File:Determinants of Gastric Acid Secretion.svg
Appearance
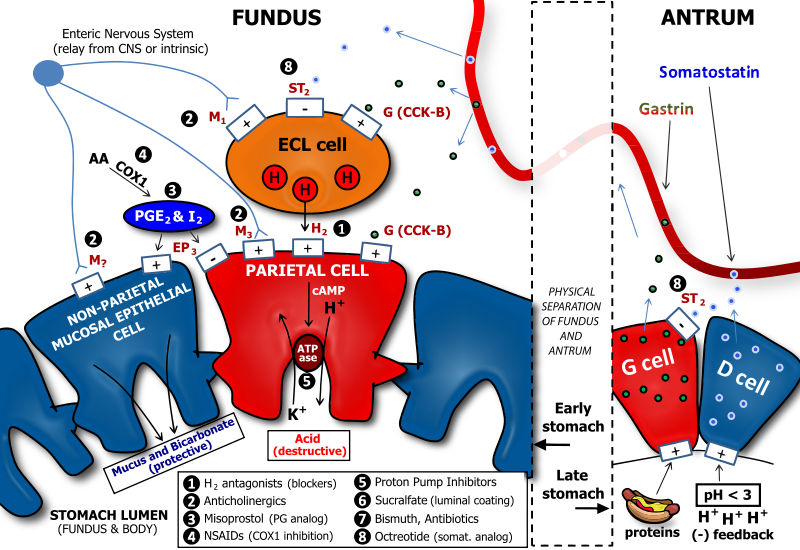
Size of this PNG preview of this SVG file: 800 × 550 pixels. Other resolutions: 320 × 220 pixels | 640 × 440 pixels | 1,024 × 704 pixels | 1,280 × 880 pixels | 2,560 × 1,760 pixels | 1,206 × 829 pixels.
Original file (SVG file, nominally 1,206 × 829 pixels, file size: 741 KB)
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 11:03, 16 January 2011 |  | 1,206 × 829 (741 KB) | Vanwa71 | .. |
| 10:57, 16 January 2011 |  | 1,206 × 829 (486 KB) | Vanwa71 | Reverted to version as of 10:39, 16 January 2011 | |
| 10:55, 16 January 2011 |  | 1,206 × 829 (1.33 MB) | Vanwa71 | Linked instead of embedded new graphics last time. | |
| 10:39, 16 January 2011 |  | 1,206 × 829 (486 KB) | Vanwa71 | Reverted to version as of 06:03, 16 January 2011 | |
| 10:37, 16 January 2011 |  | 1,206 × 829 (437 KB) | Vanwa71 | cool effects | |
| 06:03, 16 January 2011 |  | 1,206 × 829 (486 KB) | Vanwa71 | Small detail edits. | |
| 05:57, 16 January 2011 |  | 1,206 × 829 (484 KB) | Vanwa71 | Fixed gastrin and somatostatin flaws | |
| 05:14, 16 January 2011 |  | 1,206 × 829 (472 KB) | Vanwa71 | Forgot categories. | |
| 05:11, 16 January 2011 |  | 1,206 × 829 (472 KB) | Vanwa71 | I finally started using my head, and converted all the text to outlines to keep it exactly as I wanted it. | |
| 05:05, 16 January 2011 |  | 1,206 × 829 (214 KB) | Vanwa71 | Please bear with me, I finally looked up websafe fonts instead of trial and error. Let's hope this works. |
File usage
The following 5 pages use this file:
Global file usage
The following other wikis use this file:
- Usage on el.wikipedia.org
- Usage on fr.wikipedia.org
- Usage on hi.wikipedia.org
- Usage on id.wikipedia.org
- Usage on ja.wikipedia.org
- Usage on ko.wikipedia.org
- Usage on sq.wikipedia.org
- Usage on te.wikipedia.org
- Usage on uz.wikipedia.org
- Usage on zh.wikipedia.org
- Usage on zh.wikibooks.org
