Hurricane Baker (1950)
 Surface weather map of Hurricane Baker on August 31 | |
| Meteorological history | |
|---|---|
| Formed | August 18, 1950 |
| Dissipated | September 1, 1950 |
| Category 2 hurricane | |
| 1-minute sustained (SSHWS/NWS) | |
| Highest winds | 105 mph (165 km/h) |
| Lowest pressure | ≤978 mbar (hPa); ≤28.88 inHg |
| Overall effects | |
| Fatalities | 38 direct |
| Damage | $2.55 million (1950 USD) |
| Areas affected | Leeward Islands, Puerto Rico, Hispaniola, Cuba, Gulf Coast of the United States |
| IBTrACS | |
Part of the 1950 Atlantic hurricane season | |
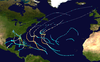
Hurricane Baker was a Category 2 hurricane that affected the Leeward Islands, Greater Antilles, and the Gulf Coast of the United States. The tropical cyclone was the second tropical storm and second hurricane of the 1950 Atlantic hurricane season. Originating as a tropical depression east of the Windward Islands on August 18, Baker became a tropical storm on August 19, and further intensified into a hurricane on August 21. It attained an initial peak intensity with maximum sustained winds of 100 mph (160 km/h) on August 22 before weakening to a tropical storm as it made landfall on the island of Antigua. Baker weakened to a tropical depression late on August 23 while southwest of Puerto Rico. By the following morning, it had restrengthened into a tropical storm, though a landfall in Cuba caused it to weaken once again. Entering the Gulf of Mexico, Baker began to strengthen once more, regaining hurricane strength on August 29 and reaching its peak intensity with maximum sustained winds of 105 mph (169 km/h) early the following day. The cyclone weakened before making its final landfall in the United States near Gulf Shores, Alabama, with winds of 85 mph (137 km/h). Hurricane Baker produced extensive damage in the Lesser Antilles and Cuba, but impacts were minimal in the United States.
Meteorological history
[edit]
Tropical storm (39–73 mph, 63–118 km/h)
Category 1 (74–95 mph, 119–153 km/h)
Category 2 (96–110 mph, 154–177 km/h)
Category 3 (111–129 mph, 178–208 km/h)
Category 4 (130–156 mph, 209–251 km/h)
Category 5 (≥157 mph, ≥252 km/h)
Unknown
On the morning of August 20, a strong tropical storm developed about 446 miles (718 km) east of Basse-Terre, Guadeloupe.[1] The tropical storm deepened to hurricane intensity. On August 21, it rapidly attained maximum sustained winds of 120 mph (190 km/h), equivalent to a Category 3 hurricane. The hurricane passed over Antigua during the evening,[2] while still producing winds of 115 mph (185 km/h).[1] On August 22, it lost intensity and weakened to a tropical storm. On August 23, Baker made landfall near the Puerto Rican town of Guánica as a minimal tropical storm.[1] The highest winds on the island of Puerto Rico were 35–40 mph (56–64 km/h).[2] The storm then degenerated into an easterly tropical wave,[2] and moved west-northwestward over northeastern Hispaniola. On August 24, it re-entered the Atlantic Ocean, and Tropical Depression Baker crossed the coast of eastern Cuba early on the next day.[1]
On August 25, Baker redeveloped a center over the Caribbean Sea off southern Cuba,[2] and re-intensified to tropical storm status.[1] On August 27, Baker affected the Pinar del Río Province with 60 mph (97 km/h) winds, and then turned northward over the southern Gulf of Mexico.[2] On August 28, Baker re-strengthened to hurricane intensity; reconnaissance and ship reports[2] suggest the hurricane attained a second peak intensity of 110 mph (180 km/h) on August 30. The minimum central pressure was 979 mbar (28.9 inHg) on this date.[1] The cyclone diminished in intensity prior to landfall.[2] On August 31, the hurricane struck Gulf Shores, Alabama[1] as a Category 1 hurricane[3] with sustained winds estimated near 85 mph (137 km/h).[1][2] The estimated central pressure at landfall was 980 mbar (29 inHg).[3] Baker moved inland over Alabama and dissipated over southeastern Missouri on September 1.[1]
Impact
[edit]
On Antigua, the Pan American Airways station's power failed when winds reached 85 mph (137 km/h) around midnight on August 22.[4] Unofficial estimates placed winds between 95–120 mph (153–193 km/h) at the location, although damages and casualties were unknown.[5] Subsequent reports indicated light damage occurred on the island;[6] later, information from the island indicated extensive damage. More than 100 homes were destroyed or damaged in the Willkie and Piggott areas, and large homes were destroyed in Prestown. Additionally, a manse was also demolished in Prestown. Electronic communications were dismantled, and thousands of homeless people sheltered in churches and schools. No deaths occurred on the island, but damages were expected to reach several thousand dollars.[7] In Cuba, 37 people died, and the property losses reached several million dollars.[8]
In the United States, the greatest property and crop damage occurred from Mobile, Alabama to Saint Marks, Florida, where losses approached $2,550,000 (1950 USD);[2] high tides and winds inflicted minimal damage in both cities.[9] Panama City, Florida incurred heavy damage to homes and businesses from high tides and rainfall, which peaked at 14.96 inches (380 mm).[10][page needed] The highest rainfall total was 15.49 inches (393 mm) at Caryville, Florida.[11] Peak gusts exceeded 100 mph (160 km/h) on Santa Rosa Island, Florida.[10]: 188 200 to 300 cottages received damage in Panama City, and homes were flooded near the bay.[12] Losses reached $200,000 (1950 USD) in Gulf Shores, Alabama.[8] Hurricane Baker spawned two tornadoes.[2] On August 30, a F1 tornado[13] touched down in Apalachicola, Florida, destroying four dwellings and a store building and damaging another eleven buildings.[2] On August 31, a F0 tornado[13] demolished one building near Marianna, Florida, in Jackson County.[2] Inland, Birmingham International Airport recorded 50 mph (80 km/h) wind gusts; higher gusts were estimated near 75 mph (121 km/h) in elevated, mountainous locations.[2] Hundreds of trees were prostrated as far north as the Birmingham, Alabama area,[10]: 188 and one person was killed and two more injured by live wires falling from utility poles.[2]
See also
[edit]- List of Category 2 Atlantic hurricanes
- List of Florida hurricanes
- List of United States hurricanes
- List of Atlantic hurricanes
Notes
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g h i Atlantic hurricane research division (2008). "Atlantic hurricane best track (1851–2007)". NOAA. Retrieved October 24, 2008.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Norton, Grady (1950). "Hurricanes of the 1950 Season" (PDF). U.S. Weather Bureau. Retrieved October 24, 2008.
- ^ a b Atlantic hurricane research division (2008). "All U.S. Hurricanes (1851-2007)". NOAA. Archived from the original on September 21, 2008. Retrieved October 24, 2008.
- ^ The Associated Press (1950). "Second Hurricane Fades Out". The Lowell Sun. Retrieved October 24, 2008.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Season's Second Hurricane Has Blown Itself Out". Newport News. Vol. 106, no. 174. Newport, Rhode Island. Associated Press. August 23, 1950. p. 5. Retrieved July 3, 2019 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ "Coast is at Last Clear of Storms". Nevada State Journal. No. 236. Reno, Nevada. United Press. August 24, 1950. p. 15. Retrieved July 3, 2019 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ "Storm Wrecks 100 Houses in Antigua". The Daily Gleaner. Vol. 116, no. 187. Kingston, Jamaiaca. Trinidad Guardian. August 26, 1950. p. 1 – via NewspaperArchive.com.
- ^ a b Staff Writer (September 1, 1950). "Hurricane Only a "Whisper" Now". The Milwaukee Journal. Associated Press. Retrieved January 1, 2011.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Gulf Storm Taps Coast Lightly; Hurricane Moves On Puerto Rico". Fort Myers News-Press. Fort Myers, Florida. Associated Press. September 1, 1950. p. 1. Retrieved July 3, 2019 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ a b c Barnes, Jay (1998). Florida's Hurricane History. Chapel Hill Press. ISBN 9780807830680. Retrieved October 27, 2008.
- ^ Roth, David (October 21, 2008). "Hurricane Baker - August 22-September 3, 1950". Hydrometeorological Prediction Center. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ "Gulf Hurricane Blows Itself Out". Joplin Globe. Vol. 55, no. 19. Joplin, Missouri. Associated Press. September 1, 1950. p. 1. Retrieved July 3, 2019 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ a b National Climatic Data Center. "Storm Events Database". NOAA. Archived from the original on August 14, 2008. Retrieved October 24, 2008.
Further reading
[edit]- Barnes, Jay (1998). Florida's Hurricane History. Chapel Hill Press. ISBN 0-8078-2443-7.
- 1950 Atlantic hurricane season
- Category 3 Atlantic hurricanes
- Hurricanes in the Leeward Islands
- Hurricanes in Antigua and Barbuda
- Hurricanes in Guadeloupe
- Hurricanes in Montserrat
- Hurricanes in Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Hurricanes in Sint Eustatius
- Hurricanes in Saba (island)
- Hurricanes in Saint Martin (island)
- Hurricanes in Saint Barthélemy
- Hurricanes in Anguilla
- Hurricanes in Florida
- Hurricanes in Alabama
- 1950 meteorology
- 1950 natural disasters in the United States
- 1950 in the Caribbean
- 1950 in Saint Kitts-Nevis-Anguilla