Long thoracic nerve
| Long thoracic nerve | |
|---|---|
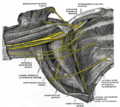
 Nerves of the left upper extremity. (Long thoracic labeled vertically at shoulder, to left of artery.) | |
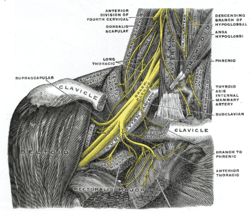 The right brachial plexus with its short branches, viewed from in front. (Long thoracic labeled at center, third from top.) | |
| Details | |
| From | Brachial plexus (C5-C7) |
| Innervates | Serratus anterior muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus thoracicus longus |
| TA98 | A14.2.03.012 |
| TA2 | 6410 |
| FMA | 65275 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The long thoracic nerve (also: external respiratory nerve of Bell or posterior thoracic nerve) is a branch of the brachial plexus derived from cervical nerves C5-C7 that innervates the serratus anterior muscle.
Structure
[edit]Origin
[edit]The long thoracic nerve arises from the anterior rami of cervical spinal nerves C5, C6, and C7.[1][2][3] The root from C7 may occasionally be absent.[4] The roots from C5 and C6 pierce through the scalenus medius, while the C7 root passes in front of the muscle.[citation needed]
Course and relations
[edit]The long thoracic nerve descends through the cervicoaxillary canal. It is posterior to the brachial plexus,[3] and the axillary artery and vein.[4] This takes it deep to the clavicle.[2] It rests on the outer surface of the serratus anterior muscle. It extends along the side of the thorax to the lower border of the serratus anterior muscle, supplying fibres to each of the muscle's digitations.[5][6]
Function
[edit]The long thoracic nerve innervates the serratus anterior muscle.[1] It supplies filaments to each of its digitations (finger-like projections).[5][6]
Clinical significance
[edit]Due to its long, relatively superficial course, the long thoracic nerve is susceptible to injury, either through direct trauma or stretch.[7] Mechanisms of injury include:
- nerve lesions.[3]
- various sports injuries, typically occurring from a blow to the ribs underneath an outstretched arm.
- surgery for shoulder and thorax.[8] Treating breast cancer with removal of axillary lymph nodes.[9]
- carrying weight, such as heavy bags, over the shoulder for a prolonged time.[10]
- Parsonage Turner Syndrome, an autoimmune disease.[11]
- trauma or infection.[8]
Symptoms are often minimal – if symptomatic, a posterior shoulder or scapular burning type of pain may be reported. Some injuries, particularly lesions, can paralyse the serratus anterior muscle to produce a winged scapula.[3][12] This is most prominent when the arm is lifted forward or when the patient pushes the outstretched arm against a wall. However, even winging may not be evident until the trapezius stretches enough to reveal an injury several weeks later.[13]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Rakocevic, G. (January 1, 2014), "Thoracic Nerve, Long", in Aminoff, Michael J.; Daroff, Robert B. (eds.), Encyclopedia of the Neurological Sciences (Second Edition), Oxford: Academic Press, pp. 448–450, doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-385157-4.00699-0, ISBN 978-0-12-385158-1, retrieved October 25, 2020
- ^ a b Tubbs, R. Shane; Goodrich, Dylan; Watanabe, Koichi; Loukas, Marios (January 1, 2015), Tubbs, R. Shane; Rizk, Elias; Shoja, Mohammadali M.; Loukas, Marios (eds.), "Chapter 43 - Anatomic Landmarks for Selected Nerves of the Head, Neck, and Upper and Lower Limbs", Nerves and Nerve Injuries, San Diego: Academic Press, pp. 575–588, doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-410390-0.00045-7, ISBN 978-0-12-410390-0, retrieved October 25, 2020
- ^ a b c d Ryan, Monique M.; Jones, H. Royden (January 1, 2015), Darras, Basil T.; Jones, H. Royden; Ryan, Monique M.; De Vivo, Darryl C. (eds.), "Chapter 14 – Mononeuropathies", Neuromuscular Disorders of Infancy, Childhood, and Adolescence (Second Edition), San Diego: Academic Press, pp. 243–273, doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-417044-5.00014-7, ISBN 978-0-12-417044-5, retrieved October 25, 2020
- ^ a b Tomberlin, John (January 1, 2009), Wilk, Kevin E.; Reinold, Michael M.; Andrews, James R. (eds.), "CHAPTER 53 - Neurodynamic Techniques for the Athlete's Shoulder", The Athlete's Shoulder (Second Edition), Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone, pp. 707–717, doi:10.1016/b978-044306701-3.50056-6, ISBN 978-0-443-06701-3, retrieved October 25, 2020
- ^ a b Fischer, J. (2012). Anatomy of the Axilla. Fischer's Mastery of Surgery, 2 Volume Set. Retrieved September 20, 2015 from http://www.r2library.com/Resource/Title/1608317404/ch0046s1193
- ^ a b Bertelli, Jayme Augusto (2005). "Long Thoracic Nerve: Anatomy and Functional Assessment". The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume. 87 (5): 993–8. doi:10.2106/JBJS.D.02383. ISSN 0021-9355. PMID 15866961.
- ^ Ostrowska, Monika; de Carvalho, Mamede (January 1, 2015), Tubbs, R. Shane; Rizk, Elias; Shoja, Mohammadali M.; Loukas, Marios (eds.), "Chapter 34 - Injuries of the Nerves of the Thorax", Nerves and Nerve Injuries, San Diego: Academic Press, pp. 525–543, doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-802653-3.00083-x, ISBN 978-0-12-802653-3, retrieved October 25, 2020
- ^ a b "An Isolated Long Thoracic Nerve Injury in a Navy Airman". Military Medicine. 2004.
- ^ Belmonte, Roser; Monleon, Sandra; Bofill, Neus; Alvarado, Martha Ligia; Espadaler, Josep; Royo, Inmaculada (2015). "Long thoracic nerve injury in breast cancer patients treated with axillary lymph node dissection". Supportive Care in Cancer. 23 (1): 169–175. doi:10.1007/s00520-014-2338-5. ISSN 1433-7339. PMID 25035064. S2CID 25547808.
- ^ Berthold, Justin B.; Burg, Timothy M.; Nussbaum, Ryan Paul (February 1, 2017). "Long Thoracic Nerve Injury Caused by Overhead Weight Lifting Leading to Scapular Dyskinesis and Medial Scapular Winging". Journal of Osteopathic Medicine. 117 (2): 133–137. doi:10.7556/jaoa.2017.025. ISSN 2702-3648. PMID 28134956. S2CID 25777654.
- ^ Monteiro dos Santos, Ricardo Barreto; dos Santos, Saulo Monteiro; Carneiro Leal, Flávio José Câmara; Lins, Otávio Gomes; Magalhães, Carmem; Mertens Fittipaldi, Ricardo Bruno (April 17, 2015). "Parsonage–Turner syndrome". Revista Brasileira de Ortopedia. 50 (3): 336–341. doi:10.1016/j.rboe.2015.04.002. ISSN 2255-4971. PMC 4519651. PMID 26229940.
- ^ Le Nail, L. R.; Bacle, G.; Marteau, E.; Corcia, P.; Favard, L.; Laulan, J. (June 2014). "Isolated paralysis of the serratus anterior muscle: surgical release of the distal segment of the long thoracic nerve in 52 patients". Orthopaedics & Traumatology, Surgery & Research. 100 (4 Suppl): S243–248. doi:10.1016/j.otsr.2014.03.004. ISSN 1877-0568. PMID 24703793.
- ^ Preston, David C.; Shapiro, Barbara E. (January 1, 2013), Preston, David C.; Shapiro, Barbara E. (eds.), "31 - Proximal Neuropathies of the Shoulder and Arm", Electromyography and Neuromuscular Disorders (Third Edition), London: W.B. Saunders, pp. 487–500, doi:10.1016/b978-1-4557-2672-1.00031-3, ISBN 978-1-4557-2672-1, retrieved October 25, 2020
Additional images
[edit]-
The right brachial plexus (infraclavicular portion) in the axillary fossa; viewed from below and in front.
-
Brachial plexus
-
Brachial plexus with courses of spinal nerves shown
External links
[edit]- Long thoracic nerve at the Duke University Health System's Orthopedics program
- synd/2384 at Who Named It?
- Anatomy figure: 05:03-07 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The major subdivisions and terminal nerves of the brachial plexus."
- Long Thoracic Nerve - BlueLink Anatomy - University of Michigan Medical School