File:Cartesian to polar.gif
Appearance
Cartesian_to_polar.gif (500 × 500 pixels, file size: 739 KB, MIME type: image/gif, looped, 70 frames, 18 s)
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 14:54, 6 September 2010 | 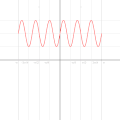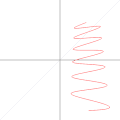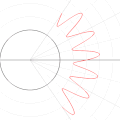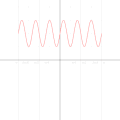 | 500 × 500 (739 KB) | LucasVB | Changing f(x) to y |
| 13:40, 6 September 2010 |  | 500 × 500 (741 KB) | LucasVB | Function labels. | |
| 11:28, 6 September 2010 |  | 500 × 500 (630 KB) | LucasVB | Rotation in 3D makes the animation easier to understand, and cooler! :D | |
| 05:06, 6 September 2010 | 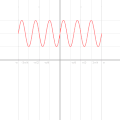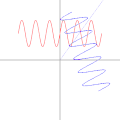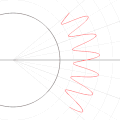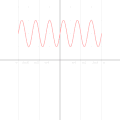 | 500 × 500 (668 KB) | LucasVB | Optimized dithering, smooth loop. | |
| 04:14, 6 September 2010 | 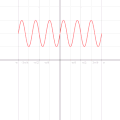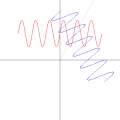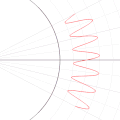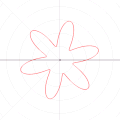 | 500 × 500 (689 KB) | LucasVB | {{Information |Description={{en|1=A function in the cartesian plane can be transformed into polar coordinates by wrapping one axis around itself and collapsing it to a point. This is illustrated here with the function f(x) = sin(6x)+2}} |Source={{own}} |A |
File usage
The following 4 pages use this file:
Global file usage
The following other wikis use this file:
- Usage on el.wikipedia.org
- Usage on he.wikipedia.org
- Usage on hi.wikipedia.org
- Usage on id.wikipedia.org
- Usage on lv.wikipedia.org
- Usage on mk.wikipedia.org
- Usage on pt.wikipedia.org
- Usage on ta.wikipedia.org
- Usage on uk.wikipedia.org
- Usage on vi.wikipedia.org





