White-fronted manakin
| White-fronted manakin | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Pipridae |
| Genus: | Lepidothrix |
| Species: | L. serena
|
| Binomial name | |
| Lepidothrix serena (Linnaeus, 1766)
| |
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Pipra serena Linnaeus, 1766 | |
The white-fronted manakin (Lepidothrix serena) is a species of bird in the family Pipridae, the manakins. It is native to French Guiana, Guyana, Suriname and northeastern Brazil where it inhabits subtropical and tropical moist lowland forest. The male is mainly black, with a blue rump, yellow belly patches and a conspicuous patch of white feathers extending forwards from its forehead. The female is gray and black with a pale yellow belly and white eye ring. This is a fairly common species with a wide range, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated its conservation status as being of "least concern".
Taxonomy
[edit]
In 1760 the French zoologist Mathurin Jacques Brisson included a description of the white-fronted manakin in his Ornithologie based on a specimen collected from Cayenne in French Guiana. He used the French name Le manakin à front blanc and the Latin Manacus alba fronte.[2] Although Brisson coined Latin names, these do not conform to the binomial system and are not recognised by the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature.[3] When in 1766 the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus updated his Systema Naturae for the twelfth edition, he added 240 species that had been previously described by Brisson.[3] One of these was the white-fronted manakin. Linnaeus included a brief description, coined the binomial name Pipra serena and cited Brisson's work.[4] The specific name serena is from the Latin serenus "bright", "fair", "serene".[5] This species is now placed in the genus Lepidothrix was introduced by the French naturalist Charles Lucien Bonaparte in 1854.[6] The species is monotypic.[7]
Description
[edit]It is a deep black bird, and is named for its conspicuous bright-white forehead-patch feathers that extend forward beyond the bill's base; the female does not have the patch. Besides the black body and white forehead, a distinctive light blue, narrow patch of feathers covers the lower back-upper rump; a further distinctive color of this bird are bright sulphur-yellow breast patches. The bird has black legs, and dark eyes. The species is dimorphic with the female's colors being grayish and black with the sulphur-yellow belly; she has a white eye-ring.
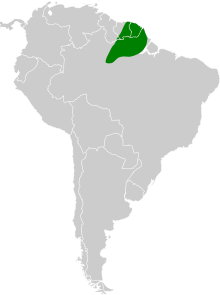
Distribution and habitat
[edit]It is found in the Atlantic coastal Guianas and the eastern Guiana Shield of Surname and French Guiana; also regions of Guyana and the northeastern Amazon states of Brazil. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical moist lowland forest.
The range of the white-fronted manakin is in the eastern Guianas, (only southeast border region of Guyana in the center-west of range), and the northeastern Amazon Basin; specifically, the eastern half of its range is all of Brazil's northeastern state of Amapá, with Amapá's south-flowing Jari River the centerline of its range. The range approaches the Amazon River but avoids the Amazon River corridor by about 100 km; further upstream its range is on the Amazon River, its north bank for 500 km, starting at the Rio Negro confluence and downriver past the confluence of the Madeira River. This portion of the range covers nearly all of the northern part of Pará state, north of the Amazon River. The species is not found south of the Amazon River into the southeast Amazon Basin.
The contiguous range in the Guianas, in the east encompasses all of French Guiana, and in the center country of Suriname, divides the country diagonally, being found in the southeast parts bordering French Guiana. Some disjunct locale areas of Guyana besides the southeast continuous range occur in Guyana's southwest at the headwaters of the Essequibo River and the Guiana Shield.
Status
[edit]This bird has a very wide range, is fairly common and is presumed to have a large total population. The population trend is thought to be stable and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated the bird's conservation status as being of "least concern".[1]
References
[edit]- ^ a b BirdLife International (2016). "Lepidothrix serena". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22701027A93810106. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22701027A93810106.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ^ Brisson, Mathurin Jacques (1760). Ornithologie, ou, Méthode contenant la division des oiseaux en ordres, sections, genres, especes & leurs variétés (in French and Latin). Vol. 4. Paris: Jean-Baptiste Bauche. pp. 547–549, Plate 36 fig 2. The two stars (**) at the start of the section indicates that Brisson based his description on the examination of a specimen.
- ^ a b Allen, J.A. (1910). "Collation of Brisson's genera of birds with those of Linnaeus". Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History. 28: 317–335. hdl:2246/678.
- ^ Linnaeus, Carl (1766). Systema naturae : per regna tria natura, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis (in Latin). Vol. 1, Part 1 (12th ed.). Holmiae (Stockholm): Laurentii Salvii. p. 340.
- ^ Jobling, J.A. (2018). del Hoyo, J.; Elliott, A.; Sargatal, J.; Christie, D.A.; de Juana, E. (eds.). "Key to Scientific Names in Ornithology". Handbook of the Birds of the World Alive. Lynx Edicions. Retrieved 27 June 2018.
- ^ Bonaparte, Charles Lucien (1854). "Conspectus Volucrum Anisodactylorum". L'Ateneo Italiano. Raccolta di Documenti e Memorie Relative al Progresso delle Scienze Fisiche. 2 (11): 311–321 [316].
- ^ Gill, Frank; Donsker, David, eds. (2018). "Cotingas, manakins, tityras, becards". World Bird List Version 8.2. International Ornithologists' Union. Retrieved 27 June 2018.
External links
[edit]- White-fronted manakin photo gallery VIREO
- Photo-(thumbnail); Article w/ photos, Photo-High Res
- Photo-High Res; Article, [1] https://www.nhlstenden.com/"Suriname Birds"
Maps of northeast Basin:
- Pará state, (showing North Region of Pará) v-Brazil.com
- Amapá state, showing Jari River, etc. v-Brazil.com

