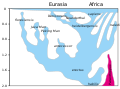
File:Homo-Stammbaum, Version Stringer-en.svg
Appearance

Size of this PNG preview of this SVG file: 633 × 467 pixels. Other resolutions: 320 × 236 pixels | 640 × 472 pixels | 1,024 × 755 pixels | 1,280 × 944 pixels | 2,560 × 1,889 pixels.
Original file (SVG file, nominally 633 × 467 pixels, file size: 18 KB)
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 14:09, 27 October 2014 |  | 633 × 467 (18 KB) | Conquistador | Y-axis x2 |
| 22:35, 26 October 2014 |  | 630 × 472 (27 KB) | Conquistador | Y-axis fixed; image resized | |
| 21:36, 26 October 2014 |  | 384 × 290 (26 KB) | Conquistador | {{Information |Description ={{en|1=Chris Stringers' hypothesis of the family tree of genus Homo, published in Stringer, C. (2012). "What makes a modern human". Nature 485 (7396): 33–35. doi:10.1038/485033a.}} {{hr|1=Hipoteza Chrisa Stringersa o ob... |
File usage
The following 7 pages use this file:
Global file usage
The following other wikis use this file:
- Usage on bn.wikipedia.org
- Usage on bs.wikipedia.org
- Usage on cs.wikipedia.org
- Usage on de.wikipedia.org
- Usage on en.wikibooks.org
- Usage on es.wikipedia.org
- Usage on et.wikipedia.org
- Usage on fa.wikipedia.org
- Usage on fi.wikipedia.org
- Usage on fr.wikipedia.org
- Usage on gl.wikipedia.org
- Usage on he.wikipedia.org
- Usage on hr.wikipedia.org
- Usage on id.wikipedia.org
- Usage on it.wikipedia.org
- Usage on kn.wikipedia.org
- Usage on lv.wikipedia.org
- Usage on mk.wikipedia.org
- Usage on nl.wikipedia.org
- Usage on no.wikipedia.org
- Usage on simple.wikipedia.org
- Usage on sw.wikipedia.org
- Usage on te.wikipedia.org
- Usage on vi.wikipedia.org