File:Eimeria life cycle usda.jpg
Appearance

Size of this preview: 800 × 560 pixels. Other resolutions: 320 × 224 pixels | 640 × 448 pixels | 850 × 595 pixels.
Original file (850 × 595 pixels, file size: 98 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 15:45, 27 January 2008 | 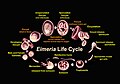 | 850 × 595 (98 KB) | Wlodzimierz | {{Information |Description= '''Eimeria Life Cycle'''<br><br> Eimeria have a complex life cycle that begins after oocysts that are in the litter are ingested by chickens. The grinding action of the gizzard coupled to the enzymes in the gut of chickens lea |
File usage
The following 3 pages use this file:
Global file usage
The following other wikis use this file:
- Usage on ar.wikipedia.org
- Usage on cs.wikipedia.org
- Usage on eo.wikipedia.org
- Usage on es.wikipedia.org
- Usage on fr.wikipedia.org
- Usage on id.wikipedia.org
- Usage on is.wikipedia.org
- Usage on ja.wikipedia.org
- Usage on nl.wikipedia.org
- Usage on pt.wikipedia.org
- Usage on wa.wikipedia.org

