Maltese people
 | |
 Map of Maltese Diaspora | |
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| c.400,000–700,000[a] | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| 198,996[2] | |
| 41,920[3] | |
| 40,230[4] (Maltese-born) | |
| 40,820 (2016)[5] | |
| 31,000[6] | |
| 1,000[7] | |
| 1,000[8] | |
| ~1,000–2,000[9][10] | |
| < 200 (Many resettled in Malta after the 1950s)[11] | |
| Languages | |
| Maltese English • Italian | |
| Religion | |
| Predominantly Roman Catholicism[12][13] | |
a The total figure is merely an estimation from all the referenced populations. | |
The Maltese (Maltese: Maltin) people are an ethnic group native to Malta who speak Maltese, a Semitic language and share a common culture and Maltese history. Malta, an island country in the Mediterranean Sea, is an archipelago that also includes an island of the same name together with the islands of Gozo (Maltese: Għawdex) and Comino (Maltese: Kemmuna); people of Gozo, Gozitans (Maltese: Għawdxin) are considered a subgroup of the Maltese.
History
[edit]The current Maltese people, characterised by the use of the Maltese language and by Roman Catholicism, are the descendants – through much mixing and hybridisation – of colonists from Sicily and Calabria who repopulated the Maltese islands in the beginning of the second millennium after a two-century lapse of depopulation that followed the Ifriqiyian conquest by the Aghlabids in AD 870.[14][15]
A genetic study by Capelli et al. indicates that Malta was barely inhabited at the turn of the tenth century and was likely to have been repopulated by settlers from Sicily and Calabria who spoke Siculo-Arabic.[16][15] Previous inhabitants of the islands – Phoenicians, Romans, Byzantines – did not leave many traces, as most nameplaces were lost and replaced. The Normans conquered the island in 1091 and completely re-Christianised them by 1249.[17] This re-Christianisation created the conditions for the evolution of the Maltese language from the now extinct Siculo-Arabic dialect.[18]
The influences on the population after this have been fiercely debated among historians and geneticists. The origins question is complicated by numerous factors, including Malta's turbulent history of invasions and conquests, with long periods of depopulation followed by periods of immigration to Malta and intermarriage with the Maltese by foreigners from the Mediterranean, Western and Southern European countries that ruled Malta. The many demographic influences on the island include:
- The exile to Malta of the entire male population of the town of Celano (Italy) in 1223
- The removal of all remaining North African Muslims from Malta in 1224[19]
- The stationing of Swabian and Sicilian Italian troops on Malta in 1240
- Further waves of European repopulation throughout the 13th century[20]
- The arrival of several thousand Aragonese (i.e. Catalans, Valencians, Majorcans, and proper Aragonese, from current Spain) soldiers in 1283 to 1425.
- The settlement in Malta of noble families from Sicily (Italy) and the Crown of Aragon (now mostly part of Spain) between 1372 and 1450
- The arrival of several thousand Greek Rhodian sailors, soldiers and slaves with the Knights of St. John in 1530
- The introduction of several thousand Sicilian laborers in 1551 and again in 1566
- The emigration of some 891 Italian exiles to Malta during the Risorgimento in 1849
- The posting of some 22,000 British servicemen in Malta from 1807 to 1979 (only a small number of whom remained in the islands),[21] as well as other British and Irish who settled in Malta over the decades
- The mass emigration occurring after World War II and continuing well into the 1960s and 1970s. Many Maltese left the island for the United Kingdom, Australia, Canada and the United States. Following Malta's accession to the European Union in 2004 expatriate communities grew in European countries such as in Belgium.
Over time, the various rulers of Malta published their own view of the ethnicity of the population.[22] The Knights of Malta downplayed the role of Islam in Malta and promoted the idea of a continuous Roman Catholic presence on the islands.[23]
Genetics
[edit]
Paternal lineages
[edit]According to Capelli et al. (2005), Y-DNA haplogroups are found at the following frequencies in Malta: R1 (35.55% including 32.2% R1b), J (28.90% including 21.10% J2 and 7.8% J1), I (12.20%), E (11.10% including 8.9% E1b1b), F (6.70%), K (4.40%), P (1.10%).[24] Haplogroup R1 and I are typical in European populations and E, K, F and J haplogroups consist of lineages with differential distribution mostly in the Middle East and North Africa. The study by Capelli et al. has concluded that the contemporary males of Malta most likely originated from Southern Italy[25] and that there is a minuscule input from the Eastern Mediterranean with affinity to Lebanese Christians.[26] The study also indicates that Malta was barely inhabited at the turn of the tenth century and was likely to have been repopulated by settlers from Sicily and Calabria who spoke Siculo-Arabic.[16][15] These findings confirm the onomastic and linguistic evidence presented in 1993 by Geoffrey Hull, who traced the oldest Maltese surnames to southern and south-eastern Sicily, especially the Agrigento district.[27]



Another study carried out by geneticists Spencer Wells and Pierre Zalloua et al. in 2008 claimed that more than 50% of Y-chromosomes from Maltese men could have Phoenician origins.[29][30]
Autosomal DNA
[edit]According to a 2014 study by Iosif Lazaridis et al., the genetic makeup of most European populations is a mixture of three ancestral sources: Western Hunter-Gatherer, Ancient North Eurasian and Early European Farmer, but this model does not work for groups like the Maltese people and Sicilians. They have more Near Eastern-related ancestry than can be explained by EEF admixture. They "also cannot be jointly fit with other Europeans", as they are shifted towards Near Eastern populations.[31]
Culture
[edit]The culture of Malta is a reflection of various cultures that have come into contact with the Maltese Islands throughout the centuries, including neighbouring Mediterranean cultures, and the cultures of the nations that ruled Malta for long periods of time prior to its independence in 1964.
The culture of modern Malta has been described as a "rich pattern of traditions, beliefs and practices," which is the result of "a long process of adaptation, assimilation and cross fertilisation of beliefs and usages drawn from various conflicting sources." It has been subjected to the same complex, historic processes that gave rise to the linguistic and ethnic admixture that defines who the people of Malta and Gozo are today.[32]
Language
[edit]
Maltese people speak the Maltese language, a Semitic language with a substantial Romance (Italian) superstratum and morphology, and written in the Latin alphabet in its standard form. The language is descended from Siculo-Arabic, an extinct dialect of Arabic that was spoken in Sicily by indigenous people who were at that time divided in religion into continuing Greek-rite Christians and Muslims whose recent ancestors were Sicilian converts from Christianity.[33] In the course of Malta's history, the language has adopted massive amounts of vocabulary from Sicilian and Italian, to a much lesser degree, borrowings from English (anglicisms being more common in colloquial Maltese than in the literary language), and a few dozen French loanwords. A large number of superficially Arabic words and idioms are actually loan translations (calques) from Sicilian and Italian which would make little or no sense to speakers of other Arabic-derived languages.
Maltese became an official language of Malta in 1934, replacing Italian and joining English. There are an estimated 371,900 speakers in Malta of the language, with statistics citing that 100% of the people are able to speak Maltese, 88% English, 66% Italian and 17% French, showing a greater degree of linguistic capabilities than most other European countries.[34] In fact multilingualism is a common phenomenon in Malta, with English, Maltese and on occasion Italian, used in everyday life. Whilst Maltese is the national language, it has been suggested that with the ascendancy of English a language shift may begin;[35][36] though a survey dating to 2005 suggested that the percentage speaking Maltese as their mother tongue within Malta remained at 97%.[37]
Religion
[edit]The Constitution of Malta provides for freedom of religion but establishes Roman Catholicism as the state religion.[38] Malta is described in the Book of Acts (Acts 27:39–42 and Acts 28:1–11) as the place where Saint Paul the Apostle was shipwrecked on his way to Rome, awaiting trial. Freedom House and the World Factbook report that 98% of the Maltese are Roman Catholic (mostly Roman-Rite, with a Byzantine-Rite minority), making the nation one of the most Roman Catholic countries in the world in terms of total population.[39]
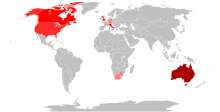
Emigration
[edit]Malta has long been a country of emigration, with big Maltese communities in English-speaking countries abroad as well as in France.

Mass emigration picked up in the 19th century, reaching its peak in the decades after World War II. Migration was initially to North African countries (particularly Algeria, Tunisia and Egypt); later Maltese migrants headed towards the United Kingdom, the United States, Canada and Australia. There is little trace left of the Franco-Maltese communities in North Africa, most of them having been displaced, after the rise of independence movements, to places like France (especially Marseille and the Riviera), the United Kingdom or Australia. The Franco-Maltese are culturally distinct from the Maltese from Malta, in that the former have remained attached to the use of the Italian language (often, but not always, alongside Maltese) as well as speaking French. Although migration has ceased to be a social phenomenon of significance there are still important Maltese communities in Australia, Canada, the United States and the United Kingdom. Emigration dropped dramatically after the mid-1970s and has since ceased to be a social phenomenon of significance.
Since Malta joined the EU in 2004, expatriate communities emerged in a number of European countries particularly in Belgium and Luxembourg.[citation needed]
See also
[edit]Further reading
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ Census of population and housing 2021 Archived 2022-08-09 at the Wayback Machine. pp. 30. National Statistics Office of Malta
- ^ "Australia General Community Profile". Australian Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 28 June 2022.
- ^ "Census Profile, 2016 Census: Ethnic origin population". Statistics Canada. Retrieved 3 December 2021.
- ^ "Population data". OECD. Archived from the original (xls) on 2009-06-17.
- ^ "2016 American Community Survey 1-year estimates". Retrieved 2018-05-18.
- ^ "Italy | Joshua Project".
- ^ "Immigrant and Emigrant Populations by Country of Origin and Destination". 10 February 2014.
- ^ "Immigrant and Emigrant Populations by Country of Origin and Destination". 10 February 2014.
- ^ "Maltese living in Turkey celebrate traditional feast". 20 September 2015.
- ^ "The Great Exodus (Maltese in Turkey from Lancs to the Levant)". 10 March 2015.
- ^ "Maltese in Tunisia". 14 September 2021.
- ^ "Malta". State.gov. 1 January 2004. Retrieved 17 August 2012.
- ^ Sansone, Kurt (16 February 2023). "Census 2021: Maltese citizens overwhelmingly identify as Roman Catholics". Malta Today. Archived from the original on 17 January 2024.
- ^ "Gozo". IslandofGozo.org. 7 October 2007. Archived from the original on 22 August 2008.
- ^ a b c So who are the 'real' Maltese. 14 September 2014.
There's a gap between 800 and 1200 where there is no record of civilisation. It doesn't mean the place was completely uninhabited. There may have been a few people living here and there, but not much……..The Arab influence on the Maltese language is not a result of Arab rule in Malta, Prof. Felice said. The influence is probably indirect, since the Arabs raided the island and left no-one behind, except for a few people. There are no records of civilisation of any kind at the time. The kind of Arabic used in the Maltese language is most likely derived from the language spoken by those that repopulated the island from Sicily in the early second millennium; it is known as Siculo-Arab. The Maltese are mostly descendants of these people.
- ^ a b Genetic Origin of Contemporary Maltese People. 5 August 2007.
Repopulation is likely to have occurred by a clan or clans (possibly of Arab or Arab-like speaking people) from neighbouring Sicily and Calabria. Possibly, they could have mixed with minute numbers of residual inhabitants, with a constant input of immigrants from neighbouring countries and later, even from afar. There seems to be little input from North Africa.
- ^ The origin of the Maltese surnames.
Ibn Khaldun puts the expulsion of Islam from the Maltese Islands to the year 1249. It is not clear what actually happened then, except that the Maltese language, derived from Arabic, certainly survived. Either the number of Christians was far larger than Giliberto had indicated, and they themselves already spoke Maltese, or a large proportion of the Muslims themselves accepted baptism and stayed behind. Henri Bresc has written that there are indications of further Muslim political activity on Malta during the last Suabian years. Anyhow there is no doubt that by the beginning of Angevin times no professed Muslim Maltese remained either as free persons or even as serfs on the island.
- ^ Joseph M. Brincat (Feb 2005). "Maltese – an unusual formula". MED Magazine. Archived from the original on Apr 1, 2023.
Originally Maltese was an Arabic dialect but it was immediately exposed to Latinisation because the Normans conquered the islands in 1090, while Christianisation, which was complete by 1250, cut off the dialect from contact with Classical Arabic. Consequently Maltese developed on its own, slowly but steadily absorbing new words from Sicilian and Italian according to the needs of the developing community.
- ^ Debattista, Martin. "Timeline of Malta History". AboutMalta.com. Archived from the original on May 18, 2008. Retrieved 2008-05-14.
- ^ Constantiae Imperatricis et Reginae Siciliae Diplomata: 1195–1198, ed. T.K.Slzer (Vienna, 1983), 237–240.
- ^ Joseph M. Brincat, "Language and Demography in Malta: The Social Foundations of the Symbiosis between Semitic and Romance in Standard Maltese," in Malta: A Case Study in International Cross-Currents. Proceedings of the First International Colloquium on the history of the Central Mediterranean held at the University of Malta, 13–17 December 1989. Ed: S. Fiorini and V. Mallia-Milanes (Malta University Publications, Malta Historical Society, and Foundation for International Studies, University of Malta) at 91–110. Last visited 5 August 2007.
- ^ Anthony Luttrell, "Medieval Malta: the Non-written and the Written Evidence", in Malta: A Case Study in International Cross-Currents. Proceedings of the First International Colloquium on the history of the Central Mediterranean held at the University of Malta, 13–17 December 1989. Ed: S. Fiorini and V. Mallia-Milanes (Malta University Publications, Malta Historical Society, and Foundation for International Studies, University of Malta) at 33–45. Last visited 5 August 2007.
- ^ Anthony T. Luttrell, "Girolamo Manduca and Gian Francesco Abela: Tradition and invention in Maltese Historiography," in Melita Historica, 7 (1977) 2 (105–132). Last visited 5 August 2007.
- ^ (n=90), Population structure in the Mediterranean basin: a Y chromosome perspective, Capelli et al. 2005
- ^ A.E. Felice; "The Genetic Origin of Contemporary Maltese", The Sunday Times of Malta, 5 August 2007.
- ^ Genetic Origin of Contemporary Maltese People. 5 August 2007.
Together with colleagues from other institutions across the Mediterranean and in collaboration with the group led by David Goldstein at the University College, London, we have shown that the contemporary males of Malta most likely originated from Southern Italy, including Sicily and up to Calabria. There is a minuscule amount of input from the Eastern Mediterranean with genetic affinity to Christian Lebanon....We documented clustering of the Maltese markers with those of Sicilians and Calabrians. The study is published in the Annals of Human Genetics by C. Capelli, N. Redhead, N. Novelletto, L. Terrenato, P. Malaspina, Z. Poulli, G. Lefranc, A. Megarbane, V. Delague, V. Romano, F. Cali, V.F. Pascali, M. Fellous, A.E. Felice, and D.B. Goldstein; "Population Structure in the Mediterranean Basin; A Y Chromosome Perspective", AHG, 69, 1–20, 2005..
- ^ Geoffrey Hull, The Malta Language Question: A Case Study in Cultural Imperialism, Valletta: Said International, 1993, pp. 317–330. Scientific etymologies of the longest-established Maltese family names are given in Geoffrey Hull, “The Oldest Maltese Surnames: A Window on Sicily’s Medieval History”, in Claudia Karagoz and Giovanna Summerfield (eds), Sicily and the Mediterranean: Migration, Exchange, Reinvention, New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2015, pp. 78–108; "Late Medieval Maltese Surnames of Arabic and Greek Origin", Symposia Melitensia No. 11 (2015), pp. 129–143
- ^ "The last għonnella". Times of Malta. 18 June 2020. Retrieved 2021-01-28.
- ^ "Phoenicians Online Extra @ National Geographic Magazine". Archived from the original on September 22, 2004. Retrieved 12 January 2017.
- ^ Zalloua, Pierre A.; Platt, Daniel E.; El Sibai, Mirvat; Khalife, Jade; Makhoul, Nadine; Haber, Marc; Xue, Yali; Izaabel, Hassan; Bosch, Elena; Adams, Susan M.; Arroyo, Eduardo; López-Parra, Ana María; Aler, Mercedes; Picornell, Antònia; Ramon, Misericordia; Jobling, Mark A.; Comas, David; Bertranpetit, Jaume; Wells, R. Spencer; Tyler-Smith, Chris (2008). "Identifying Genetic Traces of Historical Expansions: Phoenician Footprints in the Mediterranean". The American Journal of Human Genetics. 83 (5): 633–642. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.10.012. PMC 2668035. PMID 18976729.
- ^ Lazaridis, Iosif; Patterson, Nick; Mittnik, Alissa; Renaud, Gabriel; Mallick, Swapan; Kirsanow, Karola; Sudmant, Peter H.; Schraiber, Joshua G.; Castellano, Sergi; Lipson, Mark; Berger, Bonnie; Economou, Christos; Bollongino, Ruth; Fu, Qiaomei; Bos, Kirsten I. (2014). "Ancient human genomes suggest three ancestral populations for present-day Europeans". Nature. 513 (7518): 409–413. arXiv:1312.6639. Bibcode:2014Natur.513..409L. doi:10.1038/nature13673. ISSN 0028-0836. PMC 4170574. PMID 25230663.
- ^ J. Cassar Pullicino, "Determining the Semitic Element in Maltese Folklore", in Studies in Maltese Folklore, Malta University Press (1992), p. 68.
- ^ "MED Magazine". 9 May 2008. Archived from the original on 9 May 2008. Retrieved 12 January 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ "Europeans and their Languages" (PDF). Ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 12 December 2017.
- ^ European Commission, "Malta: Country Profile", Euromosaic Study (September 2004)
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2006-09-19. Retrieved 2006-12-04.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "EUROPEANS AND LANGUAGES" (PDF). Ec.europa.eu. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 January 2007. Retrieved 12 December 2017.
- ^ "Chapter 1 – The Republic of Malta". Legal-Malta. Archived from the original on 27 August 2011. Retrieved 4 September 2011.
- ^ "Catholic Church in Malta". GCatholic.org. Retrieved 17 August 2012.
References
[edit]- Bonanno A. (2005). Malta: Phoenician, Punic and Roman. Midsea Books: Valletta.
External links
[edit] Media related to People of Malta at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to People of Malta at Wikimedia Commons- Joëlle Pawelczyk, "The Origin of the 'Maltese' Surnames"




