Hexafluoro-2-butyne
Appearance
(Redirected from Hexafluorobutyne)
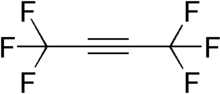
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,1,1,4,4,4-Hexafluorobut-2-yne | |
| Other names
HFB
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.667 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4F6 | |
| Molar mass | 162.034 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless gas |
| Density | 1.602 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −117 °C (−179 °F; 156 K) |
| Boiling point | −25 °C (−13 °F; 248 K) |
| Insoluble | |
| Structure | |
| 0 D | |
| Hazards[1] | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Toxic gas |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Danger | |
| H331 | |
| P261, P311, P410+P403 | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate Hexachlorobutadiene Acetylene |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Hexafluoro-2-butyne (HFB) is a fluorocarbon with the chemical structure CF3C≡CCF3. HFB is a particularly electrophilic acetylene derivative, and hence a potent dienophile for Diels–Alder reactions.[2][3]
Synthesis and reactions
[edit]HFB is prepared by the action of sulfur tetrafluoride on acetylenedicarboxylic acid or by the reaction of potassium fluoride (KF) with hexachlorobutadiene.
It reacts with sulfur to give 3,4-bis(trifluoromethyl)-1,2-dithiete.
Cycloaddition of HFB and dithionitronium (NS2+) gives the 1,2,5-dithiazolium cation. This derivative can be reduced to the 7 electron neutral radical. This particular 1,3,5-dithiazole is also rare example of a radical that can be obtained as solid, liquid, and gaseous states. As a gas, it is blue.[4]
References
[edit]- ^ "Hexafluoro-2-butyne 99%". Sigma-Aldrich.
- ^ Essers, Michael; Haufe, Günter (2006). "Hexafluoro-2-butyne". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rn00669. ISBN 0471936235.
- ^ E S Turbanova, A A Petrov (1991). "Perfluoroalkyl(aryl)acetylenes". Russian Chemical Reviews. 60 (5): 501–523. Bibcode:1991RuCRv..60..501T. doi:10.1070/RC1991v060n05ABEH001092.
- ^ Brownridge, Scott; Du, Hongbin; Fairhurst, Shirley A.; Haddon, Robert C.; Oberhammer, Heinz; Parsons, Simon; Passmore, Jack; Schriver, Melbourne J.; Sutcliffe, Leslie H.; Westwood, Nicholas P. C. (2000). "The Isolation, Characterisation, Gas Phase Electron Diffraction and Crystal Structure of the Thermally Stable Radical CF3CSNSCCF3". Journal of the Chemical Society, Dalton Transactions (19): 3365–3382. doi:10.1039/B001489N.
