Board Changes as Govt Takes Over". Reuters. Retrieved 15 October 2008.
- ^ "New Northern Rock boss appointed". BBC News. 23 July 2008. Retrieved 23 July 2008.
- ^ "The Board – Biographies". Northern Rock. Retrieved 14 October 2008.
- ^ Power, Helen (15 October 2008). "Northern Rock's former chief executive Adam Applegarth escapes threat of legal action". The Times. London. Archived from the original on 12 June 2011. Retrieved 15 October 2008.
- ^ Jordan, Dearbail (9 January 2009). "Northern Rock finance chief exits with £900,000". The Times. London. Archived from the original on 12 June 2011. Retrieved 10 January 2009.
- ^ "Northern Rock former directors fined and banned by FSA". BBC News. 13 April 2010. Retrieved 13 April 2010.
- ^ Treanor, Jill (21 April 2010). "Northern Rock finance director David Jones departs". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 21 April 2010.
- ^ Armitstead, Louise (28 July 2010). "Northern Rock's former FD fined and banned from City". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- ^ Winnett, Robert (21 February 2008). "Northern Rock's 'best mortgages' sold offshore". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 26 February 2008. Retrieved 21 February 2008.
- ^ Pierce, Andrew (22 February 2008). "Charity used to raise billions – but got nothing". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 25 February 2008. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ Aldrick, Philip; Griffiths, Katherine (20 February 2008). "The state of Northern Rock: anything but usual". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ "Northern Rock calls it a day on Granite vehicle". Financial Times. 21 November 2008. Retrieved 22 November 2008.
- ^ Aldrick, Philip (18 March 2008). "Northern Rock to axe a third of staff". The Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 23 March 2008. Retrieved 18 March 2008.
- ^ Jordan, Dearbail (1 May 2008). "Northern Rock starts talks to cut one third of staff". The Times. London. Archived from the original on 19 July 2008. Retrieved 1 May 2008.
- ^ "Northern Rock – Quarter 3 Trading Statement". Northern Rock. 14 October 2008. Retrieved 14 October 2008.
- ^ "S&P release on Northern Rock PLC". Forbes. 21 October 2008. Retrieved 22 October 2008.[dead link]
- ^ "Northern bonus scheme sparks concern". The Press Association. 22 October 2008. Retrieved 22 October 2008.[dead link]
- ^ "Northern Rock bonuses defended". Press Association. 21 January 2009. Retrieved 21 January 2009.[dead link]
- ^ "2008 Annual Report and Accounts". Northern Rock plc. 3 March 2009. Retrieved 3 March 2009.
- ^ "Northern Rock 'bad bank' pays £1bn". Press Association. 1 October 2010. Retrieved 16 October 2010.[dead link]
- ^ Treanor, Jill (31 July 2008). "Northern Rock to make 800 compulsory redundancies". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 1 August 2008.
- ^ Jordan, Dearbail; Seib, Christine (18 March 2008). "Northern Rock cuts mortgages and axes 2,000 jobs". The Times. London. Archived from the original on 17 May 2008. Retrieved 18 March 2008.
- ^ "Northern Rock to cut 650 jobs by year end". BBC News. 8 June 2010. Retrieved 8 June 2010.
- ^ "£800m cost to North East of Northern rock fiasco". The Journal. 16 October 2010. Archived from the original on 4 April 2012. Retrieved 16 October 2010.
- ^ a b "Northern Rock to consult on further restructuring of the business". Northern Rock plc. 28 March 2011. Retrieved 28 March 2011.
- ^ "Northern Rock lukker sin danske afdeling" (PDF) (in Danish). Northern Rock Bank Danmark. 18 March 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 April 2008. Retrieved 25 March 2008.
- ^ "Lloyds TSB in 3-year deal to offer mortgages to Northern Rock customers". Forbes. 5 June 2008. Archived from the original on 8 June 2008. Retrieved 5 June 2008.
- ^ Bond, David (21 February 2008). "Newcastle seek Northern Rock talks". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ Griffiths, Katherine (28 February 2008). "Northern Rock bought rugby fields three weeks before crisis". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 3 March 2008. Retrieved 28 February 2008.
- ^ "Northumbria University buys Newcastle Falcons' ground". The Journal. 4 December 2008. Archived from the original on 2 October 2011. Retrieved 8 December 2008.
- ^ "Northern Rock plc to sponsor Newcastle United". Northern Rock plc. 18 January 2010. Retrieved 18 January 2010.
- ^ "Northern Rock ends long-standing Newcastle Falcons deal". BBC News. 3 June 2010. Retrieved 3 June 2010.
- ^ "Redundant Northern Rock staff leave". The Press Association. 29 August 2008. Archived from the original on 15 July 2012. Retrieved 29 August 2008.
- ^ "Rainton Bridge". Rainton Bridge. Retrieved 23 December 2008.
- ^ "Npower shifts 900 jobs to Sunderland". Sunderland Echo. 6 April 2009. Archived from the original on 13 September 2012. Retrieved 6 April 2009.
- ^ "New offices for eaga". eaga. 22 April 2009. Archived from the original on 31 March 2022. Retrieved 23 April 2009.
- ^ Farrell, Sean (24 May 2008). "Legal & General joins legal action over Rock valuation". The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 25 May 2008. Retrieved 24 May 2008.
- ^ Jameson, Angela (8 May 2008). "Northern Rock investors begin legal battle". The Times. London. Archived from the original on 6 July 2008. Retrieved 8 May 2008.
- ^ "Northern Rock shareholders step up their fight". The Journal. 22 December 2008. Archived from the original on 7 February 2009. Retrieved 22 December 2008.
- ^ Evans, Simon (6 July 2008). "10 names in frame to value the Rock". The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 18 June 2022. Retrieved 6 July 2008.
- ^ Marlow, Ben (3 August 2008). "American investment bank favourite to value Northern Rock shares". The Times. London. Archived from the original on 23 September 2008. Retrieved 3 August 2008.
- ^ Costello, Miles (9 September 2008). "Northern Rock valuers to be paid £4.5m". The Times. London. Retrieved 30 September 2008.[dead link]
- ^ Wighton, David (7 January 2008). "All eyes on Northern Rock as investors go to court". The Times. London. Archived from the original on 12 June 2011. Retrieved 7 January 2008.
- ^ "Rock shareholders to stage protest". Press Association. 6 January 2009. Retrieved 6 January 2009.[dead link]
- ^ King, Ian (19 January 2009). "Treasury man appears to pin blame for Northern Rock leak on advisers". The Times. London. Archived from the original on 12 June 2011. Retrieved 21 January 2009.
- ^ "Rock shareholders await High Court decision". Financial Times Adviser. 22 January 2009. Archived from the original on 9 July 2012. Retrieved 22 January 2009.
- ^ Wearden, Graeme (13 February 2009). "Northern Rock shareholders lose compensation case". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 13 February 2009.
- ^ "SRM Global Master Fund LP v Commissioners of Her Majesty's Treasury (EWHC 227)". British and Irish Legal Information Institute. 2009. Retrieved 14 February 2009.
- ^ "Rock investors consider appeal". BBC News. 14 February 2009. Retrieved 14 February 2009.
- ^ "Campaigner greets Rock shares move". The Sunderland Echo. 6 May 2009. Archived from the original on 9 May 2009. Retrieved 10 May 2009.
- ^ "Northern Rock shareholders begin High Court appeal". The Daily Telegraph. London. 9 June 2009. Archived from the original on 30 January 2010. Retrieved 9 June 2009.
- ^ "Appeal defeat for Rock investors". BBC News. 28 July 2009. Retrieved 28 July 2009.
- ^ "Appeal bid denied for Northern Rock shareholders". The Journal. 22 December 2009. Archived from the original on 25 December 2009. Retrieved 22 December 2009.
- ^ Davey, James (16 June 2010). "Northern Rock shareholders take case to Europe". Reuters. Archived from the original on 15 July 2012. Retrieved 17 June 2010.
- ^ Treanor, Jill (8 December 2009). "Northern Rock investors will not get compensation". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 8 December 2009.
- ^ "Northern Rock Decision final" (PDF). 6 October 2011. Retrieved 22 January 2013.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Harbinger Seeks Payout for Northern Rock Stake in U.K. Appeal". Bloomberg. 22 January 2013. Retrieved 22 January 2013.
- ^ "Mortgage rates static since base rate cut". Which?. 20 October 2008. Archived from the original on 22 October 2008. Retrieved 20 October 2008.
- ^ Charles, James (17 October 2008). "Northern Rock accused over rising repossessions". The Times. London. Retrieved 20 October 2008.[dead link]
- ^ "Commitment to Competitive Framework – Savings Product Changes". Northern Rock. 2 October 2008. Retrieved 10 October 2008.
- ^ Budworth, David (3 October 2008). "Northern Rock might have to turn away savers". The Times. London. Archived from the original on 12 June 2011. Retrieved 5 October 2008.
- ^ Griffiths, Katherine (16 January 2009). "Government will use Northern Rock to boost lending". The Telegraph. London. Retrieved 18 January 2009.
- ^ "Strategic Review". Northern Rock plc. 19 January 2009. Retrieved 19 January 2009.
- ^ "New Northern Rock lending policy". BBC News. 19 January 2009. Retrieved 19 January 2009.
- ^ Croft, Adrian (23 January 2009). "UK may inject $13.8 billion into Northern Rock: report". Reuters. Retrieved 23 January 2009.
- ^ Croft, Adrian (23 January 2009). "EU resists UK's revised Northern Rock plan- report". Reuters. Archived from the original on 27 January 2009. Retrieved 23 January 2009.
- ^ "Northern Rock Bailout by U.K. Faces Extended EU Probe". Bloomberg. 10 May 2009. Retrieved 10 May 2009.
- ^ Treanor, Jill (22 February 2009). "Rock to be reborn as a 'good bank'". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 22 February 2009.
- ^ "Northern Rock Returns to Mortgage Market". Northern Rock. 23 February 2009. Retrieved 23 February 2009.
- ^ "Northern Rock unveils £14 billion bid to kick-start mortgage lending". Daily Record. 23 February 2009. Archived from the original on 1 April 2009. Retrieved 24 March 2009.
- ^ "Borrowers flock to Northern Rock". BBC News. 27 April 2009. Retrieved 27 April 2009.
- ^ "Q1 Trading Statement". Northern Rock. 23 April 2009. Retrieved 27 April 2009.
- ^ Griffiths, Katherine; Costello, Miles (20 February 2010). "Northern Rock could buy RBS and Lloyds branches". The Times. London. Archived from the original on 11 June 2011. Retrieved 20 February 2010.
- ^ "Northern Rock's strength allows Government to release savings guarantee". Northern Rock. 24 February 2010. Retrieved 24 February 2010.
- ^ Gammell, Kara (11 February 2010). "Northern Rock to remove 100pc savings guarantee". The Times. London. Retrieved 10 February 2010.
- ^ Dey, Iain (26 April 2009). "Northern Rock to be sold by end of year". The Times. London. Retrieved 26 April 2009.[dead link]
- ^ Elliott, Francis; Jagger, Suzy; Griffiths, Katherine (1 July 2009). "Tesco linked to early sale of Northern Rock". The Times. London. Archived from the original on 1 July 2009. Retrieved 1 July 2009.
- ^ Deighton, Ben (26 April 2009). "Northern Rock to be "sold by end of year"". Reuters. Archived from the original on 30 April 2009. Retrieved 26 April 2009.
- ^ Charter, David (9 May 2009). "EU deepens probe into Northern Rock rescue". The Times. London. Archived from the original on 10 May 2009. Retrieved 30 May 2009.
- ^ Neligan, Myles (16 June 2009). "Northern Rock mulling debt buyback – source". Reuters. Retrieved 19 June 2009.
- ^ Howley, Victoria (27 April 2009). "UK mulls early Northern Rock sale, no formal talks: sources". Reuters. Retrieved 27 April 2009.
- ^ "Darling promises "no rushed sale" on Northern Rock". The Journal. 28 April 2009. Archived from the original on 18 January 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2009.
- ^ "NAB set to pounce on Northern Rock". SMH. 4 January 2010. Retrieved 8 January 2010.
- ^ Walsh, Dominic (8 January 2010). "Virgin Money buys minnow for retail bank launch". The Times. London. Archived from the original on 4 October 2010. Retrieved 8 January 2010.
- ^ "Big guns set their sights on Northern Rock". The Journal. 9 July 2010. Archived from the original on 19 November 2011. Retrieved 11 July 2010.
- ^ "City bosses look to snap up banks". Press Association. 8 July 2010. Retrieved 11 July 2010.[dead link]
- ^ Kar-Gupta, Sudip (5 November 2010). "UK's N.Rock outgoing CEO waives pay during time off". Reuters. Retrieved 6 November 2010.
- ^ "Directorate Change". Northern Rock. 4 November 2010. Retrieved 4 November 2010.
- ^ Treanor, Jill (17 January 2011). "Northern Rock seeks potential buyers". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 13 February 2011.
- ^ Menon, Jon (17 January 2011). "Northern Rock and UKFI Begin Sale Adviser Selection". Bloomberg. Retrieved 13 February 2011.
- ^ "Appointment of Corporate Finance Adviser". Northern Rock Plc. 11 March 2011. Retrieved 11 March 2011.
- ^ "Osborne plans to sell Northern Rock to a single buyer". BBC News. 15 June 2011. Retrieved 16 June 2011.
- ^ "Northern Rock confirms split plan". BBC News. 26 June 2009. Retrieved 26 June 2009.
- ^ "Update on State Aid approval process for Northern Rock". Northern Rock. 26 June 2009. Retrieved 26 June 2009.
- ^ "Brussels backs Rock restructuring". The Financial Times. 28 October 2009. Retrieved 28 October 2009.
- ^ "Treasury confirms 1 January restructuring of Northern Rock". HM Treasury. 8 December 2009. Archived from the original on 16 December 2009. Retrieved 9 December 2009.
- ^ "Government guarantee arrangements for Northern Rock plc" (PDF). HM Treasury. 8 December 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 August 2010. Retrieved 9 December 2009.
- ^ "Our Plans for the Future". Northern Rock. Retrieved 9 December 2009.
- ^ "Information about the plans of Northern Rock plc". Northern Rock (Guernsey) Limited. Archived from the original on 27 July 2010. Retrieved 19 December 2009.
- ^ "Our Plans for the Future". Northern Rock plc. Retrieved 19 December 2009.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Board appointments at Northern Rock". Northern Rock. 15 December 2009. Retrieved 19 December 2009.
- ^ "Northern Rock losses see sharp fall". BBC News. 10 March 2010. Retrieved 10 March 2010.
- ^ "Northern Rock closes offshore business". City Wire. 2 June 2010. Archived from the original on 24 July 2012. Retrieved 2 June 2010.
- ^ "Northern Rock sells Irish deposits to Permanent TSB in €650m deal". Irish Independent. 31 August 2011. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- ^ "U.K. Asset Resolution Sells Mortgages to Virgin Money". Bloomberg. 23 July 2012. Retrieved 23 July 2012.
- ^ Abhishek Takle (17 July 2013). "J.C. Flowers set to buy portion of Northern Rock loans: paper". Reuters.
- ^ "UKAR response to Ministerial statement regarding NRAM". Northern Rock (Asset Management) plc. 11 December 2012. Archived from the original on 14 January 2013. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ "Northern Rock's £270m error means borrowers pay no interest". The Times. 11 December 2012. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ "Northern Rock reveals B&B talks". Financial Times. 14 October 2008. Retrieved 15 October 2008.
- ^ Murphy, Joe; Cecil, Nicholas (19 March 2009). "Darling: I won't rule out merging Northern Rock & Bingley". Evening Standard. Retrieved 16 October 2020.
- ^ "Bradford & Bingley plc and Northern Rock (Asset Management) plc" (PDF). UKFI. 24 March 2010. Retrieved 24 March 2010. [dead link]
- ^ "UK Sets Holding Co For Northern Rock Asset, Bradford & Bingley". Wall Street Journal. 1 October 2010. Retrieved 16 October 2010.[dead link]
- ^ "Osborne Says U.K. Plans Faster Sale of Lloyds Shares in 2015". Bloomberg. 18 March 2015. Retrieved 4 April 2015.
- ^ Treanor, Jill (4 October 2009). "Government considers remutualising Northern Rock". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 4 October 2009.
- ^ "General Election 2010: Northern Rock customers to get shares". The Daily Telegraph. London. 12 April 2010. Retrieved 12 April 2010.
- ^ "At-a-glance: Lib Dem general election 2010 manifesto". BBC News. 14 April 2010. Retrieved 14 April 2010.
- ^ a b "Yorkshire Building Society in bid for Northern Rock". NE Business. 1 February 2010. Retrieved 2 April 2010.
- ^ "Coventry Building Society statement on Northern Rock" (PDF). Coventry Building Society. 31 March 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 July 2011. Retrieved 2 April 2010.
- ^ "JC Flowers, Virgin Money Bid for Northern Rock, FT Reports". Bloomberg. 30 July 2011. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- ^ "Wilbur Ross says Virgin Money to bid for Northern Rock". Reuters. 24 October 2011. Archived from the original on 25 January 2016. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- ^ a b "NBNK joins Northern Rock auction". The Scotsman. 27 October 2011. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- ^ "Virgin Money repays Treasury £150m it got in Northern Rock deal". The Telegraph. 25 July 2014. Retrieved 20 August 2014.
- ^ "Chancellor announces sale of Northern Rock plc". HM Treasury. 17 November 2011. Retrieved 17 November 2011.
- ^ "Virgin Money acquires Northern Rock". Virgin Group. 17 November 2011. Archived from the original on 18 November 2011. Retrieved 17 November 2011.
- ^ "National Audit Office to investigate Northern Rock sale". BBC News. 17 December 2011. Retrieved 17 December 2011.
- ^ "The creation and sale of Northern Rock plc – NAO report". National Audit Office (NAO). 18 May 2012. Retrieved 11 May 2024.
- ^ "Virgin Money announces float plan". BBC News. 2 October 2014. Retrieved 2 October 2014.
- ^ Mines, Josh (7 May 2018). "Richard Branson-backed Virgin Money receives takeover bid from Clydesdale and Yorkshire Bank owner CYBG". City AM. Archived from the original on 8 May 2018. Retrieved 8 May 2018.
- ^ Kalyeena Makortoff (21 March 2024). "Nationwide agrees £2.9bn deal to take over Virgin Money". The Guardian. Retrieved 10 May 2024.
External links
[edit]- NRAM – Northern Rock (Asset Management) plc
- Virgin Money UK Archived 31 December 2011 at the Wayback Machine
