Nonlinear dimensionality reduction

Nonlinear dimensionality reduction, also known as manifold learning, is any of various related techniques that aim to project high-dimensional data, potentially existing across non-linear manifolds which cannot be adequately captured by linear decomposition methods, onto lower-dimensional latent manifolds, with the goal of either visualizing the data in the low-dimensional space, or learning the mapping (either from the high-dimensional space to the low-dimensional embedding or vice versa) itself.[1][2] The techniques described below can be understood as generalizations of linear decomposition methods used for dimensionality reduction, such as singular value decomposition and principal component analysis.
Applications of NLDR
[edit]High dimensional data can be hard for machines to work with, requiring significant time and space for analysis. It also presents a challenge for humans, since it's hard to visualize or understand data in more than three dimensions. Reducing the dimensionality of a data set, while keep its essential features relatively intact, can make algorithms more efficient and allow analysts to visualize trends and patterns.

The reduced-dimensional representations of data are often referred to as "intrinsic variables". This description implies that these are the values from which the data was produced. For example, consider a dataset that contains images of a letter 'A', which has been scaled and rotated by varying amounts. Each image has 32×32 pixels. Each image can be represented as a vector of 1024 pixel values. Each row is a sample on a two-dimensional manifold in 1024-dimensional space (a Hamming space). The intrinsic dimensionality is two, because two variables (rotation and scale) were varied in order to produce the data. Information about the shape or look of a letter 'A' is not part of the intrinsic variables because it is the same in every instance. Nonlinear dimensionality reduction will discard the correlated information (the letter 'A') and recover only the varying information (rotation and scale). The image to the right shows sample images from this dataset (to save space, not all input images are shown), and a plot of the two-dimensional points that results from using a NLDR algorithm (in this case, Manifold Sculpting was used) to reduce the data into just two dimensions.

By comparison, if principal component analysis, which is a linear dimensionality reduction algorithm, is used to reduce this same dataset into two dimensions, the resulting values are not so well organized. This demonstrates that the high-dimensional vectors (each representing a letter 'A') that sample this manifold vary in a non-linear manner.
It should be apparent, therefore, that NLDR has several applications in the field of computer-vision. For example, consider a robot that uses a camera to navigate in a closed static environment. The images obtained by that camera can be considered to be samples on a manifold in high-dimensional space, and the intrinsic variables of that manifold will represent the robot's position and orientation.
Invariant manifolds are of general interest for model order reduction in dynamical systems. In particular, if there is an attracting invariant manifold in the phase space, nearby trajectories will converge onto it and stay on it indefinitely, rendering it a candidate for dimensionality reduction of the dynamical system. While such manifolds are not guaranteed to exist in general, the theory of spectral submanifolds (SSM) gives conditions for the existence of unique attracting invariant objects in a broad class of dynamical systems.[3] Active research in NLDR seeks to unfold the observation manifolds associated with dynamical systems to develop modeling techniques.[4]
Some of the more prominent nonlinear dimensionality reduction techniques are listed below.
Important concepts
[edit]Sammon's mapping
[edit]Sammon's mapping is one of the first and most popular NLDR techniques.
Self-organizing map
[edit]The self-organizing map (SOM, also called Kohonen map) and its probabilistic variant generative topographic mapping (GTM) use a point representation in the embedded space to form a latent variable model based on a non-linear mapping from the embedded space to the high-dimensional space.[6] These techniques are related to work on density networks, which also are based around the same probabilistic model.
Kernel principal component analysis
[edit]Perhaps the most widely used algorithm for dimensional reduction is kernel PCA.[7] PCA begins by computing the covariance matrix of the matrix
It then projects the data onto the first k eigenvectors of that matrix. By comparison, KPCA begins by computing the covariance matrix of the data after being transformed into a higher-dimensional space,
It then projects the transformed data onto the first k eigenvectors of that matrix, just like PCA. It uses the kernel trick to factor away much of the computation, such that the entire process can be performed without actually computing . Of course must be chosen such that it has a known corresponding kernel. Unfortunately, it is not trivial to find a good kernel for a given problem, so KPCA does not yield good results with some problems when using standard kernels. For example, it is known to perform poorly with these kernels on the Swiss roll manifold. However, one can view certain other methods that perform well in such settings (e.g., Laplacian Eigenmaps, LLE) as special cases of kernel PCA by constructing a data-dependent kernel matrix.[8]
KPCA has an internal model, so it can be used to map points onto its embedding that were not available at training time.
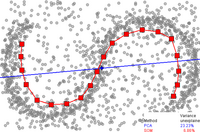
Principal curves and manifolds
[edit]
Principal curves and manifolds give the natural geometric framework for nonlinear dimensionality reduction and extend the geometric interpretation of PCA by explicitly constructing an embedded manifold, and by encoding using standard geometric projection onto the manifold. This approach was originally proposed by Trevor Hastie in his 1984 thesis,[11] which he formally introduced in 1989.[12] This idea has been explored further by many authors.[13] How to define the "simplicity" of the manifold is problem-dependent, however, it is commonly measured by the intrinsic dimensionality and/or the smoothness of the manifold. Usually, the principal manifold is defined as a solution to an optimization problem. The objective function includes a quality of data approximation and some penalty terms for the bending of the manifold. The popular initial approximations are generated by linear PCA and Kohonen's SOM.
Laplacian eigenmaps
[edit]Laplacian eigenmaps uses spectral techniques to perform dimensionality reduction.[14] This technique relies on the basic assumption that the data lies in a low-dimensional manifold in a high-dimensional space.[15] This algorithm cannot embed out-of-sample points, but techniques based on Reproducing kernel Hilbert space regularization exist for adding this capability.[16] Such techniques can be applied to other nonlinear dimensionality reduction algorithms as well.
Traditional techniques like principal component analysis do not consider the intrinsic geometry of the data. Laplacian eigenmaps builds a graph from neighborhood information of the data set. Each data point serves as a node on the graph and connectivity between nodes is governed by the proximity of neighboring points (using e.g. the k-nearest neighbor algorithm). The graph thus generated can be considered as a discrete approximation of the low-dimensional manifold in the high-dimensional space. Minimization of a cost function based on the graph ensures that points close to each other on the manifold are mapped close to each other in the low-dimensional space, preserving local distances. The eigenfunctions of the Laplace–Beltrami operator on the manifold serve as the embedding dimensions, since under mild conditions this operator has a countable spectrum that is a basis for square integrable functions on the manifold (compare to Fourier series on the unit circle manifold). Attempts to place Laplacian eigenmaps on solid theoretical ground have met with some success, as under certain nonrestrictive assumptions, the graph Laplacian matrix has been shown to converge to the Laplace–Beltrami operator as the number of points goes to infinity.[15]
Isomap
[edit]Isomap[17] is a combination of the Floyd–Warshall algorithm with classic Multidimensional Scaling (MDS). Classic MDS takes a matrix of pair-wise distances between all points and computes a position for each point. Isomap assumes that the pair-wise distances are only known between neighboring points, and uses the Floyd–Warshall algorithm to compute the pair-wise distances between all other points. This effectively estimates the full matrix of pair-wise geodesic distances between all of the points. Isomap then uses classic MDS to compute the reduced-dimensional positions of all the points. Landmark-Isomap is a variant of this algorithm that uses landmarks to increase speed, at the cost of some accuracy.
In manifold learning, the input data is assumed to be sampled from a low dimensional manifold that is embedded inside of a higher-dimensional vector space. The main intuition behind MVU is to exploit the local linearity of manifolds and create a mapping that preserves local neighbourhoods at every point of the underlying manifold.
Locally-linear embedding
[edit]Locally-linear Embedding (LLE) was presented at approximately the same time as Isomap.[18] It has several advantages over Isomap, including faster optimization when implemented to take advantage of sparse matrix algorithms, and better results with many problems. LLE also begins by finding a set of the nearest neighbors of each point. It then computes a set of weights for each point that best describes the point as a linear combination of its neighbors. Finally, it uses an eigenvector-based optimization technique to find the low-dimensional embedding of points, such that each point is still described with the same linear combination of its neighbors. LLE tends to handle non-uniform sample densities poorly because there is no fixed unit to prevent the weights from drifting as various regions differ in sample densities. LLE has no internal model.
LLE computes the barycentric coordinates of a point Xi based on its neighbors Xj. The original point is reconstructed by a linear combination, given by the weight matrix Wij, of its neighbors. The reconstruction error is given by the cost function E(W).
The weights Wij refer to the amount of contribution the point Xj has while reconstructing the point Xi. The cost function is minimized under two constraints: (a) Each data point Xi is reconstructed only from its neighbors, thus enforcing Wij to be zero if point Xj is not a neighbor of the point Xi and (b) The sum of every row of the weight matrix equals 1.
The original data points are collected in a D dimensional space and the goal of the algorithm is to reduce the dimensionality to d such that D >> d. The same weights Wij that reconstructs the ith data point in the D dimensional space will be used to reconstruct the same point in the lower d dimensional space. A neighborhood preserving map is created based on this idea. Each point Xi in the D dimensional space is mapped onto a point Yi in the d dimensional space by minimizing the cost function
In this cost function, unlike the previous one, the weights Wij are kept fixed and the minimization is done on the points Yi to optimize the coordinates. This minimization problem can be solved by solving a sparse N X N eigen value problem (N being the number of data points), whose bottom d nonzero eigen vectors provide an orthogonal set of coordinates. Generally the data points are reconstructed from K nearest neighbors, as measured by Euclidean distance. For such an implementation the algorithm has only one free parameter K, which can be chosen by cross validation.
Hessian locally-linear embedding (Hessian LLE)
[edit]Like LLE, Hessian LLE is also based on sparse matrix techniques.[19] It tends to yield results of a much higher quality than LLE. Unfortunately, it has a very costly computational complexity, so it is not well-suited for heavily sampled manifolds. It has no internal model.
Modified Locally-Linear Embedding (MLLE)
[edit]Modified LLE (MLLE)[20] is another LLE variant which uses multiple weights in each neighborhood to address the local weight matrix conditioning problem which leads to distortions in LLE maps. Loosely speaking the multiple weights are the local orthogonal projection of the original weights produced by LLE. The creators of this regularised variant are also the authors of Local Tangent Space Alignment (LTSA), which is implicit in the MLLE formulation when realising that the global optimisation of the orthogonal projections of each weight vector, in-essence, aligns the local tangent spaces of every data point. The theoretical and empirical implications from the correct application of this algorithm are far-reaching.[21]
Local tangent space alignment
[edit]LTSA[22] is based on the intuition that when a manifold is correctly unfolded, all of the tangent hyperplanes to the manifold will become aligned. It begins by computing the k-nearest neighbors of every point. It computes the tangent space at every point by computing the d-first principal components in each local neighborhood. It then optimizes to find an embedding that aligns the tangent spaces.
Maximum variance unfolding
[edit]Maximum Variance Unfolding, Isomap and Locally Linear Embedding share a common intuition relying on the notion that if a manifold is properly unfolded, then variance over the points is maximized. Its initial step, like Isomap and Locally Linear Embedding, is finding the k-nearest neighbors of every point. It then seeks to solve the problem of maximizing the distance between all non-neighboring points, constrained such that the distances between neighboring points are preserved. The primary contribution of this algorithm is a technique for casting this problem as a semidefinite programming problem. Unfortunately, semidefinite programming solvers have a high computational cost. Like Locally Linear Embedding, it has no internal model.
Autoencoders
[edit]An autoencoder is a feed-forward neural network which is trained to approximate the identity function. That is, it is trained to map from a vector of values to the same vector. When used for dimensionality reduction purposes, one of the hidden layers in the network is limited to contain only a small number of network units. Thus, the network must learn to encode the vector into a small number of dimensions and then decode it back into the original space. Thus, the first half of the network is a model which maps from high to low-dimensional space, and the second half maps from low to high-dimensional space. Although the idea of autoencoders is quite old,[23] training of deep autoencoders has only recently become possible through the use of restricted Boltzmann machines and stacked denoising autoencoders. Related to autoencoders is the NeuroScale algorithm, which uses stress functions inspired by multidimensional scaling and Sammon mappings (see above) to learn a non-linear mapping from the high-dimensional to the embedded space. The mappings in NeuroScale are based on radial basis function networks.
Gaussian process latent variable models
[edit]Gaussian process latent variable models (GPLVM)[24] are probabilistic dimensionality reduction methods that use Gaussian Processes (GPs) to find a lower dimensional non-linear embedding of high dimensional data. They are an extension of the Probabilistic formulation of PCA. The model is defined probabilistically and the latent variables are then marginalized and parameters are obtained by maximizing the likelihood. Like kernel PCA they use a kernel function to form a non linear mapping (in the form of a Gaussian process). However, in the GPLVM the mapping is from the embedded(latent) space to the data space (like density networks and GTM) whereas in kernel PCA it is in the opposite direction. It was originally proposed for visualization of high dimensional data but has been extended to construct a shared manifold model between two observation spaces. GPLVM and its many variants have been proposed specially for human motion modeling, e.g., back constrained GPLVM, GP dynamic model (GPDM), balanced GPDM (B-GPDM) and topologically constrained GPDM. To capture the coupling effect of the pose and gait manifolds in the gait analysis, a multi-layer joint gait-pose manifolds was proposed.[25]
t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding
[edit]t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (t-SNE)[26] is widely used. It is one of a family of stochastic neighbor embedding methods. The algorithm computes the probability that pairs of datapoints in the high-dimensional space are related, and then chooses low-dimensional embeddings which produce a similar distribution.
Other algorithms
[edit]Relational perspective map
[edit]Relational perspective map is a multidimensional scaling algorithm. The algorithm finds a configuration of data points on a manifold by simulating a multi-particle dynamic system on a closed manifold, where data points are mapped to particles and distances (or dissimilarity) between data points represent a repulsive force. As the manifold gradually grows in size the multi-particle system cools down gradually and converges to a configuration that reflects the distance information of the data points.
Relational perspective map was inspired by a physical model in which positively charged particles move freely on the surface of a ball. Guided by the Coulomb force between particles, the minimal energy configuration of the particles will reflect the strength of repulsive forces between the particles.
The Relational perspective map was introduced in.[27] The algorithm firstly used the flat torus as the image manifold, then it has been extended (in the software VisuMap to use other types of closed manifolds, like the sphere, projective space, and Klein bottle, as image manifolds.
Contagion maps
[edit]Contagion maps use multiple contagions on a network to map the nodes as a point cloud.[28] In the case of the Global cascades model the speed of the spread can be adjusted with the threshold parameter . For the contagion map is equivalent to the Isomap algorithm.
Curvilinear component analysis
[edit]Curvilinear component analysis (CCA) looks for the configuration of points in the output space that preserves original distances as much as possible while focusing on small distances in the output space (conversely to Sammon's mapping which focus on small distances in original space).[29]
It should be noticed that CCA, as an iterative learning algorithm, actually starts with focus on large distances (like the Sammon algorithm), then gradually change focus to small distances. The small distance information will overwrite the large distance information, if compromises between the two have to be made.
The stress function of CCA is related to a sum of right Bregman divergences.[30]
Curvilinear distance analysis
[edit]CDA[29] trains a self-organizing neural network to fit the manifold and seeks to preserve geodesic distances in its embedding. It is based on Curvilinear Component Analysis (which extended Sammon's mapping), but uses geodesic distances instead.
Diffeomorphic dimensionality reduction
[edit]Diffeomorphic Dimensionality Reduction or Diffeomap[31] learns a smooth diffeomorphic mapping which transports the data onto a lower-dimensional linear subspace. The methods solves for a smooth time indexed vector field such that flows along the field which start at the data points will end at a lower-dimensional linear subspace, thereby attempting to preserve pairwise differences under both the forward and inverse mapping.
Manifold alignment
[edit]Manifold alignment takes advantage of the assumption that disparate data sets produced by similar generating processes will share a similar underlying manifold representation. By learning projections from each original space to the shared manifold, correspondences are recovered and knowledge from one domain can be transferred to another. Most manifold alignment techniques consider only two data sets, but the concept extends to arbitrarily many initial data sets.[32]
Diffusion maps
[edit]Diffusion maps leverages the relationship between heat diffusion and a random walk (Markov Chain); an analogy is drawn between the diffusion operator on a manifold and a Markov transition matrix operating on functions defined on the graph whose nodes were sampled from the manifold.[33] In particular, let a data set be represented by . The underlying assumption of diffusion map is that the high-dimensional data lies on a low-dimensional manifold of dimension . Let X represent the data set and represent the distribution of the data points on X. Further, define a kernel which represents some notion of affinity of the points in X. The kernel has the following properties[34]
k is symmetric
k is positivity preserving
Thus one can think of the individual data points as the nodes of a graph and the kernel k as defining some sort of affinity on that graph. The graph is symmetric by construction since the kernel is symmetric. It is easy to see here that from the tuple (X,k) one can construct a reversible Markov Chain. This technique is common to a variety of fields and is known as the graph Laplacian.
For example, the graph K = (X,E) can be constructed using a Gaussian kernel.
In the above equation, denotes that is a nearest neighbor of . Properly, Geodesic distance should be used to actually measure distances on the manifold. Since the exact structure of the manifold is not available, for the nearest neighbors the geodesic distance is approximated by euclidean distance. The choice modulates our notion of proximity in the sense that if then and if then . The former means that very little diffusion has taken place while the latter implies that the diffusion process is nearly complete. Different strategies to choose can be found in.[35]
In order to faithfully represent a Markov matrix, must be normalized by the corresponding degree matrix :
now represents a Markov chain. is the probability of transitioning from to in one time step. Similarly the probability of transitioning from to in t time steps is given by . Here is the matrix multiplied by itself t times.
The Markov matrix constitutes some notion of local geometry of the data set X. The major difference between diffusion maps and principal component analysis is that only local features of the data are considered in diffusion maps as opposed to taking correlations of the entire data set.
defines a random walk on the data set which means that the kernel captures some local geometry of data set. The Markov chain defines fast and slow directions of propagation through the kernel values. As the walk propagates forward in time, the local geometry information aggregates in the same way as local transitions (defined by differential equations) of the dynamical system.[34] The metaphor of diffusion arises from the definition of a family diffusion distance
For fixed t, defines a distance between any two points of the data set based on path connectivity: the value of will be smaller the more paths that connect x to y and vice versa. Because the quantity involves a sum over of all paths of length t, is much more robust to noise in the data than geodesic distance. takes into account all the relation between points x and y while calculating the distance and serves as a better notion of proximity than just Euclidean distance or even geodesic distance.
Local multidimensional scaling
[edit]Local Multidimensional Scaling performs multidimensional scaling in local regions, and then uses convex optimization to fit all the pieces together.[36]
Nonlinear PCA
[edit]Nonlinear PCA (NLPCA) uses backpropagation to train a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) to fit to a manifold.[37] Unlike typical MLP training, which only updates the weights, NLPCA updates both the weights and the inputs. That is, both the weights and inputs are treated as latent values. After training, the latent inputs are a low-dimensional representation of the observed vectors, and the MLP maps from that low-dimensional representation to the high-dimensional observation space.
Data-driven high-dimensional scaling
[edit]Data-driven high-dimensional scaling (DD-HDS)[38] is closely related to Sammon's mapping and curvilinear component analysis except that (1) it simultaneously penalizes false neighborhoods and tears by focusing on small distances in both original and output space, and that (2) it accounts for concentration of measure phenomenon by adapting the weighting function to the distance distribution.
Manifold sculpting
[edit]Manifold Sculpting[39] uses graduated optimization to find an embedding. Like other algorithms, it computes the k-nearest neighbors and tries to seek an embedding that preserves relationships in local neighborhoods. It slowly scales variance out of higher dimensions, while simultaneously adjusting points in lower dimensions to preserve those relationships. If the rate of scaling is small, it can find very precise embeddings. It boasts higher empirical accuracy than other algorithms with several problems. It can also be used to refine the results from other manifold learning algorithms. It struggles to unfold some manifolds, however, unless a very slow scaling rate is used. It has no model.
RankVisu
[edit]RankVisu[40] is designed to preserve rank of neighborhood rather than distance. RankVisu is especially useful on difficult tasks (when the preservation of distance cannot be achieved satisfyingly). Indeed, the rank of neighborhood is less informative than distance (ranks can be deduced from distances but distances cannot be deduced from ranks) and its preservation is thus easier.
Topologically constrained isometric embedding
[edit]Topologically constrained isometric embedding (TCIE)[41] is an algorithm based on approximating geodesic distances after filtering geodesics inconsistent with the Euclidean metric. Aimed at correcting the distortions caused when Isomap is used to map intrinsically non-convex data, TCIE uses weight least-squares MDS in order to obtain a more accurate mapping. The TCIE algorithm first detects possible boundary points in the data, and during computation of the geodesic length marks inconsistent geodesics, to be given a small weight in the weighted stress majorization that follows.
Uniform manifold approximation and projection
[edit]Uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) is a nonlinear dimensionality reduction technique.[42] It is similar to t-SNE.[43]
Methods based on proximity matrices
[edit]A method based on proximity matrices is one where the data is presented to the algorithm in the form of a similarity matrix or a distance matrix. These methods all fall under the broader class of metric multidimensional scaling. The variations tend to be differences in how the proximity data is computed; for example, isomap, locally linear embeddings, maximum variance unfolding, and Sammon mapping (which is not in fact a mapping) are examples of metric multidimensional scaling methods.
Software
[edit]- Waffles is an open source C++ library containing implementations of LLE, Manifold Sculpting, and some other manifold learning algorithms.
- UMAP.jl implements the method for the programming language Julia.
- The method has also been implemented in Python (code available on GitHub)
See also
[edit]- Manifold hypothesis
- Spectral submanifold
- Taken's theorem
- Whitney embedding theorem
- Discriminant analysis
- Elastic map
- Feature learning
- Growing self-organizing map (GSOM)
- Self-organizing map (SOM)
References
[edit]- ^ Lawrence, Neil D (2012). "A unifying probabilistic perspective for spectral dimensionality reduction: insights and new models". Journal of Machine Learning Research. 13 (May): 1609–38. arXiv:1010.4830. Bibcode:2010arXiv1010.4830L.
- ^ Lee, John A.; Verleysen, Michel (2007). Nonlinear Dimensionality Reduction. Springer. ISBN 978-0-387-39350-6.
- ^ Haller, George; Ponsioen, Sten (2016). "Nonlinear normal modes and spectral submanifolds: Existence, uniqueness and use in model reduction". Nonlinear Dynamics. 86 (3): 1493–1534. arXiv:1602.00560. doi:10.1007/s11071-016-2974-z. S2CID 44074026.
- ^ Gashler, M.; Martinez, T. (2011). Temporal Nonlinear Dimensionality Reduction (PDF). Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks IJCNN'11. pp. 1959–66.
- ^ The illustration is prepared using free software: Mirkes, E.M. (2011). "Principal Component Analysis and Self-Organizing Maps: applet". University of Leicester.
- ^ Yin, Hujun (2007). "3. Learning Nonlinear Principal Manifolds by Self-Organising Maps". In Gorban, A.N.; Kégl, B.; Wunsch, D.C.; Zinovyev, A. (eds.). Principal Manifolds for Data Visualization and Dimension Reduction. Lecture Notes in Computer Science and Engineering. Vol. 58. Springer. pp. 68–95. ISBN 978-3-540-73749-0.
- ^ Schölkopf, B.; Smola, A.; Müller, K.-R. (1998). "Nonlinear Component Analysis as a Kernel Eigenvalue Problem". Neural Computation. 10 (5). MIT Press: 1299–1319. doi:10.1162/089976698300017467. S2CID 6674407.
- ^ Ham, Jihun; Lee, Daniel D.; Mika, Sebastian; Schölkopf, Bernhard. "A kernel view of the dimensionality reduction of manifolds". Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Machine Learning, Banff, Canada, 2004. doi:10.1145/1015330.1015417.
- ^ Gorban, A. N.; Zinovyev, A. (2010). "Principal manifolds and graphs in practice: from molecular biology to dynamical systems". International Journal of Neural Systems. 20 (3): 219–232. arXiv:1001.1122. doi:10.1142/S0129065710002383. PMID 20556849. S2CID 2170982.
- ^ A. Zinovyev, ViDaExpert - Multidimensional Data Visualization Tool Institut Curie, Paris.
- ^ Hastie, T. (November 1984). Principal Curves and Surfaces (PDF) (PhD). Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, Stanford University. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 2, 2019.
- ^ Hastie, T.; Stuetzle, W. (June 1989). "Principal Curves" (PDF). Journal of the American Statistical Association. 84 (406): 502–6. doi:10.1080/01621459.1989.10478797.
- ^ Gorban, A. N.; Kégl, B.; Wunsch, D. C.; Zinovyev, A., eds. (2007). Principal Manifolds for Data Visualisation and Dimension Reduction. Lecture Notes in Computer Science and Engineering (LNCSE). Vol. 58. Springer. ISBN 978-3-540-73749-0.
- ^ Belkin, Mikhail; Niyogi, Partha (2001). "Laplacian Eigenmaps and Spectral Techniques for Embedding and Clustering" (PDF). Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 14. MIT Press: 586–691. ISBN 0-262-27173-7. OCLC 52710683.
- ^ a b Belkin, Mikhail (August 2003). Problems of Learning on Manifolds (PhD). Department of Mathematics, The University of Chicago. Matlab code for Laplacian Eigenmaps can be found in algorithms at Ohio-state.edu
- ^ Bengio, Yoshua; Paiement, Jean-Francois; Vincent, Pascal; Delalleau, Olivier; Le Roux, Nicolas; Ouimet, Marie (2004). "Out-of-Sample Extensions for LLE, Isomap, MDS, Eigenmaps, and Spectral Clustering" (PDF). Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Vol. 16. MIT Press. ISBN 0-262-20152-6.
- ^ Tenenbaum, J B.; de Silva, V.; Langford, J.C. (2000). "A Global Geometric Framework for Nonlinear Dimensionality Reduction" (PDF). Science. 290 (5500): 2319–23. Bibcode:2000Sci...290.2319T. doi:10.1126/science.290.5500.2319. PMID 11125149. S2CID 221338160.
- ^ Roweis, S. T.; Saul, L. K. (2000). "Nonlinear Dimensionality Reduction by Locally Linear Embedding". Science. 290 (5500): 2323–6. Bibcode:2000Sci...290.2323R. doi:10.1126/science.290.5500.2323. PMID 11125150. S2CID 5987139.
- ^ Donoho, D.; Grimes, C. (2003). "Hessian eigenmaps: Locally linear embedding techniques for high-dimensional data". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 100 (10): 5591–6. Bibcode:2003PNAS..100.5591D. doi:10.1073/pnas.1031596100. PMC 156245. PMID 16576753.
- ^ Zhang, Z.; Wang, J. (2006). "MLLE: Modified Locally Linear Embedding Using Multiple Weights". NIPS'06: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems: 1593–1600.
- ^ Sidhu, Gagan (2019). "Locally Linear Embedding and fMRI feature selection in psychiatric classification". IEEE Journal of Translational Engineering in Health and Medicine. 7: 1–11. arXiv:1908.06319. doi:10.1109/JTEHM.2019.2936348. PMC 6726465. PMID 31497410. S2CID 201832756.
- ^ Zhang, Zhenyue; Hongyuan Zha (2005). "Principal Manifolds and Nonlinear Dimension Reduction via Local Tangent Space Alignment". SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing. 26 (1): 313–338. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.211.9957. doi:10.1137/s1064827502419154.
- ^ DeMers, D.; Cottrell, G.W. (1993). "Non-linear dimensionality reduction". Advances in neural information processing systems. Vol. 5. pp. 580–7. ISBN 1558600159. OCLC 928936290.
- ^ Lawrence, N. (2005). "Probabilistic Non-linear Principal Component Analysis with Gaussian Process Latent Variable Models". Journal of Machine Learning Research. 6: 1783–1816.
- ^ Ding, M.; Fan, G. (2015). "Multilayer Joint Gait-Pose Manifolds for Human Gait Motion Modeling". IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics. 45 (11): 2413–24. doi:10.1109/TCYB.2014.2373393. PMID 25532201. S2CID 15591304.
- ^ van der Maaten, L.J.P.; Hinton, G.E. (2008). "Visualizing High-Dimensional Data Using t-SNE" (PDF). Journal of Machine Learning Research. 9: 2579–2605.
- ^ Li, James X. (2004). "Visualizing high-dimensional data with relational perspective map" (PDF). Information Visualization. 3: 49–59. doi:10.1057/palgrave.ivs.9500051. S2CID 7566939.
- ^ Taylor, D.; Klimm, F.; Harrington, H. A.; Kramár, M.; Mischaikow, K.; Porter, M. A.; Mucha, P. J. (2015). "Topological data analysis of contagion maps for examining spreading processes on networks". Nature Communications. 6: 7723. arXiv:1408.1168. Bibcode:2015NatCo...6.7723T. doi:10.1038/ncomms8723. PMC 4566922. PMID 26194875.
- ^ a b Demartines, P.; Hérault, J. (1997). "Curvilinear Component Analysis: A Self-Organizing Neural Network for Nonlinear Mapping of Data Sets" (PDF). IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks. 8 (1): 148–154. doi:10.1109/72.554199. PMID 18255618.
- ^ Sun, Jigang; Crowe, Malcolm; Fyfe, Colin (2010). "Curvilinear component analysis and Bregman divergences" (PDF). European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks (Esann). d-side publications. pp. 81–86.
- ^ Walder, Christian; Schölkopf, Bernhard (2009). "Diffeomorphic Dimensionality Reduction" (PDF). Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Vol. 22. MIT Press. pp. 1713–20.
- ^ Wang, Chang; Mahadevan, Sridhar (July 2008). Manifold Alignment using Procrustes Analysis (PDF). The 25th International Conference on Machine Learning. pp. 1120–7.
- ^ Lafon, Stephane (May 2004). Diffusion Maps and Geometric Harmonics (PhD). Yale University.
- ^ a b Coifman, Ronald R.; Lafon, Stephane (July 2006). "Diffusion Maps" (PDF). Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis. 21 (1): 5–30. doi:10.1016/j.acha.2006.04.006. S2CID 17160669.
- ^ Bah, B. (2008). Diffusion Maps: Applications and Analysis (Masters). University of Oxford.
- ^ Venna, J.; Kaski, S. (2006). "Local multidimensional scaling". Neural Networks. 19 (6–7): 889–899. doi:10.1016/j.neunet.2006.05.014. PMID 16787737.
- ^ Scholz, M.; Kaplan, F.; Guy, C. L.; Kopka, J.; Selbig, J. (2005). "Non-linear PCA: a missing data approach". Bioinformatics. 21 (20). Oxford University Press: 3887–95. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bti634. hdl:11858/00-001M-0000-0014-2B1F-2. PMID 16109748.
- ^ S. Lespinats, M. Verleysen, A. Giron, B. Fertil, DD-HDS: a tool for visualization and exploration of high-dimensional data, IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 18 (5) (2007) 1265–1279.
- ^ Gashler, M. and Ventura, D. and Martinez, T., Iterative Non-linear Dimensionality Reduction with Manifold Sculpting, In Platt, J.C. and Koller, D. and Singer, Y. and Roweis, S., editor, Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 20, pp. 513–520, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 2008
- ^ Lespinats S., Fertil B., Villemain P. and Herault J., Rankvisu: Mapping from the neighbourhood network, Neurocomputing, vol. 72 (13–15), pp. 2964–2978, 2009.
- ^ Rosman, G.; Bronstein, M.M.; Bronstein, A.M.; Kimmel, R. (2010). "Nonlinear Dimensionality Reduction by Topologically Constrained Isometric Embedding" (PDF). International Journal of Computer Vision. 89 (1): 56–68. doi:10.1007/s11263-010-0322-1. S2CID 1365750.
- ^ McInnes, Leland; Healy, John; Melville, James (2018-12-07). "Uniform manifold approximation and projection for dimension reduction". arXiv:1802.03426.
- ^ "UMAP: Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection for Dimension Reduction — umap 0.3 documentation". umap-learn.readthedocs.io. Retrieved 2019-05-04.
Further reading
[edit]- Murphy, Kevin P. (2022). "Manifold Learning". Probabilistic Machine Learning. MIT Press. pp. 682–699. ISBN 978-0-262-04682-4.










![{\displaystyle t\in [0,1]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/31a5c18739ff04858eecc8fec2f53912c348e0e5)

![{\displaystyle \mathbf {X} =[x_{1},x_{2},\ldots ,x_{n}]\in \Omega \subset \mathbf {R^{D}} }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/27767b00cc5714632b393ff3d9173e6eece42867)
























