File:Regression elliptique distance algebrique donnees gander.svg
Page contents not supported in other languages.
Tools
Actions
General
In other projects
Appearance

Size of this PNG preview of this SVG file: 452 × 364 pixels. Other resolutions: 298 × 240 pixels | 596 × 480 pixels | 954 × 768 pixels | 1,272 × 1,024 pixels | 2,543 × 2,048 pixels.
Original file (SVG file, nominally 452 × 364 pixels, file size: 21 KB)
| This is a file from the Wikimedia Commons. Information from its description page there is shown below. Commons is a freely licensed media file repository. You can help. |
Summary
| DescriptionRegression elliptique distance algebrique donnees gander.svg |
English: Ellipse fitting, using the method of the algebraic distance. Fitzgibbon algorithm (Halíř and Flusser 1998), with test data from Gander et al. 1994.
Français : Régression elliptique, méthode de la distance algébrique. Algorithme de Fitzgibbon, avec les données test de Gander et coll. 1994. |
| Date | |
| Source |
Own work
|
| Author | Cdang |
Parameters of the ellipse:
- center: (4.64 ; 4.80);
- major semi-axis: a = 3.91;
- minor semi-axis: b = 2.96;
- tilt angle: φ = -9.21°.
Scilab source
| This media was created with Scilab, a free open-source software. Here is a listing of the Scilab source used to create this file. |
// **********
// Initialisation
// **********
clear;
// **********
// Données
// **********
X0 = [1, 2, 5, 7, 9, 6, 3, 8];
Y0 = [7, 6, 8, 7, 5, 7, 2, 4];
// **********
// Fonctions
// **********
function [a] = regression_elliptique(X, Y) // Fitzgibbon
// méthode de la distance algébrique
// X, Y : points expérimentaux, matrices colonnes réelles
// a : coefficients de la formule quadratique (matrice colonne réelle)
D = [X.*X, X.*Y, Y.*Y, X, Y, ones(X)]; // matrice de conception (design m.)
S = D'*D; // matrice de dispersion (scatter m.)
C = zeros(6,6);
C(1,3) = 2; C(2,2) = -1; C(3,1) = 2; // matrice de contrainte
[vecpropres, valpropres] = spec(inv(S)*C); // détermination du
// système propre
if imag(vecpropres) <> 0 then
error('Les vecteurs propres contiennent des valeurs complexes')
end
if imag(valpropres) <> 0 then
error('Les valeurs propres contiennent des valeurs complexes')
end
vecpropres = real(vecpropres); // complexes -> réels
valpropres = real(valpropres);
[PosLigne, PosColonne] = find((valpropres > 0 & ~isinf(valpropres)));
// recherche les indices des valeurs propres positives
a = vecpropres(:, PosLigne); // vecteur propre correspondant
endfunction
function [phi]=trouve_rotation(A)
// A : coefficients de la formule quadratique (matrice colonne réelle)
// phi : angle que fait un axe de l'ellipse avec x (radians)
delta = 1 - 1/(1 + (A(3) - A(1))^2/A(2)^2);
absphi = acos(sqrt((1 + sqrt(delta))/2));
signephi = sign(A(2)*(cos(absphi)^2 - sin(absphi)^2)/(A(1) - A(3)));
phi = signephi*absphi;
endfunction
function [x,y]=trouve_centre(A)
// A : coefficients de la formule quadratique (matrice colonne réelle)
// x, y : coordonées du centre de l'ellipse (réels)
delta = A(2)^2 - 4*A(1)*A(3);
x = (2*A(3)*A(4) - A(2)*A(5))/delta;
y = (2*A(1)*A(5) - A(2)*A(4))/delta;
endfunction
function [rx, ry]=trouve_rayons(a, phi, xc, yc)
// a : coefficients de la formule quadratique (matrice colonne réelle)
// phi : angle que fait un axe de l'ellipse avec x
// xc, yc : coordonnées du centre de l'ellipse
// rx, ry : rayons (grand et petit demi-grands axes) de l'ellipse
A = [a(1), a(2)/2 ; a(2)/2, a(3)];
Q = rotate([1,0;0,1], phi); // matrice de rotation
t = [xc;yc]; // matrice de translation
Abar = Q'*A*Q;
b = [a(4);a(5)];
bbar = (2*t'*A + b')*Q;
c = a(6);
cbar = t'*A*t + b'*t + c;
rx = sqrt(-cbar/Abar(1,1));
ry = sqrt(-cbar/Abar(2,2));
endfunction
function [] = trace_ellipse(xc, yc, a, b, phi)
// trace l'ellipse de centre (xc, yc)
// de rayons a et b et tournée de phi
pas = 0.1;
t = 0:pas:%pi/2;
X = a*cos(t);
Y = b*sin(t);
n = 4*size(X,'*');
XY1 = [X, -flipdim(X,2), -X, flipdim(X,2);...
Y, flipdim(Y,2), -Y, -flipdim(Y,2)];
XY = rotate(XY1, phi) + [xc*ones(1,n);yc*ones(1,n)];
xpoly(XY(1,:), XY(2,:));
endfunction
// **********
// Programme principal
// **********
// lecture des données
Xdef = X0';
Ydef = Y0';
// Régression
aopt = regression_elliptique(Xdef, Ydef);
// affichage des paramètres
disp(aopt)
phi = trouve_rotation(aopt);
phideg = phi*180/%pi;
[xc, yc] = trouve_centre(aopt);
[a, b] = trouve_rayons(aopt, phi, xc, yc);
disp('phi = '+string(phi)+' rad = '+string(phideg)+'°.');
disp('C('+string(xc)+' ; '+string(yc)+').');
disp('a = '+string(a)+' ; b = '+string(b)+'.');
// tracé
clf;
plot(Xdef, Ydef, 'b+')
isoview(0, 10, 1, 9);
plot(xc, yc, 'r+')
trace_ellipse(xc, yc, a, b, phi);
ell = gce();
ell.foreground = 5;
It is also possible to use the Halíř algorithm (split matrices). The algorithm is more stable, and the result is the same.
function [a] = regression_elliptique(X, Y) // Halir
// méthode de la distance algébrique
// X, Y : points expérimentaux, matrices colonnes réelles
// a : coefficients de la formule quadratique (matrice colonne réelle)
D1 = [X.*X, X.*Y, Y.*Y];
D2 = [X, Y, ones(X)];
// matrices de conception (design m.)
S1 = D1'*D1;
S2 = D1'*D2;
S3 = D2'*D2;
// matrices de dispersion (scatter m.)
T = -inv(S3)*S2';
N = S1+ S2*T;
M = [0.5*N(3, :) ; -N(2,:) ; 0.5*N(1, :)]; // mult par inv(C1) à gauche
// matrice de dispersion réduite
[vecpropres, valpropres] = spec(M);
vep = real(vecpropres);
// détermination du système propre
condition = 4*vep(1, :).*vep(3, :) - vep(2, :).^2;
// évaluation de a'Ca
a1 = vep(:, find(condition > 0));
a = [a1 ; T*a1]; // vecteur propre correspondant à la solution
endfunction
Licensing
I, the copyright holder of this work, hereby publish it under the following licenses:

|
Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no Invariant Sections, no Front-Cover Texts, and no Back-Cover Texts. A copy of the license is included in the section entitled GNU Free Documentation License.http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.htmlGFDLGNU Free Documentation Licensetruetrue |
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported, 2.5 Generic, 2.0 Generic and 1.0 Generic license.
- You are free:
- to share – to copy, distribute and transmit the work
- to remix – to adapt the work
- Under the following conditions:
- attribution – You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- share alike – If you remix, transform, or build upon the material, you must distribute your contributions under the same or compatible license as the original.
You may select the license of your choice.
Captions
Add a one-line explanation of what this file represents
Items portrayed in this file
depicts
19 December 2012
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 10:02, 21 December 2012 |  | 452 × 364 (21 KB) | Cdang | {{Information |Description ={{en|1=sign error in algorithm}} |Source ={{own}} |Author =Cdang |Date = |Permission = |other_versions = }} |
| 13:30, 19 December 2012 | 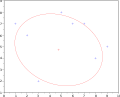 | 452 × 364 (21 KB) | Cdang | {{Information |Description ={{en|1=Ellipse fitting, using the method of the algebraic distance. Fitzgibbon algorithm, with test data from Gander et al.}} {{fr|1=Régression elliptique, méthode de la distance algébrique. Algorithme de Fitzgibbon, a... |
File usage
The following page uses this file:
Global file usage
The following other wikis use this file:
- Usage on fr.wikipedia.org
- Usage on ru.wikipedia.org
Metadata
This file contains additional information, probably added from the digital camera or scanner used to create or digitize it.
If the file has been modified from its original state, some details may not fully reflect the modified file.
| Short title | Régression elliptique |
|---|---|
| Image title | Creator: GL2PS 1.3.2, (C) 1999-2006 Christophe Geuzaine (geuz@geuz.org)
For: Scilab CreationDate: Fri Dec 21 10:55:52 2012 |
| Width | 451.52246 |
| Height | 364.31445 |

