Eastern European Time
| Eastern European Time | |
|---|---|
| Time zone | |
 Eastern European Time | |
| UTC offset | |
| EET | UTC+02:00 |
| EEST | UTC+03:00 |
| Current time | |
| 01:32, 23 November 2024 EET [refresh] | |
| Observance of DST | |
| DST is observed throughout this time zone. | |

| Light Blue | Western European Time / Greenwich Mean Time (UTC) |
| Blue | Western European Time / Greenwich Mean Time (UTC) |
| Western European Summer Time / British Summer Time / Irish Standard Time (UTC+1) | |
| Red | Central European Time (UTC+1) |
| Central European Summer Time (UTC+2) | |
| Yellow | Eastern European Time / Kaliningrad Time (UTC+2) |
| Ochre | Eastern European Time (UTC+2) |
| Eastern European Summer Time (UTC+3) | |
| Green | Moscow Time / Turkey Time (UTC+3) |
| Turquoise | Armenia Time / Azerbaijan Time / Georgia Time / Samara Time (UTC+4) |
▉▉▉ Dark colours: Summer time observed
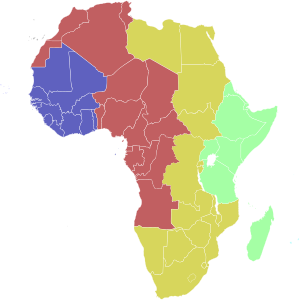
| Light Blue | Cape Verde Time[a] (UTC−1) |
| Blue | Greenwich Mean Time (UTC) |
| Red | (UTC+1) |
| Ochre | (UTC+2) |
| Green | East Africa Time (UTC+3) |
| Turquoise | (UTC+4) |
b Mauritius and the Seychelles are to the east and north-east of Madagascar respectively.

▉▉▉ Standard time observed all year
▉ Daylight saving time observed
Eastern European Time (EET) is one of the names of UTC+02:00 time zone, 2 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. The zone uses daylight saving time, so that it uses UTC+03:00 during the summer.
A number of African countries use UTC+02:00 all year long, where it is called Central Africa Time (CAT),[1] although Egypt and Libya also use the term Eastern European Time.[2]
The most populous city in the Eastern European Time zone is Cairo, with the most populous EET city in Europe being Kyiv.
Usage
[edit]The following countries, parts of countries, and territories use Eastern European Time all year round:
- Egypt, since 21 April 2015; used EEST (UTC+02:00; UTC+03:00 with daylight saving time) from 1988 to 2010 and 16 May – 26 September 2014. See also Egypt Standard Time.
- Kaliningrad Oblast (Russia), since 26 October 2014; also used EET in the years 1945 and 1991–2011. See also Kaliningrad Time.
- Libya, since 27 October 2013; switched from Central European Time, which was used in 2012. Used year-round EET from 1980 to 1981, 1990–1996 and 1998–2012.
The following countries, parts of countries, and territories use Eastern European Time during the winter only:
- Bulgaria, since 1894, except between 1942 and 1945
- Estonia, in the years 1921–40 and since 1990
- Finland, since 1921
- Greece, since 1916
- Israel, since 1948 (see also Israel Standard Time)
- Latvia, in the years 1926–40 and since 1990
- Lebanon
- Lithuania, in 1920–40 and since 1990 with break 1998–1999
- Moldova, in the years 1918–40, 1941–44 and since 1991
- Including Transnistria
- Palestine (see also Palestine Standard Time)
- Romania
- Ukraine, in the years 1922–30 and since 1990[3]
The following countries, parts of countries, and territories used Eastern European Time in the past:
- Moscow used EET in the years 1922–30 and 1991–92.
- Belarus, in the years 1922–30 and 1990–2011[4]
- Jordan used EET until permanently switching to DST in 2022.[5]
- In Poland, this time was used in the years 1919–22.
- Crimea used EET as part of Ukraine between 1991–1994 and 1996–2014 and started using Moscow Time due to the annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation in 2014.
- Syria used EET until permanently switching to DST in 2022.[5]
- Turkey, used EET in the years 1910–1978 and re-used it again in the years 1985–2016.[6]
Sometimes, due to its use on Microsoft Windows,[7] FLE Standard Time (for Finland, Lithuania, Estonia,[8] or sometimes Finland, Latvia, Estonia[9]) or GTB Standard Time (for Greece, Turkey, Bulgaria) are used to refer to Eastern European Time.
Anomalies
[edit]Since political, in addition to purely geographical, criteria are used in the drawing of time zones, it follows that time zones do not precisely adhere to meridian lines. The EET (UTC+02:00) time zone, were it drawn by purely geographical terms, would consist of exactly the area between meridians 22°30' E and 37°30' E. As a result, there are European locales that despite lying in an area with a "physical" UTC+02:00 time, are in another time zone; likewise, there are European areas that have gone for UTC+02:00, even though their "physical" time zone is different from that. Following is a list of such anomalies:
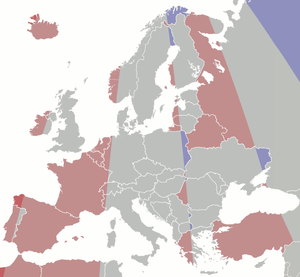
| Colour | Legal time vs local mean time |
|---|---|
| 1 h ± 30 m behind | |
| 0 h ± 30 m | |
| 1 h ± 30 m ahead | |
| 2 h ± 30 m ahead | |
| 3 h ± 30 m ahead |
- The westernmost part of Greece, including the cities of Patras and Ioannina, and the Ionian Islands
- The very westernmost parts of the Bulgarian provinces of Vidin and Kyustendil
- The westernmost part of Romania, including most of the area of the counties of Caraș-Severin, Timiș (capital Timișoara), Arad, and Bihor, as well as the westernmost tips of the counties of Mehedinți and Satu Mare
- The extreme westernmost tip of Ukraine, near the border with Hungary and Slovakia, at the Ukrainian Transcarpathian Oblast (Zakarpattia Oblast), essentially comprising the city of Uzhhorod and its environs
- Most of the Kaliningrad Oblast, including the cities of Kaliningrad and Baltiysk
- Western Lithuania, including the cities of Klaipėda, Tauragė, and Telšiai
- Western Latvia, including the cities of Liepāja and Ventspils
- The westernmost parts of the Estonian islands of Saaremaa and Hiiumaa, including the capital of the Saare County, Kuressaare
- The southwestern coast of Finland, including the city of Turku; also the Åland islands (of Finnish jurisdiction) – the Åland islands are the westernmost locale applying EET in the whole of Europe
- Most of Libya including the capital Tripoli
- The western half of the munincipality of Enontekiö in northwestern Finland
Areas east of 37°30' E ("physical" UTC+03:00) that use UTC+02:00
These areas have sunrises and sunsets at least half an hour earlier than places on the UTC+01:00 meridian.
- The easternmost part of North Macedonia, including the city of Strumica.
- The absolutely easternmost part of Serbia, in the Pirot District, including the city of Pirot.
- The extreme easternmost tips of Hungary and Slovakia, bordering to the north and south respectively the Ukrainian Transcarpathian Oblast (Zakarpattia Oblast), a bit to the east of the Vásárosnamény, Hungary – Uzhhorod, Ukraine (both at 22°18' E) line
- The easternmost part of Poland, including the cities of Lublin and Białystok
- The extreme northeast of Sweden, in the Norrbotten province, including the cities of Kalix and Haparanda
- The northeast of Norway, lying north of Finland, roughly coinciding with the county of Finnmark. The easternmost town in Norway, Vardø, lies at 30°51' E, which is east of the central meridian of UTC+02:00, i.e. east of Istanbul and Alexandria. The Norwegian-Russian border and Belarus–Poland border are the only places where CET (UTC+1) borders Moscow time (UTC+03:00), resulting in a one (or two in winter) hour time change when crossing that border. There is a "tri-zone" point (where UTC+01:00, UTC+02:00, and UTC+03:00 meet) at the Norway-Finland-Russia tripoint, near the town of Rayakoski.
Most of the following countries use winter time year round, so they coincide with Eastern European Summer Time in summer.
- Belarus is between 23°11′E and 32°47′E and is thus fully within the physical UTC+02:00 area, but it uses UTC+03:00 year around.
- Practically all European Russia west of Moscow (except Kaliningrad Oblast); this includes the chunk of land from Murmansk all the way south to Belgorod, including the cities of St. Petersburg, Novgorod, and Pskov, to name only a few. (The westernmost point of contiguous Russia, near Lavry, Pskov Oblast, 27°19' E, is the westernmost point in European Russia where UTC+03:00 is applied.) This also includes the city of Anapa, at the westernmost tip of the Krasnodar Krai near the entrance to the Sea of Azov, at 37°22' E.
- Parts of western Syria, including the capital Damascus
- Most of Jordan, including the capital Amman
- Western half of Turkey, including the capital Ankara and the most populous city Istanbul
Tripoints and borders between zones
[edit]- The Norway–Russia–Finland "tri-zone" point at Muotkavaara (see Central European Time) is surrounded by three different times in winter, two in summer. It had three time zones year-around before 2014.
- Two of the four tripoints of Belarus and the tripoint of the Kaliningrad Region are surrounded by three different times in winter.
Major metropolitan areas
[edit]Winter only
- Athens, Greece
- Beirut, Lebanon
- Brașov, Romania
- Bucharest, Romania
- Chișinău, Moldova
- Cluj-Napoca, Romania
- Constanța, Romania
- Daugavpils, Latvia
- Dnipro, Ukraine
- Gaza, Palestine
- Helsinki, Finland
- Iași, Romania
- Jerusalem, Israel/Palestine
- Kaunas, Lithuania
- Kharkiv, Ukraine
- Kyiv, Ukraine
- Nicosia, Cyprus
- Odesa, Ukraine
- Oradea, Romania
- Oulu, Finland
- Plovdiv, Bulgaria
- Ramallah, Palestine
- Riga, Latvia
- Sofia, Bulgaria
- Tallinn, Estonia
- Tampere, Finland
- Tel Aviv, Israel
- Thessaloniki, Greece
- Timișoara, Romania
- Turku, Finland
- Varna, Bulgaria
- Vilnius, Lithuania
Year round
- Alexandria, Egypt
- Benghazi, Libya
- Cairo, Egypt
- Giza, Egypt
- Kaliningrad, Russia
- Port Said, Egypt
- Tripoli, Libya
References
[edit]- ^ "CAT – Central Africa Time (Time Zone Abbreviation)". www.timeanddate.com. Retrieved 2019-04-10.
- ^ "EET – Eastern European Time (Time Zone Abbreviation)". www.timeanddate.com. Retrieved 2019-04-10.
- ^ Ukraine to return to standard time on Oct. 30 (updated) Archived October 18, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Eternal Daylight Saving Time (DST) in Belarus".
- ^ a b "Syria and Jordan to Remain on Permanent DST". timeanddate. 5 October 2022. Retrieved 14 March 2024.
- ^ "Time Zone & Clock Changes in Istanbul, Turkey". timeanddate.com. Retrieved 6 May 2020.
- ^ "TimeZone". Microsoft.
- ^ "FLE". TheFreeDictionary.com.
- ^ "Finland Latvia Estonia Time". TheFreeDictionary.com.
