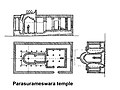
English: The Parasurameswara temple – Parasuramesvara temple – is found in Gudimallam village near Tirupati, Andhra Pradesh. It is an old temple that was rebuilt and restored several times, most significant of which were completed during Bana, Chola and Vijayanagara eras.
The Parasurameswara temple is unlike vast majority of post 6th-century Hindu temple architecture found in India, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Malaysia, Cambodia, Vietnam and Indonesia which favor a square-principle garbhagriya (sanctum). The sanctum of Parasurameswara temple is apsidal, likely from ancient wooden temples that were replaced with brick and then stone temple designs. Archaeological studies at the Parasurameswara temple have revealed a brick core that was in later centuries replaced with stone structure. Further, the Shiva Lingam made of polished rock and housed in the temple is among the most ancient known in the world, variously dated by most scholars between 3rd century BCE and 2nd century CE. A combination of such evidences suggests that the core portions of the Parasurameswara temple reflects an ancient Hindu temple architecture.
The temple walls, particularly the outer surfaces of the pradakshina (also called parikrama) has inscriptions in different scripts. The epigraphical analysis and translation confirms that the temple was restored and rebuilt several times with support of kings from many dynasties over many centuries of late 1st-millennium CE and early 2nd-century millennium. The square mandapam where the Nandi sits was added later, as were the rectangular outer walls (two adjacent squares). The Shiva temple reverentially includes Vaishnava and Shakta pratima (murti) along the inner passage.
The temple compound has smaller shrines and additional old inscription stones which are not shown in the plan above. These are dedicated to Hindu deities Surya, Kartikiya-Murugan, Ganesha and others.
The plan above is based on the drawings published in April 1911 by T.A. Gopinatha Rao, in
Indian Antiquary, volume XL, pages 104–105 (edited by Richard Temple, Cambridge, British India Press). Since it was published before 1926, this work is in public domain. Any creative rights I have in reproducing the work, I herewith donate to Wikimedia Commons under public domain CC0 license.