G20
Group of Twenty | |
 | |
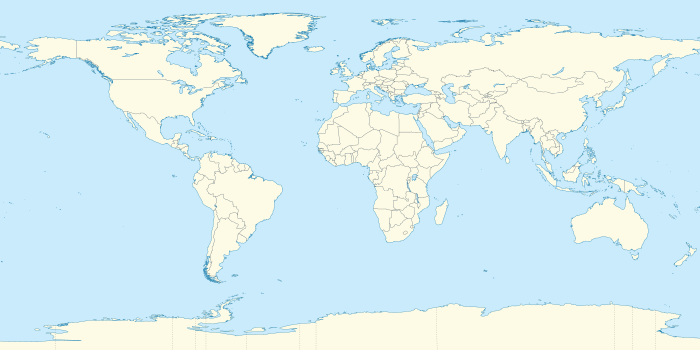
 Member countries of the G20
Countries represented through the membership of the European Union
Countries represented through the membership of the African Union
Countries permanently invited (Spain) | |
| Predecessor | 2024 G20 Rio de Janeiro summit |
|---|---|
| Successor | 2025 G20 Johannesburg Summit |
| Formation | 26 September 1999 2008 |
| Type | International organization |
| Purpose | Bring together systemically important industrialized and developing economies to discuss key issues in the global economy.[1] |
| Membership | |
Chairman (Incumbent) | |
| Website | g20 |
The G20 or Group of 20 is an intergovernmental forum comprising 19 sovereign countries, the European Union (EU), and the African Union (AU).[2][3] It works to address major issues related to the global economy, such as international financial stability, climate change mitigation and sustainable development, through annual meetings of Heads of State and Heads of Government.[4]
The sovereign states of the G20 (without its international members, like the EU or AU) account for around 85% of gross world product (GWP),[5] 75% of international trade, 56% of the global population,[5] and 60% of the world's land area. Including the EU and AU, the G20 comprises 78.9% of global population and 83.9% of global CO2 emissions from fossil energy.[6]
The G20 was founded in 1999 in response to several world economic crises.[7] Since 2008, it has convened at least once a year, with summits involving each member's head of government or state, finance minister, or foreign minister, and other high-ranking officials; the EU is represented by the European Commission and the European Central Bank.[8][9][b] Other countries, international organizations, and nongovernmental organizations are invited to attend the summits, some permanently. In 2023, during its 2023 summit, the African Union joined as its 21st member and was officially represented at the 2024 G20 summit in Brazil.
In its 2009 summit, the G20 declared itself the primary venue for international economic and financial cooperation.[10] The group's stature has risen during the subsequent decade, and it is recognised by analysts as exercising considerable global influence;[11] it is also criticised for its limited membership,[12] lack of enforcement powers,[13] and for the alleged undermining of existing international institutions.[12] Summits are often met with protests, particularly by anti-globalization groups.[14][15]
History
[edit]The G20 is the latest in a series of post–World War II initiatives aimed at international coordination of economic policy, which include institutions such as the "Bretton Woods twins", the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank, and what is now the World Trade Organization.[16]
The G20 was foreshadowed at the Cologne summit of the G7 in June 1999, and formally established at the G7 Finance Ministers' meeting on 26 September 1999 with an inaugural meeting on 15–16 December 1999 in Berlin. Canadian finance minister Paul Martin was chosen as the first chairman and German finance minister Hans Eichel hosted the meeting.[17]
A 2004 report by Colin I. Bradford and Johannes F. Linn of the Brookings Institution asserted the group was founded primarily at the initiative of Eichel, the concurrent chair of the G7.[18] However, Bradford later described then-Finance Minister of Canada (and future Prime Minister of Canada) Paul Martin as "the crucial architect of the formation of the G20 at finance minister level", and as the one who later "proposed that the G20 countries move to leaders level summits".[19] Canadian academic and journalistic sources have also identified the G20 as a project initiated by Martin and his American counterpart then-Treasury Secretary Larry Summers.[20][21][22][23] All acknowledge, however, that Germany and the United States played a key role in bringing their vision into reality.[citation needed]
Martin and Summers conceived of the G20 in response to the series of massive debt crises that had spread across emerging markets in the late 1990s, beginning with the Mexican peso crisis and followed by the 1997 Asian financial crisis, the 1998 Russian financial crisis, and eventually impacting the United States, most prominently in the form of the collapse of the prominent hedge fund Long-Term Capital Management in the autumn of 1998.[20][21][22] It illustrated to them that in a rapidly globalizing world, the G7, G8, and the Bretton Woods system would be unable to provide financial stability, and they conceived of a new, broader permanent group of major world economies that would give a voice and new responsibilities in providing it.[20][22]
The G20 membership was decided by Eichel's deputy Caio Koch-Weser and Summers's deputy Timothy Geithner. According to the political economist Robert Wade:
"Geithner and Koch-Weser went down the list of countries saying, Canada in, Portugal out, South Africa in, Nigeria and Egypt out, and so on; they sent their list to the other G7 finance ministries; and the invitations to the first meeting went out."[24]
Early topics
[edit]The G20's primary focus has been governance of the global economy. Summit themes have varied from year to year. The theme of the 2006 G20 ministerial meeting was "Building and Sustaining Prosperity". The issues discussed included domestic reforms to achieve "sustained growth", global energy and resource commodity markets, reform of the World Bank and IMF, and the impact of demographic changes.
In 2007, South Africa hosted the secretariat with Trevor A. Manuel, South African Minister of Finance as chairperson of the G20.
In 2008, Guido Mantega, Brazil's Minister of Finance, was the G20 chairperson and proposed dialogue on competition in financial markets, clean energy, economic development and fiscal elements of growth and development.
On 11 October 2008 after a meeting of G8 finance ministers, US President George W. Bush stated that the next meeting of the G20 would be important in finding solutions to the burgeoning economic crisis of 2008.
Summits
[edit]The Summit of G20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors, who prepare the leaders' summit and implement their decisions, was created as a response both to the 2007–2008 financial crisis and to a growing recognition that key emerging powers were not adequately included in the core of global economic discussion and governance. Additionally, G20 summits of heads of state or government were held.
After the 2008 debut summit in Washington, DC, G20 leaders met twice a year: in London and Pittsburgh in 2009, and in Toronto and Seoul in 2010.[25]
Since 2011, when France chaired and hosted the G20, the summits have been held only once a year.[26] The 2016 summit was held in Hangzhou, China,[27] the 2017 summit was held in Hamburg, Germany, the 2018 summit was held in Buenos Aires, Argentina, the 2019 summit was held in Osaka, Japan, the 2020 summit was scheduled in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia but it was held virtually due to COVID-19, the 2021 summit was held in Rome, Italy, the 2022 summit was held in Bali, Indonesia and the 2023 summit was held in New Delhi, India. The 2024 Group of 20 (G20) Summit will take place from 18-19 November in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.[28]
Several other ministerial-level G20 meetings have been held since 2010. Agriculture ministerial meetings were conducted in 2011 and 2012; meetings of foreign ministers were held in 2012 and 2013; trade ministers met in 2012 and 2014, and employment ministerial meetings have taken place annually since 2010.[29]
In 2012, the G20 Ministers of Tourism and Heads of Delegation of G20 member countries and other invited States, as well as representatives from the World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC), World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) and other organisations in the Travel & Tourism sector met in Mérida, Mexico, on May 16 at the 4th G20 meeting and focused on 'Tourism as a means to Job Creation'. As a result of this meeting and The World Travel & Tourism Council's Visa Impact Research, later on the Leaders of the G20, convened in Los Cabos on 18–19 June, would recognise the impact of Travel & Tourism for the first time. That year, the G20 Leaders Declaration added the following statement: "We recognise the role of travel and tourism as a vehicle for job creation, economic growth and development, and, while recognizing the sovereign right of States to control the entry of foreign nationals, we will work towards developing travel facilitation initiatives in support of job creation, quality work, poverty reduction and global growth."[30]
In March 2014, the former Australian foreign minister Julie Bishop, when Australia was hosting the 2014 G20 summit in Brisbane, proposed to ban Russia from the summit over its annexation of Ukrainian Crimea.[31] The BRICS foreign ministers subsequently reminded Bishop that "the custodianship of the G20 belongs to all Member States equally and no one Member State can unilaterally determine its nature and character."
The 2015 G20 Summit in Antalya, Turkey, focused on "Inclusiveness, Investment, and Implementation," gathering leaders to address global economic challenges, development, climate change, and urgent issues like terrorism and refugees. Key outcomes included the Antalya Action Plan and commitments to financial stability, tax regulation, and energy policy.[32][33]
In 2016, the G20 framed its commitment to the 2030 Agenda, Sustainable Development Goals in three key themes; the promotion of strong sustainable and balanced growth; protection of the planet from degradation; and furthering co-operation with low-income and developing countries. At the G20 Summit in Hangzhou, members agreed on an action plan and issued a high level principles document to member countries to help facilitate the agenda's implementation.[34][35]
Japan hosted the 2019 summit,[36] The 2020 summit was to be held in Saudi Arabia,[37] but was instead held virtually on 21–22 November 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic under the presidency of Saudi Arabia. 2021 G20 Rome summit which was held in Rome, the capital city of Italy, on 30–31 October 2021.
Indonesia held the 2022 summit in November 2022. During its presidency, Indonesia focused on the global COVID-19 pandemic and how to collectively overcome the challenges related to it. The three priorities of Indonesia's G20 presidency were global health architecture, digital transformations, and sustainable energy transitions.[38] The G20 Presidency of Indonesia, in partnership with the Pandemic Fund secretariat, also officially launched the Pandemic Fund at a high-level event. The Pandemic Fund to be expected as a key part of the solution for reducing risks from epidemics and pandemics in the most vulnerable parts of the world and contributing to a healthier and safer world [39]

India held the 2023 summit in September 2023.[40] The presidency's theme was Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam (Sanskrit: वसुधैव कुटुम्बकम्; English:"One Earth, One Family, One Future"[c]).[41][42] In an interview on 26 August 2023, Prime Minister Narendra Modi expressed optimism about the G20 countries' evolving agenda under India's presidency, shifting toward a human-centric development approach that aligns with the concerns of the Global South, including addressing climate change, debt restructuring through the G20's Common Framework for debt, and a strategy for regulation of global cryptocurrencies. G20 expanded by the inclusion of African Union, it is also the first inclusion since 1999.[43][44][45]
The Brazilian presidency launched the G20 Social, a place where for the first time the organization will bring the civil society into the debate where it can participate and contribute to discussions and policy formulations regarding to the summit.[46]
Chair rotation
[edit]To decide which member nation gets to chair the G20 leaders' meeting for a given year, all country members are assigned to one of five different groupings, with all but one group having four members, the other having three. States from the same region are placed in the same group, except Group 1 and Group 2. All countries within a group are eligible to take over the G20 Presidency when it is their group's turn. Therefore, the states within the relevant group need to negotiate among themselves to select the next G20 President. Each year, a different G20 member country assumes the presidency starting from 1 December until 30 November. This system has been in place since 2010, when South Korea, which is in Group 5, held the G20 chair. The table below lists the nations' groupings:[47][48]
| Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 (Latin America) | Group 4 (Western Europe) | Group 5 (East/Southeast Asia) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
To ensure continuity, the presidency is supported by a "troika" made up of the current, immediate past and next host countries.[49]
Organization
[edit]The G20 operates without a permanent secretariat or staff. The group's chair (the presidency) rotates annually among the members and is selected from a different regional grouping of countries. The incumbent chair establishes a temporary secretariat for the duration of its term, which coordinates the group's work and organizes its meetings. Together with the previous and following presidency a so-called troika is formed, to provide a smooth transition of secretariat functions.[50]
The 2022 summit was held in Bali, Indonesia. India was the chair in 2023 and hosted the 2023 summit. Brazil is the current chair and will host the 2024 summit.[51]
Additionally because of the lacking of a permanent secretariat the G20 has been relying on the OECD for more institutional competences substituting permanent secretariat functions.[52]
Proposed permanent secretariat
[edit]In 2010, President of France Nicolas Sarkozy proposed the establishment of a permanent G20 secretariat, similar to the United Nations. Seoul and Paris were suggested as possible locations for its headquarters.[53] Brazil and China supported the establishment of a secretariat, while Italy and Japan expressed opposition to the proposal.[53] South Korea proposed a "cyber secretariat" as an alternative.[53]
Members
[edit]As of 2023[update], there are 21 members in the group: Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, South Korea, Turkey, the United Kingdom, the United States, the European Union and the African Union. Guest invitees include, amongst others, Spain, the United Nations, the World Bank and ASEAN.[54][55]
Representatives include, at the leaders' summits, the leaders of nineteen countries, the African Union and of the European Union, and, at the ministerial-level meetings, the finance ministers and central bank governors of nineteen countries, the African Union and of the European Union.
In addition, each year, the G20's guests include Spain;[56] the Chair of ASEAN; a representative of the New Partnership for Africa's Development (NEPAD) and a country (sometimes more than one) invited by the presidency, usually from its own region.[57][58][59]
The first of the tables below lists the member entities and their leaders, finance ministers and central bank governors. The second table lists relevant statistics such as population and GDP figures for each member, as well as detailing memberships of other international organizations, such as the G7, BRICS and MIKTA. Total GDP figures are given in millions of US dollars.
In September 2023, at the 18th G20 Summit, Indian PM Narendra Modi announced that the African Union has been included as a member of the G20, making it the 21st member.[60]
Leaders
[edit]Member country data
[edit]| Member | Trade bil. USD (2022)[66] |
Nom. GDP mil. USD (2024)[67] |
PPP GDP mil. USD (2024)[67] |
Nom. GDP per capita USD (2024)[67] |
PPP GDP per capita USD (2024)[67] |
HDI (2022)[68] |
Population (2022)[69] |
Area km2 |
P5 | G4 | G7 | BRICS | MIKTA | DAC | OECD | C'wth | NATO | SCO | IMF economy classification[70][71] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 170.1 | 604,382 | 1,353,804 | 12,814 | 28,704 | 0.849 | 46,300,000 | 2,780,400 | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Emerging | |
| 721.4 | 1,802,006 | 1,897,885 | 65,966 | 69,475 | 0.946 | 26,141,369 | 7,692,024 | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | global partner | No | Advanced | |
| 626.4 | 2,188,419 | 4,702,004 | 10,296 | 22,123 | 0.760 | 217,240,060 | 8,515,767 | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | Emerging | |
| 1,179.1 | 2,214,796 | 2,582,228 | 53,834 | 62,766 | 0.935 | 38,743,000 | 9,984,670 | No | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Advanced | |
| 6,309.6 | 18,273,357 | 37,072,086 | 12,969 | 26,310 | 0.788 | 1,411,750,000 | 9,596,960 | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | Emerging | |
| 1,435.8 | 3,174,099 | 4,359,372 | 48,012 | 65,940 | 0.910 | 68,305,148 | 640,679 | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Advanced | |
| 3,226.9 | 4,710,032 | 6,017,222 | 55,521 | 70,930 | 0.950 | 84,316,622 | 357,114 | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Advanced | |
| 1,176.8 | 3,889,130 | 16,019,970 | 2,698 | 11,112 | 0.644 | 1,406,632,000 | 3,287,263 | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | Emerging | |
| 529.4 | 1,402,590 | 4,658,321 | 4,981 | 16,542 | 0.713 | 279,088,893 | 1,904,569 | No | No | No | partner state[72] | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | Emerging | |
| 1,346.4 | 2,376,510 | 3,597,954 | 40,287 | 60,993 | 0.906 | 61,095,551 | 301,336 | No | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Advanced | |
| 1,644.2 | 4,070,094 | 6,572,198 | 32,859 | 53,059 | 0.920 | 125,592,404 | 377,930 | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | global partner | No | Advanced | |
| 1,204.5 | 1,848,125 | 3,303,067 | 13,972 | 24,971 | 0.781 | 131,541,424 | 1,964,375 | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | Emerging | |
| 1,415.0 | 1,869,916 | 3,258,366 | 36,132 | 62,960 | 0.929 | 51,844,834 | 100,210 | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | global partner | No | Advanced | |
| 772.3 | 2,184,316 | 6,909,381 | 14,953 | 47,299 | 0.821 | 145,807,429 | 17,098,242 | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | PfP[d] | Yes | Emerging | |
| 598.8 | 1,100,706 | 2,112,880 | 32,881 | 63,118 | 0.875 | 36,168,000 | 2,149,690 | No | No | No | invited | No | No | No | No | No | Dialogue partner | Emerging | |
| 259.1 | 403,045 | 993,745 | 6,377 | 15,723 | 0.717 | 61,060,000 | 1,221,037 | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | Emerging | |
| 617.9 | 1,344,318 | 3,456,771 | 15,666 | 40,283 | 0.855 | 85,551,932 | 783,562 | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | Dialogue partner | Emerging | |
| 1,353.3 | 3,587,545 | 4,282,173 | 52,423 | 62,574 | 0.940 | 68,492,933 | 242,495 | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Advanced | |
| 5,441.0 | 29,167,779 | 29,167,779 | 86,601 | 86,601 | 0.927 | 337,341,954 | 9,833,517 | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Advanced | |
| [e]5,858.4 | 19,403,162 | 28,044,235 | 43,353 | 62,660 | 0.900 | 446,828,803 | 4,233,262 | No | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | Advanced (majority)[f] | |
| 1,379.0 | 2,780,597 | 10,155,027 | 1,941[g] | 7,087[h] | 0.577[i] | 1,393,676,444[j] | 29,922,059 | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Emerging |
In addition to these 21 members, the chief executive officers of several other international forums and institutions participate in meetings of the G20.[57] These include the managing director and Chairman of the International Monetary Fund, the President of the World Bank, the International Monetary and Financial Committee and the Chairman of the Development Assistance Committee.
The G20's membership does not reflect exactly the 21 largest economies of the world in any given year; as the organization states:[1]
In a forum such as the G20, it is particularly important for the number of countries involved to be restricted and fixed to ensure the effectiveness and continuity of its activity. There are no formal criteria for G20 membership and the composition of the group has remained unchanged since it was established. Because of the objectives of the G20, it was considered important that countries and regions of systemic significance for the international financial system be included. Aspects such as geographical balance and population representation also played a major part.
Role of Asian countries
[edit]A 2011 report released by the Asian Development Bank (ADB) predicted that large Asian economies such as China and India would play a more important role in global economic governance in the future. The report claimed that the rise of emerging market economies heralded a new world order, in which the G20 would become the global economic steering committee.[73] The ADB furthermore noted that Asian countries had led the global recovery following the late-2000s recession. It predicted that the region would have a greater presence on the global stage, shaping the G20's agenda for balanced and sustainable growth through strengthening intraregional trade and stimulating domestic demand.[73]
Invitees
[edit]
Typically, several participants that are not full members of the G20 are extended invitations to participate in the summits. Permanent guest invitees are: the government of Spain; the Chair of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations and a representative of the New Partnership for Africa's Development are invited in their capacities as leaders of their organisations and as heads of government of their home states. In addition, the leaders of the Financial Stability Board, the International Labour Organization, the International Monetary Fund, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, the United Nations, the World Bank Group and the World Trade Organization are invited and participate in pre-summit planning within the policy purview of their respective organisation.[74][56][75]
Other invitees are chosen by the host country, usually one or two countries from its region.[75] For example, South Korea invited Singapore. International organisations which have been invited in the past include the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC), the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS), the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the Eurasian Economic Community (EAEC), the European Central Bank (ECB), the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), the Global Governance Group (3G) and the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC). Previously, the Netherlands had a similar status to Spain while the rotating presidency of the Council of the European Union would also receive an invitation, but only in that capacity and not as their own state's leader (such as the Czech premiers Mirek Topolánek and Jan Fischer during the 2009 summits).
Permanent guest invitees
[edit]| Invitee | Officeholder | State | Official title |
|---|---|---|---|
| International Labour Organization (ILO) | Gilbert Houngbo | — | Director General |
| International Monetary Fund (IMF) | Kristalina Georgieva | — | Managing Director |
| Spain[56] | Pedro Sánchez | Prime Minister | |
| New Partnership for Africa's Development (AUDA-NEPAD) | Abdel Fattah El-Sisi | President (chair) | |
| Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) | Mathias Cormann | — | Secretary-General |
| United Nations (UN) | António Guterres | — | Secretary-General |
| World Bank Group (WBG) | Ajay Banga | — | President |
| World Health Organization (WHO) | Tedros Adhanom | — | Director General |
| World Trade Organization (WTO) | Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala | — | Director General |
Agenda
[edit]Financial focus
[edit]The initial G20 agenda, as conceived by US, Canadian and German policymakers, was very much focused on the sustainability of sovereign debt and global financial stability, in an inclusive format that would bring in the largest developing economies as equal partners. During a summit in November 2008, the leaders of the group pledged to contribute trillions to international financial organizations, including the World Bank and IMF, mainly for re-establishing the global financial system.[76][77]
Since inception, the recurring themes covered by G20 summit participants have related in priority to global economic growth, international trade and financial market regulation.[78]
The G20 has led the Debt Service Suspension Initiative, through which official bilateral creditors suspended debt repayments of 73 of the poorest debtor countries.[79]: 134
Growth and sustainability
[edit]The G20 countries account for almost 75% of global carbon emissions.[80] After the adoption of the UN Sustainable Development Goals and the Paris Climate Agreement in 2015, more "issues of global significance"[78][81] were added to the G20 agenda: migration, digitisation, employment, healthcare, the economic empowerment of women, development aid[82] and stopping climate change.[83]
The G20 countries account for almost 75% of the global carbon emissions and promised in 2009 to phase out 'inefficient subsidies'. Despite these promises G20 members have subsidised fossil fuel companies over $3.3 trillion between 2015 and 2021,[80] with several states increasing subsidies; Australia (+48.2%), the US (+36.7%), Indonesia (+26.6%), France (+23.8%), China (+4.1%), Brazil (+3.0%), Mexico (+2.6%).[80] China alone generates over half of the coal-generated electricity in the world.[84]
Interrelated themes
[edit]Wolfgang Schäuble, German Federal Minister of Finance, had insisted on the interconnected nature of the issues facing G20 countries, be they purely financial or developmental, and the need to reach effective, cross-cutting policy measures: "Globalization has lifted hundreds of millions out of poverty, but there is also a growing rise in frustration in some quarters […] development, [national] security and migration are all interlinked"[81]
G20 engagement groups
[edit]The G20 engagement groups and pre-conferences are independent collectives that are led by organisations of the host country. They represent a diverse group of stakeholders and work collectively to develop non-binding policy recommendations formally submitted to the G20 leaders for consideration.
For the 2022 G20 hosted by Indonesia, there are 10 engagement groups formed to facilitate independent stakeholders in developing proposals and policy recommendations for G20 leaders.
Startup20 and other few engagement groups initiated under the G20 India Presidency of 2023.[85]
Influence and accountability
[edit]The G20's prominent membership gives it a strong input on global policy despite lacking any formal ability to enforce rules. There are disputes over the legitimacy of the G20,[86] and criticisms of its organisation and the efficacy of its declarations.[87]
The G20's transparency and accountability have been questioned by critics, who call attention to the absence of a formal charter and the fact that the most important G20 meetings are closed-door.[88] In 2001, the economist Frances Stewart proposed an Economic Security Council within the United Nations as an alternative to the G20. In such a council, members would be elected by the General Assembly based on their importance to the world economy, and the contribution they are willing to provide to world economic development.[89]
The cost and extent of summit-related security is often a contentious issue in the hosting country, and G20 summits have attracted protesters from a variety of backgrounds, including information activists, opponents of fractional-reserve banking and anti-capitalists. In 2010, the Toronto G20 summit sparked mass protests and rioting, leading to the largest mass arrest in Canada's history.[90]
Views on the G20's exclusivity of membership
[edit]Although the G20 has stated that the group's "economic weight and broad membership gives it a high degree of legitimacy and influence over the management of the global economy and financial system",[91] its legitimacy has been challenged. A 2011 report for the Danish Institute for International Studies criticised the G20's exclusivity, particularly highlighting its underrepresentation of African countries and its practice of inviting observers from non-member states as a mere "concession at the margins", which does not grant the organisation representational legitimacy.[92] Concerning the membership issue, US President Barack Obama noted the difficulty of pleasing everyone: "Everybody wants the smallest possible group that includes them. So, if they're the 21st largest nation in the world, they want the G-21, and think it's highly unfair if they have been cut out."[93] Others stated in 2011 that the exclusivity is not an insurmountable problem and proposed mechanisms by which it could become more inclusive.[94]
Norwegian perspective
[edit]In line with Norway's emphasis on inclusive international processes, the United Nations, and the UN system, in a 2010 interview with Der Spiegel, the current prime minister of Norway Jonas Gahr Støre called the G20 "one of the greatest setbacks since World War II"[12] as 173 states who are all members of the UN are not among the G20. This includes Norway, a major developed economy and the seventh-largest contributor to UN international development programs,[95] which is not a member state of the EU, and thus is not represented in the G20 even indirectly.[12] Norway, like other such states, has little or no voice within the group. Støre argued that the G20 undermines the legitimacy of international organizations set up in the aftermath of World War II, such as the IMF, World Bank and United Nations:
The G20 is a self-appointed group. Its composition is determined by the major countries and powers. It may be more representative than the G7 or the G8, in which only the richest countries are represented, but it is still arbitrary. We no longer live in the 19th century, a time when the major powers met and redrew the map of the world. No one needs a new Congress of Vienna.[12]
However, Norway, has moderated this position in practice, and has contributed to a number of G20-work streams for years, in particular on health, energy and climate. Under the government of Erna Solberg, Norway attended the 2017 G20 summit in Hamburg, Germany.[96]
Spanish position on membership
[edit]Spain is the world's fifteenth largest economy by nominal GDP (the sixteenth largest by purchasing power parity), the fourth in the European Union, the second among Spanish-speaking countries, and the third in Iberoamerica. In addition, since the 1990s several Spanish companies have gained multinational status, and Spain is an important foreign investor worldwide. Its numbers[clarification needed] exceed the numbers of several current members of the G20 such as Argentina or South Africa. This has led to what Henley et al consider to be a de facto position as a member of the G20. However, Spain, a permanent guest, does not plan to request official membership.[56]
Polish aspirations
[edit]In contrast with the Spanish position, the Polish government has repeatedly asked to join the G20.
Before the 2009 G20 London summit, the Polish government expressed an interest in joining with Spain and the Netherlands and condemned an "organisational mess" in which a few European leaders spoke in the name of the collective EU without legitimate authorisation in cases which belong to the European Commission.[citation needed]
During a 2010 meeting with foreign diplomats, Polish president Lech Kaczyński said:
The Polish economy is according to our data the 18th world economy. The place of my country is among the members of the G20. This is a very simple postulate: firstly – it results from the size of the Polish economy, secondly – it results from the fact that Poland is the biggest country in its region and the biggest country that has experienced a certain story. That story is a political and economic transformation.[97]
In 2012, Tim Ferguson wrote in Forbes that swapping Argentina for Poland should be considered, claiming that the Polish economy was headed toward a leadership role in Europe and its membership would be more legitimate.[98][99] A similar opinion was expressed by Marcin Sobczyk in the Wall Street Journal.[100] Mamta Murthi from the World Bank said: "To be in 'a club', what Poland can do is to continue working as if it already is in the club it wants to join."[101]
In 2014, consulting company Ernst & Young published its report about optimal members for G20. After analyzing trade, institutional and investment links Poland was included as one of the optimal members.[102]
G20 membership has been part of the look program of Poland's Law and Justice party and President Andrzej Duda.[103] In March 2017, Deputy Prime Minister of Poland Mateusz Morawiecki took part in a meeting of G20 financial ministers in Baden-Baden as the first Polish representative.[104][105]
Global Governance Group (3G) response
[edit]In June 2010, Singapore's representative to the United Nations warned the G20 that its decisions would affect "all countries, big and small", and asserted that prominent non-G20 members should be included in financial reform discussions.[106] Singapore thereafter took a leading role in organizing the Global Governance Group (3G), an informal grouping of 30 non-G20 countries (including several microstates and many Third World countries) to collectively channel their views into the G20 process more effectively.[107][108][109] Singapore's chairing of the 3G was cited as a rationale for inviting Singapore to the November 2010 G20 summit in South Korea,[110] as well as 2011, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016, and 2017 summits.[citation needed]
Foreign Policy critiques
[edit]The American magazine Foreign Policy has published articles condemning the G20, in terms of its principal function as an alternative to the supposedly exclusive G8. It questions the actions of some of the G20 members and advances the notion that some states should not have membership in the first place. Furthermore, with the effects of the Great Recession still ongoing, the magazine has criticized the G20's efforts to implement reforms of the world's financial institutions, branding such efforts as failures.[111]
Calls for removal of Russia
[edit]This section needs to be updated. (January 2024) |
In March 2022, following the Russian invasion of Ukraine, U.S. President Joe Biden called for the removal of Russia from the group. Alternatively, he suggested that Ukraine be allowed to attend the G20 2022 summit, despite its lack of membership.[112] Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau also said the group should "re-evaluate" Russia's participation.[113] Russia claims it would not be a significant issue, as most G20 members are already fighting Russia economically due to the war.[114] China suggested that expelling Russia would be counterproductive.[112] In November 2022, Indonesia and Russia stated that Vladimir Putin would not attend the G20 summit in person, but may attend virtually.[115] During the 2022 summit, Ukrainian president Volodymyr Zelenskyy appeared in a video statement and repeatedly addressed the assembly as the 'G19' as a means of indicating his viewpoint that Russia should be removed from the group.[116]
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ 19 countries, the European Union (EU) and African Union (AU)
- ^ Summits were biannual in 2009 and 2010; since the November 2011 Cannes summit, G20 summits have been annual.
- ^ literally mean 'The World Is One Family'
- ^ Currently suspended from Partnership for Peace.
- ^ Excluding intra-EU trade. The complete number according to WTO stats dashboard: Total merchandise, Exports, 2023 in 2022 is 14,610.4 bil. USD
- ^ 23 out of 27 EU states are classified as advanced
- ^ International Monatary Fund: GDP per capita, current prices – U.S. dollars per capita
- ^ International Monatary Fund: GDP per capita, current prices – Purchasing power parity; international dollars per capita
- ^ 2020
- ^ 2021
References
[edit]- ^ a b "FAQ #5: What are the criteria for G-20 membership?". Archived 16 February 2009 at the Wayback Machine. G20.org. Retrieved 21 February 2013.
- ^ Pogge, Thomas (17 October 2023). "The African Union - Rising". Journal of Academics Stand Against Poverty. 3 (1). Department of Philosophy and Global Justice Program, Yale University, USA: 57–60. doi:10.5281/zenodo.10014908. ISSN 2690-3431. Retrieved 6 November 2024.
- ^ "The G20 has agreed to make the African Union a permanent member, Indian PM Modi says". World. NPR. Associated Press. 9 September 2023. Archived from the original on 9 September 2023. Retrieved 9 September 2023.
- ^ "G20 Finance Ministers Committed to Sustainable Development". IPS News. 9 September 2015. Archived from the original on 30 July 2022. Retrieved 4 December 2015.
- ^ a b "About". Rio Capital do G20. 17 October 2024. Retrieved 19 October 2024.
- ^ "Internationale Statistik: G20". Statistisches Bundesamt (in German). 23 November 2022. Retrieved 19 October 2024.
- ^ "About The G20 – G20 Presidency of Indonesia". Archived from the original on 9 August 2022. Retrieved 9 August 2022.
- ^ "Think Tanks". G20 Insights. Archived from the original on 12 December 2020. Retrieved 10 October 2020.
- ^ "Past Summits"
- ^ "Officials: G-20 to supplant G-8 as international economic council". CNN. 25 September 2009. Archived from the original on 6 November 2012. Retrieved 25 September 2009.
- ^ Global Politics. Andrew Heywood. 11 March 2014. ISBN 978-1-137-34926-2. Retrieved 4 December 2015.
- ^ a b c d e "Norway Takes Aim at G-20: 'One of the Greatest Setbacks Since World War II'". Der Spiegel. 22 June 2010. Archived from the original on 29 January 2012. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ Bosco, David (19 April 2012). "Who would replace Argentina on the G20?". Foreign Policy. Archived from the original on 31 October 2020. Retrieved 24 April 2012.
- ^ French, Cameron; Pav Jordan (17 June 2010). "Toronto G20 protest hints at more to come". Reuters. Toronto. Archived from the original on 27 October 2020. Retrieved 11 June 2020.
- ^ Abedi, Maham (7 July 2017). "G20 protests: Why the international summit attracts so much anger". Hamburg. Archived from the original on 11 May 2022. Retrieved 11 June 2020.
- ^ See, e.g., Woods 2006; Gilpin 2001; Markwell 2006.
- ^ "What is the G20?". University of Toronto. 2010. Archived from the original on 1 September 2022. Retrieved 12 November 2014.
- ^ Colin I. Bradford; Johannes F. Linn (2004). "Global Economics". Brookings Institution. Archived from the original on 11 May 2022. Retrieved 12 November 2014.
- ^ Bradford, Colin I. (23 June 2010). "Web Chat: Previewing the G-20 Summit". Brookings Institution. Archived from the original on 25 December 2020. Retrieved 7 July 2017.
- ^ a b c Kirton, John (17 December 2013). "Explaining G20 Summit Success". G20 Information Centre. Munk School of Global Affairs, University of Toronto. Archived from the original on 25 December 2020. Retrieved 7 July 2017.
- ^ a b "Who gets to rule the world" Archived 21 December 2013 at the Wayback Machine. Sean Kilpatrick. Maclean's magazine (Canada). 1 July 2010
- ^ a b c Ibbitson, John; Perkins, Tara (18 June 2010). "How Canada made the G20 happen". The Globe and Mail. Archived from the original on 6 September 2022. Retrieved 7 July 2017.
- ^ Thomas Axworthy. "Eight is not enough at summit." Archived 29 March 2024 at the Wayback Machine Toronto Star. 8 June 2007. Retrieved 16 April 2011.
- ^ Wade 2009, p. 553.
- ^ "US to host next G20 world meeting" Archived 31 May 2022 at the Wayback Machine. BBC News. 28 May 2009. Retrieved 9 December 2012.
- ^ "Leaders' statement, the Pittsburgh Summit," p. 19 §50 (PDF) Archived 12 June 2010 at the Wayback Machine. G20.org. 25 September 2009.
- ^ "G20". Bond.org.uk. Archived from the original on 24 June 2013. Retrieved 16 June 2013.
- ^ "Summit Rio 2024". www.g20.org.
- ^ "G20 Ministerial Meetings". G20 Research Group. Archived from the original on 21 August 2022. Retrieved 13 September 2014.
- ^ "G20 Los Cabos 2012: G20 Leaders Declaration". www.g20.utoronto.ca. Archived from the original on 31 August 2022. Retrieved 19 May 2020.
- ^ "Canberra considers barring Vladimir Putin from G20 in Brisbane over Crimea crisis" Archived 26 March 2014 at the Wayback Machine. The Australian. 20 March 2014. Retrieved 7 October 2015.
- ^ "Previous Summits". www.g20.org. Retrieved 7 April 2024.
- ^ Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Türkiye. "G20 Leaders' Summit was held in Antalya". www.mfa.gov.tr. Retrieved 7 April 2024.
- ^ Observer Research Foundation, Tanu M. Goyal and Prateek Kukreja (4 November 2020). "The Sustainable Development Agenda: Evaluating the G20 as a Stage for National and Collective Goals". Observer Research Foundation. Archived from the original on 25 April 2022. Retrieved 11 November 2020.
- ^ "G20 Action Plan on the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development" (PDF). G20 - 2016 China Summit. 8 September 2016. Archived from the original on 26 February 2021. Retrieved 11 November 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ "Japan to host G-20 summit in 2019 for 1st time". The Nikkei. 9 July 2017. Archived from the original on 7 August 2017. Retrieved 8 July 2017.
- ^ "Saudi Arabia to host G20 summit in 2020". The National. 8 July 2017. Archived from the original on 28 March 2019. Retrieved 8 July 2017.
- ^ "G20 summit, 15-16 November 2022". www.consilium.europa.eu. Archived from the original on 19 November 2022. Retrieved 19 November 2022.
- ^ "G20 hosts Official Launch of The Pandemic Fund". www.worldbank.org. Archived from the original on 14 January 2024. Retrieved 5 March 2024.
- ^ P, Rajesh (26 August 2023). "g20-summit-to-address-pressing-global-issues-2023". newsvaadi.com. Archived from the original on 26 August 2023. Retrieved 26 August 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ "'One Earth, One Family, One Future' will be theme of G-20 Presidency: PM Modi". mint. 16 November 2022. Archived from the original on 27 February 2023. Retrieved 9 August 2023.
- ^ Ghoshal, Devjyot (2 December 2022). "Explainer: India G20 presidency 2023: what does it mean and what can we expect". reuters.com. Reuters. Archived from the original on 30 May 2023. Retrieved 18 September 2023.
- ^ "PM Narendra Modi interview highlights: From G20 presidency to India as a manufacturing destination, PM lays out his expansive vision for the country". Business Today. 26 August 2023. Archived from the original on 28 August 2023. Retrieved 28 August 2023.
- ^ "Exclusive | PM Modi calls for global framework on cryptocurrency. Here's what he said". India Today. 26 August 2023. Archived from the original on 28 August 2023. Retrieved 28 August 2023.
- ^ "'G20 की अध्यक्षता कर पूरी दुनिया को नई राह दिखा रहा भारत', Exclusive इंटरव्यू में बोले पीएम मोदी". आज तक (in Hindi). 26 August 2023. Archived from the original on 28 August 2023. Retrieved 28 August 2023.
- ^ "Understand what the G20 is and what Brazil's responsibilities are". G20 org. 1 December 2023. Archived from the original on 1 December 2023. Retrieved 1 December 2023.
- ^ Carin, Barry (4 November 2010). "The Future of the G20 Process". Centre for International Governance Innovation. Archived from the original on 15 April 2012. Retrieved 19 October 2011.
- ^ "The Rotating G20 Presidency: How do member countries take turns?". boell.de. 30 November 2016. Archived from the original on 23 March 2022. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ "G20 Members". g20.org.tr. Archived from the original on 22 January 2019. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ "National Portal of India". National Portal of India. 1 December 2022. Retrieved 19 October 2024.
- ^ "India to host G20 summit in 2023 after Italy, Indonesia; Brazil to hold presidency in 2024". India Today. 22 November 2020. Archived from the original on 26 April 2022. Retrieved 23 November 2020.
- ^ Wouters & Van Kerckhoven 2011.
- ^ a b c "Who Would Host a G20 Secretariat?" Archived 16 November 2010 at the Wayback Machine Chosun Ilbo. 15 November 2010. Retrieved 14 March 2013.
- ^ "G20 Members". G20 2015 Turkey. Archived from the original on 22 January 2019. Retrieved 4 December 2018.
- ^ Joe Tambini (7 July 2017). "G20 2017 countries: Who are the members of the G20?". Express. Archived from the original on 3 July 2019. Retrieved 4 December 2018.
- ^ a b c d Henley, Peter H.; Blokker, Niels M. "The Group of 20: A Short Legal Anatomy" (PDF). Melbourne Journal of International Law. 14: 568. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 May 2017. Retrieved 23 October 2018.
Spain's peculiar but seemingly secure position within the G20 also appears to have facilitated their greater participation in the G20's work: Spain is the only outreach participant to have made policy commitments comparable to those of G20 members proper at summits since Seoul. Spain therefore appears to have become a de facto member of the G20.
- ^ a b "G20 Members". G20.org. Archived from the original on 3 February 2014. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ "The G20 and the world". G20 Australia 2014. Archived from the original on 11 February 2014. Retrieved 12 April 2014.
- ^ "What is the G-20". G20.org. Archived from the original on 20 November 2013. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ Inaugural Session Of The G20 Summit (English Audio), 8 September 2023, archived from the original on 10 September 2023, retrieved 9 September 2023
- ^ "President Xi not coming for G 20, Premier Li takes his place". Hindustan Times. 1 September 2023. Archived from the original on 3 September 2023. Retrieved 4 September 2023.
- ^ "China Premier Li Qiang to attend G20 Sept 9-10". Business Recorder. 4 September 2023. Archived from the original on 4 September 2023. Retrieved 4 September 2023.
- ^ "China Premier Li Qiang to attend G20 Sept 9-10 - foreign ministry". Devdiscourse. 4 September 2023. Archived from the original on 4 September 2023. Retrieved 4 September 2023.
- ^ "Van Rompuy and Barroso to both represent EU at G20". EUobserver. 19 March 2010. Archived from the original on 12 December 2020. Retrieved 19 May 2020.
- ^ a b "About Economic Development, Integration and Trade". Archived from the original on 21 October 2023. Retrieved 9 September 2023.
- ^ "WTO Stats". World Trade Organization. Archived from the original on 9 November 2022. Retrieved 15 April 2023.
- ^ a b c d "Report for Selected Countries and Subjects: October 2024". imf.org. International Monetary Fund.
- ^ "Human Development Report 2023/2024" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 13 March 2024. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 March 2024. Retrieved 30 April 2024.
- ^ "CIA Statistics". CIA Statistics. November 2022. Archived from the original on 1 September 2021. Retrieved 4 November 2022.
- ^ "World Economic Outlook Database: WEO Groups and Aggregates Information". International Monetary Fund. April 2017. Archived from the original on 1 September 2022. Retrieved 10 October 2017.
- ^ "World Economic Outlook: Frequently Asked Questions. Q. How does the WEO categorize advanced versus emerging market and developing economies?". International Monetary Fund. 29 July 2017. Archived from the original on 30 April 2011. Retrieved 10 October 2017.
- ^ Norman, Izzah Aqilah (24 October 2024). "Malaysia, Indonesia, Vietnam and Thailand become partner countries of BRICS". Singapore. Channel News Asia. Retrieved 6 November 2024.
- ^ a b "Asia to play bigger role on the world stage, G20: ADB report". The People's Daily. 26 April 2011. Archived from the original on 12 November 2013. Retrieved 26 April 2011.
- ^ "International Organisations". G-20 Australia. 2014. Archived from the original on 3 July 2016. Retrieved 22 December 2014.
- ^ a b "G20 and the world" Archived 16 March 2015 at the Wayback Machine. G20.org. 2015. Retrieved 16 April 2015.
- ^ Ibbitson, John (18 June 2016). "How Canada Made the G20 Happen". theglobeandmail.com. Toronto. Archived from the original on 6 September 2022. Retrieved 18 July 2017.
- ^ Liao, Rebecca (September 2016). "The End of the G-20". Foreign Affairs. Archived from the original on 12 May 2022. Retrieved 20 July 2017. – via Foreign Affairs (subscription required)
- ^ a b The Federal Government, of Germany (1 December 2016). "The G20 Presidency 2017 at a Glance". G20.org. Berlin. Archived from the original on 6 July 2017. Retrieved 6 July 2017.
- ^ Chen, Muyang (2024). The Latecomer's Rise: Policy Banks and the Globalization of China's Development Finance. Ithaca and London: Cornell University Press. ISBN 9781501775857. JSTOR 10.7591/jj.6230186.
- ^ a b c "'Reckless': G20 states subsidised fossil fuels by $3tn since 2015, says report". the Guardian. 20 July 2021. Archived from the original on 3 September 2022. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- ^ a b Firzli, M. Nicolas J. (7 July 2017). "G20 Nations Shifting the Trillions: Impact Investing, Green Infrastructure and Inclusive Growth" (PDF). Revue Analyse Financière. Paris. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 August 2017. Retrieved 7 July 2017.
- ^ Abschlusserklärung steht – Dissens bleibt. Archived 11 July 2017 at the Wayback Machine tagesschau.de. 8 July 2017, retrieved 12 July 2017.
- ^ Andersen, Inger (28 July 2023). "The G20 is a global force for sustainability". UN environment programme. United Nations. Archived from the original on 18 September 2023. Retrieved 12 September 2023.
- ^ "China generated over half world's coal-fired power in 2020: study". Reuters. 28 March 2021. Archived from the original on 1 September 2022. Retrieved 14 September 2021.
China generated 53% of the world's total coal-fired power in 2020, nine percentage points more than five years earlier
- ^ "Startup20 India Initiative by G20 India 2023 | Startup20". Archived from the original on 9 April 2023. Retrieved 9 April 2023.
- ^ Berensmann, Kathrin; Fues, Thomas; Volz, Ulrich (January 2011). "Informal power centre". D+C. Archived from the original on 1 January 2011. Retrieved 3 December 2012.
- ^ Chaturvedi, Sachin (January 2011). "Mainstream Heiligendamm". D+C. Archived from the original on 1 January 2011. Retrieved 3 December 2012.
- ^ Daniele Archibugi. "The G20 ought to be increased to 6 Billion" Archived 21 January 2010 at the Wayback Machine. OpenDemocracy.net. 31 March 2009. Retrieved 26 April 2013.
- ^ Stewart, Frances and Daws, Sam. "An Economic and Social Security Council at the United Nations" (PDF). Archived 4 March 2004 at the Wayback Machine. Oxford University. March 2001. Retrieved 8 January 2013.
- ^ Mahoney, Jill; Ann Hui (29 June 2010). "G20-related mass arrests unique in Canadian history". Toronto: The Globe and Mail. Archived from the original on 28 July 2010. Retrieved 17 March 2022.
- ^ "About G-20" Archived 5 February 2009 at the Wayback Machine. G20.org. Retrieved 11 December 2012.
- ^ Vestergaard, Jakob (April 2011). "The G20 and Beyond: Towards Effective Global Economic Governance" (PDF). DIIS Report. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 May 2013. Retrieved 25 June 2013.
- ^ Chernenkoff, Kelly (25 September 2009). "Obama to Usher In New World Order at G-20". Fox News. Archived from the original on 16 November 2018. Retrieved 24 December 2015.
- ^ Cooper 2011.
- ^ "Norway and the UN". Norway.org. 12 May 2012. Archived from the original on 3 June 2012. Retrieved 12 May 2012.
- ^ "Solberg eager to speak up at G20". News in English.no. 7 July 2017. Archived from the original on 7 July 2017. Retrieved 7 July 2017.
- ^ Kamila Wronowska (2 March 2010). "Polska w G-20 – warto się bić?" [Poland in the G-20 – is it worth the fight?]. dziennik.pl (in Polish). Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 23 March 2015.
- ^ Ferguson, Tim. "G20: Boot Argentina, Include Poland". Forbes. Archived from the original on 29 July 2017. Retrieved 28 August 2017.
- ^ Bosco, David (18 December 2023). "Who would replace Argentina on the G20?". Archived from the original on 31 October 2020. Retrieved 7 March 2017.
- ^ Sobczyk, Marcin (3 February 2010). "G20 Needs Poland". Wall Street Journal. Archived from the original on 9 July 2017. Retrieved 1 June 2017.
- ^ "World Bank in the Krynica Economic Forum – the 'Davos for Eastern Europe'". World Bank. Archived from the original on 13 August 2021. Retrieved 8 April 2021.
- ^ "Polska w grupie G20: jeśli tam nie będziemy, inni będą decydować za nas". Polskie Radio (in Polish). Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 23 March 2015.
- ^ "Wyborcza.pl". wyborcza.pl. Archived from the original on 16 July 2015. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^ "Rzeczy, które musisz wiedzieć o szczycie G20". TVN24 BiS (in Polish). Archived from the original on 17 March 2017. Retrieved 31 March 2017.
- ^ "Morawiecki wśród ministrów finansów G20 – Gospodarka". rp.pl. Archived from the original on 20 June 2021. Retrieved 31 March 2017.
- ^ "Statement by Ambassador Vanu Gopala Menon, Permanent Representative of Singapore to the United Nations". Singapore UN Mission. 8 June 2010. Archived from the original on 3 April 2015. Retrieved 16 November 2013.
- ^ "Press Statement by the Global Governance Group (3G) on its Ninth Ministerial Meeting in New York on 22 September 2016". mfa. 22 September 2016. Archived from the original on 30 July 2017. Retrieved 23 July 2017.
- ^ "SIIA welcomes new 3G initiative for small states" Archived 7 November 2021 at the Wayback Machine. Singapore Institute of International Affairs. 12 February 2010. Retrieved 16 November 2013.
- ^ "Statement by Singapore on behalf of the Global Governance Group" (PDF). Archived 14 May 2011 at the Wayback Machine. United Nations. 2 June 2010. Retrieved 12 February 2013.
- ^ "Singapore among five non-G20 nations to attend Seoul Summit" Archived 22 July 2012 at archive.today. International Business Times. 25 September 2010. Retrieved 12 February 2013.
- ^ Truman, Edwin M. (12 April 2012). "The G-20 Is Failing". Foreign Policy. Archived from the original on 29 July 2013. Retrieved 24 April 2012.
- ^ a b Sommerlad, Joe (25 March 2022). "What is the G20 and could Russia be expelled?". The Independent. Archived from the original on 25 March 2022. Retrieved 25 March 2022.
- ^ Boisvert, Nick (31 March 2022). "Trudeau calls on G20 to reconsider Russia's seat at the table". CBC News. Archived from the original on 5 July 2022. Retrieved 31 March 2022.
- ^ Pettypiece, Shannon (24 March 2022). "Biden says allies must stay united against Russia, expel it from the G-20". NBC News. Archived from the original on 25 March 2022. Retrieved 25 March 2022.
- ^ Teresia, Ananda (10 November 2022). "Russia's Putin will not attend G20 summit in Bali in person". Reuters. Archived from the original on 10 November 2022. Retrieved 12 November 2022.
- ^ Wong, Tessa (15 November 2022). "Ukraine: Zelensky snubs Russia as he addresses 'G19' at G20". BBC. Archived from the original on 15 November 2022. Retrieved 15 November 2022.
Bibliography
[edit]- Cooper, Andrew F. (2011). "The G20 and Its Regional Critics: The Search for Inclusion". Global Policy. 2 (2): 203–209. doi:10.1111/j.1758-5899.2011.00081.x. ISSN 1758-5899.
- Gilpin, Robert (2001). Global Political Economy: Understanding the International Economic Order. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-08676-7.
- Markwell, Donald (2006). John Maynard Keynes and International Relations: Economic Paths to War and Peace. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780198292364.001.0001. ISBN 978-0-19-829236-4.
- Wade, Robert (2009). "From Global Imbalances to Global Reorganisations". Cambridge Journal of Economics. 33 (4): 539–562. doi:10.1093/cje/bep032. hdl:10.1093/cje/bep032. ISSN 1464-3545.
- Woods, Ngaire (2006). The Globalizers: The IMF, the World Bank, and Their Borrowers. Cornell Studies in Money. Ithaca, New York: Cornell University Press. ISBN 978-0-8014-4424-1. JSTOR 10.7591/j.ctt1ffjpgn.
- Wouters, Jan; Van Kerckhoven, Sven (2011). "OECD and the G20: An Ever Closer Relationship" (PDF). George Washington International Law Review. 43 (2): 345–374. ISSN 1534-9977. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 August 2017. Retrieved 7 July 2017.
Further reading
[edit]- Haas, Peter M. (1992). "Introduction: Epistemic Communities and International Policy Coordination" (PDF). International Organization. 46 (1): 1–35. doi:10.1017/S0020818300001442. ISSN 1531-5088. JSTOR 2706951. S2CID 145360263. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 September 2015.
- Hajnal, Peter I. (2007). The G8 System and the G20: Evolution, Role and Documentation. Global Finance Series. Aldershot, England: Ashgate Publishing. ISBN 978-0-7546-4550-4.
- Kirton, John J. (2013). G20 Governance for a Globalized World. Global Finance Series. Abingdon, England: Routledge. ISBN 978-1-4094-2829-9.
- Reinalda, Bob; Verbeek, Bertjan, eds. (1998). Autonomous Policy Making by International Organizations. Routledge/ECPR Studies in European Political Science. Vol. 5. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-16486-3.
- Samans, Richard; Uzan, Marc; Lopez-Claros, Augusto, eds. (2007). The International Monetary System, the IMF and the G-20: A Great Transformation in the Making?. Basingstoke, England: Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-230-52495-8.
- Firzli, Nicolas J. (2017). "G20 Nations Shifting the Trillions: Impact Investing, Green Infrastructure and Inclusive Growth" (PDF). Revue Analyse Financière. 64 (3): 15–18. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 August 2017.
External links
[edit]- G20
- Economic country classifications
- Intergovernmental organizations
- Organizations established in 1999
- African Union–European Union relations
- Argentina–Australia relations
- Argentina–Brazil relations
- Argentina–Canada relations
- Argentina–China relations
- Argentina–European Union relations
- Argentina–France relations
- Argentina–Germany relations
- Argentina–India relations
- Argentina–Indonesia relations
- Argentina–Italy relations
- Argentina–Japan relations
- Argentina–Mexico relations
- Argentina–Russia relations
- Argentina–Saudi Arabia relations
- Argentina–South Africa relations
- Argentina–South Korea relations
- Argentina–Turkey relations
- Argentina–United Kingdom relations
- Argentina–United States relations
- Australia–Brazil relations
- Australia–Canada relations
- Australia–China relations
- Australia–European Union relations
- Australia–France relations
- Australia–Germany relations
- Australia–India relations
- Australia–Indonesia relations
- Australia–Italy relations
- Australia–Japan relations
- Australia–Mexico relations
- Australia–Russia relations
- Australia–Saudi Arabia relations
- Australia–South Africa relations
- Australia–South Korea relations
- Australia–Turkey relations
- Australia–United Kingdom relations
- Australia–United States relations
- Brazil–Canada relations
- Brazil–China relations
- Brazil–European Union relations
- Brazil–France relations
- Brazil–Germany relations
- Brazil–India relations
- Brazil–Indonesia relations
- Brazil–Italy relations
- Brazil–Japan relations
- Brazil–Mexico relations
- Brazil–Russia relations
- Brazil–Saudi Arabia relations
- Brazil–South Africa relations
- Brazil–South Korea relations
- Brazil–Turkey relations
- Brazil–United Kingdom relations
- Brazil–United States relations
- Canada–China relations
- Canada–European Union relations
- Canada–France relations
- Canada–Germany relations
- Canada–India relations
- Canada–Indonesia relations
- Canada–Italy relations
- Canada–Japan relations
- Canada–Mexico relations
- Canada–Russia relations
- Canada–Saudi Arabia relations
- Canada–South Africa relations
- Canada–South Korea relations
- Canada–Turkey relations
- Canada–United Kingdom relations
- Canada–United States relations
- China–France relations
- China–European Union relations
- China–Germany relations
- China–India relations
- China–Indonesia relations
- China–Italy relations
- China–Japan relations
- China–Mexico relations
- China–Russia relations
- China–Saudi Arabia relations
- China–South Africa relations
- China–South Korea relations
- China–Turkey relations
- China–United Kingdom relations
- China–United States relations
- India–European Union relations
- Indonesia–European Union relations
- Japan–European Union relations
- Mexico–European Union relations
- Russia–European Union relations
- Saudi Arabia–European Union relations
- South Africa–European Union relations
- South Korea–European Union relations
- Turkey–European Union relations
- United States–European Union relations
- France–Germany relations
- France–India relations
- France–Indonesia relations
- France–Italy relations
- France–Japan relations
- France–Mexico relations
- France–Russia relations
- France–Saudi Arabia relations
- France–South Africa relations
- France–South Korea relations
- France–Turkey relations
- France–United Kingdom relations
- France–United States relations
- Germany–India relations
- Germany–Indonesia relations
- Germany–Italy relations
- Germany–Japan relations
- Germany–Mexico relations
- Germany–Russia relations
- Germany–Saudi Arabia relations
- Germany–South Africa relations
- Germany–South Korea relations
- Germany–Turkey relations
- Germany–United Kingdom relations
- Germany–United States relations
- India–Indonesia relations
- India–Italy relations
- India–Japan relations
- India–Mexico relations
- India–Russia relations
- India–Saudi Arabia relations
- India–South Africa relations
- India–South Korea relations
- India–Turkey relations
- India–United Kingdom relations
- India–United States relations
- Indonesia–Italy relations
- Indonesia–Japan relations
- Indonesia–Mexico relations
- Indonesia–Russia relations
- Indonesia–Saudi Arabia relations
- Indonesia–South Africa relations
- Indonesia–South Korea relations
- Indonesia–Turkey relations
- Indonesia–United Kingdom relations
- Indonesia–United States relations
- Italy–Japan relations
- Italy–Mexico relations
- Italy–Russia relations
- Italy–Saudi Arabia relations
- Italy–South Africa relations
- Italy–South Korea relations
- Italy–Turkey relations
- Italy–United Kingdom relations
- Italy–United States relations
- Japan–Mexico relations
- Japan–Russia relations
- Japan–Saudi Arabia relations
- Japan–South Africa relations
- Japan–South Korea relations
- Japan–Turkey relations
- Japan–United Kingdom relations
- Japan–United States relations
- Mexico–Russia relations
- Mexico–Saudi Arabia relations
- Mexico–South Africa relations
- Mexico–South Korea relations
- Mexico–Turkey relations
- Mexico–United Kingdom relations
- Mexico–United States relations
- Russia–Saudi Arabia relations
- Russia–South Africa relations
- Russia–South Korea relations
- Russia–Turkey relations
- Russia–United Kingdom relations
- Russia–United States relations
- Saudi Arabia–South Africa relations
- Saudi Arabia–South Korea relations
- Saudi Arabia–Turkey relations
- Saudi Arabia–United Kingdom relations
- Saudi Arabia–United States relations
- South Africa–South Korea relations
- South Africa–Turkey relations
- South Africa–United Kingdom relations
- South Africa–United States relations
- South Korea–Turkey relations
- South Korea–United Kingdom relations
- South Korea–United States relations
- Turkey–United Kingdom relations
- Turkey–United States relations
- United Kingdom–United States relations
- Multilateral relations of Brazil
- Multilateral relations of China
- Multilateral relations of India
- Multilateral relations of Russia
- Multilateral relations of South Africa
- Multilateral relations of the United Kingdom
- Multilateral relations of the United States