Asterion (anatomy)
| Asterion | |
|---|---|
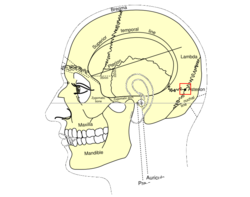 Side view of head, showing surface relations of bones. (Asterion visible at center right.) | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Skull |
| System | Skeletal |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | asterion |
| TA98 | A02.1.00.020 |
| TA2 | 422 |
| FMA | 76625 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The asterion is a meeting point between three sutures between bones of the skull. It is an important surgical landmark.
Structure
[edit]In human anatomy, the asterion is a visible (craniometric) point on the exposed skull. It is just posterior to the ear. It is the point where three cranial sutures meet:
It is also the point where three cranial bones meet:
- the parietal bone.
- the occipital bone.
- the mastoid portion of the temporal bone.
In the adult, it lies 4 cm behind and 12 mm above the center of the entrance to the ear canal.[citation needed] Its relation to other anatomical structures is fairly variable.[2]
Clinical significance
[edit]Neurosurgeons may use the asterion to orient themselves, in order to plan safe entry into the skull for some operations, such as when using a retro-sigmoid approach. The asterion marks the junction of the transverse and the sigmoid sinuses[1][3]
Etymology
[edit]The asterion receives its name from the Greek ἀστέριον (astērion), meaning "star" or "starry".
The Mercedes point is an alternative term for the asterion, for its resemblance to the Mercedes-Benz logo.
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d Ucerler, Hulya; Govsa, Figen (2006-10-01). "Asterion as a surgical landmark for lateral cranial base approaches". Journal of Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery. 34 (7): 415–420. doi:10.1016/j.jcms.2006.05.003. ISSN 1010-5182. PMID 16963269 – via ScienceDirect.
- ^ Avci, Emel; Kocaogullar, Yalcin; Fossett, Damirez; Caputy, Anthony (2003-05-01). "Lateral posterior fossa venous sinus relationships to surface landmarks". Surgical Neurology. 59 (5): 392–397. doi:10.1016/S0090-3019(03)00037-5. ISSN 0090-3019. PMID 12765815 – via ScienceDirect.
- ^ Babacan S, Yildiz-Yilmaz M, Kafa IM, Coşkun I (2019). "The Surface and Intracranial Location of Asterion". J Craniofac Surg. 30 (8): e753–e755. doi:10.1097/SCS.0000000000005757. PMID 31689738. S2CID 207889825.
