File:709 2017 1147 Fig6l.jpg
Appearance

Size of this preview: 447 × 599 pixels. Other resolutions: 179 × 240 pixels | 358 × 480 pixels | 734 × 984 pixels.
Original file (734 × 984 pixels, file size: 72 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 14:33, 8 August 2022 | 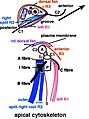 | 734 × 984 (72 KB) | Ernsts | Uploaded a work by Thomas Cavalier-Smith from Fig. 3+6 at https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00709-017-1147-3 Kingdom Chromista and its eight phyla: a new synthesis emphasising periplastid protein targeting, cytoskeletal and periplastid evolution, and ancient divergences. In: Protoplasma 255, doi:10.1007/s00709-017-1147-3 with UploadWizard |
File usage
The following page uses this file:
Global file usage
The following other wikis use this file:
- Usage on de.wikipedia.org
- Usage on hu.wikipedia.org

