Mandibular advancement splint
| Mandibular advancement splint | |
|---|---|
 A mandibular advancement splint for treatment of sleep apnea | |
| Other names | MAS |
A mandibular splint or mandibular advancement splint is a prescription custom-made medical device worn in the mouth used to treat sleep-related breathing disorders including: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), snoring, and TMJ disorders. These devices are also known as mandibular advancement devices, sleep apnea oral appliances, oral airway dilators, and sleep apnea mouth guards.
The American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) and the American Academy of Dental Sleep Medicine (AADSM) recommend that sleep physicians should prescribe sleep apnea oral appliances for adult patients who need treatment for their primary snoring (without obstructive sleep apnea) rather than no treatment and for patients who have obstructive sleep apnea but are intolerant to CPAP therapy or otherwise prefer alternate therapy.[1]
Vanderveken et al (2008) researched prescription custom-made splints head-to-head with thermoplastic over-the-counter splints: "Our results suggest that the thermoplastic device cannot be recommended as a therapeutic option nor can it be used as a screening tool to find good candidates for mandibular advancement therapy."[2]
Usage
[edit]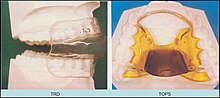

The splint treats snoring and sleep apnea by moving the lower jaw forward slightly, which tightens the soft tissue and muscles of the upper airway to prevent obstruction of the airway during sleep. The tightening created by the device also prevents the tissues of the upper airway from vibrating as air passes over them—the most common cause of snoring.[citation needed]
Mandibular advancement splints are widely used in the United States and are beginning to be used in the UK. According to the current American Academy of Sleep Medicine treatment guidelines,[1] oral appliances should be considered for patients with snoring or minor to moderate sleep apnea, or as an alternative to CPAP in non compliant patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea. Where appropriate, they are considered a good therapy choice as they are non-invasive, easily reversible, quiet, and generally well accepted by the patient. The focus of improvement in appliance design is in reducing bulk, permitting free jaw movement (permitting yawning, speaking, and drinking), and allowing the user to breathe through the mouth (early "welded gum shield"-type devices prevented oral breathing).[citation needed]
Evidence is accumulating to support the use of oral devices in the treatment of OSA, and studies demonstrating their efficacy[3] have been underpinned by increasing recognition of the importance of upper airway anatomy in the pathophysiology of OSA.[4] Oral devices have been shown to have beneficial effects relating to several areas. These include the polysomnographic indexes of OSA, subjective and objective measures of sleepiness, blood pressure, aspects of neuropsychological functioning, and quality of life.[citation needed] Elucidation of the mechanism of action of oral devices has provided insight into the factors that predict treatment response and may improve the selection of patients for this treatment modality.[4]
A 2008 study published in Sleep on the influence of nasal resistance (NAR) on oral device treatment outcome in OSA demonstrates the need for an interdisciplinary approach between ENT surgeons and sleep physicians to treating OSA. The study suggests that higher levels of NAR may negatively affect outcome with MAS[5] and subsequently methods to lower nasal resistance may improve the outcome of oral device treatment.
They are generally more successful at treating mild and moderate sleep apnea and less effective at treating severe sleep apnea, even though good success was measured even in severe sleep apnea.[6] They may bring the level of apnea a patient experiences down significantly but fail to eliminate it.[citation needed]
A meta-analysis of 51 randomized controlled trials investigating the effects of CPAP and oral devices on blood pressure found that oral devices were equally effective as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) devices in lowering the blood pressure of patients with OSA.[7] The medical dental sleep appliance, or MDSA, was clinically proven to conclusively show in a large and complex randomized controlled study that CPAP and MAS are effective in treating sleep-disordered breathing in subjects with AHI 5–30. CPAP was thought to be more effective, but randomised control evidence (such as that reviewed in 2013) suggests splints may be as effective in patients with a range of severities of obstructive sleep apnoea.[8] Both methods appear effective in alleviating symptoms, improving daytime sleepiness, quality of life and some aspects of neurobehavioral function, with CPAP usage being less than self-reported MAS usage. More test subjects and their domestic partners felt that CPAP was the most effective treatment, although MAS was easier to use. Nocturnal systemic hypertension was shown to improve with MAS but not CPAP, although the changes are small.[9]
Drawbacks
[edit]In a survey study of patients, many discontinued use because of discomfort, lack of efficacy or switching to CPAP, and frequent side-effects such as dry mouth, tooth pain, dental discomfort and jaw pain.[10][11] Long-term use is not associated with temporamandibular disorders but was associated with permanent changes in how the upper and lower teeth meet, and the appliances needed about 0.8 repairs/relines per year.[12] Some patients can find these devices somewhat uncomfortable, although many patients find them less bothersome than CPAP mask treatment, so patients are more likely to wear them consistently and comply with treatment[13] CPAP manufacturers claim that improperly fitted devices may cause teeth to shift over time, like with CPAP, but cite no evidence to support these claims.[citation needed] Patients may pay around $1900 out of pocket to secure these devices, and, in the US, some health plans do not cover these costs.[14] The high price for prescription devices has led to a proliferation of lower cost non-prescription devices that are unproven and some sleep specialists suggest may be dangerous.[15]
Adherence to oral appliance is strongly associated with patient reservations regarding the effects of the device on teeth, possible lack of efficacy, and discomfort.[16]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Ramar K, Dort LC, Katz SG, Lettieri CJ, Harrod CG, Thomas SM, Chervin RD (July 2015). "Clinical Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Snoring with Oral Appliance Therapy: An Update for 2015". J Clin Sleep Med. 11 (7): 773–827. doi:10.5664/jcsm.4858. PMC 4481062. PMID 26094920.
- ^ Vanderveken, Olivier M.; Devolder, Annick; Marklund, Marie; Boudewyns, An N.; Braem, Marc J.; Okkerse, Walter; Verbraecken, Johan A.; Franklin, Karl A.; De Backer, Wilfried A. (2008-07-15). "Comparison of a Custom-made and a Thermoplastic Oral Appliance for the Treatment of Mild Sleep Apnea". American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 178 (2): 197–202. doi:10.1164/rccm.200701-114OC. ISSN 1073-449X. PMID 17673699.
- ^ Rose E. (2004). "Identifying the Ideal Oral Appliance Candidate". Journal of Orofacial Orthopedics. 65: 6.
- ^ a b Chan AS, Lee RW, Cistulli PA (August 2007). "Dental appliance treatment for obstructive sleep apnea". Chest. 132 (2): 693–9. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.675.8333. doi:10.1378/chest.06-2038. PMID 17699143.
- ^ Zeng B, Ng AT, Qian J, Petocz P, Darendeliler MA, Cistulli PA (2008). "Influence of nasal resistance on oral appliance treatment outcome in obstructive sleep apnea". Sleep. 31 (4): 543–547. doi:10.1093/sleep/31.4.543. PMC 2279749. PMID 18457242.
- ^ Haviv Y, Bachar G, Aframian DJ, Almoznino G, Michaeli E, Benoliel R (April 2015). "A 2-year mean follow-up of oral appliance therapy for severe obstructive sleep apnea: a cohort study". Oral Dis. 21 (3): 386–92. doi:10.1111/odi.12291. PMID 25207802.
- ^ Bratton DJ, Gaisl T, Wons AM, Kohler M (December 2015). "CPAP vs Mandibular Advancement Devices and Blood Pressure in Patients With Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis". JAMA. 314 (21): 2280–93. doi:10.1001/jama.2015.16303. PMID 26624827.
- ^ Phillips CL, Grunstein RR, Darendeliler MA, Mihailidou AS, Srinivasan VK, Yee BJ, Marks GB, Cistulli PA (April 2013). "Health outcomes of continuous positive airway pressure versus oral appliance treatment for obstructive sleep apnea: a randomized controlled trial". Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 187 (8): 879–87. doi:10.1164/rccm.201212-2223OC. PMID 23413266.
- ^ Barnes M, McEvoy RD, Banks S, Tarquinio N, Murray CG, Vowles N, Pierce RJ (September 2004). "Efficacy of positive airway pressure and oral appliance in mild to moderate obstructive sleep apnea". Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 170 (6): 656–64. doi:10.1164/rccm.200311-1571OC. PMID 15201136.
- ^ de Almeida FR, Lowe AA, Tsuiki S, Otsuka R, Wong M, Fastlicht S, Ryan F (April 2005). "Long-term compliance and side effects of oral appliances used for the treatment of snoring and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome". J Clin Sleep Med. 1 (2): 143–52. doi:10.5664/jcsm.8978. ISSN 1550-9389. PMID 17561628.
- ^ Pantin CC, Hillman DR, Tennant M (March 1999). "Dental side effects of an oral device to treat snoring and obstructive sleep apnea". Sleep. 22 (2): 237–40. doi:10.1093/sleep/22.2.237. ISSN 1550-9109. PMID 10201069.
- ^ Martínez-Gomis J, Willaert E, Nogues L, Pascual M, Somoza M, Monasterio C (January 2010). "Five years of sleep apnea treatment with a mandibular advancement device. Side effects and technical complications". Angle Orthod. 80 (1): 30–6. doi:10.2319/030309-122.1. hdl:2445/20727. ISSN 0003-3219. PMC 8978723. PMID 19852636.
- ^ Glos M, Penzel T, Schoebel C, Nitzsche GR, Zimmermann S, Rudolph C, Blau A, Baumann G, Jost-Brinkmann PG, Rautengarten S, Meier JC, Peroz I, Fietze I (May 2016). "Comparison of effects of OSA treatment by MAD and by CPAP on cardiac autonomic function during daytime". Sleep Breath. 20 (2): 635–46. doi:10.1007/s11325-015-1265-0. PMC 4850173. PMID 26463420.
- ^ "Managing a Sleep Disorder Long-Term: Will Insurance Cover Your Expenses?". Health.com. Retrieved 28 June 2016.
- ^ Woolston, Chris (2011-02-28). "Over-the-counter devices probably won't help sleep apnea". Los Angeles Times. ISSN 0458-3035. Retrieved 2016-08-06.
- ^ Haviv Y, Zini A, Almoznino G, Keshet N, Sharav Y, Aframian DJ (July 2017). "Assessment of interfering factors in non-adherence to oral appliance therapy in severe sleep apnea". Oral Dis. 23 (5): 629–635. doi:10.1111/odi.12633. PMID 28054437.
