Pulse generator
This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2023) |

A pulse generator is either an electronic circuit or a piece of electronic test equipment used to generate rectangular pulses. Pulse generators are used primarily for working with digital circuits; related function generators are used primarily for analog circuits.
Bench pulse generators
[edit]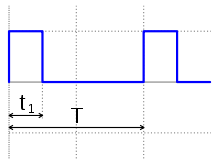
Simple bench pulse generators usually allow control of the pulse repetition rate (frequency), pulse width, delay with respect to an internal or external trigger and the high- and low-voltage levels of the pulses. More sophisticated pulse generators may allow control over the rise time and fall time of the pulses. Pulse generators are available for generating output pulses having widths (duration) ranging from minutes to under 1 picosecond.
Pulse generators are generally voltage sources, with true current pulse generators being available only from a few suppliers.
Pulse generators may use digital techniques, analog techniques, or a combination of both techniques to form the output pulses. For example, the pulse repetition rate and duration may be digitally controlled but the pulse amplitude and rise and fall times may be determined by analog circuitry in the output stage of the pulse generator. With correct adjustment, pulse generators can also produce a 50% duty cycle square wave. Pulse generators are generally single-channel, providing one frequency, delay, width and output.
Optical pulse generators
[edit]Light pulse generators are the optical equivalent to electrical pulse generators with rep rate, delay,width and amplitude control. The output in this case is light, typically from a LED or laser diode.
Multiple-channels
[edit]
A new family of pulse generators can produce multiple channels of independent widths and delays and independent outputs and polarities. Often called digital delay/pulse generators, the newest designs even offer differing repetition rates with each channel. These digital delay generators are useful in synchronizing, delaying, gating and triggering multiple devices, usually with respect to one event. One is also able to multiplex the timing of several channels onto one channel in order to trigger or even gate the same device multiple times.
A new class of pulse generator offers both multiple input trigger connections and multiple output connections. Multiple input triggers allow experimenters to synchronize both trigger events and data acquisition events using the same timing controller.
In general, generators for pulses with widths over a few microseconds employ digital counters for timing these pulses, while widths between approximately 1 nanosecond and several microseconds are typically generated by analog techniques such as RC (resistor-capacitor) networks or switched delay lines.
Microwave pulsers
[edit]Pulse generators capable of generating pulses with widths under approximately 100 picoseconds are often termed as "microwave pulsers" and typically generate these ultra-short pulses using Step recovery diode (SRD) or Nonlinear Transmission Line (NLTL) methods (for example [1]). Step Recovery Diode pulse generators are inexpensive, but typically require several volts of input drive level and have a moderately high level of random jitter (usually undesirable variation in the time at which successive pulses occur).
NLTL-based pulse generators generally have lower jitter, but are more complex to manufacture and do not suit integration in low-cost monolithic ICs. A new class of microwave pulse generation architecture, the RACE (Rapid Automatic Cascode Exchange) pulse generation circuit[1][2] is implemented using low-cost monolithic IC technology and can produce pulses as short as 1 picosecond and repetition rates exceeding 30 billion pulses per second. These pulsers are typically used in military communications applications and low-power microwave transceiver ICs. Such pulsers, if driven by a continuous frequency clock, will act as microwave comb generators, having output frequency components at integer multiples of the pulse repetition rate, and extending to well over 100 gigahertz (for example [2][permanent dead link]).
Applications
[edit]Pulses can be injected into a device that is under test and used as a stimulus, clock signal, or analyzed as they progress through the device, confirming the proper operation of the device or pinpointing a fault in the device. Pulse generators are also used to drive devices such as switches, lasers and optical components, modulators, intensifiers, and resistive loads. The output of a pulse generator may also be used as the modulation signal for a signal generator. Non-electronic applications include those in material science, medical, physics, and chemistry.
Examples
[edit]- Ballistics testing uses high voltage pulse generator [3] [dead link]
- Kieda, D. B.; Allen, D.; Hall, J.; Nagai, T.; Snure, M.; Vassilev, V. V.; Walker, G. "Signal Cable Selection for the VERITAS Observatory". International Cosmic Ray Conference. 5. Bibcode:2003ICRC....5.2835A. Retrieved 2023-07-09.
- Single channel pulse generators were in existence in the 1950s [4] [dead link]
- Korn, T.; Müller, F.; Grundler, D.; Schüller, C. (2004). "Characterization of Permalloy films on high-bandwidth striplines". Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials. 272–276. Elsevier BV: E1341–E1342. Bibcode:2004JMMM..272E1341K. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2003.12.200. ISSN 0304-8853.
- Moesta, K. Thomas; et al. (2001). "Protoporphyrin IX Occurs Naturally in Colorectal Cancers and Their Metastases". Cancer Research. 61 (3): 991–999Z. PMID 11221895.
- Arodzero, A.; Brau, J.E.; Frey, R.E.; et al. (1996). "Beam test of prototype 18 cm silicon-strip detectors with high speed electronics". IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science. 43 (3). Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): 1180–1187. Bibcode:1996ITNS...43.1180A. doi:10.1109/23.506660. ISSN 0018-9499.
- Parsonnet, Eric; Huang, Yen-Lin; Gosavi, Tanay; et al. (2020-08-06). "Toward Intrinsic Ferroelectric Switching in Multiferroic BiFeO3". Physical Review Letters. 125 (6). American Physical Society (APS): 067601. Bibcode:2020PhRvL.125f7601P. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.125.067601. ISSN 0031-9007. PMID 32845668.[5]
References
[edit]- ^ Joel M. Libove; Brendan R. Illingworth; Steven J. Chacko; Hal L. Levitt (August 2008). "Monolithic Sampler/Pulser Architecture Exceeds 100 GHz". Microwave Journal. 51 (8): 86. Archived from the original on Oct 2, 2011.
- ^ "Patent Public Search | USPTO". ppubs.uspto.gov.
