Leine
| Leine | |
|---|---|
 The Leine near Sarstedt-Ruthe | |
 Course of the Leine | |
| Location | |
| Country | Germany |
| States | Thuringia and Lower Saxony |
| Reference no. | DE: 488 |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | In Leinefelde in the Eichsfeld |
| • elevation | 340 m above sea level (NN) |
| Mouth | |
• location | Near Schwarmstedt into the Aller at km 52.26[1] |
• coordinates | 52°43′22″N 9°35′38″E / 52.72278°N 9.59389°E |
• elevation | 25 m above sea level (NN) |
| Length | 281 km (175 mi) |
| Basin size | 6,517 km2 (2,516 sq mi) [2] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | at Göttingen gauge |
| • average | 5.3 m3/s (190 cu ft/s) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Greene |
| • average | 32.0 m3/s (1,130 cu ft/s) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Herrenhausen |
| • average | 52.3 m3/s (1,850 cu ft/s) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Schwarmstedt |
| • average | 61.7 m3/s (2,180 cu ft/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Progression | Aller→ Weser→ North Sea |
| Landmarks |
|
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Espolde, Ilme, Saale, Haller, Westaue |
| • right | Garte, Rhume, Aue, Gande, Innerste, Auter |
 | |
The Leine (German: [ˈlaɪnə] ; Old Saxon Lagina) is a river in Thuringia and Lower Saxony, Germany. It is a left tributary of the Aller and the Weser and is 281 km (175 mi) long.

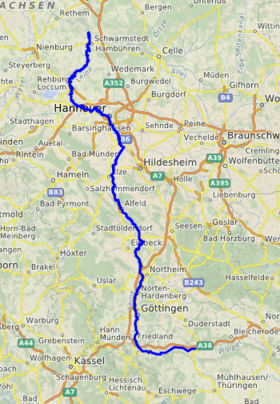
The river's source is located close to the town of Leinefelde in Thuringia. About 40 km (25 mi) downriver, the river enters Lower Saxony and runs northwards.
Important towns along its course, from upstream to downstream, are Göttingen, Einbeck, Freden, Alfeld, and Gronau, before the river enters Hanover, the largest city on its banks. Downstream some 40 km (25 mi) north of Hanover, near Schwarmstedt, the river joins the Aller and reaches the North Sea via the Weser. Its northern (lower) reaches are only navigable today by the smallest commercial carriers, though in the past, it served as an important pre-railway barge transport artery as far upriver as Göttingen.
The river is somewhat polluted by industry, so the water is not used for drinking, but the pollution has never been severe enough to prevent fish from living in it. Like many western rivers since the 1960s, it has enjoyed increasingly cleaner waters since the implementation of environmental controls. Sport fishing is enjoyed from small boats and along the banks, although yields are normally low.
At least one point of the river (Göttingen) is partially diverted into a canal that runs more or less parallel to the river.
Serial killer Fritz Haarmann disposed of most of his victims' remains in the Leine river.[3]
In fiction
[edit]In his 1986 bestseller Red Storm Rising, author Tom Clancy uses the Leine as a major obstacle to the Soviet Union's Red Army drive to the Rhine and the North Sea ports of the Netherlands and Belgium through West Germany. In reality, the river is a rather minor one, and, for most of its length, is quite narrow with a small flow volume. As such, it would not provide a significant barrier to an advancing army.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Längen (in km) der Hauptschifffahrtswege (Hauptstrecken und bestimmte Nebenstrecken) der Binnenwasserstraßen des Bundes, Wasser- und Schifffahrtsverwaltung des Bundes
- ^ Environmental map service of Lower Saxony (Umweltkartendienst des Niedersächsischen Ministeriums für Umwelt, Energie und Klimaschutz)
- ^ "The Victims of Fritz Haarmann Memorial".
Further reading
[edit]- Uwe Schmida: Die Leine - Eine fotografische Reise. ISBN 3-00-020567-5
- Gerd Lüttig: Neue Ergebnisse quartärgeologischer Forschung im Raume Alfeld-Hameln-Elze. In: Geologisches Jahrbuch vol. 77, page 337–390. Hannover, June 1960.
External links
[edit] Media related to Leine at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Leine at Wikimedia Commons- Bundesamt für Naturschutz: Landschaftssteckbrief "Leine-Ilme-Senke"
- Bundesamt für Naturschutz: Landschaftssteckbrief "Leine-Niederung"
