File:Subhash nucleoid 08.png
Page contents not supported in other languages.
Tools
Actions
General
In other projects
Appearance

Size of this preview: 800 × 538 pixels. Other resolutions: 320 × 215 pixels | 640 × 430 pixels | 1,024 × 689 pixels | 1,280 × 861 pixels | 2,714 × 1,825 pixels.
Original file (2,714 × 1,825 pixels, file size: 261 KB, MIME type: image/png)
| This is a file from the Wikimedia Commons. Information from its description page there is shown below. Commons is a freely licensed media file repository. You can help. |
Summary
| DescriptionSubhash nucleoid 08.png |
English: Nucleoid is spatially organized into chromosomal interactions domains (CIDs) and macrodomains A. Chromosome conformation capture (3C) methods probe 3D genome organization by quantifying physical interactions between genomic loci that are nearby in 3D-space but may be far away in the linear genome. A genome is cross-linked with formaldehyde to preserve physical contacts between genomic loci. Subsequently, the genome is digested with a restriction enzyme. In the next step, a DNA ligation is carried out under diluted DNA concentrations to favor intra-molecular ligation (between cross-linked fragments that are brought into physical proximity by 3D genome organization). A frequency of ligation events between distant DNA sites reflects a physical interaction. In the 3C method, ligation junctions are detected by the semi-quantitative PCR amplification in which amplification efficiency is a rough estimate of pairwise physical contact between genomic regions of interests and its frequency. The 3C method probes a physical interaction between two specific regions identified a priori, whereas its Hi-C version detects physical interactions between all possible pairs of genomic regions simultaneously. In the Hi-C method, digested ends are filled in with a biotinylated adaptor before ligation. Ligated fragments are sheared and then enriched by a biotin-pull down. Ligation junctions are then detected and quantified by the paired-end next-generation sequencing methods. B. Hi-C data are typically represented in the form of a two-dimensional matrix in which the x-axis and y-axis represent the genomic coordinates. The genome is usually divided into bins of a fixed size, e.g., 5-kb. The size of bins essentially defines the contact resolution. Each entry in the matrix, mij, represents the number of chimeric sequencing reads mapped to genomic loci in bins i and j. A quantification of the reads (represented as a heatmap) denotes the relative frequency of contacts between genomic loci of bins i and j. A prominent feature of the heatmap is a diagonal line that appears due to more frequent physical interaction between loci that are very close to each other in the linear genome. The intensity as we move away from this diagonal line represents the relative frequency of physical interaction between loci that are far away from each other in the linear genome. Triangles of high-intensity along the diagonal line represent highly self-interacting chromosomal interaction domains (CIDs) that are separated by a boundary region that consists of a smaller number of interactions. C. In many bacterial species including E. coli, it appears that supercoiled topological domains organize as CIDs. Plectonemic supercoiling promotes a high level of interaction among genomic loci within a CID, and a plectoneme-free region (PFR), created due to high transcription activity, acts as a CID boundary. Nucleoid-associated proteins, depicted as closed circles, stabilize the supercoiling-mediated interactions. The actively transcribing RNA polymerase (depicted as a green sphere) in the PFR blocks dissipation of supercoiling between the two domains thus acts as a supercoiling diffusion barrier. The size of the CIDs ranges between 30-400 kb. Several triangles (CIDs) merge to form a bigger triangle that represents a macrodomain. In other words, CIDs of a macrodomain physically interact with each other more frequently than with CIDs of a neighboring macrodomain or with genomic loci outside of that macrodomain. A macrodomain may comprise of several CIDs. For simplicity, a macrodomain comprising of only two CIDs is shown. |
| Date | |
| Source | doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1008456 Verma SC, Qian Z, Adhya SL (2019) Architecture of the Escherichia coli nucleoid. PLoS Genet 15(12): e1008456. |
| Author | Subhash C. Verma, Zhong Qian, Sankar L. Adhya |
Licensing
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
- You are free:
- to share – to copy, distribute and transmit the work
- to remix – to adapt the work
- Under the following conditions:
- attribution – You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
Captions
Add a one-line explanation of what this file represents
Items portrayed in this file
depicts
12 December 2019
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 00:15, 18 December 2019 | 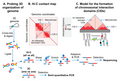 | 2,714 × 1,825 (261 KB) | Evolution and evolvability | User created page with UploadWizard |
File usage
The following page uses this file:
Global file usage
The following other wikis use this file:
- Usage on en.wikiversity.org
Metadata
This file contains additional information, probably added from the digital camera or scanner used to create or digitize it.
If the file has been modified from its original state, some details may not fully reflect the modified file.
| Short title |
|
|---|---|
| Width | 3,400 px |
| Height | 4,400 px |
| Pixel composition | RGB |
| Number of components | 3 |
| Horizontal resolution | 400 dpi |
| Vertical resolution | 400 dpi |
| Color space | sRGB |
| Image width | 3,400 px |
| Image height | 4,400 px |
| Bits per component |
|
| Software used | Adobe Illustrator CC 23.0 (Macintosh) |
| Date and time of digitizing | 11:54, 5 April 2019 |
| File change date and time | 11:55, 5 April 2019 |
| Date metadata was last modified | 11:55, 5 April 2019 |
| Unique ID of original document | uuid:9E3E5C9A8C81DB118734DB58FDDE4BA7 |
Retrieved from "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Subhash_nucleoid_08.png"
