List of National Historic Landmarks in Massachusetts

The Commonwealth of Massachusetts has a total of 192 National Historic Landmarks (NHLs) within its borders. This is the second highest statewide total in the United States after New York, which has more than 250. Of the Massachusetts NHLs, 57 are in the state capital of Boston, and are listed separately. Ten of the remaining 134 designations were made when the NHL program was formally inaugurated on October 9, 1960; the most recent were in 2021. Cambridge is the city with the most NHLs outside Boston (at 19), and Middlesex County is home to 43 NHLs (again outside the 58 from Boston, which comprise all but two of the NHLs in Suffolk County). Every county in the state has at least one NHL (Franklin County has exactly one, the Old Deerfield Historic District).
The state's NHLs were chosen for a diversity of reasons. Some of the nation's oldest surviving structures are included: a number of 17th-century houses are listed, including the Fairbanks House (late 1630s) of Dedham, which is the oldest timber-frame house in the nation. The Old Ship Church (1681) of Hingham is the nation's oldest church still used for religious purposes, and Cole's Hill in Plymouth was used in 1620 as a burial ground for the Plymouth Colony. The Nauset Archeological District documents early contact between Europeans and Native Americans, and the Old Deerfield Historic District encompasses a well-preserved colonial frontier village.
Sites associated with the American Revolution and people of the time are on the list. The Lexington Green, Buckman Tavern, and the Hancock-Clarke House all played roles in the Battles of Lexington and Concord that began the American Revolutionary War, as did Wright's Tavern in Concord. The homes of Continental Army generals Benjamin Lincoln, John Glover, and Rufus Putnam are listed. Properties occupied by army officers during the Siege of Boston include the Longfellow House (occupied by George Washington and purchased by Henry Wadsworth Longfellow in part because of that association), and the Isaac Royall House.
In addition to the Longfellow site, there are numerous NHLs with literary and artistic connections. Arrowhead in the Berkshires was where Herman Melville did much of his writing, and Concord is home to Walden Pond, the Ralph Waldo Emerson House, The Old Manse (home to Ralph Waldo Emerson's grandfather), Orchard House (childhood home to Louisa May Alcott), and The Wayside (home to Nathaniel Hawthorne). Hawthorne is also represented by the House of Seven Gables district of Salem, which includes his birthplace. Other literary landmarks include the John Greenleaf Whittier House, The Mount (Edith Wharton's Lenox estate), and Redtop, the Belmont home of William Dean Howells which was the site of many literary gatherings.
Scientific and academic pursuits are represented in the list. Homes of mathematicians, scientists, and researchers appear on the list, as do sites noted for the events that took place there. The Blue Hill Meteorological Observatory in Milton is home to the nation's longest continuous weather record, and the Goddard Rocket Launching Site in Auburn was where rocketry pioneer Robert H. Goddard performed some of his tests.
National Historic Landmarks
[edit]| # | National Historic Landmark |
|---|---|
| #+ | National Historic Landmark District |
| #* | National Historic Site |
| [1] | Landmark name | Image | Date designated[2] | Location | County | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Adams Academy |  |
April 19, 1994 (#74000379) |
Quincy 42°15′15″N 71°00′21″W / 42.2541°N 71.0059°W | Norfolk | High Gothic building, built in 1871 to a design by William Robert Ware and Henry Van Brunt, for a preparatory school funded with a bequest of John Adams.[3] |
| 2 | John Adams Birthplace |  |
December 19, 1960 (#66000129) |
Quincy 42°14′20″N 71°00′13″W / 42.2390°N 71.0035°W | Norfolk | This is the house in which United States President John Adams was born on October 30, 1735. It is now part of the Adams National Historical Park.[4][5] |
| 3 | John Quincy Adams Birthplace |  |
December 19, 1960 (#66000128) |
Quincy 42°14′22″N 71°00′12″W / 42.2394°N 71.0034°W | Norfolk | President John Quincy Adams was born in this house, which is adjacent to the John Adams Birthplace; it is also part of the Adams National Historical Park.[5][6] |
| 4 | Adventure |  |
April 19, 1994 (#89002054) |
Gloucester 42°36′32″N 70°39′21″W / 42.6089°N 70.6559°W | Essex | This schooner is one of the last surviving Gloucester-based Grand Banks fishing schooners, and one of only two surviving "knockabout" fishing schooners.[7] |
| 5 | John and Priscilla Alden Family Sites |  |
October 6, 2008 (#78000476) |
Duxbury 42°02′42″N 70°41′09″W / 42.04495°N 70.6858°W | Plymouth | These two sites in Duxbury are associated with John and Priscilla Alden, who were the inspiration for Henry Wadsworth Longfellow's The Courtship of Miles Standish.[8] |
| 6 | American Antiquarian Society |  |
October 18, 1968 (#68000018) |
Worcester 42°16′41″N 71°48′35″W / 42.2780°N 71.8098°W | Worcester | This 1910 Georgian Revival building houses the American Antiquarian Society, the third oldest (1812) historical society in the United States and the first to be national in scope.[9] |
| 7 | Arrowhead (Herman Melville House) |  |
December 29, 1962 (#66000126) |
Pittsfield 42°24′55″N 73°14′56″W / 42.4154°N 73.2488°W | Berkshire | This 18th-century farmhouse was the home of author Herman Melville (1819–91) during his most productive years from 1850 to 1863. He wrote several novels here, including Moby-Dick, as well as short stories, magazine stories and poetry. The house is now a museum.[10] |
| 8 | Maria Baldwin House |  |
May 11, 1976 (#76000272) |
Cambridge 42°22′12″N 71°06′01″W / 42.3701°N 71.1004°W | Middlesex | This 19th century duplex was the home of educator Maria Louise Baldwin (1856–1922), the first female African-American principal of a school in New England.[11][12] |
| 9 | Beauport |  |
May 27, 2003 (#03000641) |
Gloucester 42°35′28″N 70°39′38″W / 42.5911°N 70.6606°W | Essex | Seminal interior designer and decorator Henry Davis Sleeper (1878–1934) used this Shingle-style as a showcase of his work. It is owned by Historic New England and operated as a museum.[13][14] |
| 10 | Edward Bellamy House |  |
November 11, 1971 (#71000091) |
Chicopee Falls 42°09′22″N 72°35′03″W / 42.1561°N 72.5841°W | Hampden | This was the longtime home of journalist and social activist Edward Bellamy (1850–98), author of the utopian novel Looking Backward.[15] |
| 11 | George D. Birkhoff House |  |
January 15, 1975 (#75000295) |
Cambridge 42°22′42″N 71°07′43″W / 42.3783°N 71.1287°W | Middlesex | This house was the home of George David Birkhoff (1884–1944), a leading mathematician of the early 20th century.[16] |
| 12 | Blue Hill Meteorological Observatory |  |
December 20, 1989 (#80000665) |
Milton 42°12′43″N 71°06′51″W / 42.2120°N 71.1141°W | Norfolk | Described as "principal structure associated with the history of weather observation" in the United States, this observatory is home to the oldest continuous weather record in North America, and is where numerous meteorological measurement and analysis techniques were developed.[17] |
| 13 | Boardman House |  |
November 5, 1961 (#66000131) |
Saugus 42°28′20″N 71°02′16″W / 42.4723°N 71.0377°W | Essex | This house, whose early construction dates to the late 17th century, has remained little changed since the early 18th century. It is now a house museum operated by Historic New England.[18] |
| 14+ | Boston Manufacturing Company |  |
December 22, 1977 (#77001412) |
Waltham 42°22′23″N 71°14′09″W / 42.3731°N 71.2358°W | Middlesex | This building housed the eponymous company, founded in 1813 by businessman Francis Cabot Lowell, engineer Paul Moody, and others, for the manufacture of cotton textiles. At this site the manufacture of textiles under a single roof was proved, a major success leading to the American Industrial Revolution.[19] |
| 15 | Nathaniel Bowditch Home |  |
January 12, 1965 (#66000135) |
Salem 42°31′18″N 70°53′55″W / 42.5218°N 70.8987°W | Essex | This Federalist house was the home of Nathaniel Bowditch (1773–1838), the founder of modern (19th century) navigation.[20] It now serves as the headquarters of Historic Salem, Inc.[21] |
| 16 | Louis Brandeis House |  |
November 28, 1972 (#72000148) |
Chatham 41°40′16″N 69°59′00″W / 41.6710°N 69.9833°W | Barnstable | Bought in 1922 by liberal United States Supreme Court Justice Louis Brandeis (1856–1941), this Cape style house (whose construction dates to the late 19th century) was used by the Brandeis family as a summer retreat.[22] |
| 17 | Percy W. Bridgman House |  |
May 15, 1975 (#75000298) |
Cambridge 42°22′45″N 71°07′43″W / 42.3792°N 71.1286°W | Middlesex | This house served as the longtime home of Nobel prize-winning physicist Percy W. Bridgman (1882–1961). His innovations in the field of high pressure physics made possible the development of synthetic diamonds.[23] |
| 18 | Brookline Reservoir of the Cochituate Aqueduct |  |
February 27, 2015 (#15000278) |
Brookline 42°19′35″N 71°08′12″W / 42.3264°N 71.1367°W | Norfolk | This property, in addition to the reservoir, includes the end gatehouse of the Cochituate Aqueduct, and an elaborately-decorated distribution gatehouse that includes one of the earliest known uses of wrought iron for staircases. |
| 19 | William Cullen Bryant Homestead |  |
December 29, 1962 (#66000136) |
Cummington 42°28′17″N 72°56′26″W / 42.4713°N 72.9406°W | Hampshire | This property was the boyhood home and later summer residence of poet and newspaper editor William Cullen Bryant (1794–1878). It is now owned by The Trustees of Reservations and operated as a house museum.[24] |
| 20 | Buckman Tavern |  |
January 20, 1961 (#66000137) |
Lexington 42°26′57″N 71°13′47″W / 42.4493°N 71.2298°W | Middlesex | The oldest of Lexington's inns (established c. 1690), local militiamen mustered here prior to the April 19, 1775 Battles of Lexington and Concord that began the American Revolutionary War.[25] |
| 21 | Cape Ann Light Station |  |
January 3, 2001 (#71000355) |
Rockport 42°38′12″N 70°34′30″W / 42.6368°N 70.5749°W | Essex | Located on Thacher Island, this light station was established in 1771, and was the last founded in the colonial era. The two lighthouses were the first to mark a navigational hazard (Thacher Island); the current lighthouses were constructed in 1861, and are aligned on a north-south axis.[26] |
| 22 | Parson Capen House |  |
October 9, 1960 (#66000139) |
Topsfield 42°38′29″N 70°57′00″W / 42.6415°N 70.9499°W | Essex | This circa 1683 house was home to Reverend Joseph Capen, Topsfield's minister for many years. It is one of the best preserved 17th-century houses in the United States.[27] It is operated by the Topsfield Historical Society as a house museum.[28] |
| 23 | Castle Hill |  |
August 5, 1998 (#77000183) |
Ipswich 42°41′06″N 70°46′45″W / 42.6851°N 70.7792°W | Essex | This early 20th-century country estate is one of the finest of its type. The house was designed by architect David Adler of Chicago, and the landscaping was done by the Olmsted Brothers firm, among others. The estate is owned by The Trustees of Reservations, and is open to the public.[29] |
| 24 | Christ Church |  |
October 9, 1960 (#66000140) |
Cambridge 42°22′31″N 71°07′14″W / 42.3754°N 71.1205°W | Middlesex | This church, designed by architect Peter Harrison and completed in 1761, served Cambridge Anglicans. Despite numerous alterations, the church has retained much its original 18th century character.[30] |
| 25 | Jethro Coffin House |  |
October 18, 1968 (#68000019) |
Nantucket 41°17′15″N 70°06′26″W / 41.2874°N 70.1073°W | Nantucket | This saltbox house, built in 1686, is the oldest surviving residential structure on Nantucket. It is now owned by the Nantucket Historical Association, which operates it as a house museum.[31] |
| 26 | Cole's Hill |  |
October 9, 1960 (#66000142) |
Plymouth 41°57′20″N 70°39′46″W / 41.9556°N 70.6627°W | Plymouth | Cole's Hill is the site of the burial ground of the Pilgrims. Those who died in the first winter of the Plymouth Colony (1620–21) were buried there.[32] |
| 27 | Converse Memorial Library |  |
December 23, 1987 (#85002014) |
Malden 42°25′38″N 71°03′59″W / 42.4272°N 71.0663°W | Middlesex | This public library building was the last such building designed by architect H. H. Richardson, and is counted among his greatest works.[33] |
| 28 | Crane and Company Old Stone Mill Rag Room |  |
May 4, 1983 (#83004376) |
Dalton 42°28′15″N 73°10′43″W / 42.4708°N 73.1785°W | Berkshire | From 1844 to 1930 this building was used as part of Crane and Company's paper manufacturing process, and is one of the nation's oldest surviving paper manufacturing buildings; it now houses Crane's museum. Crane has since 1879 been the exclusive supplier of paper for United States paper currency.[34] |
| 29 | Crane Memorial Library |  |
December 23, 1987 (#72000143) |
Quincy 42°15′05″N 71°00′08″W / 42.2513°N 71.0021°W | Norfolk | One of five public libraries designed by H. H. Richardson, he considered it to be one of his best designs. The building incorporates stained glass by John LaFarge and sculptural elements by Augustus Saint-Gaudens.[35] |
| 30 | Paul Cuffe Farm |  |
May 30, 1974 (#74000394) |
Westport 41°32′37″N 71°04′02″W / 41.5437°N 71.0673°W | Bristol | This site was the home and farm of Paul Cuffee (1759–1817), a wealthy colonial-era African-American merchant. Cuffee was a leading advocate for minority rights in Massachusetts, and a promoter and funder of the resettlement of African-Americans to present-day Sierra Leone.[36] |
| 31 | Caleb Cushing House |  |
November 7, 1973 (#73000327) |
Newburyport 42°48′23″N 70°52′14″W / 42.8065°N 70.8705°W | Essex | This fine Federalist house was the home of diplomat and United States Attorney General Caleb Cushing (1800–79). Cushing is known for negotiating the 1844 Treaty of Wanghia, the first treaty between the United States and Qing China, and other diplomatic successes. The house now serves as the headquarters of the local historical society.[37] |
| 32 | Reginald A. Daly House |  |
January 7, 1976 (#76000305) |
Cambridge 42°22′31″N 71°07′34″W / 42.3752°N 71.1261°W | Middlesex | This Queen Anne style house was the longtime home of geologist and Harvard University professor Reginald Aldworth Daly (1871–1957). Daly was a pioneer in the application of physics and chemistry to the field of geology.[38] |
| 33 | William M. Davis House |  |
January 7, 1976 (#76000306) |
Cambridge 42°22′43″N 71°06′43″W / 42.3785°N 71.1120°W | Middlesex | This house was home to geologist and geographer William Morris Davis (1850–1934). Davis was a leading figure in the development of the study of geology, founding the Association of American Geographers and developing the first model of the cycle of erosion.[39][40] |
| 34 | Derby Summer House |  |
November 24, 1968 (#68000020) |
Danvers 42°34′24″N 70°57′58″W / 42.5732°N 70.9662°W | Essex | This is a rare example of an 18th-century American garden house. Designed in the 1790s by Samuel McIntire, it resided on the estate of Salem merchant Elias Hasket Derby until 1901, when it was moved to the Endicott family's Glen Magna Farms country estate. The estate, now owned by the Danvers Historical Society, is open to the public.[41][42] |
| 35 | Emily Dickinson Home |  |
December 29, 1962 (#66000363) |
Amherst 42°22′34″N 72°30′52″W / 42.3761°N 72.5145°W | Hampshire | This house was home of the reclusive poet Emily Dickinson (1830–86) for most of her life. The house is now owned by Amherst College and is operated as a house museum.[43][44] |
| 36 | W.E.B. Dubois Boyhood Homesite |  |
May 11, 1976 (#76000947) |
Great Barrington 42°10′42″N 73°23′37″W / 42.1783°N 73.3936°W | Berkshire | This site contains all that remains of the childhood home of African American intellectual and activist W.E.B. Du Bois (1868–1963). The property, which belonged to his family for over 200 years, is seasonally open to the public.[45][46] |
| 37 | Mary Baker Eddy House |  |
January 13, 2021 (#100006275) |
Lynn 42°27′50″N 70°56′06″W / 42.4640°N 70.9351°W | Essex | Home of Christian Science founder Mary Baker Eddy between 1875-1882. |
| 38+ | Elmwood |  |
December 29, 1962 (#66000364) |
Cambridge 42°22′34″N 71°08′18″W / 42.376°N 71.1383°W | Middlesex | This 1760s Georgian house and estate was home to three historically important individuals: Massachusetts colonial Lieutenant Governor Thomas Oliver (who had the house built), Massachusetts Governor and US Vice President Elbridge Gerry, and poet James Russell Lowell, who gave the property its name. It now serves as the home of the Harvard University president.[47][48] |
| 39 | Ralph Waldo Emerson Home |  |
December 29, 1962 (#66000365) |
Concord 42°27′28″N 71°20′36″W / 42.4577°N 71.3434°W | Middlesex | This house was purchased by writer, poet, and philosopher Ralph Waldo Emerson (1803–1882) in 1835. It was where he wrote all of his major works, and was a major meeting point for Transcendentalists, including Bronson Alcott and Henry David Thoreau. It has been a house museum since 1930.[49] |
| 40 | Ernestina (schooner) |  |
December 14, 1990 (#85000022) |
New Bedford 41°38′03″N 70°55′15″W / 41.6343°N 70.9208°W | Bristol | Ernestina is the oldest surviving Grand Banks fishing schooner, and the only surviving 19th century fishing schooner built in Gloucester. Owned by the state and under the overall aegis of the New Bedford Whaling National Historical Park, she is in 2012 sidelined from her intended educational purpose by budget constraints and the need for repairs.[50][51] |
| 41 | Fairbanks House |  |
October 9, 1960 (#66000367) |
Dedham 42°14′37″N 71°10′03″W / 42.2436°N 71.1676°W | Norfolk | Continuously owned by a single family since its construction in the late 1630s, this is probably the oldest timber-frame house in North America. It is now operated by Fairbanks Family in America, Inc., as a house museum.[52] |
| 42 | Reginald A. Fessenden House |  |
January 7, 1976 (#76000950) |
Newton 42°20′25″N 71°10′16″W / 42.3404°N 71.1712°W | Middlesex | Reginald Fessenden (1866–1932) was an inventor who worked for a time in Thomas Edison's workshop. His most notable inventions made possible the transmission of audio sounds via radio waves, and included many other radio-related innovations. This house was his last home; he was described in memoriam as "the greatest wireless inventor of the age".[53] |
| 43 | First Church Of Christ, Lancaster |  |
December 30, 1970 (#70000897) |
Lancaster 42°27′19″N 71°40′27″W / 42.4552°N 71.6741°W | Worcester | One of the finest churches designed by architect Charles Bulfinch, this building was constructed in 1816 and is occupied by a congregation whose history dates to 1653.[54][55] |
| 44 | Flying Horses Carousel |  |
February 27, 1987 (#79000342) |
Oak Bluffs 41°27′27″N 70°33′26″W / 41.4574°N 70.5571°W | Dukes | This carousel, one of two extant examples of the work of the Charles F. W. Dare Company, is the oldest operating platform carousel in the nation, and may be the oldest of any type (the Flying Horse Carousel of Watch Hill, Rhode Island, also built by the Dare Company, is possibly older).[56] |
| 45 | Capt. R.B. Forbes House |  |
November 13, 1966 (#66000651) |
Milton 42°15′53″N 71°03′55″W / 42.2646°N 71.0652°W | Norfolk | Designed by Isaiah Rogers, this 1833 Greek Revival house was built by ship captain and China Trade merchant Robert Bennet Forbes and his siblings for their mother. Furnished and decorated with acquisitions Forbes made in China, it is now a house museum.[57][58] |
| 46+ | Daniel Chester French Home and Studio |  |
December 21, 1965 (#66000652) |
Stockbridge 42°17′06″N 73°21′06″W / 42.2851°N 73.3518°W | Berkshire | Better known as Chesterwood, this was the summer home and studio of sculptor Daniel Chester French (1850–1931) from 1891 until his death. The estate was designed by French's collaborator Henry Bacon, and is now owned by the National Trust for Historic Preservation. It is open to the public on a seasonal basis.[59][60] |
| 47+ | Fruitlands |  |
May 30, 1974 (#74001761) |
Harvard 42°30′27″N 71°36′45″W / 42.5076°N 71.6126°W | Worcester | Fruitlands was the site of a short-lived (1843–44) Transcendentalist utopian community founded by Amos Bronson Alcott.[61] The property was acquired by preservationist Clara Endicott Sears in 1910 and opened as the Fruitlands Museum four years later.[62] |
| 48 | Margaret Fuller House |  |
May 30, 1974 (#71000686) |
Cambridge 42°21′52″N 71°05′51″W / 42.3644°N 71.0974°W | Middlesex | This was the birthplace and childhood home of Transcendentalist and feminist Margaret Fuller (1810–50). Her Woman in the Nineteenth Century is one of the earliest statements of feminist thought.[63][64] |
| 49 | Gardner-Pingree House |  |
December 30, 1970 (#70000541) |
Salem 42°31′20″N 70°53′28″W / 42.5223°N 70.8911°W | Essex | Salem merchant John Gardner had this Federalist-style house built in 1804–05 by Samuel McIntire.[65] It was the site of a notorious murder in 1841 that inspired Nathaniel Hawthorne and Edgar Allan Poe.[66] It is now owned by the Peabody Essex Museum, which offers guided tours.[67] |
| 50 | General John Glover House |  |
November 28, 1972 (#72001101) |
Marblehead 42°30′17″N 70°50′49″W / 42.5047°N 70.8470°W | Essex | John Glover (1732–97) had this simple frame house built in 1762, and occupied until 1782.[68] Glover, a wealthy Marblehead merchant, was an important military figure in the American Revolutionary War, leading the Marblehead Regiment early in the war as well as leading early efforts to establish the Continental Navy.[69] |
| 51 | Goddard Rocket Launching Site |  |
November 13, 1966 (#66000654) |
Auburn 42°12′59″N 71°48′46″W / 42.2165°N 71.8127°W | Worcester | This site, located on a local golf course, is where rocket scientist Robert H. Goddard launched the first liquid-fueled rocket in 1926.[70] The actual launch site is marked by a granite obelisk.[71] |
| 52 | Gore Place |  |
December 30, 1970 (#70000542) |
Waltham 42°22′24″N 71°12′45″W / 42.3733°N 71.2124°W | Middlesex | A remnant of an estate that was once much larger, Gore Place preserves an excellent Federalist mansion built in 1806 for Christopher Gore, a Massachusetts governor and United States senator. The mansion was saved from destruction in 1935, and is now open to the public as a house museum.[72] |
| 53 | John B. Gough House |  |
May 30, 1974 (#74001763) |
Boylston 42°19′31″N 71°45′14″W / 42.3254°N 71.7540°W | Worcester | This Italianate house, also known as "Hillside", was the home of orator John B. Gough (1817–86), a leading figure of the 19th century temperance movement. The estate, owned by the town of Boylston, is undergoing a lengthy restoration and conservation process.[73][74] |
| 54 | Asa Gray House |  |
January 12, 1965 (#66000655) |
Cambridge 42°23′00″N 71°07′41″W / 42.3832°N 71.1280°W | Middlesex | This Federalist house, designed by Ithiel Town and built in 1810, most notably served as the longtime home of botanist and Harvard professor Asa Gray (1810–88). Gray was one of the most important botanists of the 19th century, publishing works still referenced today and defending Charles Darwin's On the Origin of Species.[75] |
| 55 | Gropius House |  |
May 16, 2000 (#00000709) |
Lincoln 42°25′37″N 71°19′37″W / 42.4269°N 71.3269°W | Middlesex | Bauhaus architect Walter Gropius designed this house in 1937 as a personal expression of Modernism, living in it until his death in 1969. Owned by Historic New England and operated as a house museum, it contains the most important collection of Bauhaus artifacts outside Germany.[76][77] |
| 56+ | H. H. Richardson Historic District of North Easton |  |
December 23, 1987 (#87002598) |
North Easton 42°04′01″N 71°06′17″W / 42.0670°N 71.1047°W | Bristol | This landmark district contains five buildings in Easton designed by architect H. H. Richardson and landscaped by Frederick Law Olmsted, primarily through the efforts of the wealthy Ames family: Oakes Ames Memorial Hall, the Ames Free Library, the Old Colony Railroad Station, and two nearby structures on the Langwater estate of Frederick Lothrop Ames.[78] |
| 57 | Hamilton Hall |  |
December 30, 1970 (#70000543) |
Salem 42°31′11″N 70°53′58″W / 42.5196°N 70.8994°W | Essex | Named for Federalist Party leader Alexander Hamilton, this 1805 building was designed by Samuel McIntire to serve Salem's Federalist Party activities. It has been described as "one of the most outstanding Federal-era public buildings" in the nation.[79] |
| 58 | Hancock-Clarke House |  |
July 17, 1971 (#71000895) |
Lexington 42°27′13″N 71°13′42″W / 42.4535°N 71.2284°W | Middlesex | This 1737 house was the boyhood home of Revolutionary leader John Hancock, and was where he and Samuel Adams hid from British authorities at the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War.[80] It is now owned by the Lexington Historical Society, and is seasonally open to the public.[81] |
| 59+ | Hancock Shaker Village |  |
October 18, 1968 (#68000037) |
Hancock and Pittsfield 42°25′48″N 73°20′20″W / 42.43°N 73.339°W | Berkshire | This Shaker village was established in 1791 and lasted until 1960, after which it became a living history museum. It is noted for its distinctive round barn, built in 1826.[82][83] |
| 60 | Oliver Hastings House |  |
December 30, 1970 (#70000681) |
Cambridge 42°22′35″N 71°07′33″W / 42.3763°N 71.1257°W | Middlesex | This Greek Revival house was built in 1844 as the home of Cambridge businessman Oliver Hastings (1791–1879). Although nearby resident Charles Sanders Peirce considered it "ugly", the building is recognized for its elegant curved bays and elaborate wrought iron balcony railings.[84][85] |
| 61 | Oliver Wendell Holmes House |  |
November 28, 1972 (#72001301) |
Beverly 42°33′50″N 70°48′24″W / 42.5640°N 70.8068°W | Essex | This 1877 frame house was the summer home of United States Supreme Court Associate Justice Oliver Wendell Holmes Jr. (1841–1935). Holmes is known for his longevity on the bench, and his opinions on freedom of speech.[86][87] |
| 62+ | House of the Seven Gables |  |
March 29, 2007 (#73000323) |
Salem 42°31′19″N 70°53′05″W / 42.5219°N 70.8847°W | Essex | Best known for its association with Nathaniel Hawthorne's novel of the same name, this 1668 house was also a key early preservation effort, successfully restored in the early 20th century by historian and preservationist Joseph Everett Chandler. The district, which includes several other historical buildings, has been operated ever since as a history museum.[88] |
| 63+ | Jacob's Pillow Dance Festival |  |
May 27, 2003 (#03000644) |
Becket 42°15′52″N 73°07′05″W / 42.2644°N 73.1181°W | Berkshire | Jacob's Pillow was founded in 1931 by Ted Shawn as a place to develop an all-male dance company. It has since trained generations of dance professionals of all types, and continues to stage productions every summer.[89] |
| 64 | Nathan and Mary (Polly) Johnson properties |  |
February 16, 2000 (#00000260) |
New Bedford 41°37′59″N 70°55′43″W / 41.633°N 70.9286°W | Bristol | These buildings, now housing the New Bedford Historical Society, belonged to a free African-American couple active in the abolitionist movement and the Underground Railroad. They notably took in activist Frederick Douglass after his escape from slavery.[90] |
| 65 | USS Joseph P. Kennedy, Jr. (destroyer) |  |
June 29, 1989 (#76000231) |
Fall River 41°42′21″N 71°09′47″W / 41.7057°N 71.1631°W | Bristol | The only surviving United States Navy Gearing-class destroyer, this vessel is named for Joseph P. Kennedy Jr. (the brother of future President John F. Kennedy) who was killed in action during World War II.[91] It is on display at Fall River's Battleship Cove.[92] |
| 66+ | Kennedy Compound |  |
November 28, 1972 (#72001302) |
Hyannis Port 41°37′50″N 70°18′12″W / 41.6305°N 70.3032°W | Barnstable | This compound consists of three residences, each belonging at some point to Joseph P. Kennedy Sr., diplomat and patriarch of the politically influential Kennedy family, or one of his sons: President John F. Kennedy, Attorney General Robert F. Kennedy, and Senator Edward M. Kennedy.[93] |
| 67* | John F. Kennedy Birthplace |  |
July 19, 1964 (#67000001) |
Brookline 42°20′49″N 71°07′24″W / 42.3470°N 71.1233°W | Norfolk | Now a National Historic Site, this modest suburban house was the birthplace and childhood home of President John F. Kennedy (1917–63).[94] |
| 68 | Jeremiah Lee House |  |
October 9, 1960 (#66000766) |
Marblehead 42°30′13″N 70°51′05″W / 42.5036°N 70.8513°W | Essex | Jeremiah Lee was the wealthiest merchant in Massachusetts in the 1760s, when he had this Georgian mansion built. The mansion is in a remarkable state of preservation, and is operated by the local historical society as a house museum.[95] |
| 69 | Lexington Green |  |
January 20, 1961 (#66000767) |
Lexington 42°26′58″N 71°13′52″W / 42.4495°N 71.231°W | Middlesex | Lexington's town common, it was here that opening skirmish of the American Revolutionary War took place on April 19, 1775.[96] |
| 70 | Liberty Farm |  |
May 30, 1974 (#74002046) |
Worcester 42°16′49″N 71°51′34″W / 42.2803°N 71.8595°W | Worcester | This house belonged to abolitionists and suffragists Abby Kelley Foster (1811–87) and Stephen Symonds Foster (1809–81), and was used by them as a site on the Underground Railroad. The property also featured prominently in the Fosters' refusal to pay property taxes because she was unable to vote.[97] |
| 71 | General Benjamin Lincoln House |  |
November 28, 1972 (#72001303) |
Hingham 42°14′35″N 70°53′33″W / 42.243°N 70.8924°W | Plymouth | This well-preserved 18th-century house was the birthplace and lifelong home of Revolutionary War General and Massachusetts Lieutenant Governor Benjamin Lincoln (1733–1810). The house, which is not open to the public, remains in Lincoln family hands.[98] |
| 72 | USS Lionfish (submarine) |  |
January 14, 1986 (#76002270) |
Fall River 41°42′18″N 71°09′43″W / 41.7050°N 71.162°W | Bristol | An intact Balao-class submarine, USS Lionfish served two tours of duty in the Pacific during World War II and served as a training vessel before being decommissioned and placed on display at Battleship Cove.[99] |
| 73 | Arthur D. Little Inc., Building |  |
December 8, 1976 (#76001970) |
Cambridge 42°21′40″N 71°04′56″W / 42.3612°N 71.0822°W | Middlesex | This unremarkable 1917 office building was the site of the nation's first successful independent consulting laboratory, Arthur D. Little. The company pioneered the idea of commercial laboratories as independent, profit-making businesses.[100] |
| 74 | Henry Cabot Lodge Residence |  |
December 8, 1976 (#76001971) |
Nahant 42°25′17″N 70°54′38″W / 42.4213°N 70.9106°W | Essex | Henry Cabot Lodge (1850–1924) was a lifelong resident of this house. Lodge, as United States Senator from Massachusetts, was a critical voice in foreign policy debates of the early 20th century; he supported a wider role for the United States on the world stage, but led the opposition to ratification of the 1919 Treaty of Versailles that ended World War I.[101] |
| 75* | Longfellow House |  |
December 29, 1962 (#66000049) |
Cambridge 42°22′35″N 71°07′34″W / 42.3764°N 71.1262°W | Middlesex | This 1759 Georgian house was used by George Washington as his residence during the 1775–76 Siege of Boston. In the 19th century it was purchased for poet Henry Wadsworth Longfellow (1807–82) by his father-in-law, and is where Longfellow wrote many of his best-known works.[102] |
| 76+ | Lowell Locks and Canals Historic District | 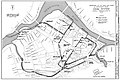 |
December 22, 1977 (#76001972) |
Lowell 42°38′44″N 71°19′12″W / 42.6456°N 71.32°W | Middlesex | Lowell was the nation's first major industrialized city. Its system of canals and waterworks was constructed between 1794 and 1848. Most of these were built to power the large number of industries that sprang up in Lowell during the early years of the American Industrial Revolution, and remain in remarkable condition despite their age.[103] |
| 77 | Lowell's Boat Shop |  |
June 21, 1990 (#88000706) |
Amesbury 42°50′31″N 70°54′49″W / 42.8420°N 70.9136°W | Essex | Founded in 1793, this boatshop has been in continuous business ever since; it is where founder Simeon Lowell developed the stackable dory. The present buildings date from the 1860s.[104] |
| 78 | Luna (tugboat) |  |
April 11, 1989 (#83004099) |
Chelsea 42°23′11″N 71°02′30″W / 42.386409°N 71.041735°W | Suffolk | The Luna, built in 1930, is the last surviving full-sized wooden ship-docking tug on the Gulf and Atlantic coasts of the United States. She was the world's first diesel-electric tugboat built for commercial service, and was a showpiece for Thomas Alva Edison's General Electric Corporation. In October 2015 she was docked in Chelsea, Massachusetts. |
| 79 | USS Massachusetts (battleship) |  |
January 14, 1986 (#76002269) |
Fall River 41°42′24″N 71°09′47″W / 41.7067°N 71.1630°W | Bristol | One of two surviving United States Navy South Dakota-class battleships, Massachusetts saw action in World War II, winning 11 battle stars. She is on display at Battleship Cove.[105] |
| 80 | Massachusetts Hall, Harvard University |  |
October 9, 1960 (#66000769) |
Cambridge 42°22′28″N 71°07′06″W / 42.3745°N 71.1183°W | Middlesex | This building, now housing administrative offices and a freshman dormitory, is the oldest surviving building (1718–20) on the campus of Harvard University, and the second oldest academic building in the nation.[106][107] |
| 81 | Memorial Hall, Harvard University |  |
December 30, 1970 (#70000685) |
Cambridge 42°22′34″N 71°06′54″W / 42.3761°N 71.1151°W | Middlesex | Designed by William Robert Ware and Henry Van Brunt, this High Gothic hall was built in the 1870s as Harvard University's memorial to its fallen in the American Civil War. Its amenities include Annenberg Hall (a dining hall) and Sanders Theater, a performance space.[108] |
| 82 | George R. Minot House |  |
January 7, 1976 (#76001976) |
Brookline 42°19′06″N 71°08′14″W / 42.3183°N 71.1373°W | Norfolk | George R. Minot (1885–1950) was awarded a Nobel Prize for his work finding a treatment for pernicious anemia, then a fatal disease. This 1920s suburban house was his home from 1929 until his death.[109] |
| 83 | Mission House |  |
October 18, 1968 (#68000038) |
Stockbridge 42°17′00″N 73°18′57″W / 42.2832°N 73.3159°W | Berkshire | This house was built in c. 1742 by Reverend John Sergeant, the first Christian missionary to the Stockbridge Indians. It is now owned and operated by The Trustees of Reservations as a house museum.[110] |
| 84 | The Mount (Edith Wharton Estate) |  |
November 11, 1971 (#71000900) |
Lenox 42°19′52″N 73°16′55″W / 42.3311°N 73.282°W | Berkshire | Designed by writer Edith Wharton (1862–1937) and built in 1902, The Mount is where she wrote the bestselling novel The House of Mirth. It is now a house museum.[111][112] |
| 85+ | Mount Auburn Cemetery |  |
May 27, 2003 (#75000254) |
Cambridge 42°22′14″N 71°08′45″W / 42.3706°N 71.1458°W | Middlesex | In an effort spearheaded by Dr. Jacob Bigelow, Mount Auburn Cemetery was laid out by Henry A. S. Dearborn in 1831 as "America's first garden cemetery". In addition to being the burial place of many famous Bostonians, it is known for its horticulture and as a birdwatching destination.[113] |
| 86+ | Nantucket Historic District |  |
November 13, 1966 (#66000772) |
Nantucket 41°17′00″N 70°05′51″W / 41.283225°N 70.09758055555555°W | Nantucket | This listing, which encompasses the entire island of Nantucket, was made in recognition of Nantucket's well-preserved historical settlements (dating to the 17th century), and its importance as the world's preeminent whaling center in the early years of the 19th century.[114] |
| 87 | Naumkeag |  |
March 29, 2007 (#75000264) |
Stockbridge 42°17′23″N 73°18′57″W / 42.2897°N 73.3159°W | Berkshire | This Gilded Age mansion and country estate was designed by McKim, Mead & White, with landscaping by Fletcher Steele. Built in the 1880s for lawyer Joseph Choate, it was given by his daughter to The Trustees of Reservations, who operate it as a museum.[115] |
| 88+ | Nauset Archeological District |  |
April 19, 1993 (#93000607) |
Eastham 41°49′08″N 69°57′46″W / 41.8189°N 69.9629°W | Barnstable | This district, located within the southern portion of the Cape Cod National Seashore, encompasses sites containing substantial ancient settlements dating to at least 4,000 BC. Some of these sites were described in the chronicles of early European explorers.[116] |
| 89+ | New Bedford Historic District |  |
November 13, 1966 (#66000773) |
New Bedford 41°38′07″N 70°55′27″W / 41.6353°N 70.9242°W | Bristol | This district encompasses the historic center of the country's leading 19th century whaling center, including as contributing properties other historic landmarks.[117] |
| 90 | Norfolk County Courthouse |  |
November 28, 1972 (#72001312) |
Dedham 42°14′56″N 71°10′34″W / 42.2488°N 71.1762°W | Norfolk | This Greek Revival courthouse was built in 1827 and expanded over the 19th century. It was site of the controversial Sacco-Vanzetti trial in 1921, and has changed little since then.[118] |
| 91+ | Old Deerfield Historic District |  |
October 9, 1960 (#66000774) |
Deerfield 42°32′49″N 72°36′15″W / 42.547°N 72.6041°W | Franklin | This well-preserved 18th century colonial village was the site of numerous Indian raids, including a famous and well-documented attack in 1704.[119] The village is administered by Historic Deerfield as a museum.[120] |
| 92 | Old Manse |  |
December 29, 1962 (#66000775) |
Concord 42°28′06″N 71°20′57″W / 42.4683°N 71.3492°W | Middlesex | This 1770 Revolutionary-era house was home for a time to both Ralph Waldo Emerson (whose grandfather had it built) and Nathaniel Hawthorne; Henry David Thoreau was a guest of Hawthorne's. The house is now owned by The Trustees of Reservations and is open to the public.[121] |
| 93 | Old Ship Meetinghouse |  |
October 9, 1960 (#66000777) |
Hingham 42°14′28″N 70°53′14″W / 42.2412°N 70.8871°W | Plymouth | This Puritan meetinghouse was constructed in 1681 and is claimed to be the oldest church in the nation still used for religious services.[122] Its name derives from its construction, which resembles an inverted wooden ship hull.[123] |
| 94* | Frederick Law Olmsted House |  |
May 23, 1963 (#66000780) |
Brookline 42°19′32″N 71°07′56″W / 42.3255°N 71.1321°W | Norfolk | Frederick Law Olmsted (1822–1903), one of America's leading landscape designers of his generation, lived and worked at this site for the last twenty years of his life.[124] It is now a National Historic Site.[125] |
| 95 | Orchard House |  |
December 29, 1962 (#66000781) |
Concord 42°27′32″N 71°20′06″W / 42.4589°N 71.3351°W | Middlesex | This early 18th-century house was the longtime home of Transcendentalist Amos Bronson Alcott (1799–1888). His daughter, writer Louisa May Alcott, set the novel Little Women here. It is now a house museum.[126] |
| 96 | Robert Treat Paine House |  |
June 30, 1989 (#75000291) |
Waltham 42°23′07″N 71°13′40″W / 42.3854°N 71.2279°W | Middlesex | Also known as Stonehurst, this city-owned estate was designed by H. H. Richardson with landscaping by Frederick Law Olmsted for Boston lawyer Robert Treat Paine Jr. (1835–1910). It is open to the public.[127] |
| 97 | The Parsonage |  |
November 11, 1971 (#71000903) |
Natick 42°16′15″N 71°18′52″W / 42.2709°N 71.3144°W | Middlesex | This 1824 house was home to the father of writer Horatio Alger (1832–99). Alger, a prolific and popular writer of juvenile fiction, frequently summered here.[128] |
| 98 | Peabody Museum of Salem |  |
December 21, 1965 (#66000783) |
Salem 42°31′18″N 70°53′33″W / 42.5218°N 70.8926°W | Essex | Now embedded within the Peabody Essex Museum, the East India Marine Hall was built in the 1820s. The museum traces its lineage to the 1799 East India Marine Society, claiming to be the nation's oldest continuously operating museum.[129] |
| 99 | Peirce-Nichols House |  |
October 18, 1968 (#68000041) |
Salem 42°31′21″N 70°53′59″W / 42.5226°N 70.8996°W | Essex | This transitional Georgian/Federal style home was built in 1782 for merchant Jerathmiel Peirce by Samuel McIntire.[130] The house is owned by the Peabody Essex Museum, which offers tours.[131] |
| 100 | Lydia Pinkham House |  |
August 25, 2014 (#12000818) |
Lynn 42°28′33″N 70°57′03″W / 42.4758°N 70.9508°W | Essex | This 1872 Second Empire house was the residence of Lydia Pinkham, whose homemade herbal remedy for dysmenorrhea was one of the bestselling such medical products of the late 19th century thanks to Pinkham's use of her own image as a marketing tool. Orders and other correspondence were received at the house's Western Avenue address; sometimes Pinkham wrote back personally, a practice continued by her company after her death.[132] |
| 101 | PT 617 |  |
December 20, 1989 (#89002465) |
Fall River 41°42′17″N 71°09′42″W / 41.7047°N 71.1616°W | Bristol | The only surviving 80 feet (24 m) Elco torpedo boat from World War II, craft of this type were workhorses throughout many theaters of the war. This boat is on display at the PT Boat Museum in Battleship Cove.[133] |
| 102 | PT 796 |  |
January 14, 1986 (#86000092) |
Fall River 41°42′17″N 71°09′42″W / 41.7048°N 71.1617°W | Bristol | This is one of three surviving Higgins PT boats, built late in World War II. It is on display at the PT Boat Museum in Battleship Cove.[134] |
| 103 | General Rufus Putnam House |  |
November 28, 1972 (#72001330) |
Rutland 42°22′17″N 71°58′03″W / 42.3713°N 71.9674°W | Worcester | Rufus Putnam (1738–1824) was a Continental Army officer in the American Revolutionary War. After the war he pioneered the settlement of the Northwest Territories, serving as its first Surveyor General. This house, built in the early 1760s, was his home in the 1780s. Although it was for a time a local museum, it is now a bed and breakfast.[135][136] |
| 104 | Quincy Homestead |  |
April 5, 2005 (#70000095) |
Quincy 42°15′30″N 71°00′27″W / 42.2582°N 71.0074°W | Norfolk | This house was built in 1686 as an early home of the Quincy family. Its well-preserved construction documents 300 years of architectural changes. The building was an early success in house preservation early in the 20th century, and is now a house museum.[137][138] |
| 105 | Josiah Quincy House |  |
September 25, 1997 (#97001274) |
Quincy 42°16′18″N 71°00′53″W / 42.2718°N 71.0147°W | Norfolk | This house, built c. 1770, was occupied by a succession of politically active Quincys, and contains architectural details unique among houses from the period. It is owned by Historic New England, who offer infrequent tours during the summer months.[139][140] |
| 106 | Red Top (William Dean Howells' House) |  |
November 11, 1971 (#71000911) |
Belmont 42°24′01″N 71°10′46″W / 42.4003°N 71.1794°W | Middlesex | William Dean Howells (1837–1920) was a major literary figure of the late 19th century, writing prolifically and editing the Atlantic Monthly. This house was designed by Howells' brother-in-law William Rutherford Mead[141] (of McKim, Mead, and White), and was home to the Howellses 1878–1882. It was the site of gatherings involving many literary notables.[142] |
| 107 | Revere Beach Reservation |  |
May 27, 2003 (#03000642) |
Revere 42°24′23″N 70°59′28″W / 42.4064°N 70.9911°W | Suffolk | Revere Beach was the first oceanside beach purchased for public access (in 1895). Architect Charles Eliot was responsible for the design and layout of the beach's roadways and facilities. Managed by the Massachusetts Department of Conservation and Recreation, the reservation continues to provide public recreation facilities.[143][144] |
| 108 | Theodore W. Richards House |  |
January 7, 1976 (#76001999) |
Cambridge 42°22′42″N 71°07′22″W / 42.3784°N 71.1228°W | Middlesex | Theodore William Richards (1868–1928) was considered the foremost experimental chemist of his time. He won the Nobel prize for his role in determine the atomic weights of many elements. This house was built in 1900 with design input from Richards, and he lived there until his death.[145] |
| 109 | William J. Rotch Gothic Cottage |  |
February 17, 2006 (#06000236) |
New Bedford 41°37′50″N 70°55′57″W / 41.6306°N 70.9326°W | Bristol | This early Gothic Revival cottage was designed by Alexander Jackson Davis in 1845 for William J. Rotch (1819–1893), scion of New Bedford's leading whaling family. It exhibits features not found in other surviving similar works by Davis, and received wide public notice after its construction. The cottage is a private residence and is not open to the public.[146] |
| 110 | William Rotch Jr. House |  |
April 5, 2005 (#05000456) |
New Bedford 41°37′49″N 70°55′42″W / 41.6303°N 70.9283°W | Bristol | This house was the first design of Richard Upjohn, a leading architect of the 19th century. He designed this Greek Revival home for William Rotch Jr. (1759–1850), the leading whaling businessman of the time. Later residents of the house were also leading New Bedford figures. The property is now a house museum.[147] |
| 111 | Isaac Royall House |  |
October 9, 1960 (#66000786) |
Medford 42°24′43″N 71°06′41″W / 42.4119°N 71.1115°W | Middlesex | This c. 1692 house was extensively expanded in the 18th century by merchant and slaveowner Isaac Royall Jr. It was occupied by John Stark during the 1775–76 Siege of Boston. A well-preserved Georgian house that is now a museum.[148][149] |
| 112 | Count Rumford Birthplace |  |
January 15, 1975 (#75001942) |
Woburn 42°30′27″N 71°09′40″W / 42.5076°N 71.1611°W | Middlesex | Inventor and scientist Benjamin Thompson (1753–1814) was born in this well-preserved 1714 house. Thompson was lauded in Europe for his discoveries (including key advances in the field of thermodynamics); he received honors including the title Count Rumford. The house is now a museum.[150] |
| 113 | Sampson-White Joiner Shop | December 11, 2023 (#100009826) |
Duxbury 42°01′19″N 70°44′42″W / 42.0219°N 70.7450°W | Plymouth | The only known surviving 18th-century woodworking shop in its original setting with original fixtures. | |
| 114* | Saugus Iron Works |  |
November 27, 1963 (#66000047) |
Saugus 42°28′04″N 71°00′32″W / 42.4678°N 71.0089°W | Essex | This National Historic Site preserves an early colonial ironworks, dating to 1646.[151] |
| 115 | Sever Hall, Harvard University |  |
December 30, 1970 (#70000732) |
Cambridge 42°22′28″N 71°06′56″W / 42.3744°N 71.1155°W | Middlesex | This mature work of H. H. Richardson is a classroom building. Richardson sought to integrate contemporary ideas of architecture into Harvard's largely Georgian campus.[152] |
| 116 | Spencer-Pierce-Little House |  |
October 18, 1968 (#68000043) |
Newbury 42°47′36″N 70°51′23″W / 42.7933°N 70.8564°W | Essex | This house is a rare example of a 17th-century stone house in New England. Relatively unchanged despite additions over the centuries, it is now owned by Historic New England, who operate the site as a farm and museum.[153][154] |
| 117* | Springfield Armory |  |
December 19, 1960 (#66000898) |
Springfield 42°06′29″N 72°34′54″W / 42.1081°N 72.5817°W | Hampden | Until 1968 this site was a part of the nation's first armories and weapons production facilities, and a major military research facility. It was a focal point of the 1787 Shays' Rebellion, a local uprising against oppressive state fiscal policies.[155] |
| 118 | Joseph Story House |  |
November 7, 1973 (#73001952) |
Salem 42°31′31″N 70°53′23″W / 42.5253°N 70.8898°W | Essex | Joseph Story (1779–1845) was an influential United States Supreme Court Justice on the John Marshall court. Story's jurisprudence and legal thought were highly influential during his tenure on the court (1811–45). Story lived in this Federalist style home from 1811 to 1829.[156] |
| 119 | Mary Fisk Stoughton House |  |
June 29, 1989 (#89001246) |
Cambridge 42°22′34″N 71°07′29″W / 42.3760°N 71.1246°W | Middlesex | This 1880s Shingle style home by H. H. Richardson was one of his last commissions, and the best surviving example of his work in that style. The house's residents included Harvard University professor and historian John Fiske.[157] |
| 120 | Elihu Thomson House |  |
January 7, 1976 (#76002002) |
Swampscott 42°28′11″N 70°55′06″W / 42.4697°N 70.9184°W | Essex | Elihu Thomson (1853–1937) was an inventor and pioneer in the field of electrical engineering. Along with Thomas Alva Edison he founded General Electric. This 1889 Georgian Revival house was Thomson's home for many years; it now serves as Swampscott's town hall.[158] |
| 121 | Peter Tufts House |  |
October 18, 1968 (#68000044) |
Medford 42°24′41″N 71°05′37″W / 42.4115°N 71.0937°W | Middlesex | This house, whose construction date is uncertain but believed to be in the mid-to-late 17th century, is quite possibly the oldest brick house in North America. It was probably built by Peter Tufts (1628–1702), an early settler of Medford.[159] It is owned by the Medford Historical Society, which seasonally offers tours.[160] |
| 122 | United First Parish Church (Unitarian) Of Quincy |  |
December 30, 1970 (#70000734) |
Quincy 42°15′04″N 71°00′11″W / 42.2512°N 71.003°W | Norfolk | Alexander Parris designed this Greek Revival church in the 1820s for the oldest congregation in Quincy. Presidents John Adams and John Quincy Adams are buried here.[161] |
| 123 | United States Customhouse |  |
December 30, 1970 (#70000735) |
New Bedford 41°38′07″N 70°55′29″W / 41.6353°N 70.9247°W | Bristol | This outstanding example of a public building in the Greek Revival style has been used as a customs facility since 1834.[162] |
| 124 | University Hall, Harvard University |  |
December 30, 1970 (#70000736) |
Cambridge 42°22′28″N 71°07′02″W / 42.3745°N 71.1171°W | Middlesex | Architect Charles Bulfinch designed, and engineer Loammi Baldwin Jr. constructed this Harvard College facility. Originally used for classes and dining, it now houses the administrative offices.[163] |
| 125 | The Vale |  |
December 30, 1970 (#70000737) |
Waltham 42°23′02″N 71°13′49″W / 42.3839°N 71.2303°W | Middlesex | Now more commonly called the Lyman Estate, this was the country estate of Boston merchant Theodore Lyman. Built in 1793, it includes one of the nation's oldest greenhouses, and has survived with most of its landscaping intact. It is open to the public.[164][165] |
| 126 | Walden Pond |  |
December 29, 1962 (#66000790) |
Concord 42°26′18″N 71°20′31″W / 42.4384°N 71.342°W | Middlesex | Now part of a state reservation, Henry David Thoreau's cabin was located here. The time Thoreau spent here was inspiration for his conservationist treatise Walden.[166] |
| 127 | John Ward House |  |
October 18, 1982 (#68000045) |
Salem 42°31′22″N 70°53′30″W / 42.5229°N 70.8916°W | Essex | Construction was begun on this house in 1684, with owner John Ward making several modifications to it prior to his death. The building, now owned by the Peabody Essex Museum, stands as a fine example of the organic growth of early colonial houses.[167] |
| 128 | The Wayside, "Home of Authors" |  |
December 29, 1962 (#80000356) |
Concord 42°27′32″N 71°19′59″W / 42.4589°N 71.3331°W | Middlesex | This c. 1700 house, part of the Minuteman National Historical Park, was home to three writers in the 19th century: Louisa May Alcott, Nathaniel Hawthorne, and Margaret Sidney. The Park Service opens the house for tours seasonally.[168] |
| 129 | Daniel Webster Law Office |  |
May 30, 1974 (#74002053) |
Marshfield 42°04′17″N 70°40′21″W / 42.0714°N 70.6725°W | Plymouth | Lawyer, politician, and orator Daniel Webster (1782–1852) used this 1832 cottage as his office and library. Originally located on his Marshfield estate, it is now on the grounds of the nearby Isaac Winslow House Museum.[169][170] |
| 130 | Wesleyan Grove |  |
April 5, 2005 (#05000458) |
Oak Bluffs 41°27′19″N 70°33′41″W / 41.4553°N 70.5614°W | Dukes | Wesleyan Grove is a Methodist camp meeting established in 1835. Its grounds, which are open to the public, feature a large number of Victorian era gingerbread cottages. As one of the earliest camps of this type, its features were influential in the development of other permanent camp meeting facilities.[171] |
| 131+ | Western Railroad Stone Arch Bridges and Chester Factory Village Depot |  |
January 13, 2021 (#100006273) |
Vicinity of Herbert Cross Road, Middlefield/Becket Line (Bridges and Roadbed); 10 Prospect Street (Depot) 42°18′20″N 73°00′19″W / 42.3055°N 73.0054°W | Berkshire, Hampden, and Hampshire | 1840s railroad engineering that proved the ability to cross mountainous terrain. Extends into Chester and Middlefield; includes a subset of the Middlefield-Becket Stone Arch Railroad Bridge District. |
| 132 | John Whipple House |  |
October 9, 1960 (#66000791) |
Ipswich 42°40′36″N 70°50′10″W / 42.6766°N 70.8361°W | Essex | The earliest portions of this house date to 1642. It has been operated as a museum (now known as the Ipswich Museum) since the 1890s.[172][173] |
| 133 | John Greenleaf Whittier Home |  |
December 29, 1962 (#66000792) |
Amesbury 42°51′21″N 70°56′07″W / 42.8558°N 70.9353°W | Essex | This house was the longtime home of poet and abolitionist John Greenleaf Whittier (1807–92). It is now a house museum.[174] |
| 134 | Winn Memorial Library |  |
December 23, 1987 (#76000290) |
Woburn 42°28′45″N 71°09′16″W / 42.4792°N 71.1545°W | Middlesex | This was the first public library building designed by H. H. Richardson; it was built between 1876 and 1879. It still houses Woburn's public library.[175] |
| 135 | Wright's Tavern |  |
January 20, 1961 (#66000793) |
Concord 42°27′36″N 71°20′55″W / 42.4601°N 71.3487°W | Middlesex | Wright's Tavern was used in October 1774 as the first meeting place of the Massachusetts Provincial Congress. In April 1775 it was the assembly point for Concord's Minutemen before the Battles of Lexington and Concord.[176] |
See also
[edit]- List of areas in the National Park System in Massachusetts
- Adams National Historical Park
- Minute Man National Historical Park
- New Bedford Whaling National Historical Park
- Salem Maritime National Historic Site
- List of U.S. National Historic Landmarks by state
- National Register of Historic Places listings in Massachusetts
- List of National Natural Landmarks in Massachusetts
Notes
[edit]- ^ Numbers represent an alphabetical ordering by significant words. Various colorings, defined here, differentiate National Historic Landmarks and historic districts from other NRHP buildings, structures, sites or objects.
- ^ The eight-digit number below each date is the number assigned to each location in the National Register Information System database, which can be viewed by clicking the number.
- ^ "NHL Summary Description of Adams Academy". National Park Service. Archived from the original on September 1, 2012. Retrieved November 6, 2012.
- ^ "NHL Summary Description of John Adams Birthplace". National Park Service. Archived from the original on May 2, 2008. Retrieved November 6, 2012.
- ^ a b "Adams National Historical Park". National Park Service. Retrieved November 6, 2012.
- ^ "NHL Summary Description of John Quincy Adams Birthplace". National Park Service. Archived from the original on May 2, 2008. Retrieved November 6, 2012.
- ^ "NHL Summary Description of Adventure schooner". National Park Service. Archived from the original on November 18, 2007. Retrieved November 6, 2012.
- ^ "NHL Summary Description of the John and Priscilla Alden Family Sites". National Park Service. Archived from the original on September 1, 2010. Retrieved November 6, 2012.
- ^ "NHL Summary Description of American Antiquarian Society". National Park Service. Retrieved November 6, 2012.
- ^ "NHL Summary Description of Arrowhead (Herman Melville House)". National Park Service. Archived from the original on June 6, 2009. Retrieved November 6, 2012.
- ^ "NHL Summary Description of Maria Baldwin House". National Park Service. Archived from the original on October 8, 2012. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Maria Baldwin House". National Park Service. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ^ "NHL Summary Description of Beauport". National Park Service. Archived from the original on June 6, 2009. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ^ "Historic New England: Beauport". Historic New England. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ^ "NHL Summary Description of Edward Bellamy House". National Park Service. Archived from the original on October 2, 2012. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ^ "NHL Summary Description of George D. Birkhoff House". National Park Service. Archived from the original on June 6, 2009. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ^ "NHL Summary Description of Blue Hill Meteorological Observatory". National Park Service. Archived from the original on June 6, 2009. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ^ "Historic New England: Boardman House". Historic New England. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Boston Manufacturing Company". National Park Service. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ^ "NHL Summary Description of Nathaniel Bowditch Home". National Park Service. Archived from the original on October 8, 2012. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ^ "The Nathaniel Bowditch House". Historic Salem, Inc. Archived from the original on February 8, 2013. Retrieved January 11, 2013.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Louis Brandeis House". National Park Service. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Percy W. Bridgman House". National Park Service. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ^ "Trustees of Reservations: William Cullen Bryant Homestead". The Trustees of Reservations. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Buckman Tavern". National Park Service. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Cape Ann Light Station". National Park Service. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ^ "NHL Summary Description of Parson Capen House". National Park Service. Archived from the original on June 6, 2009. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ^ "Parson Capen House". Topsfield Historical Society. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ^ "NHL Summary Description of Castle Hill". National Park Service. Archived from the original on October 9, 2012. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Christ Church, Cambridge". National Park Service. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ^ "Oldest House of the Nantucket Historical Association". Nantucket Historical Association. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ^ "NHL Summary Description of Cole's Hill". National Park Service. Archived from the original on October 2, 2012. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ^ "NHL Summary Description of Converse Memorial Library". National Park Service. Archived from the original on June 6, 2009. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Crane and Company Old Stone Mill Rag Room". National Park Service. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Crane Memorial Library". National Park Service. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Paul Cuffe Farm". Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Retrieved November 18, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Caleb Cushing House". National Park Service. Retrieved November 18, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Reginald A. Daly House". National Park Service. Retrieved November 18, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for William M. Davis House". National Park Service. Retrieved November 18, 2012.
- ^ "William Morris Davis". Valparaiso University. Archived from the original on August 28, 2010. Retrieved November 18, 2012.
- ^ "History of Glen Magna Farms". Danvers Historical Society. Archived from the original on November 1, 2012. Retrieved November 18, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for Derby Summerhouse". National Park Service. Archived from the original on June 6, 2009. Retrieved November 18, 2012.
- ^ "Emily Dickinson Museum". Amherst College. Archived from the original on September 24, 2015. Retrieved November 18, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for Emily Dickinson Home". National Park Service. Archived from the original on June 6, 2009. Retrieved November 18, 2012.
- ^ "W. E. B. Du Bois Boyhood Home Site". National Park Service. Retrieved November 18, 2012.
- ^ "Dubois Homesite". Friends of the W. E. B. Du Bois Homesite. Retrieved November 18, 2012.
- ^ "33 Elmwood". The Harvard Crimson. October 14, 2001. Retrieved November 18, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Elmwood". National Park Service. Retrieved November 18, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Ralph Waldo Emerson House". National Park Service. Retrieved November 18, 2012.
- ^ "History of the Ernestina". Schooner Ernestina-Morrissey Association. Retrieved November 18, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for Ernestina". National Park Service. Archived from the original on May 3, 2008. Retrieved November 18, 2012.
- ^ "Explorers and Settlers: Fairbanks House". National Park Service. Retrieved November 18, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Reginald A. Fessenden House". National Park Service. Retrieved November 18, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for First Church of Christ, Lancaster". National Park Service. Retrieved November 18, 2012.
- ^ "First Church of Christ Unitarian". First Church of Christ Unitarian. Retrieved November 18, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Flying Horses Carousel". National Park Service. Retrieved November 18, 2012.
- ^ "Forbes House Museum History". Forbes House Museum. Archived from the original on January 8, 2013. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ^ "About the Forbes House Museum". Forbes House Museum. Archived from the original on January 8, 2013. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for Daniel Chester French Home and Studio". National Park Service. Archived from the original on October 8, 2012. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ^ "Chesterwood House". National Trust for Historic Preservation. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for Fruitlands". National Park Service. Archived from the original on July 26, 2014. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ^ Felton, R. Todd. A Journey into the Transcendentalists' New England. Berkeley, California: Roaring Forties Press, 2006: 133. ISBN 0-9766706-4-X
- ^ "NHL summary listing for Margaret Fuller House". National Park Service. Archived from the original on July 26, 2014. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ^ Gura, Philip F. American Transcendentalism: A History. New York: Hill and Wang, 2007: 156. ISBN 0-8090-3477-8
- ^ "PEM Historic Houses". Peabody Essex Museum. Archived from the original on October 18, 2012. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ^ "A Murder in Salem". Smithsonian Magazine. November 2010. Retrieved November 19, 2011.
- ^ "PEM: Daily Tours". Peabody Essex Museum. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for General John Glover House". National Park Service. Archived from the original on October 2, 2012. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ^ Sanborn, Nathaniel (1903). Gen. John Glover and his Marblehead Regiment in the Revolutionary War. Marblehead, MA: Marblehead Historical Society. pp. 6–46.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for Goddard Rocket Launching Site". National Park Service. Archived from the original on July 28, 2007. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Goddard Rocket Launching Site". National Park Service. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ^ "History of Gore Place". Gore Place Society. Archived from the original on July 17, 2012. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for John B. Gough House". National Park Service. Archived from the original on October 2, 2012. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ^ "Apple pies to help Hillside restoration". The Boston Globe. September 29, 2012. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Asa Gray House". National Park Service. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for Gropius House". National Park Service. Archived from the original on October 9, 2012. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ^ "Gropius House". Historic New England. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for H. H. Richardson Historic District of North Easton". National Park Service. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Hamilton Hall". Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Hancock-Clarke House". Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ^ "Hancock-Clarke House". Lexington Historical Society. Archived from the original on June 18, 2012. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ^ "Shaker Historic Trail: Hancock Shaker Village". National Park Service. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Hancock Shaker Village". Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for Oliver Hastings House". National Park Service. Retrieved November 20, 2012.[permanent dead link]
- ^ de Waal, Cornelis; Peirce, Charles S (2010). Writings of Charles S. Peirce, Vol. 8. Bloomington, IN: Indiana University Press. p. 374.
- ^ Beverly Historical Society (2010). Bevery Revisited. Charleston, SC: Arcadia Publishing. p. 70. ISBN 9780738573588. OCLC 639158709.
- ^ White, Edward (2005). Oliver Wendell Holmes, Jr. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 107–109. ISBN 9780195305364. OCLC 163834852.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for House of Seven Gables District". Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Retrieved November 20, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for Jacob's Pillow Dance Festival". National Park Service. Archived from the original on February 12, 2012. Retrieved November 20, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for Nathan and Mary (Polly) Johnson Properties". National Park Service. Archived from the original on October 2, 2012. Retrieved November 20, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for USS Joseph P. Kennedy, Jr". National Park Service. Retrieved November 20, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for USS Joseph P. Kennedy, Jr. (destroyer)". National Park Service. Archived from the original on January 14, 2009. Retrieved November 20, 2012.
- ^ "The Presidents of the United States: Kennedy Compound". National Park Service. Retrieved November 20, 2012.
- ^ "The Presidents of the United States: Kennedy Historic Site". National Park Service. Archived from the original on October 12, 2012. Retrieved November 20, 2012.
- ^ "Lee Mansion". Marblehead Historical Society. Archived from the original on August 23, 2010. Retrieved November 20, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for Lexington Green". National Park Service. Archived from the original on July 26, 2014. Retrieved November 20, 2012.
- ^ "Liberty Farms". National Park Service. Retrieved November 23, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for General Benjamin Lincoln House". National Park Service. Retrieved November 23, 2012.
- ^ "USS Lionfish (SS-298)". Historic Naval Ships Association. Archived from the original on September 16, 2012. Retrieved November 23, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Arthur D. Little, Inc. Building". National Park Service. Retrieved November 23, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Henry Cabot Lodge House". National Park Service. Retrieved November 23, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Craigie-Longfellow House". National Park Service. Retrieved November 23, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Lowell Locks and Canals". National Park Service. Retrieved November 23, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for Lowell's Boat House". National Park Service. Archived from the original on October 2, 2012. Retrieved November 25, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for USS Massachusetts". National Park Service. Archived from the original on October 10, 2012. Retrieved November 25, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for Massachusetts Hall". National Park Service. Archived from the original on June 21, 2008. Retrieved November 25, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Massachusetts Hall". National Park Service. Retrieved November 25, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Memorial Hall". National Park Service. Retrieved November 25, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for George R. Minot House". National Park Service. Retrieved November 25, 2012.
- ^ "The Mission House". The Trustees of Reservations. Retrieved November 25, 2012.
- ^ "About Edith Wharton Restoration". Edith Wharton Restoration. Retrieved November 25, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for The Mount". National Park Service. Archived from the original on July 26, 2014. Retrieved November 25, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Mount Auburn Cemetery". National Park Service. Retrieved November 25, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Nantucket Historic District". National Park Service. Retrieved November 25, 2012.
- ^ "Naumkeag". The Trustees of Reservations. Retrieved November 25, 2012.
- ^ McManamon, Francis P. "The Nauset Archaeological District -Eastham". National Park Service. Retrieved November 25, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for New Bedford Historic District". National Park Service. Archived from the original on June 6, 2011. Retrieved November 25, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Norfolk County Courthouse". National Park Service. Retrieved November 25, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Old Deerfield Historic District". National Park Service. Retrieved November 25, 2012.
- ^ "Historic Deerfield". Historic Deerfield. Retrieved November 25, 2012.
- ^ "The Old Manse". The Trustees of Reservations. Retrieved November 25, 2012.
- ^ "Explorers and Settlers: Old Ship Church". National Park Service. Retrieved November 25, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for Old Ship Meetinghouse". National Park Service. Archived from the original on September 26, 2012. Retrieved November 25, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for Frederick law Olmsted House". National Park Service. Archived from the original on December 14, 2012. Retrieved November 26, 2012.
- ^ "Frederick Law Olmsted National Historic Site". National Park Service. Retrieved November 26, 2012.
- ^ "Alcotts and Orchard House". Louisa May Alcott's Orchard House. Retrieved November 26, 2012.
- ^ "Stonehurst". City of Waltham. Archived from the original on July 17, 2012. Retrieved November 26, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for The Parsonage". National Park Service. Retrieved November 26, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for Peabody Museum of Salem". National Park Service. Archived from the original on July 26, 2014. Retrieved November 26, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Peirce-Nichols House". National Park Service. Retrieved November 26, 2012.
- ^ "Historic Houses". Peabody Essex Museum. Archived from the original on July 25, 2014. Retrieved November 26, 2012.
- ^ "NHL nomination for Lydia Pinkham House" (PDF). National Park Service. Retrieved December 22, 2013.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for PT 617". National Park Service. Archived from the original on September 30, 2012. Retrieved November 27, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for PT 796". National Park Service. Archived from the original on October 10, 2012. Retrieved November 27, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for General Rufus Putnam House". National Park Service. Retrieved November 27, 2012.
- ^ "Rufus Putnam House". Rufus Putnam House. Retrieved November 27, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for Quincy Homestead". National Park Service. Archived from the original on December 13, 2012. Retrieved November 27, 2012.
- ^ "Quincy Homestead". National Society of Colonial Dames of America. Archived from the original on July 21, 2012. Retrieved November 27, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for Josiah Quincy House". National Park Service. Archived from the original on December 14, 2012. Retrieved November 27, 2012.
- ^ "Quincy House". Historic New England. Retrieved November 27, 2012.
- ^ Lynn, Kenneth S. William Dean Howells: An American Life. New York: Harcout Brace Jovanovich, Inc., 1970: 193. ISBN 0-15-142177-3
- ^ "NHL summary listing for Red Top". National Park Service. Archived from the original on February 12, 2012. Retrieved November 27, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Revere Beach Parkway". National Park Service. Retrieved November 27, 2012.
- ^ "Revere Beach". Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Retrieved November 27, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Theodore W. Richards House". National Park Service. Retrieved November 27, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for William J. Rotch Gothic Cottage". National Park Service. Retrieved November 29, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for William Rotch Jr. House". National Park Service. Retrieved November 29, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Isaac Royall House". National Park Service. Retrieved November 29, 2012.
- ^ "Royall House". Royall House Association. Retrieved November 29, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Count Rumford Birthplace". National Park Service. Retrieved November 29, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for Saugus Iron Works". National Park Service. Archived from the original on February 27, 2011. Retrieved November 29, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Sever Hall". National Park Service. Retrieved November 29, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Spencer-Pierce-Little House". National Park Service. Retrieved November 29, 2012.
- ^ "Spencer-Peirce-Little Farm". Historic New England. Retrieved November 29, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Springfield Armory". National Park Service. Retrieved November 29, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Joseph Story House". National Park Service. Retrieved November 29, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Mary Fisk Stoughton House". National Park Service. Retrieved November 29, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Elihu Thomson House". National Park Service. Retrieved November 30, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Peter Tufts House". National Park Service. Retrieved November 30, 2012.
- ^ "November 2011 Newsletter" (PDF). Medford Historical Society. Retrieved November 30, 2012.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "NRHP nomination for United First Parish Church (Unitarian) of Quincy". National Park Service. Retrieved November 30, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for United States Customhouse". National Park Service. Retrieved November 30, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for University Hall". National Park Service. Retrieved November 30, 2012.
- ^ "Lyman Estate". Historic New England. Retrieved November 30, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for The Vale". National Park Service. Archived from the original on October 8, 2012. Retrieved November 30, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for Walden Pond". National Park Service. Archived from the original on February 13, 2013. Retrieved November 30, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for John Ward House". National Park Service. Retrieved December 1, 2012.
- ^ "Places Where Women Made History: The Wayside". National Park Service. Retrieved December 1, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Daniel Webster Law Office". National Park Service. Retrieved December 1, 2012.
- ^ "Law Office". Daniel Webster Estate. Retrieved December 1, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Wesleyan Grove". National Park Service. Retrieved December 1, 2012.
- ^ "About Us". Ipswich Museum. Archived from the original on May 29, 2012. Retrieved December 1, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for John Whipple House". National Park Service. Retrieved December 1, 2012.
- ^ "About Whittier". Whittier Home Association. Retrieved December 1, 2012.
- ^ "NRHP nomination for Winn Memorial Library". National Park Service. Retrieved December 1, 2012.
- ^ "NHL summary listing for Wright's Tavern". National Park Service. Archived from the original on October 10, 2012. Retrieved December 1, 2012.
External links
[edit]- "National Historic Landmarks Survey: List of National Historic Landmarks by State—Massachusetts (183)" (PDF). National Park Service. Retrieved November 5, 2007.
- National Historic Landmarks Program, at National Park Service
- National Park Service listings of National Historic Landmarks

