Flowgorithm
 | |
| Paradigm | Structured, imperative |
|---|---|
| Designed by | Devin Cook |
| First appeared | 2014 |
| Stable release | 4.5.0
/ October 8, 2024 |
| Typing discipline | Static, strong, safe |
| Implementation language | C# |
| OS | Windows (planned for OS X and Linux) |
| License | Freeware |
| Filename extensions | .fprg |
| Website | flowgorithm |
| Influenced by | |
| Flowcharts | |
Flowgorithm is a graphical authoring tool which allows users to write and execute programs using flowcharts. The approach is designed to emphasize the algorithm rather than the syntax of a specific programming language.[1] The flowchart can be converted to several major programming languages. Flowgorithm was created at Sacramento State University.[2]
Origin of name
[edit]The name is a portmanteau of "flowchart" and "algorithm".[3]
Supported programming languages
[edit]Flowgorithm can interactively translate flowchart programs into source code written in other programming languages. As the user steps through their flowchart, the related code in the translated program is automatically highlighted. The following programming languages are supported:[4]
Multilingual support
[edit]Besides English, Flowgorithm supports other spoken languages. These are:[4]
- Arabic
- Chinese (Simplified & Traditional)
- Czech
- Dutch
- French
- Galician
- German
- Hungarian
- Indonesian
- Italian
- Japanese
- Mongolian
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Russian
- Slovenian
- Spanish - Mexican and Castilian dialects
- Thai
- Turkish
- Ukrainian
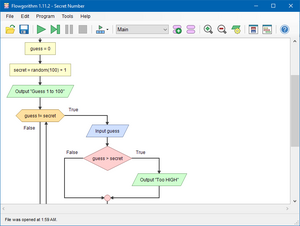
Graphical shapes
[edit]Flowgorithm combines the classic flowchart symbols and those used by SDL diagrams. The color of each shape is shared by the associated generated code and the console window. The colors can be changed to several built-in themes.
Example
[edit]The image below has the solution for 99 Bottles of Beer. A function is used to return a string that either contains the singular "bottle" or plural "bottles" depending on the value of the parameter.

See also
[edit]Other educational programming languages include:
- Alice
- DRAKON
- LARP
- Microsoft Small Basic
- Raptor
- Scratch
- Blockly, interface used by Scratch to make the code blocks
- Visual Logic
References
[edit]- ^ "ASEE PSW-2015 Conference Proceedings" (PDF). asee.org. p. 158. Retrieved 2016-05-04.
- ^ Kourouma, Mathieu (22 October 2016). "Capabilities and Features of Raptor, Visual Logic, and Flowgorithm for Program Logic and Design". ResearchGate. Retrieved 16 July 2017.
- ^ "Info". Flowgorithm. Archived from the original on 2016-03-16. Retrieved 2016-01-15.
- ^ a b "Features". Flowgorithm. Archived from the original on 2015-12-09. Retrieved 2016-01-15.

