Life imprisonment
| Criminal procedure |
|---|
| Criminal trials and convictions |
| Rights of the accused |
| Verdict |
| Sentencing |
|
| Post-sentencing |
| Related areas of law |
| Portals |
|
Life imprisonment is any sentence of imprisonment for a crime under which the convicted criminal is to remain in prison for the rest of their natural life (or until pardoned, paroled, or commuted to a fixed term). Crimes that result in life imprisonment are considered extremely serious and usually violent. Examples of these crimes are murder, torture, terrorism, child abuse resulting in death, rape, espionage, treason, illegal drug trade, human trafficking, severe fraud and financial crimes, aggravated property damage, arson, hate crime, kidnapping, burglary, robbery, theft, piracy, aircraft hijacking, and genocide.
Common law murder is one of the only crimes in which life imprisonment is mandatory; mandatory life sentences for murder are given in several countries, including some states of the United States and Canada.[1] Life imprisonment (as a maximum term) can also be imposed, in certain countries, for traffic offences causing death.[2] Life imprisonment is not used in all countries; Portugal was the first country to abolish life imprisonment, in 1884,[3] and all other Portuguese-speaking countries also have maximum imprisonment lengths, as well as all Spanish-speaking countries in the Americas except for Cuba, Peru, Argentina, Chile and the Mexican state of Chihuahua. Other countries that do not practice life sentences include Mongolia in Asia and Norway, Iceland, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Andorra and Montenegro in Europe. Where life imprisonment is a possible sentence, there may also exist formal mechanisms for requesting parole after a certain period of prison time. This means that a convict could be entitled to spend the rest of the sentence (until that individual dies) outside prison. Early release is usually conditional on past and future conduct, possibly with certain restrictions or obligations. In contrast, when a fixed term of imprisonment has ended, the convict is free. The length of time served and the conditions surrounding parole vary. Being eligible for parole does not necessarily ensure that parole will be granted. In some countries, including Sweden, parole does not exist but a life sentence may – after a successful application – be commuted to a fixed-term sentence, after which the offender is released as if the sentence served was that originally imposed.
In many countries around the world, particularly in the Commonwealth, courts have been given the authority to pass prison terms that may amount to de facto life imprisonment, meaning that the sentence would last longer than the human life expectancy.[4] For example, courts in South Africa have handed out at least two sentences that have exceeded a century, while in Tasmania, Australia, Martin Bryant, the perpetrator of the Port Arthur massacre in 1996, received 35 life sentences plus 1,035 years without parole. In the United States, James Holmes, the perpetrator of the 2012 Aurora theater shooting, received 12 consecutive life sentences plus 3,318 years without the possibility of parole.[5] In the case of mass murder in the US, Parkland mass murderer Nikolas Cruz was sentenced to 34 consecutive terms of life imprisonment (without parole) for murdering 17 people and injuring another 17 at a school.[6] Any sentence without parole effectively means a sentence cannot be suspended; a life sentence without parole, therefore, means that in the absence of unlikely circumstances such as pardon, amnesty or humanitarian grounds (e.g. imminent death), the prisoner will spend the rest of their natural life in prison. In several countries where de facto life terms are used, a release on humanitarian grounds (also known as compassionate release) is commonplace, such as in the case of Abdelbaset al-Megrahi. Since the behaviour of a prisoner serving a life sentence without parole is not relevant to the execution of such sentence, many people among lawyers, penitentiary specialists, criminologists, but most of all among human rights organizations oppose that punishment. In particular, they emphasize that when faced with a prisoner with no hope of being released ever, the prison has no means to discipline such convict effectively.
A few countries allow for a minor to be given a life sentence without parole; these include but are not limited to: Antigua and Barbuda, Argentina (only over the age of 16),[7] Australia, Belize, Brunei, Cuba, Dominica, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, the Solomon Islands, Sri Lanka, and the United States. According to a University of San Francisco School of Law study, only the U.S. had minors serving such sentences in 2008.[8] In 2009, Human Rights Watch estimated that there were 2,589 youth offenders serving life sentences without the possibility for parole in the U.S.[9][10] Since the start of 2020, that number has fallen to 1,465.[11][12] The United States has the highest population of prisoners serving life sentences for both adults and minors, at a rate of 50 people per 100,000 (1 out of 2,000) residents imprisoned for life.[13]
World view
[edit]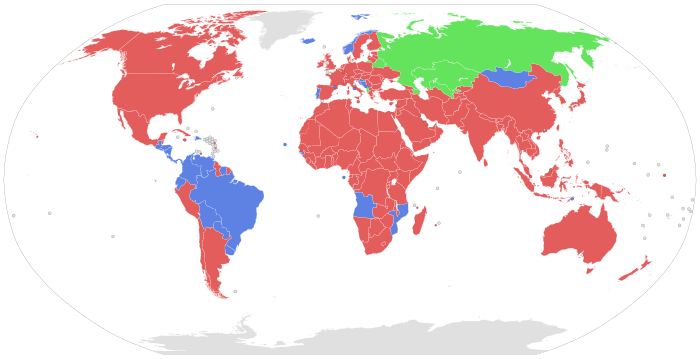
By country
[edit]In several countries, life imprisonment has been effectively abolished. Many of the countries whose governments have abolished both life imprisonment and indefinite imprisonment have been culturally influenced or colonized by Spain or Portugal and have written such prohibitions into their current constitutional laws (including Portugal itself but not Spain).[15][16]
Europe
[edit]A number of European countries have abolished all forms of indefinite imprisonment. Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina each set the maximum prison sentence at 45 years, and Portugal abolished all forms of life imprisonment with the prison reforms of Sampaio e Melo in 1884 and has a maximum sentence of 25 years.[17][18]
Life imprisonment in Spain was abolished in 1928, but reinstated in 2015 and upheld by the Constitutional Court in 2021.[15][16][19] Serbia previously had a maximum prison sentence of 40 years; life imprisonment was instated in 2019 by amendments to the country's criminal code, alongside a three-strikes law.[20]
In Europe, there are many jurisdictions where the law expressly provides for life sentences without the possibility of parole. These are England and Wales (within the United Kingdom; see Life imprisonment in England and Wales), the Netherlands, Moldova, Bulgaria,[21] Italy (only for persons who refuse to cooperate with authorities and are sentenced for mafia activities or terrorism), Ukraine, Poland, Turkey, Russia, and Serbia.[22]
In Sweden, although the law does not expressly provide for life without the possibility of release, some convicted persons may never be released, on the grounds that they are too dangerous. In Italy, persons who refuse to cooperate with authorities and are sentenced for mafia activities or terrorism are ineligible for parole and thus will spend the rest of their lives in prison. In Austria, life imprisonment will mean imprisonment for the remainder of the offender's life unless clemency is granted by the President of Austria or it can be assumed that the convicted person will not commit any further crimes; the probationary period is ten years.[23] In Malta, prior to 2018, there was previously never any possibility of parole for any person sentenced to life imprisonment, and any form of release from a life sentence was only possible by clemency granted by the President of Malta. In France, while the law does not expressly provide for life imprisonment without any possibility of parole, a court can rule in exceptionally serious circumstances that convicts are ineligible for automatic parole consideration after 30 years if convicted of child murder involving rape or torture, premeditated murder of a state official or terrorism resulting in death. In Moldova, there is never a possibility of parole for anyone sentenced to life imprisonment, as life imprisonment is defined as the "deprivation of liberty of the convict for the entire rest of his/her life". Where mercy is granted in relation to a person serving life imprisonment, imprisonment thereof must not be less than 30 years. In Ukraine, life imprisonment means for the rest of one's life with the only possibilities for release being a terminal illness or a presidential pardon.[24] In Albania, while no person sentenced to life imprisonment is eligible for standard parole, a conditional release is still possible if the prisoner is found not likely to re-offend and has displayed good behaviour, and has served at least 25 years.
Before 2016 in the Netherlands, there was never a possibility of parole for any person sentenced to life imprisonment, and any form of release for life convicted in the country was only possible when granted royal decree by the King of the Netherlands, with the last granting of a pardon taking place in 1986 when a terminally ill convict was released. As of 1970, the Dutch monarch has pardoned a total of three convicts. Although there is no possibility of parole eligibility, since 2016 prisoners sentenced to life imprisonment in the Netherlands are eligible to have their cases reviewed after serving at least 25 years. This change in law was because the European Court of Human Rights stated in 2013 that lifelong imprisonment without the chance of being released is inhuman.[25]
Even in other European countries that do provide for life without parole, courts continue to retain judicial discretion to decide whether a sentence of life should include parole or not. In Albania, the decision of whether or not a life-convicted person is eligible for parole is up to the prison complex after 25 years have been served, and release eligibility depends on the prospect of rehabilitation and how likely they are to re-offend. In Europe, only Ukraine and Moldova explicitly exclude parole or any form of sentence commutation for life sentences in all cases.
South America
[edit]In South and Central America, Honduras, Nicaragua, El Salvador, Costa Rica, Venezuela, Colombia, Uruguay, Bolivia, Ecuador, and the Dominican Republic have all abolished life imprisonment. The maximum sentence is 75 years in El Salvador, 60 years in Colombia, 50 years in Costa Rica and Panama, 40 years in Honduras and Brazil,[26] 30 years in Nicaragua, Bolivia, Uruguay, Venezuela and the Dominican Republic, and 25 years in Paraguay and Ecuador.
Canada
[edit]Life imprisonment in Canada is a criminal sentence for certain offences that lasts for the offender’s life. Parole is possible, but even if paroled, the offender remains under the supervision of Corrections Canada for their lifetime, and can be returned to prison for parole violations.
A person serving a life sentence must serve for a certain length of time before becoming eligible for parole. First degree murder and high treason carry the longest period of parole ineligibility in the Criminal Code, at 25 years. A statutory amendment to allow periods of parole ineligibility greater than 25 years was held to be unconstitutional by the Supreme Court of Canada in R v Bissonnette (2022 SCC 23), as contrary to section 12 of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, which prohibits cruel and unusual punishment. Parole eligibility for second degree murder typically varies between 10 and 25 years, and is set by the sentencing judge.
A life sentence is the most severe punishment for any crime in Canada. Criminal laws are enacted by the Parliament of Canada and apply uniformly across the country.[27]United States
[edit]In 2011, the Supreme Court of the United States ruled that sentencing minors to life without parole, automatically (as the result of a statute) or as the result of a judicial decision, for crimes other than intentional homicide, violated the Eighth Amendment's ban on "Cruel and unusual punishments", in the case of Graham v. Florida.[28]

Graham v. Florida was a significant case in juvenile justice. In Jacksonville, Florida, Terrence J. Graham tried to rob a restaurant along with three adolescent accomplices. During the robbery, one of Graham's accomplices had a metal bar that he used to hit the restaurant manager twice in the head. Once arrested, Graham was charged with attempted armed robbery and armed burglary with assault/battery. The maximum sentence he faced for these charges was life without the possibility of parole, and the prosecutor wanted to charge him as an adult. During the trial, Graham pleaded guilty to the charges, resulting in three years of probation, one year of which had to be served in jail. Since he had been awaiting trial in jail, he already served six months and, therefore, was released after six additional months.[29]
Within six months of his release, Graham was involved in another robbery. Since he violated the conditions of his probation, his probation officer reported to the trial court about his probation violations a few weeks before Graham turned 18 years old. It was a different judge presiding over his trial for the probation violations a year later. While Graham denied any involvement in the robbery, he did admit to fleeing from the police. The trial court found that Graham violated his probation by "committing a home invasion robbery, possessing a firearm, and associating with persons engaged in criminal activity",[29] and sentenced him to 15 years for the attempted armed robbery plus life imprisonment for the armed burglary. The life sentence Graham received meant he had a life sentence without the possibility of parole, "because Florida abolished their parole system in 2003".[29]
Graham's case was presented to the Supreme Court of the United States, with the question of whether juveniles should receive life without the possibility of parole in non-homicide cases. The Justices eventually ruled that such a sentence violated the juvenile's 8th Amendment rights, protecting them from punishments that are disproportionate to the crime committed,[29] resulting in the abolition of life sentences without the possibility of parole in non-homicide cases for juveniles.
In 2012, the Supreme Court ruled in the case of Miller v. Alabama in a 5–4 decision and with the majority opinion written by Associate Justice Elena Kagan that mandatory sentences of life in prison without parole for juvenile offenders are unconstitutional. The majority opinion stated that barring a judge from considering mitigating factors and other information, such as age, maturity, and family and home environment violated the Eighth Amendment ban on cruel and unusual punishment. Sentences of life in prison without parole can still be given to juveniles for aggravated first-degree murder, as long as the judge considers the circumstances of the case.[30][31]
In 2016 the Supreme Court ruled in the case of Montgomery v. Louisiana that the rulings imposed by Miller v. Alabama were to apply retroactively, causing a substantial amount of appeals to decade-old sentences for then-juvenile offenders.
In 2021, the Supreme Court ruled in Jones v. Mississippi that sentencers are not required to make a separate finding of the defendant to be "permanently incorrigible" prior to sentencing a juvenile to life without parole.
Vatican City
[edit]Pope Francis called for the abolition of both capital punishment and life imprisonment in a meeting with representatives of the International Association of Penal Law. He also stated that life imprisonment, removed from the Vatican City penal code in 2013, is just a variation of the death penalty.[32]
Malaysia
[edit]Originally in Malaysia, life imprisonment was construed as a jail term lasting the remainder of a convict's natural life, either with or without the possibility of parole. In April 2023, the Malaysian government officially abolished natural life imprisonment and instead redefined a life sentence as a jail term between 30 and 40 years. At the time of the reform, at least 117 prisoners were serving natural life imprisonment, consisting of 70 whose original death sentences were commuted to life (without parole) prior to the reform, and another 47 whose sentences of life were imposed by the courts, and all of these life convicts were allowed to have their jail terms reduced to between 30 and 40 years in jail.[33] In November 2023, four drug traffickers - Zulkipli Arshad, Wan Yuriilhami Wan Yaacob, Ghazalee Kasim and Mohamad Junaidi Hussin - became the first group of people to have their natural life sentences reduced to 30 years’ imprisonment after a re-sentencing hearing by the Federal Court of Malaysia, which was followed by many more such commutations in the months to come.[34][35]
Singapore
[edit]In Singapore, before 20 August 1997, the law decreed that life imprisonment is a fixed sentence of 20 years with the possibility of one-third reduction of the sentence (13 years and 4 months) for good behaviour. It was an appeal by Abdul Nasir bin Amer Hamsah on 20 August 1997 that led to the law in Singapore to change the definition of life imprisonment into a sentence that lasts the remainder of the prisoner's natural life, with the possibility of parole after at least 20 years. Abdul Nasir was a convicted robber and kidnapper who was, in two separate High Court trials, sentenced to 18 years' imprisonment and 18 strokes of the cane for robbery with hurt resulting in a female Japanese tourist's death at Oriental Hotel in 1994 and a consecutive sentence of life imprisonment with 12 strokes of the cane for kidnapping two police officers for ransom in 1996, which totalled up to 38 years' imprisonment and 30 strokes of the cane.[36]
Abdul Nasir's appeal for the two sentences to run concurrently led to the Court of Appeal of Singapore, which dismissed Abdul Nasir's appeal, to decide that it would be wrong to consider life imprisonment as a fixed jail term of 20 years and thus changed it to a jail term to be served for the rest of the prisoner's remaining lifespan.[36] The amended definition is applied to future crimes committed after 20 August 1997. Since Abdul Nasir committed the crime of kidnapping and was sentenced before 20 August 1997, his life sentence remained as a prison term of 20 years and thus he still had to serve 38 years behind bars.[37][38][39][40]
The appeal of Abdul Nasir, titled Abdul Nasir bin Amer Hamsah v Public Prosecutor [1997] SGCA 38,[36] was since regarded as a landmark in Singapore's legal history as it changed the definition of life imprisonment from "life" to "natural life" under the law.
Overview by jurisdiction
[edit]| Jurisdiction (link to details) | Life imprisonment | Minimum to serve before eligibility for requesting parole | Maximum length of sentence (under life) | Indefinite sentence (excl. preventive or psychiatric detainment) | Mandatory sentence | Other crimes with possible life sentence | Under age of 18 (or 21) | Pardon, amnesty, other release | Death penalty |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | Federal: For terrorism and treason offences: 22.5 years.[41] State laws vary. | None | Yes[42][43][44] See also: Immigration detention in Australia | Yes; for murder in Queensland, Western Australia, South Australia, Northern Territory; for murder of police officer in New South Wales[45] | Federal: [46] State laws vary.[47] | Federal, NSW, QLD, WA, SA, Tas, NT: Yes; | Federal: By governor general;
NSW, Vic, QLD, WA, SA, Tas, ACT, NT: by statute[51] |
No | |
| Yes | 15 years (Imprisonment for a definite period) or never (Imprisonment for lifetime, when clemency is rejected by president) |
None | Yes but only if clemency is rejected by president | Genocide | Murder, high level drug dealing, Nazi activism, production or distribution of chemical warfare agents to be used in armed conflict; abduction, robbery, rape and statutory rape if the crime causes the victim's death, sea and air piracy and arson if the crime causes the death of a large number of people |
|
By president | No (abolished in 1968) | |
| Yes, but only for men aged 18–65 | 25 years | 15 years for a single murder (up to 20 years for several crimes) | No | None | Crimes against the state, war crimes | 14–17: max. 10 years' imprisonment[54] | By president | No | |
| Yes | 15 years (no previous conviction or below 3 years), 19 years (previous conviction below 5 years), or 23 years (previous conviction 5 years or more)[55] | None | No | None | Murder |
|
Parole by Conditional Release Commission or pardon by monarch | No | |
| No[57] | Varies, depending on sentence | 40 years[58] | No | No life imprisonment sentence | No life imprisonment sentence | No | No life imprisonment sentence | Yes, but only in times of war | |
| Yes | 20 years or never | None | Yes | None | Aggravated murder, aggravated kidnapping, aggravated robbery, treason, espionage, war crimes, genocide, desertion in wartime |
|
By president | No | |
| Yes | 25 years for first-degree murder or high treason; 10 years minimum for second-degree murder. 7–25 years for any other offence where the maximum penalty is life imprisonment. | None | Yes | High treason, first-degree murder, second-degree murder | Various crimes including attempted murder, aircraft hijacking, armed robbery, kidnapping, aggravated sexual assault, conspiracy to murder and most offenses resulting in death |
|
Yes, but only through royal prerogative of mercy[61][62] | No (abolished in 1976) | |
| Yes | 13 years of the original sentence having been actually served.[63] Never in extremely serious corruption cases.[64] | 13 for a single murder if it is the perpetrator's first offence. 15–20 for a single murder that is the perpetrator's second offence if he/she serves the sentence with good behaviour | No | No | Various | Yes | By courts and by president[65] | Yes | |
| No[66] | Varies, depending on sentence | 40 years[66] | No | No life imprisonment sentence | No life imprisonment sentence |
|
No life imprisonment sentence | No (abolished in 1991) | |
| Yes |
|
30 years | No | None | Some cases of murder, public endangerment, treason, terrorism, genocide, crimes against humanity, use of forbidden combat device or forbidden combat tactics, war crimes, persecution of population, misuse of international symbols | 15–18: max. 10 years' imprisonment | By president | No | |
| Yes | 12 years[69] | none[69] | Yes | No | Treason, espionage during wartime, use of force against the parliament, terrorism, arson under circumstances that are life-threatening, hijacking of vehicles, willful release of nuclear substances, murder |
|
After 12 years entitled to request to minister of justice; granted by monarch | No | |
| Yes | 30 years | None | Yes (de facto) | None | Some cases of murder, some cases of handling drugs, crimes against humanity, genocide, acts of war against civilians, terrorism, violence against the independence of Estonia, causing an explosion using nuclear energy[70] | Maximum length 10 years. Under 14 cannot be criminally prosecuted. | Pardon by president[citation needed] | No | |
| Yes | 12 years for court release; any time for presidential pardon[72] | None | Yes | Murder | High treason, espionage, genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes, homicidal terrorist act, crime against peace |
|
By president, Helsinki Court of Appeal | No | |
| Yes (for adults between 18 and 21 only if tried as adults) |
|
None[75] | No | Aggravated murder,[76] genocide resulting in death,[77] crimes against humanity resulting in death,[78] war crimes against persons resulting in death[79] |
|
By federal president or minister-president | No (abolished in West Germany by the Constitution since 23 May 1949; abolished by law in West Germany in 1953 and in East Germany in 1987) | ||
| No | Varies, depending on sentence | ?? | No | No life imprisonment sentence | No life imprisonment sentence | No life imprisonment sentence | No life imprisonment sentence | No | |
| Yes | 12 years[81] | None | No | Murder, treason | Manslaughter, rape, aggravated sexual assault, committing a sexual act on a child less than 15 years of age, assault causing serious harm, syringe attacks, aggravated kidnapping, aggravated robbery, aggravated burglary, certain drugs offences, and other common law offences where the maximum penalty is life imprisonment[82] |
|
By president[84] | No | |
| Yes | 10 years | None | No | Aggravated murder, terrorism, treason | Rape | Yes | By president | Yes[85][86] | |
| Yes | 25 years | None | Yes | None | Genocide, prohibited mistreatment of persons under international law, war crimes, crimes against humanity, prohibited military attack, attempted assassination of the president of Lithuania, attempted assassination of a governmental official or foreign official, murder with aggravated circumstances, murder of persons protected under international humanitarian law, terrorism resulting in death, piracy (hijacking of a civilian aircraft or civilian vessel) that results in death or otherwise has grave consequences to the safety of others |
|
By president | No (abolished in 1998[87]) | |
| No | Varies, depending on sentence | 25 years (30 in exceptional circumstances)[88] | No | No life imprisonment sentence | No life imprisonment sentence | No life imprisonment sentence | No life imprisonment sentence | No | |
| No (except in Chihuahua for murder involving kidnapping) | Varies, depending on sentence | 24 years (74 years if convicted of murder involving kidnapping); in the state of Chihuahua, murder involving kidnapping provides for a mandatory life sentence | No[89] | Murder involving kidnapping | None | ?? | ?? | No | |
| Yes[90] | Never | None | Yes | None | Murder, aggravated manslaughter, various crimes against the Dutch state, attacks on the monarch, crimes with a terrorist motive, and leading a terrorist organization in especially serious circumstances |
|
After 25 years served, the Advisory College for the Lifelong Incarcerated reviews whether a return into society is advisable, but only a pardon by royal decree from the monarch can rescind a life sentence. | No | |
| Yes | Never[91] | None | Yes | ?? | ?? |
|
?? | Yes | |
| Life imprisonment only under military criminal code | No life imprisonment | Maximum sentence 21 years (30 years if convicted of aggravated terrorism)[92] with possibility to renew the sentence in exceptional cases. | No | ?? | ?? |
|
?? | No (Fully abolished in 1979, constitutional ban since 2014) | |
| Yes | Any minimum term from 30 to 50 years or never; individually set by the judge | 30 years | No | None | Treason, assassination of Polish president, war of aggression, genocide, crimes against humanity, unlawful use of weapon of mass destruction, war crimes, murder, homicide and serious bodily harm resulting in death |
|
Pardon by president | No (abolished during peacetime in 1998 and under all circumstances in 2014) | |
| Yes | 20 years | None | No; replaced by 25 years' imprisonment at age 60[93] | Genocide during wartime, inhumane treatment during wartime | Treason and other grave crimes against the state, extremely grave murder, capitulation, desertion on the battlefield, crimes against peace or humanity[94] | under 18: max. 20 years' imprisonment[95] | Pardon by president, amnesty by act of parliament | No | |
| Yes | 20 years | None | Yes, for offenders of unsound mind; see also: The President's Pleasure (Singapore) | Yes; for certain offences, including possession of firearms at time of arrest for any offence, hijacking of aircraft and piracy | Murder (if no intent to cause death), drug trafficking (if acted as couriers or mentally ill), culpable homicide not amounting to murder (manslaughter), kidnapping by ransom, criminal breach of trust by a public servant, voluntarily causing grievous hurt with dangerous weapons, and trafficking of firearms and more than 30 other offences |
|
Clemency by the President of Singapore | Yes | |
| Yes; only if necessary to protect society and given the convict is unlikely to be rehabilitated | 25 years | None | Yes | Aggravated murder,[97][98] genocide,[99] terrorism,[100] war crimes,[101][102] recidivism of certain aggravated offenses[103] | Under certain, aggravated conditions (usually causing death): crimes against humanity, drug trafficking, human trafficking, child trafficking, false imprisonment, hostage taking, kidnapping, robbery, extortion, domestic violence, kidnapping, public endangerment, air/sea piracy, treason, sabotage, espionage, assaulting a public official |
|
By president | No | |
| Yes | 25 years | None | Yes | Murder | Terrorism, drug offenses, crimes against humanity |
|
By president | No | |
| Yes[106] | 18 to 22 years for furlough, 25 to 35 years for parole, depending on the number of crimes and the crimes themselves | 30 years | No |
|
|
No | By Cabinet | No | |
| Yes |
|
None | Yes | None | Murder, kidnapping, arson, sabotage, dangerous destruction of property, hijacking, espionage, terror crimes, rebellion, endangering the public health by spread of contagion or poison, disloyalty when negotiating with foreign powers, trading in anti-personnel mines, cluster bombs or chemical or nuclear weapons, unlawful nuclear explosion, treason, genocide; in wartime only: mutiny, insubordination, undermining the will to fight, desertion, unauthorised capitulation, negligence of war preparations and negligence of battle duty; attempts, accessories, accomplices and incitements of all the above crimes might also be punished with life imprisonment.[107] |
|
By the district court of Örebro (parole hearing) or by the government (pardon)[108] | No | |
| Yes | 10 years or 15 years; individually set by judge | None | No | None | Aggravated murder,[109] aggravated hostage-taking,[110] genocide,[111] endangering the independence of the country[112] |
|
By Federal Assembly (Parliament)[114] | No | |
| Yes | 25 years | None | No |
|
By president | Yes | |||
| Yes | 15 years or longer (maximum of whole life order), but individually set by judge. A whole life order means life without parole (e.g. natural life in prison until death). However, there is, at least in theory, a possibility of release of prisoners serving such sentences, as the Secretary of State for Justice has the power to release on licence any life sentence prisoner on compassionate grounds in exceptional circumstances.[115] | None | Imprisonment for public protection – abolished in 2012 but offenders already serving that sentence remain in prison. Persons under 18 years of age may be sentenced to detention at His Majesty's pleasure for an indeterminite period. | Murder and treason | Rape, armed robbery, kidnapping, false imprisonment, manslaughter, attempted murder, soliciting murder, threats to kill, wounding with intent to cause grievous bodily harm, malicious wounding, using chloroform etc., maliciously administering poison, abandoning children, other serious crimes and other common law offences where the maximum penalty is life imprisonment.[116] | No, but offenders under 18 can be sentenced to detention for an indeterminate period. Whole life orders cannot be given to offenders under 21. | Amnesty by royal decree (by means of the royal prerogative of mercy) alone or with act of Parliament | No | |
| Yes | Individually set by judge | Between 17 and 30 years for a single murder without any additional circumstances | Yes | Murder with additional circumstances, two or more murders, attempted murder, two or more counts rape | Any other common law offence[117][118] |
|
Compassionate release by cabinet secretary for justice (Scottish government); amnesty by royal decree (by means of the royal prerogative of mercy) alone or with act of Parliament | No | |
Northern Ireland |
Yes | Individually set by judge | None | No[120][121] | Murder, rape | Robbery | ?? | General release through a referendum-based agreement in 1998 (became applicable in three cases: i, ii, iii). The royal prerogative of mercy or an act of the UK Parliament (in accordance with the principle of parliamentary sovereignty) can be used to grant amnesty like the rest of the UK. | No |
| Yes (except in Alaska) | Varies by state | Varies by state; 99 years in Alaska | Yes | Varies by state | Varies by state | Yes (de jure) | By president or governor of a state (depending on jurisdiction) | Yes (depending on state) | |
| No | Varies, depending on sentence | 45 years[122] | No | No life imprisonment sentence | No life imprisonment sentence | No life imprisonment sentence | No life imprisonment sentence | No |
See also
[edit]- 10-20-Life
- Incapacitation
- Indefinite imprisonment
- List of prison deaths
- Capital punishment by country
- List of people sentenced to more than one life imprisonment
Notes
[edit]- ^ Government of Canada, Department of Justice (23 July 2015). "How sentences are imposed - Canadian Victims Bill of Rights". www.justice.gc.ca. Retrieved 26 August 2023.
- ^ "Penalties for Drunk Driving Vehicular Homicide" (PDF) (PDF). Mothers Against Drunk Driving. May 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 September 2013.
- ^ "Crime > Punishment > Minimum life sentence to serve before eligibility for requesting parole: Countries Compared". nationmaster.com. Retrieved 3 July 2023.
- ^ McLaughlin, Eliott C.; Brown, Pamela (August 2013). "Cleveland kidnapper Ariel Castro sentenced to life, plus 1,000 years". CNN. Archived from the original on 10 June 2017. Retrieved 12 May 2017.
- ^ "Snapshot: Australia's longest sentences". SBS News. Retrieved 3 June 2021.
- ^ "Florida school mass shooter sentenced to life in prison". Today. Singapore. 3 November 2022. Retrieved 3 November 2022.
- ^ Mecon. "InfoLEG – Ministerio de Economía y Finanzas Públicas – Argentina". mecon.gov.ar. Archived from the original on 9 January 2016.
- ^ "Laws of Other Nations". usfca.edu. Archived from the original on 27 June 2015.
- ^ "The Rest of Their Lives: Life without Parole for Child Offenders in the United States Archived 27 June 2015 at the Wayback Machine", 2008.
- ^ "State Distribution of Youth Offenders Serving Juvenile Life Without Parole (JLWOP)". Human Rights Watch. 2 October 2009. Archived from the original on 8 June 2011. Retrieved 3 August 2011.
- ^ "Juvenile Life Without Parole: An Overview".
- ^ "US States Fail to Protect Children's Rights". Human Rights Watch. 13 September 2022. Retrieved 11 October 2022.
- ^ "The Sentencing Project News – New Publication: Life Goes On: The Historic Rise in Life Sentences in America". sentencingproject.org. Archived from the original on 18 October 2013.
- ^ "Life imprisonment". life-imprisonment.html.
- ^ a b "El Congreso aprueba la prisión permanente revisable con el único apoyo del Partido Popular" [Congress approves permanent revisable prison with support only from the People's Party] (in Spanish). RTVE. 26 March 2015. Retrieved 29 December 2020.
- ^ a b "El Constitucional avala la prisión permanente revisable" [Constitutional court upholds permanent reviewable prison] (in Spanish). EFE. 6 October 2021. Retrieved 9 October 2021.
- ^ Ramalho, Énio (2016). "II". THE PORTUGUESE PENAL CODE, GENERAL PART (ARTICLES 1–130) (PDF). verbojuridico. p. 12.
- ^ Bruno, Cátia. "25 anos de prisão. A história da pena máxima em Portugal". Observador (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 13 January 2021.
- ^ "Una figura instaurada en 1822 y eliminada en 1928" [A statute installed in 1822 and abolished in 1928]. El País (in Spanish). 21 January 2020. Retrieved 29 December 2020.
- ^ "Krivični zakonik". www.paragraf.rs (in Serbian). Retrieved 3 September 2022.
- ^ "Bulgaria – Criminal codes – Legislationline". www.legislationline.org. Archived from the original on 7 October 2017.
- ^ "Krivični zakonik". www.paragraf.rs (in Serbian). Retrieved 3 September 2022.
- ^ "RIS - Strafgesetzbuch § 46 - Bundesrecht konsolidiert, tagesaktuelle Fassung".
- ^ "Ukraine found in violation of the prohibition of torture over treatment of life prisoners". Kharkiv Human Rights Protection Group.
- ^ "Levenslang". rechtspraak.nl (in Dutch).
- ^ "Presidência da República - Secretaria-Geral - Subchefia para Assuntos Jurídicos - CÓDIGO PENAL - "Art. 75. O tempo de cumprimento das penas privativas de liberdade não pode ser superior a 40 (quarenta) anos".
- ^ Government of Canada, Department of Justice (23 July 2015). "How sentences are imposed - Canadian Victims Bill of Rights". www.justice.gc.ca.
- ^ Savage, David G. (17 May 2010). "Supreme Court Restricts Life Sentences Without Parole for Juveniles". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on 15 December 2013. Retrieved 17 April 2014.
- ^ a b c d Drinan, C. H. (2012, March). "Graham on the Ground". Washington Law Review, 87(1), 51–91. Criminal Justice Abstracts. Retrieved 28 October 2012.
- ^ "Court bars mandatory life without parole for youths, rejects cross case". Catholic News Service. 25 June 2012. Archived from the original on 30 June 2013. Retrieved 17 April 2014.
- ^ Liptak, Adam; Bronner, Ethan (25 June 2012). "Court Bars Mandatory Life Terms for Juveniles in Murders". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 27 May 2017. Retrieved 12 May 2017.
- ^ Rocca, Francis X. (23 October 2014). "Pope Francis calls for abolishing death penalty and life imprisonment". Catholic News Service. Archived from the original on 24 October 2014. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- ^ "Malaysia scraps mandatory death penalty, natural-life prison terms". The Straits Times. 3 April 2023.
- ^ "Malaysia commutes death penalty, life terms of 11 drug convicts". The Straits Times. 14 November 2023.
- ^ "In landmark review, apex court commutes death penalty and natural-life imprisonment of 11 convicted for drug trafficking". Malay Mail. 14 November 2023.
- ^ a b c "Abdul Nasir bin Amer Hamsah v Public Prosecutor". Webcite. Archived from the original on 26 April 2012. Retrieved 31 January 2021.
- ^ "Oriental Hotel murder | Infopedia". eresources.nlb.gov.sg.
- ^ "True Files S3". Toggle. Retrieved 21 April 2020.
- ^ "The Best I Could S1 – EP6". meWATCH. Retrieved 12 July 2020.
- ^ Abu Baker, Jalelah (16 January 2015). "Murderer fails to escape the gallows: 6 other cases involving the revised death penalty laws". The Straits Times. Archived from the original on 21 March 2018. Retrieved 11 January 2021.
- ^ Crimes Act (Cth) section 19AG 3(a)
- ^ "Indefinite detention of persons with disability within the criminal justice system". Disabled People's Organisations Australia. Archived from the original on 26 February 2019.
- ^ "A Comparative Review of National Legislation for the Indefinite Detention of 'Dangerous Criminals'", Tasmania Law Reform Institute
- ^ "Indefinite detention of people with cognitive and psychiatric impairment in Australia", Senate Community Affairs References Committee
- ^ Crimes Act 1900 (NSW) section 19B
- ^ Offences including piracy; murder of a UN or associated person; explosives and lethal device offences; treason; assisting anyone known to have committed treason escape apprehension or punishment; knowing someone intends to commit a treason offence and not reporting it to the police or taking reasonable measure to prevent its commission; assisting enemy to engage in armed conflict; treachery; espionage; aggravated espionage offences; terrorism; planning or preparing for a terrorist act; financing terrorism; financing a terrorist; murder of an Australian citizen or resident; entering a foreign country with the intention of engaging in a hostile activity; engaging in a hostile activity in a foreign country, or engaging in conduct preparatory to, including providing or participating in training, accumulating weapons or giving or receiving goods and services to commit a foreign incursion offence; allowing the use of a building, aircraft or vessel intending to commit, support or promote a foreign incursion offence; burglary of a property owned by a Commonwealth entity with the intent to commit an offence that causes harm to a person or damage to property; genocide offences; crimes against humanity (murder and extermination); war crimes; trafficking or manufacturing a commercial quantity of controlled drugs; cultivating or selling commercial quantities of controlled plants; importing or exporting commercial quantities of controlled drugs or plants; importing commercial quantities of a controlled drug or plant; possessing commercial quantities of a controlled drug or plant reasonably believed to have been imported; supplying marketable quantities of controlled drugs to children for trafficking; procuring children for trafficking marketable quantities of controlled drugs; procuring children for pre-trafficking marketable quantities of controlled precursors; procuring children for importing or exporting marketable quantities of a controlled drug or plant or for importing or exporting marketable quantities of border controlled precursors (Criminal Code Act (Cth))
- ^
- NSW: Murder; aggravated sexual assault in company; sexual intercourse with a child under 10; persistent sexual abuse of a child (Crimes Act (NSW)). Drug offences involving commercial quantities or cultivation for a commercial purpose; offences involving manufacture or production in presence of children or procuring children to supply prohibited drugs (Drug Misuse and Trafficking Act (NSW)).
- Vic: Murder; trafficking in a drug of dependence (large commercial quantity)
- QLD: Demands with menaces upon agencies of government; riot, if the offender causes grievous bodily harm to a person, causes an explosive substance to explode or destroys or starts to destroy a building, vehicle or machinery; piracy; perjury, in order to procure the conviction of another person for a crime punishable with life imprisonment; conspiracy to bring a false accusation where the offence is such that the person convicted would be liable to life imprisonment; owner etc permitting carnal knowledge of a child under 12 on premises; carnal knowledge of a child under 12, or a child under 16 by a guardian of that non-lineal descendant child; or a child under 16 with an impairment of the mind; carnal knowledge or attempted carnal knowledge of a non-lineal descendant with an impairment of the mind by a guardian; taking a child under 12 for immoral purpose and doing carnal knowledge; incest; maintaining a sexual relationship by an adult with a child under 16; attempted murder; accessory after the fact to murder; manslaughter; aiding suicide; killing unborn child; unlawful striking causing death; disabling or stupefying in order to commit an indictable offence; acts intended to cause grievous bodily harm and other malicious acts; obstructing rescue or escape from unsafe premises; endangering the safety of a person in a vehicle with intent; rape; aggravated sexual assault; aggravated robbery; aggravated attempted robbery; extortion where carrying out threat causes or would be likely to cause serious personal injury or substantial economic loss in a commercial activity; taking control of an aircraft using violence, threats of violence, in company or by fraudulent means; burglary by breaking and other circumstances of aggravation; breaking and committing an indictable offence; arson; endangering the safe use of vehicles and transport infrastructure; destroying or damaging premises by explosion; destroying sea walls and other property; communicating infectious diseases to animals; attempting to commit an indictable offence punishable by mandatory life imprisonment; being an accessory to the fact after an indictable offence punishable by mandatory life imprisonment (Criminal Code (QLD))
- WA: Attempt to unlawfully kill; criminal damage by fire (Criminal Code (WA)). Possessing, with intent to sell or supply, a trafficable quantity (>28g) of methylamphetamine; conspiring with another to, or attempting to, commit a methylamphetamine trafficking offence (Misuse of Drugs Act (WA))
- Tas: Murder; treason; accessory after the fact guilty of treason
- ACT: Murder; trafficking in a controlled drug; manufacturing a controlled drug for selling; cultivating a controlled plant for selling; selling a controlled plant; supplying controlled drug to child for selling; procuring a child to traffic a controlled drug
- NT: Manslaughter; assisting or encouraging a suicide; killing an unborn child; disabling or stupefying in order to commit an indictable offence; acts intended to cause serious harm or prevent lawful apprehension; preventing escape from wreck; intentionally endangering safety of persons travelling by railway, roadway, aircraft or ship; sexual intercourse without consent; causing a child under 12 to enter into or continue in sexual servitude; operating a business that involves the sexual servitude of a child under 12; aggravated robbery (armed, in company or causing harm to any person immediately before or after or during the robbery); discharging a firearm while armed in the course of assault with intent to steal; unlawfully taking control of an aircraft with violence or threats, in company or while armed; sabotage; arson; endangering operation of an aircraft; conspiracy to lay false charges where the person found guilty would have been liable to life imprisonment; terrorism; perjury in order to procure the conviction of an offence punishable by life imprisonment; forcibly rescuing certain offenders; aggravated sexual relationship with a child (Criminal Code Act (NT)). Supply of a commercial quantity of a dangerous drug (Schedule 1 or 2) to a child; supply of a dangerous drug (Schedule 1) to a child; cultivation of a commercial quantity of a prohibited plant in the presence of a child; manufacture of a commercial quantity of a Schedule 1 dangerous drug; manufacture of a commercial or trafficable quantity of a Schedule 1 drug in the presence of a child; procuring a child under 14 to commit an offence under the Misuse of Drugs Act (Misuse of Drugs Act (NT))
- ^ Crimes (Sentencing) Act 2005 (ACT) section 133G(4)
- ^ eManuals judicialcollege.vic.edu.au 'Young persons' may not be sentenced to indefinite sentences
- ^ Sentencing Act 1991 (Victoria) Section 18A(1)
- ^ "Royal Prerogative of Mercy and statutory referrals". Attorney-General's Department. Archived from the original on 16 January 2019.
- ^ "section 18 of the Austrian criminal code". Ris.bka.gv.at. Archived from the original on 22 March 2012. Retrieved 30 March 2012.
- ^ "The abolition of the death penalty and its alternative sanction in South Caucasus: Armenia, Azerbaijan and Georgia" (PDF). penalreform.org. p. 50. Archived (PDF) from the original on 5 February 2015.
- ^ "Уголовный кодекс Азербайджанской Республики". Retrieved 26 March 2019.
- ^ (in French and Dutch) extract from the Belgian Official Journal advocaat.be 17 March 2013.
- ^ (in Dutch) Jeugdsanctierecht in Europa: is uithandengeving een evidentie? Archived 3 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine Jura falconis, jg 44, 2007–2008, nr 1, pp. 3–38
- ^ Brazil's constitution prohibits the death penalty with a saving allowing the death penalty in wartime, if the state of war is duly declared by Congress (art. 5, item XLVII, subitem "a)"); the Constitution's next line (art. 5, item XLVII, subitem "b)"), prohibits life sentences. The clause prohibiting life imprisonment does not contain a saving similar to the death penalty clause, and thus life sentences are not allowed even in wartime. It is unclear, however, if the presidential power of mercy, that allows the president to pardon or commute a penal sentence, could be used to reduce a death penalty imposed in wartime, transforming it into a sentence of life imprisonment.
- ^ "Pacote anticrime entra em vigor com mudanças no cumprimento de penas". Jornal Nacional (in Portuguese). 23 January 2020.
- ^ "Criminal code of the Republic of Bulgaria". Legislationline.org. Archived from the original on 25 March 2012. Retrieved 30 March 2012.
- ^ Justice BC (11 September 2013). "Maximum Youth Sentences". Youth Criminal Justice Act. Archived from the original on 28 March 2014. Retrieved 17 April 2014.
- ^ Criminal Code, R.S. 1985, c. C-46, s. 748, as amended by R.S., 1985, c. 1 (4th Supp.), s. 45(F) and R.S.C., 1992, c. 22, s. 12; and R.S.C., 1995, c. 22, s. 6. (Criminal Code at CanLii)
- ^ Criminal Records Act, R.S. 1995, c. 22, s. 6(1), as amended by R.S., 1985, c. 1 (4th Supp.), s. 45(F) and R.S.C., 1992, c. 22, s. 4; and R.S.C., 2000, c. 1, s. 1(F) and R.S.C., 2010, c. 5, s. 2 and R.S.C, 2012, c. 1, s. 115. (Criminal Records Act at CanLii)
- ^ Criminal Law and Criminal Procedure Law in the People's Republic of China. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers. 2 May 2013. ISBN 9004234454. Archived from the original on 9 February 2018. Retrieved 2 January 2018.
- ^ "Is Life Without Parole a Signal of China's Will to Reduce Executions?". Dui Hua Foundation. Archived from the original on 10 February 2018. Retrieved 2 January 2018.
- ^ "Section 2 The President of the People's Republic of China". Constitution of the People's Republic of China. Archived from the original on 10 November 2017. Retrieved 9 February 2018.
- ^ a b Kovčo Vukadin, Irma; Žakman-Ban, Vladimira; Jandrić-Nišević, Anita (2010). "Prisoner Rehabilitation in Croatia" (PDF). Varstvoslovje, Journal of Criminal Justice and Security. 12 (2): 143–162. ISSN 1580-0253. Retrieved 1 December 2010.
- ^ "Czech Criminal Code". Business.center.cz. Archived from the original on 25 July 2011. Retrieved 30 March 2012.
- ^ The court may decide that only the time in less-than-maximum security prison counts for the purposes of parole and that the convict must serve at least ten years in maximum security. A record of good behavior is needed for transfer to lower security in which 20 years must be served then.
- ^ a b c "Straffeloven § 33, § 41" [Danish Penal Code § 33, § 41] (in Danish). Retsinformation (Civilstyrelsen, Ministry of Justice). 17 May 2019. Retrieved 17 May 2019.
- ^ "Estonian Penal Code (English translation)". Archived from the original on 4 September 2015. Retrieved 6 July 2013.
- ^ "Finnish criminal law" (in Finnish). Finlex. 10 December 2018. Retrieved 26 December 2018.
- ^ "Oikeuslaitos – Imprisonment and community service". Oikeus.fi. Archived from the original on 25 June 2009. Retrieved 3 August 2011.
- ^ sec. 57a(1) German Criminal Code Strafgesetzbuch
- ^ BVerfG, 22 May 1995, 2 BvR 671/95
- ^ sec. 38 German Criminal Code
- ^ sec. 211(1) German Criminal Code
- ^ sec. 6(1) German Criminal Code on crimes against international law and war crimes
- ^ sec. 7(1) German Criminal Code on crimes against international law and war crimes
- ^ sec. 8(1) German Criminal Code on crimes against international law and war crimes
- ^ A person between the ages of 18 and 21 can be tried before a juvenile court (which happens in almost all cases concerning minors) or an adult court, which is determined by the intellectual development of the accused and the severity of the crime itself.
- ^ "Types of sentences". Citizensinformation.ie.
- ^ Report. Determination of life sentences ihrec.ie
- ^ Gallagher, Conor. "Children charged with serious crimes face different criminal justice process to adults". The Irish Times.
- ^ O'Mahony, Conor (4 September 2018). "Just what can the President of Ireland actually do?". RTÉ.
- ^ "Article 549 Penal Code". english.al-akhbar.com. Archived from the original on 14 April 2014.
- ^ Ari Yashar (28 March 2014). "Lebanese Revolution? Death Sentence For Wife Beater". ArutzSheva. Archived from the original on 14 April 2014. Retrieved 17 April 2014.
- ^ "VIII-1250 Lietuvos Respublikos įstatymas dėl Europos žmogaus teisių ir pagrindinių laisvių apsaugos konvenc..." e-seimas.lrs.lt. Archived from the original on 11 June 2016. Retrieved 21 May 2016.
- ^ "Código Penal – Art. 1 a 100" (in Portuguese). Imprensa Oficial. 14 November 1995. Archived from the original on 21 February 2009. Retrieved 17 February 2009.
- ^ For details of new rulings from Mexican Supreme Court, see:
- "Wanted Fugitive Raul Gomez Garcia Extradited to the U.S." US Embassy in Mexico. Archived 15 May 2007 at the Wayback Machine.
- "Mexico alters extradition rules". BBC News. Archived 3 December 2005 at the Wayback Machine)
- ^ "Levenslang". www.rechtspraak.nl (in Dutch). Retrieved 2 August 2019.
- ^ "6 Nigerian Soldiers Bag Life Imprisonment". ConnectAfrica. 19 November 2008. Archived from the original on 18 July 2011. Retrieved 3 August 2011.
- ^ "The Penal Code - Chapter 18. Terrorist acts and terrorism-related acts - Lovdata". lovdata.no. Retrieved 4 July 2024.
- ^ "Criminal Code of Romania, art. 55" (in Romanian). Archived from the original on 31 January 2013. Retrieved 14 December 2012.
- ^ Mitrache, C. (2010). Drept penal român. Universul Juridic. p. 198.
- ^ "Criminal Code of Romania, art. 109" (in Romanian). Archived from the original on 31 January 2013. Retrieved 14 December 2012.
- ^ "How Long Is Life Imprisonment in Singapore? And Other FAQs". Singapore Legal Advice. 1 February 2021.
- ^ § 144(3) Slovak Criminal Code
- ^ Only in cases of repeat offenders, convicted of the same or as part of an organized group or during a state of emergency.
- ^ § 418(3) Slovak Criminal Code
- ^ § 419(2) Slovak Criminal Code
- ^ § 433(2) Slovak Criminal Code
- ^ Only if the crime results in the injuries or deaths of multiple persons or if the perpetrator is a mercenary.
- ^ § 47(2) Slovak Criminal Code
- ^ § 117 Slovak Criminal Code
- ^ § 89 Criminal Code of Slovenia (Kazenski zakonik, KZ), temporarily pursuant as per § 375 of (the new) Criminal Code of Slovenia (Kazenski zakonik; KZ-1)
- ^ Criminal Code. Official State Gazette
- ^ "Svensk författningssamling 1962:700". Riksdagsförvaltningen. Archived from the original on 23 June 2015.
- ^ "Svensk författningssamling 1974:152". Riksdagsförvaltningen. Archived from the original on 29 December 2015.
- ^ art. 112 Swiss Criminal Code
- ^ art. 185 Swiss Criminal Code
- ^ art. 264 Swiss Criminal Code
- ^ art. 266 Swiss Criminal Code
- ^ (in French)art. 25 Juvenile Criminal Code Archived 14 May 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ art. 173 al. 1 let. k Constitution of the Swiss Confederation
- ^ "Whole Life Orders: Attorney General's Reference (R. v McCann); Attorney General's Reference (R. v Sinaga)". 11 December 2020. Retrieved 7 May 2021.
- ^ "Indeterminate extended and life sentence". Prisoners' Families Helpline. 8 February 2011.
- ^ "Life Sentence Prisoners in Scotland: Chapter One: Historical Use of Life Sentences". Scottish Government. Archived from the original on 6 October 2017. Retrieved 10 July 2017.
- ^ This is subject to sentencing guidelines applicable to each offence and to limits on the sentences which can be applied in courts dealing with minor offences.
- ^ "Criminal Proceedings in Scotland 2014–15: Annex D: Definitions, Classifications and Notation". Archived from the original on 10 February 2018. Retrieved 10 July 2017.
- ^ Deborah McAleese; Emily Moulton (28 June 2008). "Fury over ruling that could see Attracta's killer freed". Belfast Telegraph. Retrieved 17 April 2014.
- ^ "Neutral Citation No.[2008] NICA 27". courtsni.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 22 August 2011.
- ^ "Pese a que la Justicia ha aplicado penas de 45 años, no se cumplen". El Observador. 28 November 2017.
External links
[edit]
