Marree Man


The Marree Man is a modern geoglyph created in 1998 in Outback South Australia. It depicts an Aboriginal man hunting with a boomerang or stick. It lies on a plateau at Finniss Springs, 60 km (37 mi) west of the township of Marree in central South Australia, approximately 12 km north-west of Callanna. It is just outside the 127,000-square-kilometre (49,000 sq mi)[1] Woomera Prohibited Area. The figure is 2.7 km (1.7 mi) tall with a perimeter of 28 km (17 mi), extending over an area of about 2.5 km2 (620 acres). Discovered fortuitously by a charter pilot in an overflight on 26 June 1998, it is one of the largest geoglyphs in the world, arguably second to the Sajama Lines). Its origin remains a mystery: no one claimed responsibility for its creation and no eye-witness has been found, notwithstanding the scale of the operation required to form the outline on the plateau floor. The description "Stuart's Giant" was used in anonymous faxes sent to media as press releases in July 1998, in a reference to the explorer John McDouall Stuart.
Shortly after its discovery, the South Australian government closed the site following legal action taken in late July by native title claimants, but flights over the site were not forbidden as native title fell under federal government jurisdiction.
Work
[edit]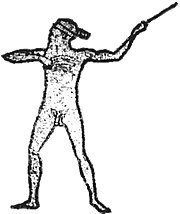

The Marree Man geoglyph depicts a man holding either a woomera (used to launch a throwing stick) or a boomerang (but see Plaque section below).
By December 1998, it had been noted that the outline matched, in reverse, that of the Artemision bronze statue of Zeus raised from the Aegean Sea in 1928.[2]
The lines outlining the figure were 20–30 cm (8–12 in) deep at the time of discovery and up to 35 metres (115 feet) wide. The image was gradually eroded through natural processes, but because the climate is extremely dry, the image was still visible in 2013.[3] Although there is a layer of white chalky material slightly below the red soil, the figure was not defined to this depth.
Marree Man was created between 27 May 1998, when NASA's Landsat-5 satellite showed the site undisturbed, and 12 June 1998, when the completed figure was visible.

In August 2016, work was carried out to redefine the geoglyph using a grader assisted by GPS. The work resulted in an outline clearly visible from the air, matching the original.[4][5] Two decades after its creation it was speculated that the work itself could not have been created without GPS technology, then in its infancy.[6]
Discovery
[edit]
Trec Smith, a charter pilot flying between Marree and Coober Pedy, spotted the geoglyph from the air on 26 June 1998.[7] It fascinated Australians because of its size and the mystery surrounding how it came to be there.[citation needed]
Subsequently, Shane Anderson from the William Creek Hotel, located 200 km (120 mi) north-west of the town of Marree, said the hotel had received an anonymous fax describing the location of the artwork.[8]
Anonymous press releases
[edit]Several anonymous press releases sent to media and local businesses in July[9] and August 1998 led to the suggestion that the Marree Man was created by people from the United States. The releases referred to "your State of SA", "Queensland Barrier Reef", and Aborigines "from the local indigenous territories" – terms not used by Australians. The press releases also mentioned the Great Serpent in Ohio, which is not well known outside the US. It was also conjectured that these features of the press releases may have been red herrings, inserted to provide an illusion of American authorship.[10]
Preservative bottle
[edit]On 16 July 1998, it was reported that a small glass jar had been found in a trough freshly dug at the site containing a satellite photo of the Marree Man[citation needed] together with a note bearing a U.S. flag and references to the Branch Davidians and "Stuart's Giant".[10][11]
Plaque
[edit]In January 1999, a fax sent to officials described a dedication plaque buried 5 metres (16 feet) south of the nose of the figure. The plaque bore an American flag, 3 cm (1.2 in) long by 2 cm (1 in) wide, with an imprint of the Olympic rings, and the words,
In honour of the land they once knew. His attainments in these pursuits are extraordinary; a constant source of wonderment and admiration.[12]
The words come from Hedley H. Finlayson's 1946 book The Red Centre, in a section describing the hunting of wallabies with throwing sticks and with photographs of hunters without loincloths and other details seen in the "Marree Man".[13] The book describes hunters of the Pitjantjatjara tribe.[14]
Possible originators
[edit]Experts who surveyed the geoglyph were reported as having concluded it was forged with an earthmoving machine and that the person responsible must have had extensive knowledge of satellite-linked global positioning systems. Bardius Goldberg, an eccentric Alice Springs artist who died in 2002 aged 61, was suggested as a possible creator of the work. A friend said:
Bardius had a good understanding of global satellite technology, he had access to earthmoving equipment and there were suspicions he was involved from the start but no one could prove anything. ... If anyone was mad enough, talented enough and cheeky enough to do it, it was Bardius. ... [He received] $10,000 around the time the Marree Man was discovered. Bardius said he was under instructions not to discuss why he was paid.[15] [failed verification]
At the time, theories abounded that American personnel from Woomera created the figure.[15] Others suggested that American soldiers stationed in Woomera were responsible, since the faxes used US spelling and references – but others suggested those clues could have been deliberately misleading.[16][17]
Reactions
[edit]Much of the public and media reaction to the discovery of the figure was positive. The Advertiser, the state's only daily newspaper, called for the figure to be made permanent by excavating the outline down to the white chalk layer.
At the time of discovery, the area was part of a Federal Court lawsuit through the National Native Title Tribunal to determine the traditional owners. The area was claimed by both the Arabunna people and the Dieri Mitha who had been in dispute for several years.[18] The Dieri Mitha publicly complained of harm and exploitation of the Dreamtime, calling for the image to be erased and for the artist to be prosecuted. As native title claimants, the Dieri Mitha took legal action to stop charter flights and vehicles visiting the site, prompting the state government to close the area to the public shortly after discovery. The Arabunna replied, through a solicitor, that the area covered points of archaeological interest and that the artist could be prosecuted.[19] In May 2012, the Federal Court handed native title to the Arabunna people.[20]
The artwork was called environmental vandalism by the former Environment Minister, Dorothy Kotz, and graffiti by the South Australian chief of Aboriginal affairs, David Ruthman.[19]
In June 2018, adventurer Dick Smith revealed that he had had a team working on investigating the origins of Marree Man for two years to no avail and was offering a A$5,000 reward for information leading to identifying its creators.[21] The Government of South Australia subsequently stated that legal proceedings would not be initiated against the creators if they were identified.[22]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Woomera Prohibited Area" (PDF). Four Wheel Drive South Australia. 14 April 2002. Retrieved 5 November 2013.
- ^ Jones, Philip (December 1998). "Zeus Stands Tall in the Desert". The Adelaide Review.
- ^ "Push to spruce up mysterious desert artwork". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 27 May 2013.
- ^ "Marree Man restored as outback tourist attraction". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 20 August 2016. Retrieved 20 August 2016.
- ^ "Giant Marree Man makes a comeback in South Australian outback". The Guardiandate=20 August 2016. Retrieved 21 August 2016.
- ^ Mao, Francis (26 June 2018). "Marree Man: The enduring mystery of a giant outback figure". BBC. Retrieved 26 June 2018.
- ^ "Marree Man". Lake Eyre Helicopters. Archived from the original on 30 June 2016. Retrieved 3 October 2024.
- ^ Henson, Elizabeth (19 August 2016). "Return of the mysterious giant Marree Man geoglyph in the desert sands". The Advertiser (Adelaide). Retrieved 26 August 2017.

subscription: the source is only accessible via a paid subscription ("paywall"). - ^ "Mystery surrounds huge image in outback SA". ABC News. 10 July 1998. Archived from the original on 26 April 2003.
- ^ a b Eccleston, Roy (5–6 September 1998). "The Mystery of Maree Man". The Weekend Australian. pp. 5–6.
- ^ Hurrell, Bronwyn; Cock, Anna (16 July 1998). "Whoever did it, it's great for tourism". Adelaide Advertiser.
- ^ "Trash City: News you may have missed". February 1999.
- ^ "Marree Man - The Evidence". Archived from the original on 26 February 2006.
- ^ "Marree Man - Australia 1998". Archived from the original on 7 February 2005.
- ^ a b Corcoran, Dee (23 August 2002). "Marree man still a mystery". Northern Territory News. News Limited. Archived from the original on 17 December 2009. Retrieved 3 October 2024.
- ^ "Marree Man: The enduring mystery of a giant outback figure". BBC News. 26 June 2018.
- ^ "Who's the giant man in the outback? | Tour SA".
- ^ In January 1995 the two groups had fought over the issue, leaving one dead and ten injured. In May 1998, only one month before the discovery of the geoglyph, the National Native Title Tribunal took the issue to the Federal Court. Although a resolution was expected to be reached quickly, the case was eventually to take 14 years before the Federal Court was able make a ruling: Dodd v State of South Australia [2012] FCA 519 (22 May 2012), Federal Court (Australia).
- ^ a b Leave our land alone Archived 17 April 2012 at the Wayback Machine The Advertiser 17 July 1998 State Library of South Australia
- ^ Court ruling on Eyre handover The Australian 22 May 2012

subscription: the source is only accessible via a paid subscription ("paywall"). - ^ "Australian entrepreneur offers cash reward to solve geoglyph mystery". CNN. 25 June 2018. Retrieved 19 November 2018.
- ^ Jones, Erin (12 October 2018). "Dick's Marree Man Plea". The Advertiser. p. 3.
External links
[edit]29°31′48″S 137°27′56″E / 29.53°S 137.4655°E
- View in Google Maps: "Google Maps". Google Maps. Retrieved 19 September 2010.
- Audio Interviews with Brad Thompson, Marree-based pilot: Centenary of Federation - Connecting the Continent
- UFO Updates: Skywatch: New Clues To Marree Man Mystery at the Wayback Machine (archived 15 September 2007)

