Lymphedema
| Lymphedema | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Lymphoedema, lymphatic obstruction, lymphatic insufficiency |
 | |
| Lower extremity lymphedema | |
| Specialty | Vascular medicine, Rheumatology,[1] Physical medicine and rehabilitation, General surgery, Plastic surgery |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms[2] |
| Differential diagnosis | Lipodystrophy, venous insufficiency[2] |
Lymphedema, also known as lymphoedema and lymphatic edema, is a condition of localized swelling caused by a compromised lymphatic system.[2] The lymphatic system functions as a critical portion of the body's immune system and returns interstitial fluid to the bloodstream.
Lymphedema is most frequently a complication of cancer treatment or parasitic infections, but it can also be seen in a number of genetic disorders. Tissues with lymphedema are at high risk of infection because the lymphatic system has been compromised.[3]
Though incurable and progressive, a number of treatments may improve symptoms.[2] This commonly includes compression therapy, good skin care, exercise, and manual lymphatic drainage (MLD), which together are known as combined decongestive therapy.[2] Diuretics are not useful.[2]
Signs and symptoms
[edit]
The most common manifestation of lymphedema is soft tissue swelling (edema). As the disorder progresses, worsening edema and skin changes including discoloration, verrucous (wart-like) hyperplasia, hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, dermal thickening, and ulcers may be seen. Additionally, there is increased risk of infection of the skin, known as erysipelas.[citation needed]
Complications
[edit]When lymphatic impairment becomes so great that the collected lymph fluid exceeds the lymphatic system's ability to transport it, an abnormal amount of protein-rich fluid collects in the tissues. Left untreated, this stagnant, protein-rich fluid causes tissue channels to increase in size and number, reducing oxygen availability. This interferes with wound healing and provides a rich medium for bacterial growth which can result in skin infections, lymphangitis, lymphadenitis, and, in severe cases, skin ulcers.[4] It is vital for lymphedema patients to be aware of the symptoms of infection and to seek immediate treatment, since recurrent infections or cellulitis, in addition to their inherent danger, further damage the lymphatic system and set up a vicious circle.[citation needed]
In rare cases, lymphedema may lead to a form of cancer called lymphangiosarcoma, although the mechanism of carcinogenesis is not understood. Lymphedema-associated lymphangiosarcoma is called Stewart–Treves syndrome.[4] Lymphangiosarcoma most frequently occurs in cases of long-standing lymphedema. The incidence of angiosarcoma five years after radical mastectomy is estimated to be 0.45% in surviving patients.[5][6] Lymphedema is also associated with a low grade form of cancer called retiform hemangioendothelioma (a low grade angiosarcoma).[7]
Lymphedema can be disfiguring, and may result in a poor body image and psychological distress.[8] Complications of lymphedema can cause difficulties in activities of daily living.[9]
Causes and risk factors
[edit]Lymphedema may be inherited (primary) or caused by injury to the lymphatic vessels (secondary).[10] There are also risk factors that may increase one's risk of developing lymphedema such as old age, being overweight or obese, and having rheumatic or psoriatic arthritis.[11]
Lymph node damage
[edit]Lymphedema is most commonly seen after lymph node dissection, surgery or radiation therapy for the treatment of cancer, most notably breast cancer. In many patients the condition does not develop until months or even years after therapy has concluded.[medical citation needed] Lymphedema may also be associated with accidents or certain diseases or conditions that may inhibit the lymphatic system from functioning properly.[4] It can also be caused by damage to the lymphatic system from infections such as cellulitis.[12] In tropical areas of the world where parasitic filarial worms are endemic, a common cause of secondary lymphedema is filariasis.[13]
Primary lymphedema may be congenital or may arise sporadically. Multiple syndromes are associated with primary lymphedema, including Turner syndrome, Milroy's disease, and Klippel–Trénaunay syndrome. In these syndromes it may occur as a result of absent or malformed lymph nodes or lymphatic channels. Lymphedema can be present at birth, develop at the onset of puberty (praecox), or not become apparent for many years into adulthood (tarda). In men, lower-limb primary lymphedema is most common, occurring in one or both legs. Some cases of lymphedema may be associated with other vascular abnormalities.[4][citation needed]
Secondary lymphedema affects both men and women, and, in Western countries, is most commonly due to cancer treatment.[14] In women, it is most prevalent in an upper limb after breast cancer surgery, especially axillary lymph node dissection,[15] and occurs on the same side of the body as the surgery. Breast and trunk lymphedema can also occur but go unrecognised as there is swelling in the area after surgery, and its symptoms (peau d'orange and an inverted nipple) can be confused with post surgery fat necrosis.[16] Between 38 and 89% of breast cancer patients have lymphedema due to axillary lymph node dissection or radiation.[14][17][18] Unilateral lymphedema of a lower limb occurs in up to 41% of patients after gynecologic cancer.[14][19] For men treated for prostate cancer, a 5-66% incidence has been reported, with the incidence rate depending on whether staging or radical removal of lymph glands was done in addition to radiotherapy.[14][20][21]
Head and neck lymphedema can be caused by surgery or radiation therapy for tongue or throat cancer. It may also occur in the lower limbs or groin after surgery for colon, ovarian or uterine cancer, if removal of lymph nodes or radiation therapy is required. Surgery or treatment for prostate, colon and testicular cancers may result in secondary lymphedema, particularly when lymph nodes have been removed or damaged.[medical citation needed]
The onset of secondary lymphedema in patients who have had cancer surgery has also been linked to aircraft flight (likely due to decreased cabin pressure or relative immobility). For cancer survivors wearing a prescribed and properly fitted compression garment may help decrease swelling during air travel.[22]
Some cases of lower-limb lymphedema have been associated with the use of tamoxifen, due to blood clots and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) associated with this medication. Resolution of the blood clots or DVT is needed before lymphedema treatment can be initiated.[medical citation needed]
At birth
[edit]Hereditary lymphedema is a primary lymphedema – swelling that results from abnormalities in the lymphatic system that are present from birth. Swelling may be present in a single limb, several limbs, genitalia, or the face. It is sometimes diagnosed prenatally by a nuchal scan or postnatally by lymphoscintigraphy.[medical citation needed]
The most common cause is Meige disease which usually presents at puberty. Another form of hereditary lymphedema is Milroy's disease, caused by mutations in the VEGFR3 gene.[4][23] Hereditary lymphedema is frequently syndromic and is associated with Turner syndrome, lymphedema–distichiasis syndrome, yellow nail syndrome, and Klippel–Trénaunay syndrome.[24]
One defined genetic cause for hereditary lymphedema is GATA2 deficiency. This deficiency is a grouping of several disorders caused by a single defect: familial or sporadic inactivating mutations in one of the two parental GATA2 genes. These autosomal dominant mutations cause a reduction, i.e. a haploinsufficiency, in the cellular levels of the gene's product, GATA2. The GATA2 protein is a transcription factor critical for the development, maintenance, and functionality of blood-forming, lymphatic-forming, and other tissue-forming stem cells. Due to these mutations cellular levels of GATA2 are deficient and over time individuals develop hematological, immunological, lymphatic, and other disorders. GATA2 deficiency-induced defects in the lymphatic vessels and valves underlies the development of lymphedema, primarily in the lower extremities but may also occur in places such as the face or testes. This form of the deficiency, when coupled with sensorineural hearing loss, which may also be due to faulty development of the lymphatic system, is sometimes termed Emberger syndrome.[25][26]
Primary lymphedema occurs in approximately one to three births out of every 10,000 births, with a female to male ratio of 3.5:1. In North America, the incidence of primary lymphedema is approximately 1.15 births out of every 100,000 births.[contradictory] Compared to secondary lymphedema, primary lymphedema is relatively rare.[27]
Inflammatory lymphedema
[edit]Bilateral lower extremity inflammatory lymphedema (BLEIL) is a distinct type of lymphedema occurring in a setting of acute and prolonged standing, such as in new recruits during basic training.[28] Possible underlying mechanisms may include venous congestion and inflammatory vasculitis.[29]
Physiology
[edit]Lymph is formed from the fluid that filters out of blood and contains proteins, cellular debris, bacteria, etc. This fluid is collected by the initial lymph collectors that are blind-ended endothelial-lined vessels with fenestrated openings that allow fluids and particles as large as cells to enter. Once inside the lumen of the lymphatic vessels, the fluid is guided along increasingly larger vessels, first with rudimentary valves to prevent backflow, later with complete valves similar to the venous valve. Once the lymph enters the fully valved lymphatic vessels, it is pumped by a rhythmic peristaltic-like action by smooth muscle cells within the lymphatic vessel walls. This peristaltic action is the primary driving force moving lymph within its vessel walls. The sympathetic nervous system regulates the frequency and power of the contractions. Lymph movement can be influenced by the pressure of nearby muscle contraction, arterial pulse pressure and the vacuum created in the chest cavity during respiration, but these passive forces contribute only a minor percentage of lymph transport. The fluids collected are pumped into continually larger vessels and through lymph nodes, which remove debris and police the fluid for dangerous microbes. The lymph ends its journey in the thoracic duct or right lymphatic duct, which drain into the blood circulation.[10]
Several research groups have hypothesized that chronic inflammation is a key regulator in the development of lymphedema. Th cells, particularly Th2 differentiation, play a crucial role in the pathophysiology of lymphedema. Research has shown that increased expression of Th2-inducing cytokines in the epidermal cells of the lymphoedematous limb. Treatment with QBX258 has been found to decrease hyperkeratosis and fibrosis, reduce the number of CD4+ cells, and normalize the expression of Th2-inducing cytokines and IL13R by keratinocytes. These findings suggest that epidermal cells may initiate or coordiate chronic Th2 responses in lymphedema.[30]
Role of T-Cell inflammation and Th2 response
[edit]Lymphedema involves a complex interplay of inflammatory processes. Recent research has shed light on the role of T-cell inflammation and the Th2 immune response in the initiation of lymphedema.[31]
T-Cell inflammation and fibrosis
[edit]Studies have revealed that sustained lymphatic stasis results in the infiltration of CD4+ T-cells, leading to inflammation and fibrosis within affected tissues.[31]
Diagnosis
[edit]Diagnosis is generally based on signs and symptoms, with testing used to rule out other potential causes.[2] An accurate diagnosis and staging may help with management.[2] A swollen limb can result from different conditions that require different treatments. Diagnosis of lymphedema is currently based on history, physical exam, and limb measurements. Imaging studies such as lymphoscintigraphy and indocyanine green lymphography are only required when surgery is being considered.[2] However, the ideal method of staging to guide treatment is controversial because of several different proposed protocols.[32][33]
Lymphedema can occur in both the upper and lower extremities, and in some cases, the head and neck. Assessment of the extremities first begins with a visual inspection; color, presence of hair, visible veins, size and any sores or ulcerations are noted. Lack of hair may indicate an arterial circulation problem.[34] In cases of swelling, the extremities' circumference is measured over time for reference. In early stages of lymphedema, elevating the limb may reduce or eliminate the swelling. Palpation of the wrist or ankle can determine the degree of swelling; assessment includes a check of the pulses. The axillary or inguinal lymph nodes may be enlarged due to the swelling. Enlargement of the nodes lasting more than three weeks may indicate infection or other illnesses (such as sequela from breast cancer surgery) requiring further medical attention.[34]
Diagnosis or early detection of lymphedema is difficult. The first signs may be subjective observations such as a feeling of heaviness in the affected extremity. These may be symptomatic of early-stage lymphedema where accumulation of lymph is mild and not detectable by changes in volume or circumference. As lymphedema progresses, definitive diagnosis is commonly based upon an objective measurement of differences between the affected or at-risk limb and the opposite unaffected limb, e.g. in volume or circumference. No generally accepted criterion is definitively diagnostic, although a volume difference of 200 ml between limbs or a 4 cm (1.6 in) difference (at a single measurement site or set intervals along the limb) is often used. Bioimpedance measurement (which measures the amount of fluid in a limb) offers greater sensitivity than other methods.[35] Devices like SOZO [36] utilize Bioimpedence Analysis (BIA) by sending a current through the body and measuring the resultant impedance. Another approach involves Tissue Dielectric Constant (TDC) measurement, used by devices such as Delfin Technology's MoistureMeterD and LymphScanner,[37] which employ microwaves to detect changes in the dielectric properties of tissue. These innovative techniques have become integral to official protocols for lymphedema detection.[38]
Chronic venous stasis changes can mimic early lymphedema, but are more often bilateral and symmetric. Lipedema can also mimic lymphedema, however lipedema characteristically spares the feet beginning abruptly at the malleolus (ankle).[2] As a part of the initial work-up before diagnosing lymphedema, it may be necessary to exclude other potential causes of lower extremity swelling such as kidney failure, hypoalbuminemia, congestive heart-failure, protein-losing kidney disease, pulmonary hypertension, obesity, pregnancy and drug-induced edema.[citation needed]
Classification
[edit]
The International Society of Lymphology (ISL) Staging System is based solely on subjective symptoms, making it prone to substantial observer bias. Imaging modalities have been suggested as useful adjuncts to the ISL staging to clarify the diagnosis, such as Cheng's Lymphedema Grading tool, which assesses the severity of extremity lymphedema based on objective limb measurements and provides appropriate options for management.[39][40][41]
I. Grading
[edit]- Grade 1: Spontaneously reversible on elevation. Mostly pitting edema.
- Grade 2: Non-spontaneously reversible on elevation. Mostly non-pitting edema.
- Grade 3: Gross increase in volume and circumference of Grade 2 lymphedema, with eight stages of severity given below based on clinical assessments.
II. Staging
[edit]As described by the Fifth WHO Expert Committee on Filariasis,[43][44] and endorsed by the American Society of Lymphology,[45][citation needed] the staging system helps to identify the severity of lymphedema. With the assistance of medical imaging, such as MRI or CT, staging can be established by the physician, and therapeutic or medical interventions may be applied:[citation needed]
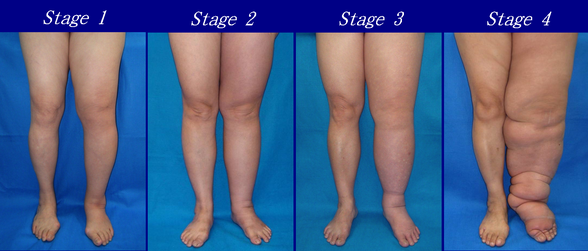
- Stage 0: The lymphatic vessels have sustained some damage that is not yet apparent. Transport capacity is sufficient for the amount of lymph being removed. Lymphedema is not present.
- Stage 1 : Swelling increases during the day and disappears overnight as the patient lies flat in bed. Tissue is still at the pitting stage: when pressed by the fingertips, the affected area indents and reverses with elevation. Usually, upon waking in the morning, the limb or affected area is normal or almost normal in size. Treatment is not necessarily required at this point.
- Stage 2: Swelling is not reversible overnight, and does not disappear without proper management. The tissue now has a spongy consistency and is considered non-pitting: when pressed by the fingertips, the affected area bounces back without indentation. Fibrosis found in Stage 2 lymphedema marks the beginning of the hardening of the limbs and increasing size.
- Stage 3: Swelling is irreversible and usually the limb(s) or affected area becomes increasingly large. The tissue is hard (fibrotic) and unresponsive; some patients consider undergoing reconstructive surgery, called "debulking". This remains controversial, however, since the risks may outweigh the benefits and further damage done to the lymphatic system may make the lymphedema worse.
- Stage 4: The size and circumference of the affected limb(s) become noticeably larger. Bumps, lumps, or protrusions (also called knobs) on the skin begin to appear.
- Stage 5: The affected limb(s) become grossly large; one or more deep skin folds is present.
- Stage 6: Knobs of small elongated or rounded sizes cluster together, giving mossy-like shapes on the limb. Mobility of the patient becomes increasingly impaired.
- Stage 7: The person becomes "handicapped", and is unable to independently perform daily routine activities such as walking, bathing and cooking. Assistance from the family and health care system is needed.
Grades
[edit]Lymphedema can also be categorized by its severity (usually compared to a healthy extremity):[46]
- Grade 1 (mild edema): Involves the distal parts such as a forearm and hand or a lower leg and foot. The difference in circumference is less than 4 cm (1.6 in) and no other tissue changes are present.
- Grade 2 (moderate edema): Involves an entire limb or corresponding quadrant of the trunk. Difference in circumference is 4–6 cm (1.6–2.4 in). Tissue changes, such as pitting, are apparent. The patient may experience erysipelas.
- Grade 3a (severe edema): Lymphedema is present in one limb and its associated trunk quadrant. Circumferential difference is greater than 6 cm (2.4 in). Significant skin alterations, such as cornification, keratosis, cysts or fistulae, are present. Additionally, the patient may experience repeated attacks of erysipelas.
- Grade 3b (massive edema): The same symptoms as grade 3a, except that two or more extremities are affected.
- Grade 4 (gigantic edema): In this stage of lymphedema, the affected extremities are huge, due to almost complete blockage of the lymph channels.
Differential
[edit]Lymphedema should not be confused with edema arising from chronic venous insufficiency, which is caused by compromise of venous drainage rather than lymphatic drainage. However, untreated venous insufficiency can progress into a combined venous/lymphatic disorder known as phlebetic lymphedema (or phlebolymphedema).[47][48][49]
Treatment
[edit]While there is no cure, treatment may improve outcomes.[2] This commonly include compression therapy, good skin care, exercise, manual lymphatic drainage (MLD) and the use of an intermittent pneumatic compression pump, which together is known as combined decongestive therapy.[2] MLD is most effective in mild to moderate disease.[50] In breast cancer-related lymphedema, MLD is safe and may offer added benefit to compression bandages for reducing swelling.[50] Most people with lymphedema can be medically managed with conservative treatment.[51] Diuretics are not useful.[2] Surgery is generally only used if symptoms are not improved by other measures.[2][52]
Compression
[edit]Garments
[edit]
Once a person is diagnosed with lymphedema, compression becomes imperative in the management of the condition. Garments are often intended to be worn all day but may be taken off for sleep, unless otherwise prescribed. Elastic compression garments are worn on the affected limb following complete de-congestive therapy to maintain edema reduction. Inelastic garments provide containment and reduction.[2] Available styles, options, and prices vary widely. A professional garment fitter or certified lymphedema therapist can help determine the best option for the patient.[citation needed]
Bandaging
[edit]Compression bandaging, also called wrapping, is the application of layers of padding and short-stretch bandages to the involved areas. Short-stretch bandages are preferred over long-stretch bandages (such as those normally used to treat sprains), as the long-stretch bandages cannot produce the proper therapeutic tension necessary to safely reduce lymphedema and may produce a tourniquet effect. Compression bandages provide resistance that assists in pumping fluid out of the affected area during exercise. This counter-force results in increased lymphatic drainage and therefore a decrease in size of the swollen area.[53]
Intermittent pneumatic compression therapy
[edit]Intermittent pneumatic compression therapy (IPC) utilizes a multi-chambered pneumatic sleeve with overlapping cells to promote movement of lymph fluid.[2] Pump therapy should only be used in addition to other treatments such as compression bandaging and manual lymph drainage. Pump therapy has been used in the past to help with controlling lymphedema. In some cases, pump therapy helps soften fibrotic tissue and therefore potentially enable more efficient lymphatic drainage.[54] However, reports link pump therapy to increased incidence of edema proximal to the affected limb, such as genital edema arising after pump therapy in the lower limb.[55] Current literature has suggested the use of IPC treatment in conjunction with an elastic therapeutic tape is more effective in the overall reduction of lymphedema as well as increasing shoulder range of motion than the traditional treatment of IPC paired with complete decongestive therapy. The tape is an elastic cotton strip with an acrylic adhesive that is used commonly used to relieve the discomfort and disability associated with sports injuries, but in the context of lymphedema, this increases the space between the dermis and the muscle which increases the opportunity for lymphatic fluid to flow out naturally.[56] The use of IPC treatments with tape, as well as subsequent lymphatic drainage, has proven to significantly reduce the circumference of lymphatic limbs in patients experiencing lymphedema secondary to breast cancer post-mastectomy.[56]
Exercise and massage
[edit]In those with lymphedema or at risk of developing lymphedema, such as following breast cancer treatment, resistance training did not increase swelling and led to decreases in some, in addition to other potential beneficial effects on cardiovascular health.[57][58] Moreover, resistance training and other forms of exercise were not associated with an increased risk of developing lymphedema in people who previously received breast cancer-related treatment. Compression garments should be worn during exercise.[59]
Physical therapy for patients with lymphedema may include trigger point release, soft tissue massage, postural improvement, patient education on condition management, strengthening, and stretching exercises.[60] Exercises may increase in intensity and difficulty over time, beginning with passive movements to increase range of motion and progressing towards using external weights and resistance in various postures.[53]
Surgery
[edit]The treatment of lymphedema is usually conservative, however the use of surgery is proposed for some cases.[61]
Suction assisted lipectomy (SAL), also known as liposuction for lymphedema, may help improve chronic non pitting edema.[62] The procedure removes fat and protein and is done alongside continued compression therapy.[62]
Vascularized lymph node transfers (VLNT) and lymphovenous bypass are supported by tentative evidence as of 2017[update] but are associated with a number of complications.[2][example needed]
Laser therapy
[edit]Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) was cleared by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of lymphedema in November 2006.[63] According to the US National Cancer Institute, LLLT may be effective in reducing lymphedema in some women. Two cycles of laser treatment were found to reduce the volume of the affected arm in approximately one-third of people with post-mastectomy lymphedema at three months post-treatment.[64][65]
A new therapeutic approach involving the drug QBX258 has shown promising results in the treatment of lymphedema. Although it did not reach statistical significance, QBX258 treatment modestly decreased periostin expression and the number of CD4+ and CD4+IL4+ cells in lymphoedematous skin. Notably, QBX258 significantly reduced the expression of Th2-inducing cytokines, improving physical and social quality-of-life measures for patients. However, psychological improvements were not observed.[30]
Epidemiology
[edit]Lymphedema affects approximately 200 million people worldwide.[4]
References
[edit]- ^ Joos E, Bourgeois P, Famaey JP (June 1993). "Lymphatic disorders in rheumatoid arthritis". Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism. 22 (6). Elsevier BV: 392–398. doi:10.1016/s0049-0172(05)80031-9. PMID 8342046.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Grada AA, Phillips TJ (December 2017). "Lymphedema: Diagnostic workup and management". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 77 (6): 995–1006. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.03.021. PMID 29132859.
- ^ Sleigh BC, Manna B (January 2020). "Lymphedema". StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. PMID 30725924.
- ^ a b c d e f Grada AA, Phillips TJ (December 2017). "Lymphedema: Pathophysiology and clinical manifestations". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 77 (6): 1009–1020. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.03.022. PMID 29132848.
- ^ Martin MB, Kon ND, Kawamoto EH, Myers RT, Sterchi JM (October 1984). "Postmastectomy angiosarcoma". The American Surgeon. 50 (10): 541–545. PMID 6541442.
- ^ Chopra S, Ors F, Bergin D (December 2007). "MRI of angiosarcoma associated with chronic lymphoedema: Stewart Treves syndrome". The British Journal of Radiology. 80 (960): e310–e313. doi:10.1259/bjr/19441948. PMID 18065640.
- ^ Requena L, Sangueza OP (February 1998). "Cutaneous vascular proliferations. Part III. Malignant neoplasms, other cutaneous neoplasms with significant vascular component, and disorders erroneously considered as vascular neoplasms". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 38 (2 Pt 1): 143–75, quiz 176–8. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(98)70237-3. PMID 9486670.
- ^ Publishing L (2009-10-28). "Body image and quality of life in secondary lymphedema of the upper limb". Servier – Phlebolymphology. Archived from the original on 2019-09-03. Retrieved 2019-09-03.
- ^ "Oncology Fact Sheet" (PDF). aota.org. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-09-20. Retrieved 2019-09-03.
- ^ a b "A Visual Guide to Lymphedema". WebMD. Archived from the original on 9 July 2021. Retrieved 7 July 2021.
- ^ "Lymphedema – Symptoms and causes". Mayo Clinic. Archived from the original on 2023-08-01. Retrieved 2023-08-02.
- ^ "Lymphoedema – Causes". nhs.uk. 2017-10-20. Archived from the original on 2022-10-21. Retrieved 2022-06-15.
- ^ Shenoy RK (2008-09-20). "Clinical and Pathological Aspects of Filarial Lymphedema and Its Management". The Korean Journal of Parasitology. 46 (3): 119–125. doi:10.3347/kjp.2008.46.3.119. ISSN 0023-4001. PMC 2553332. PMID 18830049. Archived from the original on 2021-12-02. Retrieved 2022-06-15.
- ^ a b c d Brorson H, Ohlin K, Olsson G, Svensson B, Svensson H (June 2008). "Controlled compression and liposuction treatment for lower extremity lymphedema". Lymphology. 41 (2): 52–63. PMID 18720912.
- ^ Jeannie Burt, Gwen White (1 January 2005). Lymphedema: A Breast Cancer Patient's Guide to Prevention and Healing. Hunter House. pp. 9. ISBN 978-0-89793-458-9.
- ^ Choices N. "IPS retired". nhs.uk. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 9 May 2018.
- ^ Kissin MW, Querci della Rovere G, Easton D, Westbury G (July 1986). "Risk of lymphoedema following the treatment of breast cancer". The British Journal of Surgery. 73 (7): 580–584. doi:10.1002/bjs.1800730723. PMID 3730795. S2CID 25777064.
- ^ Segerström K, Bjerle P, Graffman S, Nyström A (1992). "Factors that influence the incidence of brachial oedema after treatment of breast cancer". Scandinavian Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery and Hand Surgery. 26 (2): 223–227. doi:10.3109/02844319209016016. PMID 1411352.
- ^ Werngren-Elgström M, Lidman D (December 1994). "Lymphoedema of the lower extremities after surgery and radiotherapy for cancer of the cervix". Scandinavian Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery and Hand Surgery. 28 (4): 289–293. doi:10.3109/02844319409022014. PMID 7899840.
- ^ Pilepich MV, Asbell SO, Mulholland GS, Pajak T (1984). "Surgical staging in carcinoma of the prostate: the RTOG experience. Radiation Therapy Oncology Group". The Prostate. 5 (5): 471–476. doi:10.1002/pros.2990050502. PMID 6483687. S2CID 36177502.
- ^ Pilepich MV, Krall J, George FW, Asbell SO, Plenk HD, Johnson RJ, et al. (October 1984). "Treatment-related morbidity in phase III RTOG studies of extended-field irradiation for carcinoma of the prostate". International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics. 10 (10): 1861–1867. doi:10.1016/0360-3016(84)90263-3. PMID 6386761.
- ^ Lim CS, Davies AH (July 2014). "Graduated compression stockings". CMAJ. 186 (10): E391–E398. doi:10.1503/cmaj.131281. PMC 4081237. PMID 24591279.
- ^ Liem TK, Moneta GL (2010). "Chapter 24. Venous and Lymphatic Disease". In Brunicardi FC, Andersen DK, Billiar TR, Dunn DL, Hunter JG, Matthews JB, Pollock RE (eds.). Schwartz's Principles of Surgery (9th ed.). New York, NY: The McGraw-Hill Companies.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Burkhart CN, Adigun C, Burton CS (2012). "Chapter 174. Cutaneous Changes in Peripheral Venous and Lymphatic Insufficiency". In Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, Paller AS, Leffell DJ, Wolff K (eds.). Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine (8 ed.). New York, NY: The McGraw-Hill Companies.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Crispino JD, Horwitz MS (April 2017). "GATA factor mutations in hematologic disease". Blood. 129 (15): 2103–2110. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-09-687889. PMC 5391620. PMID 28179280.
- ^ Hirabayashi S, Wlodarski MW, Kozyra E, Niemeyer CM (August 2017). "Heterogeneity of GATA2-related myeloid neoplasms". International Journal of Hematology. 106 (2): 175–182. doi:10.1007/s12185-017-2285-2. PMID 28643018.
- ^ Kurland LT, Molgaard CA (October 1981). "The patient record in epidemiology". Scientific American. 245 (4): 54–63. Bibcode:1981SciAm.245d..54K. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican1081-54. PMID 7027437.
- ^ Fajardo KA, Keller P, Kobayashi T, Hivnor CM, Webber BJ, Federinko SP, et al. (April 2015). "Bilateral lower extremity inflammatory lymphedema in Air Force basic trainees: clinical and epidemiologic study of a new disease entity". JAMA Dermatology. 151 (4): 395–400. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2014.3794. PMID 25607253.
- ^ McCann SE, Dalton SR, Kobayashi TT (May 2017). "Histopathology of bilateral lower extremity inflammatory lymphedema in military basic trainees: A leukocytoclastic vasculitis of the deep vascular plexus". Journal of Cutaneous Pathology. 44 (5): 500–503. doi:10.1111/cup.12918. PMID 28195354. S2CID 6650610. Archived from the original on 2022-05-06. Retrieved 2021-08-08.
- ^ a b Mehrara BJ, Park HJ, Kataru RP, Bromberg J, Coriddi M, Baik JE, et al. (2021-09-18). "Pilot Study of Anti-Th2 Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Breast Cancer-Related Upper Extremity Lymphedema". Biology. 10 (9): 934. doi:10.3390/biology10090934. ISSN 2079-7737. PMC 8466465. PMID 34571811.
- ^ a b Avraham T, Zampell JC, Yan A, Elhadad S, Weitman ES, Rockson SG, et al. (March 2013). "Th2 differentiation is necessary for soft tissue fibrosis and lymphatic dysfunction resulting from lymphedema". FASEB Journal. 27 (3): 1114–1126. doi:10.1096/fj.12-222695. ISSN 1530-6860. PMC 3574290. PMID 23193171.
- ^ Burnand KM, Glass DM, Mortimer PS, Peters AM (January 2012). "Lymphatic dysfunction in the apparently clinically normal contralateral limbs of patients with unilateral lower limb swelling". Clinical Nuclear Medicine. 37 (1): 9–13. doi:10.1097/RLU.0b013e31823931f5. PMID 22157021. S2CID 34921176.
- ^ Tiwari A, Cheng KS, Button M, Myint F, Hamilton G (February 2003). "Differential diagnosis, investigation, and current treatment of lower limb lymphedema". Archives of Surgery. 138 (2): 152–161. doi:10.1001/archsurg.138.2.152. PMID 12578410.
- ^ a b Jarvis, C. (2004). Physical Examination and Health Assessment (5th ed.). Saunders Elsevier. pp. 530–553. ISBN 978-1-4160-5188-6. Archived from the original on 2023-01-13. Retrieved 2018-03-14.
- ^ Ward LC (2006). "Bioelectrical impedance analysis: proven utility in lymphedema risk assessment and therapeutic monitoring". Lymphatic Research and Biology. 4 (1): 51–56. doi:10.1089/lrb.2006.4.51. PMID 16569209.
- ^ "SOZO® Digital Health Platform | ImpediMed". www.impedimed.com. 2019-06-05. Archived from the original on 2024-03-20. Retrieved 2024-03-20.
- ^ "Delfin Technologies - Skin research instruments". Delfin Technologies. Archived from the original on 2024-03-20. Retrieved 2024-03-20.
- ^ Shah C, Whitworth P, Valente S, Schwarz GS, Kruse M, Kohli M, et al. (2023). "Bioimpedance spectroscopy for breast cancer-related lymphedema assessment: clinical practice guidelines". Breast Cancer Research and Treatment. 198 (1): 1–9. doi:10.1007/s10549-022-06850-7. ISSN 0167-6806. PMC 9883343. PMID 36566297.
- ^ International Society of Lymphology (March 2013). "The diagnosis and treatment of peripheral lymphedema: 2013 Consensus Document of the International Society of Lymphology". Lymphology. 46 (1): 1–11. PMID 23930436.
- ^ Patel KM, Lin CY, Cheng MH (July 2015). "A Prospective Evaluation of Lymphedema-Specific Quality-of-Life Outcomes Following Vascularized Lymph Node Transfer". Annals of Surgical Oncology. 22 (7): 2424–2430. doi:10.1245/s10434-014-4276-3. PMID 25515196. S2CID 13376881.
- ^ Cheng MH, Chang DW, Patel KM (13 July 2015). Principles and Practice of Lymphedema Surgery. Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 978-0-323-29897-1. Archived from the original on 13 January 2023. Retrieved 14 March 2018.
- ^ a b Principles and Practice of Lymphedema Surgery. Cheng MH, Chang DW, Patel KM (Editors). Elsevier Inc, Oxford, United Kingdom. ISBN 978-0-323-29897-1. July 2015.
- ^ "Treatment and Prevention of Problems Associated with Lymphatic Filariasis" (PDF). World Health Organization. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2012-04-18. Retrieved 2014-05-16.
- ^ "Lymphatic filariasis: the disease and its control. Fifth report of the WHO Expert Committee on Filariasis". World Health Organization Technical Report Series. 821: 1–71. 1992. PMID 1441569.
- ^ Tretbar LL, Morgan CL, Lee BB, Simonian SJ, Blondeau B (6 May 2010). Lymphedema: Diagnosis and Treatment. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-1-84628-793-0.[page needed]
- ^ Lee TS, Morris CM, Czerniec SA, Mangion AJ (February 2018). "Does Lymphedema Severity Affect Quality of Life? Simple Question. Challenging Answers". Lymphatic Research and Biology. 16 (1): 85–91. doi:10.1089/lrb.2016.0049. PMID 28453410.
- ^ Nicholls SC (2005). "Sequelae of Untreated Venous Insufficiency". Seminars in Interventional Radiology. 22 (3): 162–168. doi:10.1055/s-2005-921960. PMC 3036289. PMID 21326689.
- ^ Farrow W (2010). "Phlebolymphedema-a common underdiagnosed and undertreated problem in the wound care clinic". The Journal of the American College of Certified Wound Specialists. 2 (1): 14–23. doi:10.1016/j.jcws.2010.04.004. ISSN 1876-4983. PMC 3601853. PMID 24527138.
- ^ Publishing L, Guiboles (2009-11-24). "The causes of edema in chronic venous insufficiency". Servier – Phlebolymphology. Archived from the original on 2023-09-01. Retrieved 2023-09-01.
- ^ a b Ezzo J, Manheimer E, McNeely ML, Howell DM, Weiss R, Johansson KI, et al. (May 2015). "Manual lymphatic drainage for lymphedema following breast cancer treatment". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2015 (5): CD003475. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003475.pub2. PMC 4966288. PMID 25994425.
- ^ Koul R, Dufan T, Russell C, Guenther W, Nugent Z, Sun X, et al. (March 2007). "Efficacy of complete decongestive therapy and manual lymphatic drainage on treatment-related lymphedema in breast cancer". International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics. 67 (3): 841–846. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.09.024. PMID 17175115.
- ^ Rajaee Rizi F (2022). "Towards Better Lymphedema Rehabilitation by Interdisciplinary Approach in the Elderly". Civilica.
- ^ a b Tan C, Wilson CM (May 2019). "Clinical Outcomes After Physical Therapy Treatment for Secondary Lymphedema After Breast Cancer". Cureus. 11 (5): e4779. doi:10.7759/cureus.4779. PMC 6666846. PMID 31367497.
- ^ Cheville AL, McGarvey CL, Petrek JA, Russo SA, Taylor ME, Thiadens SR (July 2003). "Lymphedema management". Seminars in Radiation Oncology. 13 (3): 290–301. doi:10.1016/S1053-4296(03)00035-3. PMID 12903017.
- ^ Boris M, Weindorf S, Lasinski BB (March 1998). "The risk of genital edema after external pump compression for lower limb lymphedema". Lymphology. 31 (1): 15–20. PMID 9561507.
- ^ a b Kasawara KT, Mapa JM, Ferreira V, Added MA, Shiwa SR, Carvas N, et al. (May 2018). "Effects of Kinesio Taping on breast cancer-related lymphedema: A meta-analysis in clinical trials". Physiotherapy Theory and Practice. 34 (5): 337–345. doi:10.1080/09593985.2017.1419522. PMID 29308967. S2CID 3351415.
- ^ Furmaniak AC, Menig M, Markes MH (September 2016). "Exercise for women receiving adjuvant therapy for breast cancer". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2016 (9): CD005001. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005001.pub3. PMC 6457768. PMID 27650122.
- ^ Schmitz KH, Ahmed RL, Troxel A, Cheville A, Smith R, Lewis-Grant L, et al. (August 2009). "Weight lifting in women with breast-cancer-related lymphedema". The New England Journal of Medicine. 361 (7): 664–673. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0810118. PMID 19675330. S2CID 3125299.
- ^ "Position Paper: Exercise | National Lymphedema Network". Lymphnet.org. Archived from the original on 2014-05-08. Retrieved 2014-05-16.
- ^ "Lymphatic Drainage Massage in Chicago - What is MLD?". 2020-10-07. Retrieved 2024-08-18.
- ^ Carl HM, Walia G, Bello R, Clarke-Pearson E, Hassanein AH, Cho B, et al. (July 2017). "Systematic Review of the Surgical Treatment of Extremity Lymphedema". Journal of Reconstructive Microsurgery. 33 (6): 412–425. doi:10.1055/s-0037-1599100. PMID 28235214. S2CID 7791985.
- ^ a b Granzow JW, Soderberg JM, Kaji AH, Dauphine C (April 2014). "Review of current surgical treatments for lymphedema". Annals of Surgical Oncology. 21 (4): 1195–1201. doi:10.1245/s10434-014-3518-8. PMID 24558061.
- ^ dotmed.com December 27, 2006 Archived January 7, 2010, at the Wayback Machine Low Level Laser FDA Cleared for the Treatment of Lymphedema. (accessed 9 November 09)
- ^ National Cancer Institute: Low-level laser therapy Archived 2009-09-24 at the Wayback Machine accessed 9 November 09
- ^ Carati CJ, Anderson SN, Gannon BJ, Piller NB (September 2003). "Treatment of postmastectomy lymphedema with low-level laser therapy: a double blind, placebo-controlled trial". Cancer. 98 (6): 1114–1122. doi:10.1002/cncr.11641. PMID 12973834. S2CID 7043788.