Medak district
Medak District
Gulshanabad Medak | |
|---|---|
| Metuku durgam | |
 | |
 Location in Telangana | |
| Country | India |
| State | Telangana |
| Headquarters | Medak |
| Mandals | 21 |
| Government | |
| • District collector | Sri Rajarshi Shah,IAS |
| • Member of Parliament | Raghunandan Rao,BJP |
| Area | |
• Total | 2,786 km2 (1,076 sq mi) |
| Population (2011) | |
• Total | 767,428 |
| • Density | 280/km2 (710/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+05:30 (IST) |
| Vehicle registration | TG 35 |
| Website | medak |
Medak district is located in the western region of the Indian state of Telangana. Medak is the district headquarters.[1] The district shares boundaries with Sangareddy, Kamareddy, Siddipet and Medchal-Malkajgiri districts.
History
[edit]Traces of Neolithic and Megalithic culture was found at Edithanur and Wargal[2] village hillocks in the district. Rock paintings were found at Edithanur boulders[3] and Hastallapur rocks.[4]
Nizam state
[edit]In 20th century Medak district was a part of Nizam princely State before independence and merged into Hyderabad State in Independent India and presently a district of Telangana. Qutub Shahis named it as Gulshanabad which means '"city of gardens'" due to its luscious greenery. For More Info.
Geography
[edit]The district is spread over an area of 2,757.3 square kilometres (1,064.6 sq mi).[5]
Economy
[edit]In 2006 the Indian government named Medak one of the country's 250 most backward districts (out of a total of 640).[6] It is one of the thirteen districts in Andhra Pradesh currently receiving funds from the Backward Regions Grant Fund Programme (BRGF).[6]
With the emergence of the Kothapalli-Manoharabad line railway line and inauguration of the Manoharabad - Siddipet portion of the line on 3 October, 2023 with a regular Secunderabad junction-Siddipet DEMU train service, large parts of Medak district were connected on the railway map.[7][8] Also announced during this time was the full railway electrification of the rail line that Manoharabad railway station is situated on.
Demographics
[edit]At the time of the 2011 census, Medak district has a population of 767,428. Medak district has a sex ratio of 1027 females per 1000 males and a literacy rate of 56.12%. 93,874 (12.23%) were under 6 years of age. 58,854 (7.67%) lived in urban areas. Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes made up 127,970 (16.68%) and 72,900 (9.50%) of the population respectively.[10]
At the time of the 2011 census, 83.91% of the population spoke Telugu, 8.42% Lambadi, 6.44% Urdu as their first language.[11]
Administrative divisions
[edit]The district is divided into three revenue divisions of Medak, Narsapur and Tupran. These are sub-divided into 21 revenue mandals (15 Mandal Praja Parishads) and has 381 villages constituting 320 gram panchayats.[5] [12] Sri Rajarshi Shah, I.A.S.[13] is the present collector of the district.[14]
Mandals
[edit]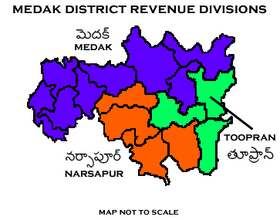
The below table categorizes 21 mandals into their respective revenue divisions in the district:[15]
| S.No. | Medak revenue division | S.No. | Narsapur revenue division | S.No. | Toopran revenue division |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Medak | 11 | Narsapur | 16 | Toopran |
| 2 | Havelighanpur | 12 | Kulcharam | 17 | Chegunta |
| 3 | Papannapet | 13 | Kowdipally | 18 | Narsingi |
| 4 | Sankarampet-R | 14 | Shivampet | 19 | Yeldurthy |
| 5 | Nizampet | 15 | Chilipched | 20 | Manoharabad |
| 6 | Ramayampet | 21 | Masaipet | ||
| 7 | Shankarampet-A | ||||
| 8 | Tekmal | ||||
| 9 | Alladurg | ||||
| 10 | Regode |
References
[edit]- ^ "Profile". Medak District. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ^ Murty, M. L. K. (2003). Comprehensive History and Culture of Andhra Pradesh: Pre- and protohistoric ... - Google Books. ISBN 9788125024750. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ^ v ramchandra rao. "Prehistoric rock art near Hyderabad, India". Indculture0.tripod.com. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ^ During the era of Qutub Shahis this was named as Gulshanabad due to its vegetation and gardens. later it was again changed to Medak district. http://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/tp-national/tp-andhrapradesh/treasuring-the-prehistoric-rock-art/article2046635.ece
- ^ a b "New districts". Andhra Jyothy.com. 8 October 2016. Retrieved 8 October 2016.
- ^ a b Ministry of Panchayati Raj (8 September 2009). "A Note on the Backward Regions Grant Fund Programme" (PDF). National Institute of Rural Development. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 April 2012. Retrieved 27 September 2011.
- ^ Geetanath, V. (28 September 2023). "PM to commission two new railway lines in Telangana". The Hindu.
- ^ "PM Modi to inaugurate Siddipet-Secunderabad train service on October 3". 2 October 2023.
- ^ "Population by Religion - Andhra Pradesh". Census of India. Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India. 2011.
- ^ "Know your district Plan your district - Medak" (PDF). trac.telangana.gov.in. Telangana State Remote Sensing Applications Centre.
- ^ a b "Table C-16 Population by Mother Tongue: Andhra Pradesh". Census of India. Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India.
- ^ "At a glance | District Medak, Government of Telangana | India". Retrieved 15 August 2022.
- ^ "Who's Who | District Medak, Government of Telangana | India". Retrieved 15 August 2022.
- ^ "K Chandrasekhar Rao appoints collectors for new districts". Deccan Chronicle. 11 October 2016. Retrieved 13 October 2016.
- ^ "Tehsil | District Medak, Government of Telangana | India". Retrieved 15 August 2022.