Ming–Tibet relations
| History of Tibet |
|---|
 |
| See also |
|
|
The Ming dynasty considered Tibet to be part of the Western Regions. While the Ming dynasty at its height had some degree of influence in Tibet, the exact nature of their relations is under dispute by modern scholars. Analysis of the relationship is further complicated by modern political conflicts and the application of Westphalian sovereignty to a time when the concept did not exist. The Historical Status of China's Tibet, a book published by the People's Republic of China, asserts that the Ming dynasty had unquestioned sovereignty over Tibet by pointing to the Ming court's issuing of various titles to Tibetan leaders, Tibetans' full acceptance of the titles, and a renewal process for successors of these titles that involved traveling to the Ming capital. Scholars in China also argue that Tibet has been an integral part of China since the 13th century and so it was a part of the Ming Empire. However, most scholars outside China, such as Turrell V. Wylie, Melvyn C. Goldstein, and Helmut Hoffman, say that the relationship was one of suzerainty, Ming titles were only nominal, Tibet remained an independent region outside Ming control, and it simply paid tribute until the Jiajing Emperor, who ceased relations with Tibet.
Some scholars note that Tibetan leaders during the Ming frequently engaged in civil war and conducted their own foreign diplomacy with neighboring states such as Nepal. Some scholars underscore the commercial aspect of the Ming–Tibetan relationship, noting the Ming dynasty's shortage of horses for warfare and thus the importance of the horse trade with Tibet. Others argue that the significant religious nature of the relationship of the Ming court with Tibetan lamas is underrepresented in modern scholarship.
In the hope of reviving the unique relationship during the Yuan dynasty, and his spiritual superior Drogön Chögyal Phagpa of the Sakya school of Tibetan Buddhism, the Yongle Emperor made a concerted effort to build a secular and religious alliance with Deshin Shekpa, the Karmapa of the Karma Kagyu school. However, the Yongle Emperor's attempts were unsuccessful.
The Ming initiated sporadic armed intervention in Tibet during the 14th century but did not garrison permanent troops there. The Tibetans also sometimes used armed resistance against Ming forays. The Wanli Emperor made attempts to re-establish Ming–Tibetan relations after the Mongol–Tibetan alliance initiated in 1578, which affected the foreign policy of the subsequent Qing dynasty in its support for the Dalai Lama of the Gelug school. By the late 16th century, the Mongols were successful armed protectors of the Gelug Dalai Lama after they increased their presence in the Amdo region. That culminated in Güshi Khan's conquest of Tibet from 1637 to 1642 and the establishment of the Ganden Phodrang regime by the 5th Dalai Lama with his help.
Background on Yuan rule over Tibet
[edit]Mongol Empire and Yuan dynasty
[edit]
Tibet was once a strong power contemporaneous with the Tang dynasty (618–907). Until the Tibetan Empire's collapse in the 9th century, it was the Tang's major rival in dominating Inner Asia.[1][2] The Yarlung rulers of Tibet also signed various peace treaties with the Tang, culminating in a treaty in 821 that fixed the borders between Tibet and China.[3]
During the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period of China (907–960), while the fractured political realm of China saw no threat in a Tibet which was in just as much political disarray, there was little in the way of Sino-Tibetan relations.[4][5] Few documents involving Sino-Tibetan contacts survive from the Song dynasty (960–1279).[5][6] The Song were far more concerned with countering northern enemy states of the Khitan-ruled Liao dynasty (907–1125) and Jurchen-ruled Jin dynasty (1115–1234).[6]
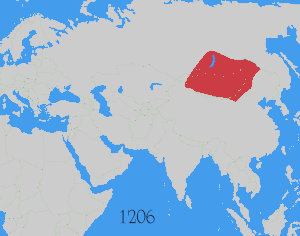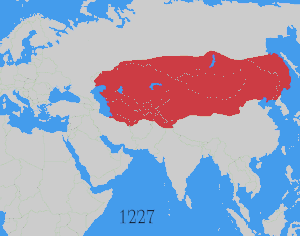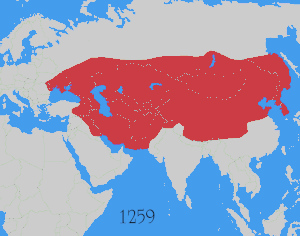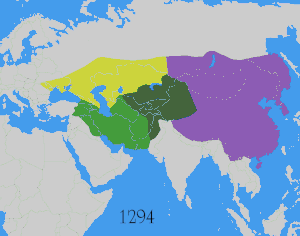
In 1207, the Mongol ruler Genghis Khan (r. 1206–1227) conquered and subjugated the Tangut-led Western Xia dynasty (1038–1227).[7] In the same year, he established diplomatic relations with Tibet by sending envoys there.[8] The conquest of the Western Xia alarmed Tibetan rulers, who decided to pay tribute to the Mongols.[7] However, when they ceased to pay tribute after Genghis Khan's death, his successor Ögedei Khan (r. 1229–1241) launched an invasion into Tibet.[9]
The Mongol prince Godan, a grandson of Genghis Khan, raided as far as Lhasa.[7][10] During his attack in 1240, Prince Godan summoned Sakya Pandita (1182–1251), leader of the Sakya school of Tibetan Buddhism, to his court in what is now Gansu in Western China.[7][10] With Sakya Pandita's submission to Godan in 1247, Tibet was officially incorporated into the Mongol Empire during the regency of Töregene Khatun (1241–1246).[10][11] Michael C. van Walt van Praag writes that Godan granted Sakya Pandita temporal authority over a still politically fragmented Tibet, stating that "this investiture had little real impact" but it was significant in that it established the unique "Priest-Patron" relationship between the Mongols and the Sakya lamas.[7]
Starting in 1236, the Mongol prince Kublai, who later ruled as Khagan from 1260 to 1294, was granted a large appanage in northern China by Ögedei Khan.[12] Karma Pakshi, 2nd Karmapa Lama (1203–1283)—the head lama of the Karma Kagyu lineage of Tibetan Buddhism—rejected Kublai's invitation, so instead Kublai invited Drogön Chögyal Phagpa (1235–1280), successor and nephew of Sakya Pandita, who came to his court in 1253.[13][14][15] Kublai instituted a unique relationship with the Phagpa lama, which recognized Kublai as a superior sovereign in political affairs and the Phagpa lama as the senior instructor to Kublai in religious affairs.[13][15][16] Kublai also made Drogön Chögyal Phagpa the director of the government agency known as the Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs and the ruling priest-king of Tibet, which comprised thirteen different states ruled by myriarchies.[15][16][17]

Tibet was later incorporated into the Yuan dynasty of China (1271–1368), the primary successor state to the Mongol Empire.[15] Van Praag writes that this conquest "marked the end of independent China," which was then incorporated into the Yuan dynasty that ruled modern-day China proper, Tibet, Mongolia, Korea, parts of Siberia and Upper Burma.[18] Morris Rossabi, a professor of Asian history at Queens College, City University of New York, writes that "Khubilai wished to be perceived both as the legitimate Khan of Khans of the Mongols and as the Emperor of China. Though he had, by the early 1260s, become closely identified with China, he still, for a time, claimed universal rule", and yet "despite his successes in China and Korea, Khubilai was unable to have himself accepted as the Great Khan".[19] Thus, with such limited acceptance of his position as Great Khan, Kublai Khan increasingly became identified with China and sought support as Emperor of China.[20]
Overthrow of the Sakya and Yuan
[edit]In 1358, the Sakya viceregal regime installed by the Mongols in Tibet was overthrown in a rebellion by the Phagmodru myriarch Tai Situ Changchub Gyaltsen (1302–1364).[18][21][22] The Mongol Yuan court was forced to accept him as the new viceroy, and Changchub Gyaltsen and his successors, the Phagmodrupa dynasty, gained de facto rule over Tibet.[18][21][22]
In 1368, a Han revolt known as the Red Turban Rebellion toppled the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. Zhu Yuanzhang then established the Ming dynasty, ruling as the Hongwu Emperor (r. 1368–1398).[23] It is not clear how much the early Ming court understood the civil war going on in Tibet between rival religious sects, but the first emperor was anxious to avoid the same trouble that Tibet had caused for the Tang dynasty.[21][24] Instead of recognizing the Phagmodru ruler, the Hongwu Emperor sided with the Karmapa of the nearer Kham region and southeastern Tibet, sending envoys out in the winter of 1372–1373 to ask the Yuan officeholders to renew their titles for the new Ming court.[21]
As evident in his imperial edicts, the Hongwu Emperor was well aware of the Buddhist link between Tibet and China and wanted to foster it.[25][26] Rolpe Dorje, 4th Karmapa Lama (1340–1383) rejected the Hongwu Emperor's invitation, although he did send some disciples as envoys to the court in Nanjing.[21] The Hongwu Emperor also entrusted his guru Zongluo, one of many Buddhist monks at court, to head a religious mission into Tibet in 1378–1382 in order to obtain Buddhist texts.[25][26]
However, the early Ming government enacted a law, later rescinded, which forbade ethnic Han to learn the tenets of Tibetan Buddhism.[27] There is little detailed evidence of Chinese—especially lay Chinese—studying Tibetan Buddhism until the Republican era (1912–1949).[27] Despite these missions on behalf of the Hongwu Emperor, Morris Rossabi writes that the Yongle Emperor (r. 1402–1424) "was the first Ming ruler actively to seek an extension of relations with Tibet."[28]
Assertions in the History of Ming
[edit]The History of Ming is one of the official Twenty-Four Histories that covers the history of the Ming dynasty, compiled by the subsequent Qing dynasty (1644–1912). The compilation started in 1645 and was completed in 1739. The History of Ming follows the traditional division of official history since the Records of the Grand Historian into Annals(本紀), Treatises(志), Tables(表) and Biographies(列傳). The territories of Ming was described under Treatises on geography(地理志) and Tibet was not included in this section. Other countries were described under Biographies, and Tibet was described under Western Regions(西域), after Foreign states(外國) such as Korea(朝鲜), Vietnam(安南) and Mongol.[29][30][31]
According to the History of Ming, the Ming dynasty created the "Ngari Military-Civilian Marshal Office" for western Tibet, the "Ü-Tsang Regional Military Commission" for Ü-Tsang, and "Amdo-Kham Regional Military Commission" (Dokham) for Amdo and Kham regions.[32][33] The History of Ming further states that administrative offices were set up under these high commanderies, including one Itinerant Commandery, three Pacification Commissioner's Offices, six Expedition Commissioner's Offices, four Wanhu offices (myriarchies, in command of 10,000 households each) and seventeen Qianhu offices (chiliarchies, each in command of 1,000 households).[34]
The Ming court recognized three Princes of Dharma (法王) and five Princes (王), and granted many other titles, such as Grand State Tutors (大國師) and State Tutors (國師), to key leaders of Tibetan Buddhism, including the Karma Kagyu, Sakya, and Gelug.[30] According to the government of PRC, leading officials of these organs were all appointed by the central government and were subject to the rule of law.[35] Yet Van Praag describes the distinct and long-lasting Tibetan law code established by the Phagmodru ruler Tai Situ Changchub Gyaltsen as one of many reforms to revive old Imperial Tibetan traditions.[36]
The late Turrell V. Wylie, a former professor of the University of Washington, and Li Tieh-tseng argue that the reliability of the heavily censored History of Ming as a credible source on Sino-Tibetan relations is questionable, in the light of modern scholarship.[37] Other historians also assert that these Ming titles were nominal and did not actually confer the authority that the earlier Yuan titles had.[38][39] Van Praag writes that the "numerous economically motivated Tibetan missions to the Ming Court are referred to as 'tributary missions'" in the History of Ming.[40] Van Praag writes that these "tributary missions" were simply prompted by China's need for horses from Tibet, since a viable horse market in Mongol lands was closed as a result of incessant conflict.[40] Morris Rossabi also writes that "Tibet, which had extensive contacts with China during the Yuan, scarcely had diplomatic relations with the Ming."[41]
Maps made during the Ming dynasty
[edit]Maps made during the Ming dynasty usually drew Tibet outside the boundary of the Ming dynasty. The official Treatise on unity under Great Ming (大明一統志) described Tibet in volume 89 (out of 90 volumes) under foreign barbarians(外夷) who pay tribute to Ming. The overview map at the beginning shows Tibet to be distinct from China proper; regional names in China proper were in rectangles. Gui E, Minister of the Ministry of Officials, presented "Preface to Guang Yu Tu" to Jiajing Emperor, and the emperor praised it as "clear and concise". However, the map puts Tibet beyond the borders of Ming.[42]In 1594, Ming official Wang Pan made a map of the Ming dynasty, and Tibet was not included in the territory of Ming. Sancai Tuhui published by Ming official Wang Yi in 1609 included a world map, and Tibet was shown as a state as well as Great Ming.
Modern scholarly debates on Tibet-Ming relations
[edit]Inheritance, reappointments, and titles
[edit]Transition from Yuan to Ming
[edit]Historians disagree on what the relationship was between the Ming court and Tibet and whether or not Ming China had sovereignty over Tibet. Van Praag writes that Chinese court historians viewed Tibet as an independent foreign tributary and had little interest in Tibet besides a lama-patron relationship.[43][44] The historian Tsepon W. D. Shakabpa supports van Praag's position.[43] However, Wang Jiawei and Nyima Gyaincain state that these assertions by van Praag and Shakabpa are "fallacies".[43]
The government of PRC argues that the Ming emperor sent edicts to Tibet twice in the second year of the Ming dynasty, and demonstrated that he viewed Tibet as a significant region to pacify by urging various Tibetan tribes to submit to the authority of the Ming court.[43] They note that at the same time, the Mongol Prince Punala, who had inherited his position as ruler of areas of Tibet, went to Nanjing in 1371 to pay tribute and show his allegiance to the Ming court, bringing with him the seal of authority issued by the Yuan court.[45] They also state that since successors of lamas granted the title of "prince" had to travel to the Ming court to renew this title, and since lamas called themselves princes, the Ming court therefore had "full sovereignty over Tibet."[46] They state that the Ming dynasty, by issuing imperial edicts to invite ex-Yuan officials to the court for official positions in the early years of its founding, won submission from ex-Yuan religious and administrative leaders in the Tibetan areas, and thereby incorporated Tibetan areas into the rule of the Ming court. Thus, they conclude, the Ming court won the power to rule Tibetan areas formerly under the rule of the Yuan dynasty.[46]
Journalist and author Thomas Laird, in his book The Story of Tibet: Conversations with the Dalai Lama, writes that The Historical Status of China's Tibet presents the government viewpoint of the People's Republic of China, and fails to realize that China was "absorbed into a larger, non-Chinese political unit" during the Mongol Yuan dynasty, which the book paints as a characteristic Chinese dynasty succeeded by the Ming.[47] Laird asserts that the ruling Mongol khans never administered Tibet as part of China and instead ruled them as separate territories, comparing the Mongols with the British ruling over India and New Zealand, reasoning that much like Tibet, this did not make India part of New Zealand as a consequence.[48] Of later Mongol and Tibetan accounts interpreting the Mongol conquest of Tibet, Laird asserts that "they, like all non-Chinese historical narratives, never portray the Mongol subjugation of Tibet as a Chinese one."[48]

The Columbia Encyclopedia distinguishes between the Yuan dynasty and the other Mongol Empire khanates of Ilkhanate, Chagatai Khanate and the Golden Horde. It describes the Yuan dynasty as "A Mongol dynasty of China that ruled from 1271 to 1368, and a division of the great empire conquered by the Mongols. Founded by Kublai Khan, who adopted the Chinese dynastic name of Yüan in 1271."[50] The Encyclopedia Americana describes the Yuan dynasty as "the line of Mongol rulers in China" and adds that the Mongols "proclaimed a Chinese-style Yüan dynasty at Khanbaliq (Beijing)."[51] The Metropolitan Museum of Art writes that the Mongol rulers of the Yuan dynasty "adopted Chinese political and cultural models; ruling from their capitals in Dadu, they assumed the role of Chinese emperors,"[52] although Tibetologist Thomas Laird dismissed the Yuan dynasty as a non-Chinese polity and plays down its Chinese characteristics. The Metropolitan Museum of Art also noted that in spite of the gradual assimilation of Yuan monarchs, the Mongol rulers largely ignored the literati and imposed harsh policies discriminating against southern Chinese.[52] In his Kublai Khan: His Life and Times, Rossabi explains that Kublai "created government institutions that either resembled or were the same as the traditional Chinese ones", and he "wished to signal to the Chinese that he intended to adopt the trappings and style of a Chinese ruler".[53]
Nevertheless, the ethno-geographic caste hierarchy favoring the Mongols and other ethnicities were accorded higher status than the Han Chinese majority. Although Han Chinese who were recruited as advisers were often actually more influential than high officials, their status was not as well defined. Kublai also abolished the imperial examinations of China's civil service legacy, which was not reinstated until Ayurbarwada Buyantu Khan's reign (1311–1320).[54] Rossabi writes that Kublai recognized that in order to rule China, "he had to employ Chinese advisors and officials, yet he could not rely totally on Chinese advisers because he had to maintain a delicate balancing act between ruling the sedentary civilization of China and preserving the cultural identity and values of the Mongols."[19] And "in governing China, he was concerned with the interests of his Chinese subjects, but also with exploiting the resources of the empire for his own aggrandizement. His motivations and objectives alternated from one to the other throughout his reign," according to Rossabi.[55] Van Praag writes in The Status of Tibet that the Tibetans and Mongols, on the other hand, upheld a dual system of rule and an interdependent relationship that legitimated the succession of Mongol khans as universal Buddhist rulers, or chakravartin.[15] Van Praag writes that "Tibet remained a unique part of the Empire and was never fully integrated into it," citing examples such as a licensed border market that existed between China and Tibet during the Yuan.[15]
David M. Robinson contends that various edicts and laws issued by the Hongwu Emperor, founder of the Ming dynasty, seem to reject the Mongol influence in China with the banning of Mongolian marriage and burial practices, clothing, speech and even music.[56] However, Robinson highlights how this rhetoric contradicts the Hongwu Emperor's continuation of Yuan institutions such as the hereditary garrison system and occupations. He initiated campaigns to conquer areas not previously controlled by native Chinese dynasties, including territories in Yunnan, Liaodong (Manchuria), and Mongolia.[57] He continued to recruit Mongols into the military and maintained the Yuan-era tradition of bringing Korean concubines and eunuchs into the imperial palace.[57] Robinson claims that the Ming dynasty "was in many ways a true successor" to the Yuan, as the Ming emperors sought to legitimize their rule through the Yuan legacy, especially since the rival Northern Yuan dynasty continued to exist.[58] The Yongle Emperor was far more explicit in invoking a comparison between his rule and that of Kublai Khan, as reflected in his very active foreign policy, projection of Ming Chinese power abroad and expansionist military campaigns.[59] Following the 1449 Tumu Crisis, the Ming government actively discouraged further immigration of Mongol peoples (favoring occasional relocation policies for those who already lived in China).[60] Mongols continued to serve as Ming military officers even after Mongol involvement in the failed 1461 Rebellion of Cao Qin, yet their numbers began to decline as hereditary officers in general were gradually replaced by men of more humble origins.[61]
Ming practices of giving titles to Tibetans
[edit]The official position of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the People's Republic of China is that the Ming implemented a policy of managing Tibet according to conventions and customs, granting titles and setting up administrative organs over Tibet.[62] The State Council Information Office of the People's Republic states that the Ming dynasty's Ü-Tsang Commanding Office governed most areas of Tibet.[63] It also states that while the Ming abolished the policy council set up by the Mongol Yuan to manage local affairs in Tibet and the Mongol system of Imperial Tutors to govern religious affairs, the Ming adopted a policy of bestowing titles upon religious leaders who had submitted to the Ming dynasty.[63] For example, an edict of the Hongwu Emperor in 1373 appointed the Tibetan leader Choskunskyabs as the General of the Ngari Military and Civil Wanhu Office, stating:[64]
I, the sovereign of the Empire, courteously treat people from all corners of the Empire who love righteousness and pledge allegiance to the Court and assign them official posts. I have learned with great pleasure that you, Chos-kun-skyabs, who live in the Western Region, inspired by my power and reputation, are loyal to the Court and capable of safeguarding the territory in your charge. The mNgav-ris Military and Civil Wanhu Office has just been established. I, therefore, appoint you head of the office with the title of General Huaiyuan, believing that you are most qualified for the post. I expect you to be even more conscientious in your work than in the past, to comply with discipline and to care for your men so that security and peace in your region can be guaranteed.[64]

Chen Qingying, Professor of History and Director of the History Studies Institute under the China Tibetology Research Center in Beijing, writes that the Ming court conferred new official positions on ex-Yuan Tibetan leaders of the Phachu Kargyu and granted them lower-ranking positions.[65] Of the county (zong or dzong) leaders of Neiwo Zong and Renbam Zong, Chen states that when "the Emperor learned the actual situation of the Phachu Kargyu, the Ming court then appointed the main Zong leaders to be senior officers of the Senior Command of Dbus and Gtsang."[65] The official posts that the Ming court established in Tibet, such as senior and junior commanders, offices of Qianhu (in charge of 1,000 households), and offices of Wanhu (in charge of 10,000 households), were all hereditary positions according to Chen, but he asserts that "the succession of some important posts still had to be approved by the emperor," while old imperial mandates had to be returned to the Ming court for renewal.[65]
According to Tibetologist John Powers, Tibetan sources counter this narrative of titles granted by the Chinese to Tibetans with various titles which the Tibetans gave to the Chinese emperors and their officials. Tribute missions from Tibetan monasteries to the Chinese court brought back not only titles, but large, commercially valuable gifts which could subsequently be sold. The Ming emperors sent invitations to ruling lamas, but the lamas sent subordinates rather than coming themselves, and no Tibetan ruler ever explicitly accepted the role of being a vassal of the Ming.[66]
Hans Bielenstein writes that as far back as the Han dynasty (202 BCE–220 CE), the Han Chinese government "maintained the fiction" that the foreign officials administering the various "Dependent States" and oasis city-states of the Western Regions (composed of the Tarim Basin and oasis of Turpan) were true Han representatives due to the Han government's conferral of Chinese seals and seal cords to them.[67]
Changchub Gyaltsen
[edit]PRC government states that after the official title "Education Minister" was granted to Tai Situ Changchub Gyaltsen (1302–1364) by the Yuan court, this title appeared frequently with his name in various Tibetan texts, while his Tibetan title "Degsi" (sic properly sde-srid or desi) is seldom mentioned.[68] The book takes this to mean that "even in the later period of the Yuan Dynasty, the Yuan imperial court and the Phagmo Drupa regime maintained a Central-local government relation."[68] The Tai Situpa is even supposed to have written in his will: "In the past I received loving care from the emperor in the east. If the emperor continues to care for us, please follow his edicts and the imperial envoy should be well received."[68]

However, Lok-Ham Chan, a professor of history at the University of Washington, writes that Changchub Gyaltsen's aims were to recreate the old Tibetan Kingdom that existed during the Chinese Tang dynasty, to build "nationalist sentiment" amongst Tibetans, and to "remove all traces of Mongol suzerainty."[21] Georges Dreyfus, a professor of religion at Williams College, writes that it was Changchub Gyaltsen who adopted the old administrative system of Songtsän Gampo (c. 605–649)—the first leader of the Tibetan Empire to establish Tibet as a strong power—by reinstating its legal code of punishments and administrative units.[69] For example, instead of the 13 governorships established by the Mongol Sakya viceroy, Changchub Gyaltsen divided Central Tibet into districts (dzong) with district heads (dzong dpon) who had to conform to old rituals and wear clothing styles of old Imperial Tibet.[69] Van Praag asserts that Changchub Gyaltsen's ambitions were to "restore to Tibet the glories of its Imperial Age" by reinstating secular administration, promoting "national culture and traditions," and installing a law code that survived into the 20th century.[36]
According to Chen, the Ming officer of Hezhou (modern day Linxia) informed the Hongwu Emperor that the general situation in Dbus and Gtsang "was under control," and so he suggested to the emperor that he offer the second Phagmodru ruler, Jamyang Shakya Gyaltsen, an official title.[70] According to the Records of the Founding Emperor, the Hongwu Emperor issued an edict granting the title "Initiation State Master" to Sagya Gyaincain, while the latter sent envoys to the Ming court to hand over his jade seal of authority along with tribute of colored silk and satin, statues of the Buddha, Buddhist scriptures, and sarira.[70]
Dreyfus writes that after the Phagmodrupa lost its centralizing power over Tibet in 1434, several attempts by other families to establish hegemonies failed over the next two centuries until 1642 with the 5th Dalai Lama's effective hegemony over Tibet.[69]
Je Tsongkhapa
[edit]The Ming dynasty granted titles to lamas of schools such as the Karmapa Kargyu, but the latter had previously declined Mongol invitations to receive titles.[71] When the Ming Yongle Emperor invited Je Tsongkhapa (1357–1419), founder of the Gelug school, to come to the Ming court and pay tribute, the latter declined.[71] The Historical Status of China's Tibet says that this was due to old age and physical weakness, and also because of efforts being made to build three major monasteries.[72] Chen Qingying states that Tsongkhapa wrote a letter to decline the Emperor's invitation, and in this reply, Tsongkhapa wrote:[73]

It is not that I don't know it is the edict of the Great dominator of the world for the sake of Buddhist doctrine, or that I do not obey the edict of Your Majesty. I am seriously ill whenever I meet the public, so I cannot embark on a journey in compliance with the imperial edict. I wish that Your Majesty might be merciful, and not be displeased; it will really be a great mercy.[73]
A. Tom Grunfeld says that Tsongkhapa claimed ill health in his refusal to appear at the Ming court,[74] while Rossabi adds that Tsongkhapa cited the "length and arduousness of the journey" to China as another reason not to make an appearance.[75] This first request by the Ming was made in 1407, but the Ming court sent another embassy in 1413, this one led by the eunuch Hou Xian (候顯; fl. 1403–1427), which was again refused by Tsongkhapa.[75] Rossabi writes that Tsongkhapa did not want to entirely alienate the Ming court, so he sent his disciple Chosrje Shākya Yeshes to Nanjing in 1414 on his behalf, and upon his arrival in 1415 the Yongle Emperor bestowed upon him the title of "State Teacher"—the same title earlier awarded the Phagmodrupa ruler of Tibet.[71][74][75] The Xuande Emperor (r. 1425–1435) even granted this disciple Chosrje Shākya Yeshes the title of a "King" (王).[71] This title does not appear to have held any practical meaning, or to have given its holder any power, at Tsongkhapa's Ganden Monastery. Wylie notes that this—like the Karma Kargyu—cannot be seen as a reappointment of Mongol Yuan offices, since the Gelug school was created after the fall of the Yuan dynasty.[71]
Implications on the question of rule
[edit]Dawa Norbu argues that modern Chinese Communist historians tend to be in favor of the view that the Ming simply reappointed old Yuan dynasty officials in Tibet and perpetuated their rule of Tibet in this manner.[76] Norbu writes that, although this would have been true for the eastern Tibetan regions of Amdo and Kham's "tribute-cum-trade" relations with the Ming, it was untrue if applied to the western Tibetan regions of Ü-Tsang and Ngari. After the Phagmodrupa Changchub Gyaltsen, these were ruled by "three successive nationalistic regimes," which Norbu writes "Communist historians prefer to ignore."[76]
Laird writes that the Ming appointed titles to eastern Tibetan princes, and that "these alliances with eastern Tibetan principalities are the evidence China now produces for its assertion that the Ming ruled Tibet," despite the fact that the Ming did not send an army to replace the Mongols after they left Tibet.[77] Yiu Yung-chin states that the furthest western extent of the Ming dynasty's territory was Gansu, Sichuan, and Yunnan while "the Ming did not possess Tibet."[78]
Shih-Shan Henry Tsai writes that the Yongle Emperor sent his eunuch Yang Sanbao into Tibet in 1413 to gain the allegiance of various Tibetan princes, while the Yongle Emperor paid a small fortune in return gifts for tributes in order to maintain the loyalty of neighboring vassal states such as Nepal and Tibet.[79] However, Van Praag states that Tibetan rulers upheld their own separate relations with the kingdoms of Nepal and Kashmir, and at times "engaged in armed confrontation with them."[40]

Even though the Gelug exchanged gifts with and sent missions to the Ming court up until the 1430s,[80] the Gelug was not mentioned in the History of Ming or the Ming Veritable Records.[37] On this, historian Li Tieh-tseng says of Tsongkhapa's refusal of Ming invitations to visit the Yongle Emperor's court:[37]
In China not only the emperor could do no wrong, but also his prestige and dignity had to be upheld at any cost. Had the fact been made known to the public that Ch'eng-tsu's repeated invitations extended to Tsong-ka-pa were declined, the Emperor's prestige and dignity would have been considered as lowered to a contemptible degree, especially at a time when his policy to show high favours toward lamas was by no means popular and had already caused resentment among the people. This explains why no mention of Tsong-k'a-pa and the Yellow Sect was made in the Ming Shih and Ming Shih lu.[37]
Wylie asserts that this type of censorship of the History of Ming distorts the true picture of the history of Sino-Tibetan relations, while the Ming court granted titles to various lamas regardless of their sectarian affiliations in an ongoing civil war in Tibet between competing Buddhist factions.[81][82] Wylie argues that Ming titles of "King" granted indiscriminately to various Tibetan lamas or even their disciples should not be viewed as reappointments to earlier Yuan dynasty offices, since the viceregal Sakya regime established by the Mongols in Tibet was overthrown by the Phagmodru myriarchy before the Ming existed.[83]
Helmut Hoffman states that the Ming upheld the facade of rule over Tibet through periodic missions of "tribute emissaries" to the Ming court and by granting nominal titles to ruling lamas, but did not actually interfere in Tibetan governance.[38] Melvyn C. Goldstein writes that the Ming had no real administrative authority over Tibet, as the various titles given to Tibetan leaders did not confer authority as the earlier Mongol Yuan titles had.[39] He asserts that "by conferring titles on Tibetans already in power, the Ming emperors merely recognized political reality."[84] Hugh Edward Richardson writes that the Ming dynasty exercised no authority over the succession of Tibetan ruling families, the Phagmodru (1354–1435), Rinpungpa (1435–1565), and Tsangpa (1565–1642).[85]
Religious significance
[edit]In his usurpation of the throne from the Jianwen Emperor (r. 1398–1402), the Yongle Emperor was aided by the Buddhist monk Yao Guangxiao, and like his father, the Hongwu Emperor, the Yongle Emperor was "well-disposed towards Buddhism", claims Rossabi.[26] On March 10, 1403, the Yongle Emperor invited Deshin Shekpa, 5th Karmapa Lama (1384–1415), to his court, even though the fourth Karmapa had rejected the invitation of the Hongwu Emperor.[86] A Tibetan translation in the 16th century preserves the letter of the Yongle Emperor, which the Association for Asian Studies notes is polite and complimentary towards the Karmapa.[86] The letter of invitation reads,
My father and both parents of the queen are now dead. You are my only hope, essence of buddhahood. Please come quickly. I am sending as offering a large ingot of silver, one hundred fifty silver coins, twenty rolls of silk, a block of sandalwood, one hundred fifty bricks of tea and ten pounds of incense."[87]
In order to seek out the Karmapa, the Yongle Emperor dispatched his eunuch Hou Xian and the Buddhist monk Zhi Guang (d. 1435) to Tibet.[88] Traveling to Lhasa either through Qinghai or via the Silk Road to Khotan, Hou Xian and Zhi Guang did not return to Nanjing until 1407.[89]

During his travels beginning in 1403, Deshin Shekpa was induced by further exhortations by the Ming court to visit Nanjing by April 10, 1407.[86] Norbu writes that the Yongle Emperor, following the tradition of Mongol emperors and their reverence for the Sakya lamas, showed an enormous amount of deference towards Deshin Shekpa. The Yongle Emperor came out of the palace in Nanjing to greet the Karmapa and did not require him to kowtow like a tributary vassal.[90] According to Karma Thinley, the emperor gave the Karmapa the place of honor at his left, and on a higher throne than his own.[87] Rossabi and others describe a similar arrangement made by Kublai Khan and the Sakya Phagpa lama, writing that Kublai would "sit on a lower platform than the Tibetan cleric" when receiving religious instructions from him.[91][92]
Throughout the following month, the Yongle Emperor and his court showered the Karmapa with presents.[87] At Linggu Temple in Nanjing, he presided over the religious ceremonies for the Yongle Emperor's deceased parents, while twenty-two days of his stay were marked by religious miracles that were recorded in five languages on a gigantic scroll that bore the Emperor's seal.[86][88] During his stay in Nanjing, Deshin Shekpa was bestowed the title "Great Treasure Prince of Dharma" by the Yongle Emperor.[93] Elliot Sperling asserts that the Yongle Emperor, in bestowing Deshin Shekpa with the title of "King" and praising his mystical abilities and miracles, was trying to build an alliance with the Karmapa as the Mongols had with the Sakya lamas, but Deshin Shekpa rejected the Yongle Emperor's offer.[94] In fact, this was the same title that Kublai Khan had offered the Sakya Phagpa lama, but Deshin Shekpa persuaded the Yongle Emperor to grant the title to religious leaders of other Tibetan Buddhist sects.[75]

Tibetan sources say Deshin Shekpa also persuaded the Yongle Emperor not to impose his military might on Tibet as the Mongols had previously done.[86] Thinley writes that before the Karmapa returned to Tibet, the Yongle Emperor began planning to send a military force into Tibet to forcibly give the Karmapa authority over all the Tibetan Buddhist schools but Deshin Shekpa dissuaded him.[95] However, Hok-Lam Chan states that "there is little evidence that this was ever the emperor's intention" and that evidence indicates that Deshin Skekpa was invited strictly for religious purposes.[80]
Marsha Weidner states that Deshin Shekpa's miracles "testified to the power of both the emperor and his guru and served as a legitimizing tool for the emperor's problematic succession to the throne," referring to the Yongle Emperor's conflict with the previous Jianwen Emperor.[96] Tsai writes that Deshin Shekpa aided the legitimacy of the Yongle Emperor's rule by providing him with portents and omens which demonstrated Heaven's favor of the Yongle Emperor on the Ming throne.[88]
With the example of the Ming court's relationship with the fifth Karmapa and other Tibetan leaders, Norbu states that Chinese Communist historians have failed to realize the significance of the religious aspect of the Ming-Tibetan relationship.[97] He writes that the meetings of lamas with the Emperor of China were exchanges of tribute between "the patron and the priest" and were not merely instances of a political subordinate paying tribute to a superior.[97] He also notes that the items of tribute were Buddhist artifacts which symbolized "the religious nature of the relationship."[97] Josef Kolmaš writes that the Ming dynasty did not exercise any direct political control over Tibet, content with their tribute relations that were "almost entirely of a religious character."[98] Patricia Ann Berger writes that the Yongle Emperor's courting and granting of titles to lamas was his attempt to "resurrect the relationship between China and Tibet established earlier by the Yuan dynastic founder Khubilai Khan and his guru Phagpa."[49] She also writes that the later Qing emperors and their Mongol associates viewed the Yongle Emperor's relationship with Tibet as "part of a chain of reincarnation that saw this Han Chinese emperor as yet another emanation of Manjusri."[49]

The Information Office of the State Council of the PRC preserves an edict of the Zhengtong Emperor (r. 1435–1449) addressed to the Karmapa in 1445, written after the latter's agent had brought holy relics to the Ming court.[99] Zhengtong had the following message delivered to the Great Treasure Prince of Dharma, the Karmapa:
Out of compassion, Buddha taught people to be good and persuaded them to embrace his doctrines. You, who live in the remote Western Region, have inherited the true Buddhist doctrines. I am deeply impressed not only by the compassion with which you preach among the people in your region for their enlightenment, but also by your respect for the wishes of Heaven and your devotion to the Court. I am very pleased that you have sent bSod-nams-nyi-ma and other Tibetan monks here bringing with them statues of Buddha, horses and other specialties as tributes to the court.[99]
Despite this glowing message by the Emperor, Chan writes that a year later in 1446, the Ming court cut off all relations with the Karmapa hierarchs.[80] Until then, the court was unaware that Deshin Shekpa had died in 1415.[80] The Ming court had believed that the representatives of the Karma Kagyu who continued to visit the Ming capital were sent by the Karmapa.[80]
Tribute and exchanging tea for horses
[edit]

Tsai writes that shortly after the visit by Deshin Shekpa, the Yongle Emperor ordered the construction of a road and of trading posts in the upper reaches of the Yangzi and Mekong Rivers in order to facilitate trade with Tibet in tea, horses, and salt.[89][101] The trade route passed through Sichuan and crossed Shangri-La County in Yunnan.[89] The Historical Status of China's Tibet asserts that this "tribute-related trade" of the Ming exchanging Chinese tea for Tibetan horses—while granting Tibetan envoys and Tibetan merchants explicit permission to trade with Han Chinese merchants—"furthered the rule of the Ming dynasty court over Tibet".[102] Rossabi and Sperling note that this trade in Tibetan horses for Chinese tea existed long before the Ming.[28][103] Peter C. Perdue says that Wang Anshi (1021–1086), realizing that China could not produce enough militarily capable steeds, had also aimed to obtain horses from Inner Asia in exchange for Chinese tea.[104] The Chinese needed horses not only for cavalry but also as draft animals for the army's supply wagons.[104] The Tibetans required Chinese tea not only as a common beverage but also as a religious ceremonial supplement.[28] The Ming government imposed a monopoly on tea production and attempted to regulate this trade with state-supervised markets, but these collapsed in 1449 due to military failures and internal ecological and commercial pressures on the tea-producing regions.[28][104]
Van Praag states that the Ming court established diplomatic delegations with Tibet merely to secure urgently needed horses.[105] The Historical Status of China's Tibet argues that these were not diplomatic delegations at all, that Tibetan areas were ruled by the Ming since Tibetan leaders were granted positions as Ming officials, that horses were collected from Tibet as a mandatory "corvée" tax, and therefore Tibetans were "undertaking domestic affairs, not foreign diplomacy".[106] Sperling writes that the Ming simultaneously bought horses in the Kham region while fighting Tibetan tribes in Amdo and receiving Tibetan embassies in Nanjing.[25] He also argues that the embassies of Tibetan lamas visiting the Ming court were for the most part efforts to promote commercial transactions between the lamas' large, wealthy entourage and Ming Chinese merchants and officials.[107] Kolmaš writes that while the Ming maintained a laissez-faire policy towards Tibet and limited the numbers of the Tibetan retinues, the Tibetans sought to maintain a tributary relationship with the Ming because imperial patronage provided them with wealth and power.[108] Laird writes that Tibetans eagerly sought Ming court invitations since the gifts the Tibetans received for bringing tribute were much greater in value than the latter.[109] As for the Yongle Emperor's gifts to his Tibetan and Nepalese vassals such as silver wares, Buddha relics, utensils for Buddhist temples and religious ceremonies, and gowns and robes for monks, Tsai writes "in his effort to draw neighboring states to the Ming orbit so that he could bask in glory, the Yongle Emperor was quite willing to pay a small price".[110] The Information Office of the State Council of the PRC lists the Tibetan tribute items as oxen, horses, camels, sheep, fur products, medical herbs, Tibetan incenses, thangkas (painted scrolls), and handicrafts; while the Ming awarded Tibetan tribute-bearers an equal value of gold, silver, satin and brocade, bolts of cloth, grains, and tea leaves.[63] Silk workshops during the Ming also catered specifically to the Tibetan market with silk clothes and furnishings featuring Tibetan Buddhist iconography.[100]
While the Ming dynasty traded horses with Tibet, it upheld a policy of outlawing border markets in the north, which Laird sees as an effort to punish the Mongols for their raids and to "drive them from the frontiers of China."[111] However, after Altan Khan (1507–1582)—leader of the Tümed Mongols who overthrew the Oirat Mongol confederation's hegemony over the steppes—made peace with the Ming dynasty in 1571, he persuaded the Ming to reopen their border markets in 1573.[111] This provided the Chinese with a new supply of horses that the Mongols had in excess; it was also a relief to the Ming, since they were unable to stop the Mongols from periodic raiding.[111] Laird says that despite the fact that later Mongols believed Altan forced the Ming to view him as an equal, Chinese historians argue that he was simply a loyal Chinese citizen.[111] By 1578, Altan Khan formed a formidable Mongol-Tibetan alliance with the Gelug that the Ming viewed from afar without intervention.[112][113][114]
Armed intervention and border stability
[edit]Patricia Ebrey writes that Tibet, like Joseon Korea and other neighboring states to the Ming, settled for its tributary status while there were no troops or governors of Ming China stationed in its territory.[115] Laird writes that "after the Mongol troops left Tibet, no Ming troops replaced them."[77] The Historical Status of China's Tibet states that, despite the fact that the Ming refrained from sending troops to subdue Tibet and refrained from garrisoning Ming troops there, these measures were unnecessary so long as the Ming court upheld close ties with Tibetan vassals and their forces.[35] However, there were instances in the 14th century when the Hongwu Emperor did use military force to quell unrest in Tibet. John D. Langlois writes that there was unrest in Tibet and western Sichuan, which the Marquis Mu Ying (沐英) was commissioned to quell in November 1378 after he established a Taozhou garrison in Gansu.[116] Langlois notes that by October 1379, Mu Ying had allegedly captured 30,000 Tibetan prisoners and 200,000 domesticated animals.[116] Yet invasion went both ways; the Ming general Qu Neng, under the command of Lan Yu, was ordered to repel a Tibetan assault into Sichuan in 1390.[117]
One of the Ming princes was noted for delinquent behavior involving Tibetans. Zhu Shuang (Prince of Qin), a son of the Hongwu Emperor, had some Tibetan boys castrated and Tibetan women seized while under the influence of drugs, following a war against minority Tibetan peoples. After his death in 1395 from either a drug overdose or toxins mixed with his medicine, Zhu Shuang was posthumously reprimanded by his father for various actions, including those against Tibetan prisoners of war (involving the slaughter of nearly two-thousand captives).[118]

Discussions of strategy in the mid Ming dynasty focused primarily on recovery of the Ordos region, which the Mongols used as a rallying base to stage raids into Ming China.[119] Norbu states that the Ming dynasty, preoccupied with the Mongol threat to the north, could not spare additional armed forces to enforce or back up their claim of sovereignty over Tibet; instead, they relied on "Confucian instruments of tribute relations" of heaping unlimited number of titles and gifts on Tibetan lamas through acts of diplomacy.[120] Sperling states that the delicate relationship between the Ming and Tibet was "the last time a united China had to deal with an independent Tibet," that there was a potential for armed conflict at their borders, and that the ultimate goal of Ming foreign policy with Tibet was not subjugation but "avoidance of any kind of Tibetan threat."[121] P. Christiaan Klieger argues that the Ming court's patronage of high Tibetan lamas "was designed to help stabilize border regions and protect trade routes."[122]
Historians Luciano Petech and Sato Hisashi argue that the Ming upheld a "divide-and-rule" policy towards a weak and politically fragmented Tibet after the Sakya regime had fallen.[76] Chan writes that this was perhaps the calculated strategy of the Yongle Emperor, as exclusive patronage to one Tibetan sect would have given it too much regional power.[123] Sperling finds no textual evidence in either Chinese or Tibetan sources to support this thesis of Petech and Hisashi.[76] Norbu asserts that their thesis is largely based on the list of Ming titles conferred on Tibetan lamas rather than "comparative analysis of developments in China and Tibet."[76] Rossabi states that this theory "attributes too much influence to the Chinese," pointing out that Tibet was already politically divided when the Ming dynasty began.[28] Rossabi also discounts the "divide-and-rule" theory on the grounds of the Yongle Emperor's failed attempt to build a strong relationship with the fifth Karmapa—one which he hoped would parallel Kublai Khan's earlier relationship with the Sakya Phagpa lama.[75] Instead, the Yongle Emperor followed the Karmapa's advice of giving patronage to many different Tibetan lamas.[75]

The Association for Asian Studies states that there is no known written evidence to suggest that later leaders of the Gelug—Gendün Drup (1391–1474) and Gendün Gyatso (1475–1571)—had any contacts with Ming China.[124] These two religious leaders were preoccupied with an overriding concern for dealing with the powerful secular Rinpungpa princes, who were patrons and protectors of the Karma Kargyu lamas.[124] The Rinpungpa leaders were relatives of the Phagmodrupa, yet their authority shifted over time from simple governors to rulers in their own right over large areas of Ü-Tsang.[125] The prince of Rinbung occupied Lhasa in 1498 and excluded the Gelug from attending New Years ceremonies and prayers, the most important event in the Gelug.[126] While the task of New Years prayers in Lhasa was granted to the Karmapa and others, Gendün Gyatso traveled in exile looking for allies.[126] However, it was not until 1518 that the secular Phagmodru ruler captured Lhasa from the Rinbung, and thereafter the Gelug was given rights to conduct the New Years prayer.[126] When the Drikung Kagyu abbot of Drigung Monastery threatened Lhasa in 1537, Gendün Gyatso was forced to abandon the Drepung Monastery, although he eventually returned.[126]
The Zhengde Emperor (r. 1505–1521), who enjoyed the company of lamas at court despite protests from the censorate, had heard tales of a "living Buddha" which he desired to host at the Ming capital; this was none other than the Rinpung-supported Mikyö Dorje, 8th Karmapa Lama then occupying Lhasa.[127] Zhengde's top advisors made every attempt to dissuade him from inviting this lama to court, arguing that Tibetan Buddhism was wildly heterodox and unorthodox.[27] Despite protests by the Grand Secretary Liang Chu, in 1515 the Zhengde Emperor sent his eunuch official Liu Yun of the Palace Chancellery on a mission to invite this Karmapa to Beijing.[128] Liu commanded a fleet of hundreds of ships requisitioned along the Yangtze, consuming 2,835 g (100 oz) of silver a day in food expenses while stationed for a year in Chengdu of Sichuan.[129] After procuring necessary gifts for the mission, he departed with a cavalry force of about 1,000 troops.[129] When the request was delivered, the Karmapa lama refused to leave Tibet despite the Ming force brought to coerce him.[129] The Karmapa launched a surprise ambush on Liu Yun's camp, seizing all the goods and valuables while killing or wounding half of Liu Yun's entire escort.[129] After this fiasco, Liu fled for his life, but only returned to Chengdu several years later to find that the Zhengde Emperor had died.[129]
Tibetans as a "national minority"
[edit]

Elliot Sperling, a specialist of Indian studies and the director of the Tibetan Studies program at Indiana University’s Department of Central Eurasia Studies, writes that "the idea that Tibet became part of China in the 13th century is a very recent construction."[131] He writes that Chinese writers of the early 20th century were of the view that Tibet was not annexed by China until the Manchu Qing dynasty invasion during the 18th century.[131] He also states that Chinese writers of the early 20th century described Tibet as a feudal dependency of China, not an integral part of it.[131] Sperling states that this is because "Tibet was ruled as such, within the empires of the Mongols and the Manchus" and also that "China's intervening Ming dynasty ... had no control over Tibet."[131] He writes that the Ming relationship with Tibet is problematic for China's insistence of its unbroken sovereignty over Tibet since the 13th century.[131] As for the Tibetan view that Tibet was never subject to the rule of the Yuan or Qing emperors of China, Sperling also discounts this by stating that Tibet was "subject to rules, laws and decisions made by the Yuan and Qing rulers" and that even Tibetans described themselves as subjects of these emperors.[131]
Josef Kolmaš, a sinologist, Tibetologist, and Professor of Oriental Studies at the Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, writes that it was during the Qing dynasty "that developments took place on the basis of which Tibet came to be considered an organic part of China, both practically and theoretically subject to the Chinese central government."[132] Yet he states that this was a radical change in regards to all previous eras of Sino-Tibetan relations.[132]
P. Christiaan Klieger, an anthropologist and scholar of the California Academy of Sciences in San Francisco, writes that the vice royalty of the Sakya regime installed by the Mongols established a patron and priest relationship between Tibetans and Mongol converts to Tibetan Buddhism.[122] According to him, the Tibetan lamas and Mongol khans upheld a "mutual role of religious prelate and secular patron," respectively.[122] He adds that "Although agreements were made between Tibetan leaders and Mongol khans, Ming and Qing emperors, it was the Republic of China and its Communist successors that assumed the former imperial tributaries and subject states as integral parts of the Chinese nation-state."[122]
Marina Illich, a scholar of Indo-Tibetan Buddhism, while discussing the life of the Gelug lama Chankya Rolpe Dorje (1717–1786), mentions the limitations of both Western and Chinese modern scholarship in their interpretation of Tibetan sources. As for the limitations imposed on scholars by the central government of the People's Republic of China on issues regarding the history of Tibet, Illich writes:[130]
PRC scholars ... work under the strict supervision of censor bureaus and must adhere to historiographic guidelines issued by the state [and] have little choice but to frame their discussion of eighteenth-century Tibetan history in the anachronistic terms of contemporary People's Republic of China (P.R.C.) state discourse ... Bound by Party directives, these scholars have little choice but to portray Tibet as a trans-historically inalienable part of China in a way that profoundly obscures questions of Tibetan agency.[130]
Chinese state media publication China Daily states in a 2008 article that although there were dynastic changes after Tibet was incorporated into the territory of Yuan dynasty's China in the 13th century, "Tibet has remained under the jurisdiction of the central government of China."[133] It also states that the Ming dynasty "inherited the right to rule Tibet" from the Yuan dynasty, and repeats the claims in the History of Ming about the Ming establishing two itinerant high commands over Tibet.[133] China Daily states that the Ming handled Tibet's civil administration, appointed all leading officials of these administrative organs, and punished Tibetans who broke the law.[133] The article was republished in other Chinese state media publications, such as People's Daily, Xinhua News Agency, China Central Television.[134][135]
Mongol-Tibetan alliance
[edit]Altan Khan and the Dalai Lama
[edit]
During the reign of the Jiajing Emperor (r. 1521–1567), the native Chinese ideology of Daoism was fully sponsored at the Ming court, while Tibetan Vajrayana and even Chinese Buddhism were ignored or suppressed.[37] Even the History of Ming states that the Tibetan lamas discontinued their trips to Ming China and its court at this point.[37] Grand Secretary Yang Tinghe under Jiajing was determined to break the eunuch influence at court which typified the Zhengde era,[136] an example being the costly escort of the eunuch Liu Yun as described above in his failed mission to Tibet. The court eunuchs were in favor of expanding and building new commercial ties with foreign countries such as Portugal, which Zhengde deemed permissible since he had an affinity for foreign and exotic people.[136]
With the death of Zhengde and ascension of Jiajing, the politics at court shifted in favor of the Neo-Confucian establishment which not only rejected the Portuguese embassy of Fernão Pires de Andrade (d. 1523),[136] but had a predisposed animosity towards Tibetan Buddhism and lamas.[128] Evelyn S. Rawski, a professor in the Department of History of the University of Pittsburgh, writes that the Ming's unique relationship with Tibetan prelates essentially ended with Jiajing's reign while Ming influence in the Amdo region was supplanted by the Mongols.[137]
The Chinese Ming dynasty also deliberately helped to propagate Tibetan Buddhism instead of Chinese Buddhism among the Mongols. The Ming assisted Altan Khan, King of the Tümed Mongols, when he requested aid in propagating Vajrayana Buddhism.[138]
Meanwhile, the Tumed Mongols began moving into the Kokonor region (modern Qinghai), raiding the Ming Chinese frontier and even as far as the suburbs of Beijing under Altan Khan (1507–1582).[37][139] Klieger writes that Altan Khan's presence in the west effectively reduced Ming influence and contact with Tibet.[140] After Altan Khan made peace with the Ming dynasty in 1571, he invited the third hierarch of the Gelug—Sönam Gyatso (1543–1588)—to meet him in Amdo (modern Qinghai) in 1578, where he accidentally bestowed him and his two predecessors with the title of Dalai Lama—"Ocean Teacher".[37][141] The full title was "Dalai Lama Vajradhara", "Vajradhara" meaning "Holder of the Thunderbolt" in Sanskrit.[141][142] Victoria Huckenpahler notes that Vajradhara is considered by Buddhists to be the primordial Buddha of limitless and all-pervasive beneficial qualities, a being that "represents the ultimate aspect of enlightenment."[143] Goldstein writes that Sönam Gyatso also enhanced Altan Khan's standing by granting him the title "king of religion, majestic purity".[112] Rawski writes that the Dalai Lama officially recognized Altan Khan as the "Protector of the Faith".[144]

Laird writes that Altan Khan abolished the native Mongol practices of shamanism and blood sacrifice, while the Mongol princes and subjects were coerced by Altan to convert to Gelug Buddhism—or face execution if they persisted in their shamanistic ways.[145] Committed to their religious leader, Mongol princes began requesting the Dalai Lama to bestow titles on them, which demonstrated "the unique fusion of religious and political power" wielded by the Dalai Lama, as Laird writes.[146] Kolmaš states that the spiritual and secular Mongol-Tibetan alliance of the 13th century was renewed by this alliance constructed by Altan Khan and Sönam Gyatso.[147] Van Praag writes that this restored the original Mongol patronage of a Tibetan lama and "to this day, Mongolians are among the most devout followers of the Gelugpa and the Dalai Lama."[148] Angela F. Howard writes that this unique relationship not only provided the Dalai Lama and Panchen Lama with religious and political authority in Tibet, but that Altan Khan gained "enormous power among the entire Mongol population."[149]
Rawski writes that Altan Khan's conversion to the Gelug "can be interpreted as an attempt to expand his authority in his conflict with his nominal superior, Tümen Khan."[144] To further cement the Mongol-Tibetan alliance, the great-grandson of Altan Khan—the 4th Dalai Lama (1589–1616)—was made the fourth Dalai Lama.[37][142] In 1642, the 5th Dalai Lama (1617–1682) became the first to wield effective political control over Tibet.[69]
Contact with the Ming dynasty
[edit]
Sonam Gyatso, after being granted the grandiose title by Altan Khan, departed for Tibet. Before he left, he sent a letter and gifts to the Ming Chinese official Zhang Juzheng (1525–1582), which arrived on March 12, 1579.[150] Sometime in August or September of that year, Sonam Gyatso's representative stationed with Altan Khan received a return letter and gift from the Wanli Emperor (r. 1572–1620), who also conferred upon Sonam Gyatso a title; this was the first official contact between a Dalai Lama and a government of China.[150] However, Laird states that when Wanli invited him to Beijing, the Dalai Lama declined the offer due to a prior commitment, even though he was only 400 km (250 mi) from Beijing.[146] Laird adds that "the power of the Ming emperor did not reach very far at the time."[146] Although not recorded in any official Chinese records, Sonam Gyatso's biography states that Wanli again conferred titles on Sonam Gyatso in 1588, and invited him to Beijing for a second time, but Sonam Gyatso was unable to visit China as he died the same year in Mongolia working with Altan Khan's son to further the spread of Buddhism.[146][150]
Of the third Dalai Lama, China Daily states that the "Ming dynasty showed him special favor by allowing him to pay tribute."[133] China Daily then says that Sonam Gyatso was granted the title Dorjichang or Vajradhara Dalai Lama in 1587 [sic!],[133] but China Daily does not mention who granted him the title. Without mentioning the role of the Mongols, China Daily states that it was the successive Qing dynasty which established the title of Dalai Lama and his power in Tibet: "In 1653, the Qing emperor granted an honorific title to the fifth Dalai Lama and then did the same for the fifth Panchen Lama in 1713, officially establishing the titles of the Dalai Lama and the Panchen Erdeni, and their political and religious status in Tibet."[133]
Chen states that the fourth Dalai Lama Yonten Gyatso was granted the title "Master of Vajradhara" and an official seal by the Wanli Emperor in 1616.[151] This was noted in the Biography of the Fourth Dalai Lama, which stated that one Soinam Lozui delivered the seal of the Emperor to the Dalai Lama.[151] The Wanli Emperor had invited Yonten Gyatso to Beijing in 1616, but just like his predecessor he died before being able to make the journey.[151]
Kolmaš writes that, as the Mongol presence in Tibet increased, culminating in the conquest of Tibet by a Mongol leader in 1642, the Ming emperors "viewed with apparent unconcern these developments in Tibet."[113] He adds that the Ming court's lack of concern for Tibet was one of the reasons why the Mongols pounced on the chance to reclaim their old vassal of Tibet and "fill once more the political vacuum in that country."[98] On the mass Mongol conversion to Tibetan Buddhism under Altan Khan, Laird writes that "the Chinese watched these developments with interest, though few Chinese ever became devout Tibetan Buddhists."[114]
Civil war and Güshi Khan's conquest
[edit]
In 1565, the powerful Rinbung princes were overthrown by one of their own ministers, Karma Tseten who styled himself as the Tsangpa, "the one of Tsang", and established his base of power at Shigatse.[85][141][152] The second successor of this first Tsang king, Karma Phuntsok Namgyal, took control of the whole of Central Tibet (Ü-Tsang), reigning from 1611 to 1621.[153] Despite this, the leaders of Lhasa still claimed their allegiance to the Phagmodru as well as the Gelug, while the Ü-Tsang king allied with the Karmapa.[153] Tensions rose between the nationalistic Ü-Tsang ruler and the Mongols who safeguarded their Mongol Dalai Lama in Lhasa.[141] The fourth Dalai Lama refused to give an audience to the Ü-Tsang king, which sparked a conflict as the latter began assaulting Gelug monasteries.[141] Chen writes of the speculation over the fourth Dalai Lama's mysterious death and the plot of the Ü-Tsang king to have him murdered for "cursing" him with illness, although Chen writes that the murder was most likely the result of a feudal power struggle.[154] In 1618, only two years after Yonten Gyatso died, the Gelug and the Karma Kargyu went to war, the Karma Kargyu supported by the secular Ü-Tsang king.[155] The Ü-Tsang ruler had a large number of Gelugpa lamas killed, occupied their monasteries at Drepung and Sera, and outlawed any attempts to find another Dalai Lama.[155] In 1621, the Ü-Tsang king died and was succeeded by his young son Karma Tenkyong, an event which stymied the war effort as the latter accepted the six-year-old Lozang Gyatso as the new Dalai Lama.[141] Despite the new Dalai Lama's diplomatic efforts to maintain friendly relations with the new Ü-Tsang ruler, Sonam Rapten (1595–1657), the Dalai Lama's chief steward and treasurer at Drepung, made efforts to overthrow the Ü-Tsang king, which led to another conflict.[156] In 1633, the Gelugpas and several thousand Mongol adherents defeated the Ü-Tsang king's troops near Lhasa before a peaceful negotiation was settled.[155] Goldstein writes that in this the "Mongols were again playing a significant role in Tibetan affairs, this time as the military arm of the Dalai Lama."[155]

When an ally of the Ü-Tsang ruler threatened destruction of the Gelugpas again, the fifth Dalai Lama Lozang Gyatso pleaded for help from the Mongol prince Güshi Khan (1582–1655), leader of the Khoshut (Qoshot) tribe of the Oirat Mongols, who was then on a pilgrimage to Lhasa.[142][157][158][159] Güshi Khan accepted his role as protector, and from 1637 to 1640 he not only defeated the Gelugpas' enemies in the Amdo and Kham regions, but also resettled his entire tribe into Amdo.[142][157] Sonam Chöpel urged Güshi Khan to assault the Ü-Tsang king's homebase of Shigatse, which Güshi Khan agreed upon, enlisting the aid of Gelug monks and supporters.[157][159] In 1642, after a year's siege of Shigatse, the Ü-Tsang forces surrendered.[159] Güshi Khan then captured and summarily executed Karma Tenkyong, the ruler of Ü-Tsang, King of Tibet.[157][158]
Soon after the victory in Ü-Tsang, Güshi Khan organized a welcoming ceremony for Lozang Gyatso once he arrived a day's ride from Shigatse, presenting his conquest of Tibet as a gift to the Dalai Lama.[159] In a second ceremony held within the main hall of the Shigatse fortress, Güshi Khan enthroned the Dalai Lama as the ruler of Tibet, but conferred the actual governing authority to the regent Sonam Chöpel.[157][158][159] Although Güshi Khan had granted the Dalai Lama "supreme authority" as Goldstein writes, the title of 'King of Tibet' was conferred upon Güshi Khan, spending his summers in pastures north of Lhasa and occupying Lhasa each winter.[113][157][160] Van Praag writes that at this point Güshi Khan maintained control over the armed forces, but accepted his inferior status towards the Dalai Lama.[160] Rawski writes that the Dalai Lama shared power with his regent and Güshi Khan during his early secular and religious reign.[161] However, Rawski states that he eventually "expanded his own authority by presenting himself as Avalokiteśvara through the performance of rituals," by building the Potala Palace and other structures on traditional religious sites, and by emphasizing lineage reincarnation through written biographies.[162] Goldstein states that the government of Güshi Khan and the Dalai Lama persecuted the Karma Kagyu sect, confiscated their wealth and property, and even converted their monasteries into Gelug monasteries.[157] Rawski writes that this Mongol patronage allowed the Gelugpas to dominate the rival religious sects in Tibet.[162]

Meanwhile, the Chinese Ming dynasty fell to the rebellion of Li Zicheng (1606–1645) in 1644, yet his short-lived Shun dynasty was crushed by the Manchu invasion and the Han Chinese general Wu Sangui (1612–1678). China Daily states that when the following Qing dynasty replaced the Ming dynasty, it merely "strengthened administration of Tibet."[133] However, Kolmaš states that the Dalai Lama was very observant of what was going on in China and accepted a Manchu invitation in 1640 to send envoys to their capital at Mukden in 1642, before the Ming collapsed.[163][164] Dawa Norbu, William Rockhill, and George N. Patterson write that when the Shunzhi Emperor (r. 1644–1661) of the subsequent Qing dynasty invited the fifth Dalai Lama Lozang Gyatso to Beijing in 1652, Shunzhi treated the Dalai Lama as an independent sovereign of Tibet.[97][165] Patterson writes that this was an effort of Shunzhi to secure an alliance with Tibet that would ultimately lead to the establishment of Manchu rule over Mongolia.[165] In this meeting with the Qing emperor, Goldstein asserts that the Dalai Lama was not someone to be trifled with due to his alliance with Mongol tribes, some of which were declared enemies of the Qing.[166] Van Praag states that Tibet and the Dalai Lama's power was recognized by the "Manchu Emperor, the Mongolian Khans and Princes, and the rulers of Ladakh, Nepal, India, Bhutan, and Sikkim."[164]
When the Dzungar Mongols attempted to spread their territory from what is now Xinjiang into Tibet, the Kangxi Emperor (r. 1661–1722) responded to Tibetan pleas for aid with his own expedition to Tibet, occupying Lhasa in 1720.[115][167] By 1751, during the reign of the Qianlong Emperor (r. 1735–1796), a protectorate and permanent Qing dynasty garrison was established in Tibet.[115][167] As of 1751, Albert Kolb writes that "Chinese claims to suzerainty over Tibet date from this time."[167]
Administrative offices and officials' titles of the Ming
[edit]| Ming administrative divisions established in Tibet according to the History of Ming[34] | |
|---|---|
| Itinerant High Commandery (都指揮使司, Regional Military Commission) | Dbus-Gtsang (烏思藏, U-Tsang), Mdo-khams (朵甘, Dokham) |
| Itinerant Commandery (指揮使司) | Longda (隴答) |
| Pacification Commissioner's Office (宣尉使司) | Duogan (朵甘, Dokham), Dongbuhanhu (董卜韓胡), Changhexiyutongningyuan (長河西魚通寧遠) |
| Military-civil Marshall's office (军民元帅府) | Elis(俄力思, E Li Si) |
| Expedition Commissioner's Office (招討司) | Duogansi (朵甘思), Duoganlongda (朵甘隴答), Duogandan (朵甘丹), Duogancangtang (朵甘倉溏), Duoganchuan (朵甘川), Moerkan (磨兒勘) |
| Wanhu offices (萬戶府) | Shaerke (沙兒可), Naizhu (乃竹), Luosiduan (羅思端), Biesima (別思麻) |
| Qianhu offices (千戶所) | Duogansi (朵甘思), Suolazong (所剌宗), Suobolijia (所孛里加), Suochanghexi (所長河西), Suoduobasansun (所多八三孫), Suojiaba (所加八), Suozhaori (所兆日), Nazhu (納竹), Lunda (倫答), Guoyou (果由), Shalikehahudi (沙里可哈忽的), Bolijiasi (孛里加思), Shalituer (撒裏土兒), Canbulang (參卜郎), Lacuoya (剌錯牙), Xieliba (泄里壩), Runzelusun (潤則魯孫) |
| Ming titles granted to Tibetan leaders | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Name | Sect | Year | |
| Princes of Dharma (法王) | Great Treasure Prince of Dharma (大寶法王) | Tulku Tsurphu Karmapa Deshin Shekpa[93] | Karma Kagyu Sect | 1407 |
| Great Vehicle Prince of Dharma (大乘法王) | Prince of Dharma of the Sakya Sect (represented by Gunga Zhaxi)[93] | Sakya Sect | 1413 | |
| Great Mercy Prince of Dharma (大慈法王) | Shākya Yeshes (representative of Je Tsongkhapa)[93] | Gelug | 1434 | |
| Princes (王) | Prince of Persuasion (闡化王) | Zhaba Gyaincain[168] | Phagmo Drupa Sect | 1406 |
| Promotion Prince of Virtue (贊善王) | Zhusibar Gyaincain[168] | Lingzang | 1407 | |
| Guardian Prince of Doctrine (護教王) | Namge Bazangpo[73] | Guanjor | 1407 | |
| Propagation Prince of Doctrine (闡教王) | Linzenbal Gyangyanzang[93] | Zhigung Gagyu Sect | 1413 | |
| Assistant Prince of Doctrine (輔教王) | Namkelisiba (Namkelebei Lobzhui Gyaincain Sangpo)[73] | Sakya Sect | 1415 | |
See also
[edit]- Foreign relations of imperial China
- Foreign relations of Tibet
- History of China
- History of Tibet
- Patron and priest relationship
- Tibetan sovereignty debate
- Tang–Tibet relations
- Song–Tibet relations
- Tibet under Yuan rule
- Tibet under Qing rule
- Ming dynasty in Inner Asia
- Manchuria under Ming rule
- Fourth Chinese domination of Vietnam
References
[edit]- ^ Melvyn C. Goldstein, Snow Lion and the Dragon: China, Tibet and the Dalai Lama (Berkeley: University of California Press, 1997), 1.
- ^ Denis Twitchett, "Tibet in Tang's Grand Strategy", in Warfare in Chinese History (Leiden: Koninklijke Brill, 2000), 106–179.
- ^ Michael C. van Walt van Praag, The Status of Tibet: History, Rights, and Prospects in International Law (Boulder: Westview Press, 1987), 1–2.
- ^ Josef Kolmas, Tibet and Imperial China: A Survey of Sino-Tibetan Relations Up to the End of the Manchu Dynasty in 1912: Occasional Paper 7 (Canberra: The Australian National University, Centre of Oriental Studies, 1967), 12–14.
- ^ a b Van Praag, The Status of Tibet, 4.
- ^ a b Kolmas, Tibet and Imperial China, 14–17.
- ^ a b c d e Van Praag, The Status of Tibet, 5.
- ^ Hok-Lam Chan, "The Chien-wen, Yung-lo, Hung-shi, and Hsuan-te reigns", in The Cambridge History of China: Volume 7, The Ming Dynasty, 1368–1644, Part 1 (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1988), 261.
- ^ Goldstein, The Snow Lion and the Dragon, 2–3.
- ^ a b c Goldstein, The Snow Lion and the Dragon, 3.
- ^ Morris Rossabi, Khubilai Khan: His Life and Times (Berkeley: University of California Press, 1988), 18.
- ^ Rossabi, Khubilai Khan, 14–41.
- ^ a b Rossabi, Khubilai Khan, 40–41.
- ^ George N. Patterson, "China and Tibet: Background to the Revolt", The China Quarterly, no. 1 (January–March 1960): 88.
- ^ a b c d e f Van Praag, The Status of Tibet, 6.
- ^ a b Patterson, "China and Tibet", 88–89.
- ^ Turrell V. Wylie, "The First Mongol Conquest of Tibet Reinterpreted", Harvard Journal of Asiatic Studies 37, no. 1 (June 1997): 104.
- ^ a b c Van Praag, The Status of Tibet, 6–7.
- ^ a b Rossabi, Khubilai Khan, 115.
- ^ Denis Twitchett, Herbert Franke, John K. Fairbank, in The Cambridge History of China: Volume 6, Alien Regimes and Border States (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1994), 454.
- ^ a b c d e f Chan, "The Chien-wen, Yung-lo, Hung-shi, and Hsuan-te reigns", 262.
- ^ a b Goldstein, The Snow Lion and the Dragon, 4.
- ^ Patricia B. Ebrey, Cambridge Illustrated History of China (New York: Cambridge University Press, 1999), 190–191.
- ^ Morris Rossabi, "The Ming and Inner Asia," in The Cambridge History of China: Volume 8, The Ming Dynasty, 1368–1644, Part 2 (New York: Cambridge University Press, 1998), 242–243.
- ^ a b c Elliot Sperling, "The 5th Karma-pa and some aspects of the relationship between Tibet and the Early Ming", in The History of Tibet: Volume 2, The Medieval Period: c. AD 850–1895, the Development of Buddhist Paramountcy (New York: Routledge, 2003), 475.
- ^ a b c Rossabi, "The Ming and Inner Asia," 242.
- ^ a b c Gray Tuttle, Tibetan Buddhists in the Making of Modern China (New York: Columbia University Press, 2005), 27.
- ^ a b c d e Rossabi, "The Ming and Inner Asia," 243.
- ^ 劉漢城 2019, pp. 27–30.
- ^ a b History of Ming-Western Regions III 《明史·卷三百三十一·列傳第二百十七·西域三》
- ^ For Korea, Vietnam and Mongol in the History of Ming, see 明史·卷三百二十·列傳第二百八·外國一·朝鮮, 明史·卷三百二十一·列傳第二百〇九·外國二·安南, 明史·卷三百二十七·列傳第二百十五·外國八·韃靼
- ^ History of Ming-Geography I 《明史·志第十六·地理一》:計明初封略,東起朝鮮,西據吐番,南包安南,北距大磧。Note here it refers to the extent of fiefdoms that pays tribute to Ming, not territory of Ming, as Korea, Vietnam and Mongol were categorized under foreign states in the History of Ming.
- ^ History of Ming-Geography III 《明史·地理三》: 七年七月置西安行都衛於此,領河州、朵甘、烏斯藏、三衛。
- ^ a b History of Ming-Military II 《明史•兵二》
- ^ a b Wang & Nyima, The Historical Status of China's Tibet, 38.
- ^ a b Van Praag, The Status of Tibet, 7.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Turrell V. Wylie, "Lama Tribute in the Ming Dynasty", in The History of Tibet: Volume 2, The Medieval Period: c. AD 850–1895, the Development of Buddhist Paramountcy (New York: Routledge, 2003), 470.
- ^ a b Helmut Hoffman, "Early and Medieval Tibet", in The History of Tibet: Volume 1, The Early Period to c. AD 850, the Yarlung Dynasty (New York: Routledge, 2003), 65.
- ^ a b Goldstein, The Snow Lion and the Dragon, 4–5.
- ^ a b c Van Praag, The Status of Tibet, 8.
- ^ Morris Rossabi, "The Ming and Inner Asia," in The Cambridge History of China: Volume 8, The Ming Dynasty, 1368–1644, Part 2 (New York: Cambridge University Press, 1998), 241.
- ^ 劉漢城 2019, pp. 43–44.
- ^ a b c d Wang & Nyima, The Historical Status of China's Tibet, 31.
- ^ Van Praag, The Status of Tibet, 7–8.
- ^ Wang & Nyima, The Historical Status of China's Tibet, 32.
- ^ a b Wang & Nyima, The Historical Status of China's Tibet, 37.
- ^ Thomas Laird, The Story of Tibet: Conversations with the Dalai Lama (New York: Grove Press, 2006), 106–107.
- ^ a b Laird, The Story of Tibet, 107.
- ^ a b c Patricia Ann Berger, Empire of Emptiness: Buddhist Art and Political Authority in Qing China (Manoa: University of Hawaii Press, 2003), 184.
- ^ The Columbia Encyclopedia, Sixth Edition (2001–07). Yuan Archived 2008-05-09 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved on 2008-04-28.
- ^ Encyclopedia Americana. (2008). Grolier Online. "Hucker, Charles H. "Yüan Dynasty"[permanent dead link] Retrieved on 2008-04-28.
- ^ a b The Metropolitan Museum of Art. "Yuan Dynasty (1279–1368)". In Timeline of Art History. Retrieved on 2008-04-28.
- ^ Rossabi, Khubilai Khan, 56.
- ^ Rossabi, Khubilai Khan, 30, 71–72, 117, 130.
- ^ Rossabi, Khubilai Khan, 115–116.
- ^ Robinson, "The Ming Court and the Legacy of the Yuan Mongols", pp 367-368.
- ^ a b Robinson, "The Ming Court and the Legacy of the Yuan Mongols", p. 368.
- ^ Robinson, "The Ming Court and the Legacy of the Yuan Mongols", p. 368-369.
- ^ Robinson, "The Ming Court and the Legacy of the Yuan Mongols", pp 369-370.
- ^ Robinson, "Politics, Force and Ethnicity in Ming China", pp 84-85.
- ^ Robinson, "Politics, Force and Ethnicity in Ming China", pp 116-117.
- ^ Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the People's Republic of China (November 15, 2000). "Did Tibet Become an Independent Country after the Revolution of 1911?". Retrieved on 2008-05-02.
- ^ a b c Information Office of the State Council of the People's Republic of China, Testimony of History (China Intercontinental Press, 2002), 73.
- ^ a b Information Office of the State Council, Testimony of History, 75.
- ^ a b c Chen, Tibetan History, 48.
- ^ Powers 2004, pp. 58–9
- ^ Hans Bielenstein, The Bureaucracy of Han Times (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1980), 110.
- ^ a b c Wang & Nyima, The Historical Status of China's Tibet, 42.
- ^ a b c d Georges Dreyfus, "Cherished memories, cherished communities: proto-nationalism in Tibet", in The History of Tibet: Volume 2, The Medieval Period: c. AD 850–1895, the Development of Buddhist Paramountcy (New York: Routledge, 2003), 504.
- ^ a b Chen, Tibetan History, 44.
- ^ a b c d e Wylie, "Lama Tribute in the Ming Dynasty", 469–470.
- ^ Wang & Nyima, The Historical Status of China's Tibet, 35.
- ^ a b c d Chen Qingying, Tibetan History (Beijing: China Intercontinental Press, 2003), 51; original text: 余非不知此是大地之大主宰為佛法著想之諭旨,亦非不遵不敬陛下之詔書,但我每與眾人相會,便發生重病,故不能遵照聖旨而行,惟祈陛下如虛空廣大之胸懷,不致不悅,實為幸甚。
- ^ a b A. Tom Grunfeld, The Making of Modern Tibet (New York: M.E. Sharpe, Inc., 1996), 40.
- ^ a b c d e f Rossabi, "The Ming and Inner Asia," 244.
- ^ a b c d e Dawa Norbu, China's Tibet Policy (Richmond: Curzon, 2001), 58.
- ^ a b Laird, The Story of Tibet, 137.
- ^ Yiu Yung-chin, "Two Focuses of the Tibet Issue", in Tibet Through Dissident Chinese Eyes: Essays on Self-determination (New York: M.E. Sharpe, Inc., 1998), 121.
- ^ Shih-Shan Henry Tsai, Perpetual Happiness: The Ming Emperor Yongle (Seattle: University of Washington Press, 2001), 187–188.
- ^ a b c d e Chan, "The Chien-wen, Yung-lo, Hung-shi, and Hsuan-te reigns", 263.
- ^ Wylie, "Lama Tribute in the Ming Dynasty", 470–471.
- ^ Riggs, "Tibet in Extremis", Far Eastern Survey 19, no. 21 (1950): 226.
- ^ Wylie, "Lama Tribute in the Ming Dynasty", 468–469.
- ^ Goldstein, The Snow Lion and the Dragon, 5.
- ^ a b Kolmas, Tibet and Imperial China, 29.
- ^ a b c d e The Ming Biographical History Project of the Association for Asian Studies, Dictionary of Ming Biography, 1368–1644: 明代名人傳: Volume 1, A-L (New York: Columbia University Press, 1976), 482.
- ^ a b c Karma Thinley, The History of the Sixteen Karmapas of Tibet (Boulder: Prajna Press, 1980), 72.
- ^ a b c Tsai, Perpetual Happiness, 84.
- ^ a b c Tsai, Perpetual Happiness, 187.
- ^ Norbu, China's Tibet Policy, 51–52.
- ^ Rossabi, Khubilai Khan, 41.
- ^ Powers 2004, p. 53.
- ^ a b c d e Chen Qingying, Tibetan History (China Intercontinental Press, 2003), 52.
- ^ Sperling, "The 5th Karma-pa and some aspects of the relationship between Tibet and the Early Ming", 477.
- ^ Thinley, The History of the Sixteen Karmapas of Tibet, 74.
- ^ Marsha Weidner, "Imperial Engagements with Buddhist Art and Architecture: Ming Variations of an Old Theme", in Cultural Intersections in Later Chinese Buddhism (Manoa: University of Hawaii Press, 2001), 121.
- ^ a b c d Norbu, China's Tibet Policy, 52.
- ^ a b Kolmas, Tibet and Imperial China, 32.
- ^ a b Information Office of the State Council, Testimony of History, 95.
- ^ a b John E. Vollmer, Silk for Thrones and Altars: Chinese Costumes and Textiles from the Liao through the Qing Dynasty (Berkeley: Ten Speed Press, 2004), 98–100.
- ^ 'The Tea Horse Road in Historical Perspective', in: Forbes, Andrew, and Henley, David, China's Ancient Tea Horse Road. Chiang Mai, Cognoscenti Books, 2011.
- ^ Wang & Nyima, The Historical Status of China's Tibet, 39.
- ^ Sperling, "The 5th Karma-pa and some aspects of the relationship between Tibet and the Early Ming", 474–475.
- ^ a b c Peter C. Perdue, "Culture, History, and Imperial Chinese Strategy: Legacies of the Qing Conquests", in Warfare in Chinese History (Leiden: Koninklijke Brill, 2000), 273.
- ^ Wang & Nyima, The Historical Status of China's Tibet, 39–40.
- ^ Wang & Nyima, The Historical Status of China's Tibet 40.
- ^ Sperling, "The 5th Karma-pa and some aspects of the relationship between Tibet and the Early Ming", 478.
- ^ Kolmas, Tibet and Imperial China, 28–29.
- ^ Laird, The Story of Tibet, 131.
- ^ Tsai, Perpetual Happiness, 188.
- ^ a b c d Laird, The Story of Tibet, 141.
- ^ a b Goldstein, The Snow Lion and the Dragon, 8.
- ^ a b c Kolmas, Tibet and Imperial China, 31–32.
- ^ a b Laird, The Story of Tibet, 144.
- ^ a b c Ebrey, Cambridge Illustrated History of China, 227.
- ^ a b John D. Langlois, "The Hung-wu reign, 1368–1398", in The Cambridge History of China: Volume 7, The Ming Dynasty, 1368–1644, Part 1 (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1988), 139.
- ^ Langlois, "The Hung-wu reign, 1368–1398", 161.
- ^ Chan, "Ming Taizu's Problem with His Sons," pp 74-77, 82.
- ^ Perdue, "Culture, History, and Imperial Chinese Strategy", 266–267.
- ^ Norbu, China's Tibet Policy, 59.
- ^ Sperling, "The 5th Karma-pa and some aspects of the relationship between Tibet and the Early Ming", 475–477.
- ^ a b c d P. Christiaan Klieger, "Riding High on the Manchurian Dream: Three Paradigms in the Construction of the Tibetan Question", in Contemporary Tibet: Politics, Development, and Society in a Disputed Region (New York: M.E. Sharpe, Inc., 2006), 217.
- ^ Chan, "The Chien-wen, Yung-lo, Hung-shi, and Hsuan-te reigns", 263–264.
- ^ a b Dictionary of Ming Biography, 412–413.
- ^ Jose Ignacio Cabezon and Geshe Lobsang Dargyay, Freedom from Extremes: Gorampa's Distinguishing the Views and the Polemics of Emptiness (Somerville: Wisdom Publications, 2007), 43–44, 270.
- ^ a b c d Dictionary of Ming Biography, 413.
- ^ James Geiss, "The Cheng-te reign, 1506–1521", in The Cambridge History of China: Volume 7, The Ming Dynasty, 1368–1644, Part 1 (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1988), 417.
- ^ a b Geiss, "The Cheng-te reign, 1506–1521", 417–418.
- ^ a b c d e Geiss, "The Cheng-te reign, 1506–1521", 418.
- ^ a b c Marina Illich, "Imperial Stooge or Emissary to the Dge lugs Throne? Rethinking the Biographies of Chankya Rolpé Dorjé", in Power, Politics, and the Reinvention of Tradition: Tibet in the Seventeenth and Eighteenth Centuries (Leiden: Koninklijke Brill, 2006), 19.
- ^ a b c d e f Sperling, Elliot. (April 13, 2008). Don't Know Much About Tibetan History. The New York Times. Retrieved on 2008-04-24.
- ^ a b Kolmas, Tibet and Imperial China, 33.
- ^ a b c d e f g China Daily. (April 9, 2008). From Dynasty to Republic. Chinadaily.com.cn. Retrieved on 2008-04-25.
- ^ People's Daily. (April 14, 2008). Tell you a true Tibet – Ownership of Tibet. English.peopledaily.com.cn. Retrieved on 2008-04-26.
- ^ Xinhua News Agency. (April 15, 2008). Tell you a true Tibet – Sovereignty of Tibet Archived 2008-04-29 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved on 2008-05-06.
- ^ a b c John E. Wills, Jr., "Relations with Maritime Europe, 1514–1662", in The Cambridge History of China: Volume 8, The Ming Dynasty, 1368–1644, Part 2, 333–375, ed. Denis Twitchett, John King Fairbank, and Albert Feuerwerker (New York: Cambridge University Press, 1998), 338–339.
- ^ Evelyn S. Rawski, The Last Emperors: A Social History of Qing Imperial Institutions (Berkeley: University of California Press, 1998), 245.
- ^ Patrick Taveirne (1 January 2004). Han-Mongol Encounters and Missionary Endeavors: A History of Scheut in Ordos (Hetao) 1874-1911. Leuven University Press. pp. 67–. ISBN 978-90-5867-365-7.
- ^ David M. Robinson, "Politics, Force and Ethnicity in Ming China: Mongols and the Abortive Coup of 1461", in Harvard Journal of Asiatic Studies 59, no. 1 (June 1999): 81.
- ^ Klieger, "Riding High on the Manchurian Dream", 217–218.
- ^ a b c d e f Samten Karmay, Secret Visions of the Fifth Dalai Lama (London: Serindia Publications, 1988), 3.
- ^ a b c d Kolmas, Tibet and Imperial China, 31.
- ^ Victoria Huckenpahler, "Introduction," in The Great Kagyu Masters: The Golden Lineage Treasury (Ithaca: Snow Lion Publications, 1990), xiii.
- ^ a b Rawski, The Last Emperors, 246.
- ^ Laird, The Story of Tibet, 143–144.
- ^ a b c d Laird, The Story of Tibet, 146.
- ^ Kolmas, Tibet and Imperial China, 30–31.
- ^ Van Praag, The Status of Tibet, 8–9.
- ^ Angela F. Howard, "Introduction", in Chinese Sculpture (New Haven: Yale University Press, 2006), 13.
- ^ a b c Dictionary of Ming Biography, 23.
- ^ a b c Chen Qingying, The System of the Dalai Lama Reincarnation (Beijing: China Intercontinental Press, 2005), 33.
- ^ Laird, The Story of Tibet, 152.
- ^ a b Karmay, Secret Visions of the Fifth Dalai Lama, 2.
- ^ Chen, The System of the Dalai Lama Reincarnation, 33–34.
- ^ a b c d Goldstein, The Snow Lion and the Dragon, 6.
- ^ Karmay, Secret Visions of the Fifth Dalai Lama, 3–4.
- ^ a b c d e f g Goldstein, The Snow Lion and the Dragon, 9.
- ^ a b c Van Praag, The Status of Tibet, 10
- ^ a b c d e Karmay, Secret Visions of the Fifth Dalai Lama, 4.
- ^ a b Van Praag, The Status of Tibet, 10–11.
- ^ Rawski, The Last Emperors, 250–251.
- ^ a b Rawski, The Last Emperors, 251.
- ^ Kolmas, Tibet and Imperial China, 34–35.
- ^ a b Van Praag, The Status of Tibet, 11.
- ^ a b Patterson, "China and Tibet: Background to the Revolt", 89.
- ^ Goldstein, The Snow Lion and the Dragon, 10.
- ^ a b c Albert Kolb, East Asia: China, Japan, Korea, Vietnam: Geography of a Cultural Region, trans. C.A.M. Sym (New York: Routledge, 1971), 368.
- ^ a b Chen, Tibetan History, 50.
Bibliography
[edit]- By organizations
- The Information Office of the State Council of the People's Republic of China. (2002). Testimony of History. Edited by Hongjia Xiang and Yuxin Zhan. China Intercontinental Press. ISBN 7-80113-885-6.
- The Ming Biographical History Project of the Association for Asian Studies. (1976). Dictionary of Ming Biography, 1368–1644: Volume 1, A-L. Edited by L. Carrington Goodrich and Chaoying Fang. New York: Columbia University Press. ISBN 0-231-03801-1.
- By individual authors
- 劉漢城 (2019-10-17), 《西藏自古以來就不是中國的一部份:用中國的官方/權威文獻明證》 [Tibet has not been a part of China since ancient times: Proved by Chinese official/authoritative documents] (PDF) (in Traditional Chinese), 雪域出版社, ISBN 9789869619394, archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-04-21
- Berger, Patricia Ann. (2003). Empire of Emptiness: Buddhist Art and Political Authority in Qing China. Manoa: University of Hawaii Press. ISBN 0-8248-2563-2.
- Bielenstein, Hans. (1980). The Bureaucracy of Han Times. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-22510-8.
- Cabezon, Jose Ignacio and Geshe Lobsang Dargyay. (2007). Freedom from Extremes: Gorampa's Distinguishing the Views and the Polemics of Emptiness. Somerville: Wisdom Publications, Inc. ISBN 0-86171-523-3.
- Denis Twitchett, Herbert Franke, John K. Fairbank, in The Cambridge History of China: Volume 6, Alien Regimes and Border States. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-24331-9, ISBN 978-0-521-24331-5.
- Chan, Hok-Lam. (1988). "The Chien-wen, Yung-lo, Hung-shi, and Hsuan-te reigns", in The Cambridge History of China: Volume 7, The Ming Dynasty, 1368–1644, Part 1, 182–384, edited by Denis Twitchett and John K. Fairbank. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-24332-7.
- Chan, Hok-Lam. "Ming Taizu's Problem with His Sons: Prince Qin's Criminality and Early-Ming Politics," in Asia Major THIRD SERIES, Vol. 20, No. 1 (2007): 45–103. Web. Accessed 13 October 2016.
- Chen, Qingying. (2003). Tibetan History. Beijing: China Intercontinental Press. ISBN 7-5010-1660-7.
- Chen, Qingying. (2005). The System of the Dalai Lama Reincarnation. Beijing: China Intercontinental Press. ISBN 7-5085-0745-2.
- Dreyfus, Georges. (2003). "Cherished memories, cherished communities: proto-nationalism in Tibet", in The History of Tibet: Volume 2, The Medieval Period: c. AD 850–1895, the Development of Buddhist Paramountcy, 492–522, ed. Alex McKay. New York: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-30842-9.
- Ebrey, Patricia Buckley (1999). The Cambridge Illustrated History of China. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-66991-X
- Forbes, Andrew ; Henley, David (2011). China's Ancient Tea Horse Road. Chiang Mai: Cognoscenti Books. ASIN B005DQV7Q2
- Geiss, James. (1988). "The Cheng-te reign, 1506–1521", in The Cambridge History of China: Volume 7, The Ming Dynasty, 1368–1644, Part 1, 403–439, edited by Denis Twitchett and John K. Fairbank. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-24332-7.
- Goldstein, Melvyn C. (1997). The Snow Lion and the Dragon: China, Tibet and the Dalai Lama. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-21951-1.
- Grunfeld, A. Tom. (1996). The Making of Modern Tibet. New York: M.E. Sharpe, Inc. ISBN 1-56324-714-3.
- Hoffman, Helmut. (2003). "Early and Medieval Tibet", in The History of Tibet: Volume 1, The Early Period to c. AD 850, the Yarlung Dynasty, 45–69, edited by Alex McKay. New York: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-30842-9.
- Howard, Angela F. (2006). "Introduction", in Chinese Sculpture, 7–16, edited by Angela F. Howard. New Haven: Yale University Press. ISBN 0-300-10065-5.
- Huckenpahler, Victoria. (1990). "Introduction" in The Great Kagyu Masters: The Golden Lineage Treasury. Translated by Khenpo Könchog Gyaltsan. Edited by Victoria Huckenpahler. Ithaca: Snow Lion Publications. ISBN 1-55939-244-4.
- Illich, Marina. (2006). "Imperial Stooge or Emissary to the Dge lugs Throne? Rethinking the Biographies of Chankya Rolpé Dorjé", in Power, Politics, and the Reinvention of Tradition: Tibet in the Seventeenth and Eighteenth Centuries, 17–32. Edited by Bryan J. Cuevas & Kurtis R. Schaeffer. Leiden: Koninklijke Brill. ISBN 90-04-15351-9.
- Karmay, Santen. (1988). Secret Visions of the Fifth Dalai Lama. London: Serindia Publications. ISBN 0-906026-47-4.
- Klieger, P. Christiaan. (2006). "Riding High on the Manchurian Dream: Three Paradigms in the Construction of the Tibetan Question", in Contemporary Tibet: Politics, Development, and Society in a Disputed Region, 214–229, edited by Barry Sautman and June Teufel Dreyer. New York: M.E. Sharpe, Inc. ISBN 0-7656-1354-9.
- Kolb, Albert. (1971). East Asia: China, Japan, Korea, Vietnam: Geography of a Cultural Region. Translated by C.A.M. Sym. New York: Routledge. ISBN 0-416-08420-6.
- Kolmaš, Josef. (1967). Tibet and Imperial China: A Survey of Sino-Tibetan Relations Up to the End of the Manchu Dynasty in 1912: Occasional Paper 7. Canberra: The Australian National University, Centre of Oriental Studies.
- Laird, Thomas. (2006). The Story of Tibet: Conversations with the Dalai Lama. New York: Grove Press. ISBN 0-8021-4327-X.
- Langlois, John D., Jr. (1988). "The Hung-wu reign, 1368–1398", in The Cambridge History of China: Volume 7, The Ming Dynasty, 1368–1644, Part 1, 107–181, edited by Denis Twitchett and John K. Fairbank. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-24332-7.
- Lopez, Donald S., Jr. "'Lamaism' and the Disappearance of Tibet", Comparative Studies in Society and History (Volume 38, Number 1, January 1996): 3–25.
- Norbu, Dawa. (2001). China's Tibet Policy. Richmond: Curzon. ISBN 0-7007-0474-4.
- Patterson, George N. "China and Tibet: Background to the Revolt", The China Quarterly (Number 1, January–March 1960): 87–102.
- Perdue, Peter C. (2000). "Culture, History, and Imperial Chinese Strategy: Legacies of the Qing Conquests", in Warfare in Chinese History, 252–287, edited by Hans van de Ven. Leiden: Koninklijke Brill. ISBN 90-04-11774-1.
- Powers, John. History as Propaganda: Tibetan Exiles versus the People's Republic of China (2004) Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-517426-7
- Van Praag, Michael C. van Walt. (1987). The Status of Tibet: History, Rights, and Prospects in International Law. Boulder: Westview Press. ISBN 0-8133-0394-X.
- Rawski, Evelyn S. (1998). The Last Emperors: A Social History of Qing Imperial Institutions. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-22837-5.
- Riggs, Fred W. "Tibet in Extremis", Far Eastern Survey (Volume 19, Number 21, 1950): 224–230.
- Robinson, David M. "Politics, Force and Ethnicity in Ming China: Mongols and the Abortive Coup of 1461", Harvard Journal of Asiatic Studies (Volume 59, Number 1, June 1999): 79–123.
- Robinson, David M. (2008). "The Ming Court and the Legacy of the Yuan Mongols," in David M. Robinson (ed), Culture, Courtiers, and Competition: the Ming Court (1368-1644), 365–411. Cambridge, MA and London: Harvard University Asia Center and Harvard University Press.
- Rossabi, Morris (1988). Khubilai Khan: His Life and Times. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-05913-1.
- Rossabi, Morris (1998). "The Ming and Inner Asia," in The Cambridge History of China: Volume 8, The Ming Dynasty, 1368–1644, Part 2, 221–271. Edited by Frederick W. Mote and Denis Twitchett. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-24333-5.
- Sperling, Elliot. (2003). "The 5th Karma-pa and some aspects of the relationship between Tibet and the Early Ming", in The History of Tibet: Volume 2, The Medieval Period: c. AD 850–1895, the Development of Buddhist Paramountcy, 473–482, ed. Alex McKay. New York: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-30842-9.
- Thinley, Karma. (1980). The History of the Sixteen Karmapas of Tibet. Boulder: Prajna Press. ISBN 0-87773-716-9.
- Tsai, Shih-Shan Henry. (2001). Perpetual Happiness: The Ming Emperor Yongle. Seattle: University of Washington Press. ISBN 0-295-98124-5.
- Tuttle, Gray. (2005). Tibetan Buddhists in the Making of Modern China. New York: Columbia University Press. ISBN 0-231-13446-0.
- Twitchett, Denis. (2000). "Tibet in Tang's Grand Strategy" in Warfare in Chinese History, 106–179, edited by Hans van de Ven. Leiden: Koninklijke Brill. ISBN 90-04-11774-1.
- Vollmer, John E. (2004). Silk for Thrones and Altars: Chinese Costumes and Textiles from the Liao through the Qing Dynasties. Berkeley: Ten Speed Press. ISBN 1-58008-590-3.
- Wang, Jiawei and Nyima Gyaincain. (1997). The Historical Status of China's Tibet. Beijing: China Intercontinental Press. ISBN 7-80113-304-8.
- Weidner, Marsha. (2001). "Imperial Engagements with Buddhist Art and Architecture: Ming Variations of an Old Theme", in Cultural Intersections in Later Chinese Buddhism, 117–144, edited by Marsha Weidner. Manoa: University of Hawaii Press. ISBN 0-8248-2308-7.
- Wills, John E., Jr. (1998). "Relations with Maritime Europe, 1514–1662", in The Cambridge History of China: Volume 8, The Ming Dynasty, 1368–1644, Part 2, 333–375. Edited by Denis Twitchett, John King Fairbank, and Albert Feuerwerker. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-24333-5.
- Wylie, Turrell V. "The First Mongol Conquest of Tibet Reinterpreted", Harvard Journal of Asiatic Studies (Volume 37, Number 1, June 1977): 103–133.
- Wylie, Turrell V. (2003). "Lama Tribute in the Ming Dynasty", in The History of Tibet: Volume 2, The Medieval Period: c. AD 850–1895, the Development of Buddhist Paramountcy, 467–472, ed. Alex McKay. New York: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-30842-9.
- Yiu, Yung-chin. (1998). "Two Focuses of the Tibet Issue", in Through Dissident Chinese Eyes: Essays on Self-determination, 121–123, edited by Cao Changqing and James D. Seymour. New York: M.E. Sharpe, Inc. ISBN 1-56324-922-7.