Expulsion of congregations

The expulsion of religious congregations in 1880 was a political event in France during the Third Republic, involving the dispersal of unauthorized, primarily male, religious congregations. These expulsions were enacted after the enactment of two decrees on March 29, 1880, by the government of Charles de Freycinet, specifically by Charles Lepère, Minister of the Interior, and Jules Cazot, Minister of Justice. The initial decree mandated the dissolution of the Society of Jesus (Jesuits) within French territory. At the same time, the subsequent directive required that all other unrecognized religious groups seek legal recognition, with the implicit threat of facing the same fate as the Jesuits.
These decrees were issued in the context of the establishment of the Republic. This strengthening of the regime was marked by militant anticlericalism from moderate Republicans and Radicals and by a desire to remove education from the influence of congregations, which were mocked as a "Roman militia" and accused of being seeds of counter-revolution.
The implementation of the initial decree resulted in the eviction of the Jesuits from all their establishments, commencing on June 30, 1880. In solidarity with the Society of Jesus, other congregations declined to submit authorization requests. Charles de Freycinet, who was not genuinely intent on expelling them, initiated discussions to secure their declared allegiance to the Republic. The revelation of these secret negotiations by the newspaper La Guienne resulted in Freycinet's resignation and the ascension of Jules Ferry to power. Ferry enforced the second decree with great rigor, leading to the expulsion of numerous other unauthorized male congregations. Many members of these congregations barricaded themselves within their premises, prompting prefects to repeatedly request military intervention. This resulted in occasionally violent scenes, including doors being broken open with axes and locks being destroyed.
The implementation of the decrees encountered considerable opposition. They were contested in civil courts and became the subject of debates and incidents in the Chamber of Deputies and the Senate. Groups of devout and Catholic activists attended the expulsions to express support for the religious and deride the police. Furthermore, several hundred magistrates and officials responsible for enforcing the decrees resigned in protest, motivated by their convictions.
The expulsion of the congregations resulted in the dispersal of 6,589 religious members. Some opted to persist in living in small community groups in houses provided by laypeople, while others chose to exile themselves to reconstitute their congregations abroad, with Spain being the principal destination for Congregationalists. The return of the religious to their establishments occurred gradually in the following years as a détente developed between the Holy See and the French government starting in 1885. This eventually led to the Ralliement of 1892. Nevertheless, the Republicans persisted in their efforts to secularize education. The decline of congregational teaching commenced, and the final blow was delivered by the suppression of teaching congregations in 1904, twenty-four years after the expulsion of 1880.
Background
[edit]The State of congregations in France
[edit]Under the Second Empire
[edit]The Second Empire, a period of the Second Empire, was a decade of prosperity for religious congregations, whose activities, including education, were encouraged by government policy. Consequently, their numbers increased, and new foundations were established. However, the shift to the Liberal Empire resulted in a change of circumstances. While the government maintained its favorable stance towards the Catholic Church, it became increasingly concerned about the power of the congregations and sought to exert greater control over them. This intensified scrutiny, initiated by the Ministers of Public Instruction, resulted in administrative challenges and the suppression of certain congregations. This period began in 1860 with Minister Gustave Rouland, whose Gallicanism was well documented. Rouland justified this shift in policy by asserting that male congregations were subject to Rome's authority[N 1] and beyond France's control.[1] His 1860 report presented the situation as follows:[2]
Religious establishments are the refuge of children from families that do not adhere to the principles of 1789 or the government of the Emperor. The education provided there aligns with these regrettable tendencies. […] The regular clergy is simply a militia shaking off the yoke of the ordinary, having neither homeland nor personality, obeying perinde ac cadaver to the absolute government of a foreigner, a superior general residing in Rome.
Rouland prohibited the establishment of new male congregations and made it challenging to obtain authorization for female congregations. However, he was a staunch proponent of public education, which he viewed as a means of counterbalancing these restrictions. In 1861, the Capuchin and Redemptorist houses were dissolved, and all Belgian Redemptorists were expelled from France. This anti-congregation policy continued under his successor, Victor Duruy.[2] Duruy attempted to remove secondary education for girls from the influence of the congregations, which provoked protests from clerical supporters. These protests ultimately succeeded in derailing the project.[3]
Under the moral order
[edit]
Following the collapse of the Second Empire, religious congregations experienced a resurgence in strength during the period of the Moral Order. Notably, Jesuit colleges witnessed a resurgence of prosperity. By 1879, the 29 colleges had an enrollment of 11,144 students, representing over half of the total enrollment in Catholic secondary schools.[4] These institutions were among the most esteemed in France.[5] The flagship of their educational enterprise, the Collège de la Montagne Sainte-Geneviève, located on Rue des Postes, prepared its students for the entrance examinations to the École Polytechnique and Saint-Cyr. Consequently, these two esteemed institutions had numerous students who had received their education at the Collège de la Montagne Sainte-Geneviève in their classes, a fact that caused concern among the Republicans.[4]
As a result of the regulatory delays of the Second Empire and the dynamism observed under the Moral Order, congregations were subjected to a complex regime distinct from the Concordat. While a significant minority had obtained legal authorization, a considerable majority[N 2] had been established without the government's approval and was, therefore, merely tolerated.[4] Upon their creation, congregations had the option of acquiring a legal existence and benefiting from legal person or remaining a simple aggregation of individuals.[6] Many communities opted for the latter, exhibiting a distrust in state control.[7]
The legal authorization in question, as outlined in Article 4 of the decree-law of 8 Messidor Year XII (June 27, 1804), was initially granted by the government and subsequently by Parliament, beginning in 1825. Congregations lacking authorization were not deemed illegal, as evidenced by the 1817 and 1825 legislative acts, which did not mandate such authorization requests, and the renowned consultation of the jurist Lefebvre de Vatimesnil,[7] which established the prevailing French legal doctrine on the matter.[8]
In 1876, the number of male congregations was as follows: The number of religious members in authorized congregations was 22,759, while the number in unauthorized congregations[9] (including Jesuits, Benedictines, Capuchins, Discalced Carmelites, Dominicans, Franciscans, and Assumptionists[10]) was 7,488. This represents a proportion of 25% for the former and 11% for the latter. For female congregations, the proportion was lower: 113,750 authorized nuns versus 14,003 unauthorized nuns,[9] representing 11%.
The anticlerical Republic
[edit]
In the final years of the Second Empire, France witnessed a notable resurgence of anticlerical sentiment. This trend persisted and intensified during the Paris Commune and subsequently during the struggles of the Republicans to establish the new regime. During the 1870s and 1880s, this animosity toward clericalism was indistinguishable from anti-Catholicism. This sentiment was espoused by the emergent bourgeoisie and the working classes, comprising rural populations from the de-Christianized countryside and "red" workers. Religious congregations perceived as exerting considerable influence were particularly targeted. These were portrayed as a "Roman militia" and perceived as adversaries of individual liberties.[4] This anticlericalism was further fueled by French Freemasonry, which sought to eradicate the regular clergy, viewing their vow of obedience as enslaving their lives to an obscurantist authority, in contradiction to Article 1780 of the Civil Code, which states that "no one can bind their services except for a limited time."[7]

It is incontestable that the Society of Jesus provoked the greatest degree of animosity among all the congregations. The intense propaganda against them drew inspiration from 18th-century polemics, which had been reactivated during the Restoration by the Gallican royalist Reynaud de Montlosier and during the July Monarchy by the lectures at the Collège de France by Michelet and Quinet in 1843. This opinion campaign portrayed the Jesuits as the driving force behind the counter-revolution, with an alleged secret influence over mothers through the confessional and over sons through religious colleges. Their religious teachings were also subjected to criticism, with casuistry being accused of promoting immorality; this was particularly evident in the pamphlet La Morale des Jésuites by Republican Paul Bert, who later became the founder of secular education.[4]
The consolidation of the 1875 regime, as perceived by the Republican faction, necessitated the combating of clericalism and the secularization of educational institutions.[11] From 1877, the year in which the Center-Left assumed power and permanently displaced the monarchists, a purge of the civil service commenced, intending to remove officials affiliated with the Moral Order.[12] From 1878 to 1880, a series of violent attacks on religious congregations accompanied a press campaign targeting the clergy in the context of the secularization of communal schools by the Paris Municipal Council, which had been authorized by a circular issued in 1878.[11] Removing religious figures from their schools resulted in a legal dispute that was brought before the Council of State. The latter was purged in July 1879 to ensure an anticlerical judgment and, as a result, dismissed the congregations' appeals for abuse of power.[12] Building on this momentum, Jules Ferry had the law of February 27, 1880, passed, which excluded ecclesiastical figures from the Supreme Council of Public Instruction.[11] Consequently, the Republicans gradually moved towards revising the Falloux Law, which granted congregations complete freedom in education.[13]
In this context of militant anticlericalism among the founders of the Third Republic, the law of March 18, 1880, was discussed and resulted in the issuance of decrees that expelled the congregations.[4]
March 1880 decrees
[edit]Law on the freedom of higher education
[edit]
On March 15, 1879, the anniversary of the Falloux Law, Jules Ferry, Minister of Public Education in the new Waddington government, introduced a bill on the freedom of higher education in the Chamber of Deputies. For Ferry, the objective was to remove education from the Church's control and target the Jesuits, whom he suspected of inspiring the counter-revolution.[14] The minister did not disguise the targets of his vendetta, stating, "The Society of Jesus is not only unauthorized but it is prohibited by all our history."[5]
The Chamber enacted the legislation on July 15, 1879. However, the deliberations in the Senate on Article 7 reached an impasse. The article in question stipulated that "no one is allowed to run a public or private educational establishment, of any order, nor to teach there if they belong to an unauthorized congregation."[5] In response, the Center-Left, led by Jules Simon, joined forces with the monarchists of the Union des droites to oppose the alliance of the Republican Left and the Republican Union.[15] After a series of impassioned debates, the Senate ultimately rejected Article 7 on March 9 and again on March 15, 1880.[5]
On March 16, 1880, the Republican majority in the Chamber, incensed, enacted the law without Article 7[14] but accompanied it with the vote of a protest motion,[5] thereby initiating a conflict between the two assemblies.[16]
- Main opponents of Article 7 in the Senate
-
Jules Simon, the bill's rapporteur in the Senate and a leading figure on the center-left.
-
Legitimist Senator Charles Chesnelong, one of the leaders of the Catholic opposition to the Higher Education Act.[17]
-
Jules Dufaure, former Minister of Justice, who gave a speech on March 8 arguing that unauthorized congregations were not illegal.[17]
Publication of the decrees
[edit]To bring the parliamentary confrontation to a swift conclusion and align himself with the Chamber, Charles de Freycinet drafted two decrees on March 29, 1880.[16] He did so at the advice of Léon Gambetta[18] and Jules Ferry.[19] These decrees served to address the removal of Article 7. The first of these decrees ordered the dissolution of the Society of Jesus within three months. The second required other unauthorized male congregations to apply for authorization within the same timeframe. Failure to do so would result in the same fate as that which had befallen the Society of Jesus.[16]
The day following the publication of the decrees, the superiors of the primary male congregations convened a war council at the Oratorians in Paris. They unanimously declared their solidarity with the Jesuits and refused to submit authorization requests.[16] The Catholic laity assisted the religious (notably through Catholic committees) and established several groups of legal experts to organize a legal response.[18]
Concurrently, the congregations initiated a public relations campaign through the publication of written works designed to enhance public awareness of their activities. Jacques Monsabré, a Dominican, authored a memoir entitled Mémoire pour la défense des congrégations religieuses, while Émile Keller contributed a book titled Les congrégations religieuses en France, leurs œuvres et leurs services,[18] among other publications.
Appointed in 1879, Mgr Czacki, the nuncio, took a definitive stance by the instructions provided by Cardinal Nina, Secretary of State of Pope Leo XIII. He requested that the bishops organize widespread protests and informed the congregations that the Cardinal Congregation, which was responsible for French affairs, supported their decision not to seek legal authorization. Ultimately, he pressured the President of the Council, threatening him with a public protest from the Pope. This was a significant disavowal that Charles de Freycinet sought to avoid and which he believed would result in his immediate resignation.[20]
However, in response to mounting pressure from the Chamber of Deputies, the government remained unyielding in its stance.[18] On June 10, 1880, the Minister of Justice summoned the attorneys general to the ministry and provided them with verbal instructions, emphasizing the necessity of strict adherence to the established standards to avoid dismissal. In response to these developments, the Attorney General of the Douai Court, along with three other magistrates from his jurisdiction, submitted their resignations in protest.[21] On June 30, Ernest Constans ordered the expulsion of the Society of Jesus, a highly controversial organization in France known for its ultramontanist beliefs. The Jesuits, in an act of resistance, barricaded themselves within their religious houses with the faithful, resulting in the implementation of forceful expulsions by government forces. These expulsions, carried out with the use of force and intimidation tactics, occurred in 31 departments where the Jesuits had a presence.[18]
Fall of the Freycinet cabinet
[edit]
Charles de Freycinet, who espoused liberal views, was disinclined to expel other male congregations.[N 3] Mgr Czacki endeavored to reestablish concord, convening clandestine conferences with the Freycinet administration[18] and the Director of Worship Émile Flourens[22] as early as May 1880.[23] He was aided in his endeavors by Cardinal de Bonnechose, a close associate of Leo XIII.[24] Initially maintaining a reserved and cautious stance,[25] the Pope ultimately endorsed these endeavors.[26] He endeavored to achieve religious concord in France, even at the cost of recognizing the Republic, excluding the clergy from political life, and relinquishing the Society of Jesus.[27]
The negotiations were unsuccessful in July 1880 due to the opposition of Father Ange Le Doré, the superior of the Eudists. However, clandestine discussions resumed, and the resulting accord entailed the following stipulations: in exchange for the congregations' formal attestation of their fidelity and acquiescence to the Republican order, the government would refrain from enforcing the second decree.[28] Freycinet conveyed this information to the Holy See through Cardinal Guibert, Archbishop of Paris.[29] The aforementioned declaration was drafted by Mgr Lavigerie, Archbishop of Algiers, and Cardinal de Bonnechose,[26] and submitted to the Pope, who revised and approved it.[28] Following the expulsion of the Jesuits on August 18, 1880, Charles de Freycinet delivered the Montauban speech, which announced a policy of religious détente.[29] On August 19, 1880, the declaration was transmitted to the congregations for their signatures. It explained that the common law regime was deemed sufficient for their purposes and that no legal authorizations had been sought. To disassociate themselves from the Moral Order, they also assured the government of their respect and submission to the country's existing political institutions and rejected any form of solidarity with political parties or partisan interests. The objections of the most intransigent religious figures were overcome, and only the Benedictines of the Abbey of Solesmes refused to join the declaration.[28]
On August 31, 1880,[26] however, La Guienne, a legitimist newspaper in Bordeaux, revealed Charles de Freycinet's secret negotiations[29] and the content of the declaration.[30] Lavigerie alleged that Mgr Freppel, who was opposed to the recognition of the Republic by the clergy, was responsible for orchestrating the leak.[31] In the face of vehement opposition from the radicals,[28] he promptly issued a statement disavowing any commitment to the Holy See. On September 16, the President of the Council opted to delay the implementation of the second decree. However, Ernest Constans, an ardent anticlerical, further exacerbated the situation by orchestrating the leakage of an unofficial circular anticipating a rapprochement with the congregations.[29] On September 19, Constans reiterated his opposition by rejecting multiple authorization requests submitted by the congregations. Confronted with mounting pressure from extremists,[30] Charles de Freycinet resigned from his government that same day.[29]
Implementation by Jules Ferry
[edit]
Jules Ferry, a principal architect of the decrees, assumed the role of Prime Minister on September 22 and retained his portfolio of Public Instruction and Worship.[29] He was unwavering in his resolve to enforce the second decree with the utmost rigor and established the implementation dates for the period between October 16 and November 9.[28]
The prefectural body, which had been purged by the Republicans in December 1877, presented no significant obstacles to the implementation of the decrees.[32] In a circular dated June 1, 1880, Constans sought the opinions of the relevant parties on the feasibility of implementing the decrees and the potential backlash that the expulsions might elicit. The majority of responses indicated that no significant public opposition was anticipated and that retreating from enforcing the decrees would be perceived as a sign of weakness by the clerical party.[33]
To effectively "stifle" the congregants' protests, the Ministry of the Interior and the Ministry of Justice collaborated in a coordinated effort. The government issued detailed instructions to prefects on how to challenge the jurisdiction of judicial courts in cases where officials were sued. Concurrently, the public prosecutor's office was ordered to file a jurisdictional declinatory in each of these cases. This strategy aimed to compel the judiciary to recuse itself from these legal matters.[34]
Contestation of the decrees
[edit]Political reactions
[edit]Parliamentary protests
[edit]| The minutes of the proceedings established by the right-wing deputies regarding the incident that occurred on November 11th are as follows:[35]
"Through the back door of the chamber, Colonel Riu suddenly enters. He is in uniform, kepi on his head, sword at his side. He advances slowly, descending the steps of the chamber, his face betraying intense emotion. [...] He is followed by the men forming the honor guard of the palace, with the captain and sub-lieutenant leading, belonging to the 23rd Battalion of Chasseurs à Pied. Some men from the 25th Line Regiment form the rearguard. They descend one by one; people watch them curiously, but no one moves. Colonel Riu rushes through the benches, descends into the hemicycle, checking to see if his men are following him, imitating his valiant ardor, then he ascends towards Mr. Baudry d'Asson, adopts a courteous demeanor, and orders his soldiers to form a circle around the honorable deputy and his friends. Mr. Riu arrives in front of General de Vendeuvre; the latter stands proudly: 'You shall not pass, Colonel.' The colonel steps back and finds himself facing Mr. Delafosse, deputy of Vire. He tries to climb onto a bench. Mr. de Launay stops him and says: 'Colonel, show me your orders.' Flustered, the colonel responds: 'I will go get them.' Gradually, the bulk of the troops arrive; the circle tightens and imprisons part of the right-wing members. The deputies protest energetically [...]. Everyone resists, and the tumult becomes indescribable. The soldiers try to climb over the benches; they climb onto the desks, which are scratched and soiled by their shoes. The assault is general. Soldiers are seen falling, and getting up. It's a terrible melee. Mr. Livois is thrown to the ground. Mr. Brame, deputy of the North, is rolled over in turn. Baron Dufour grabs an usher and throws him over the balustrade outside the hemicycle. [...] Mr. Bourgeois is seized by the throat by a soldier, the Marquis d'Aulan, Mr. de la Rochette, Mr. Blachère, Mr. de la Billais, Mr. de Kermenguy, Mr. de La Rochefoucauld, Mr. Laroche-Joubert, Mr. de la Bassetière, Mr. de Breteuil are odiously mistreated. Finally, the soldiers reach Mr. Baudry d’Asson. He is seized, grappled, and dragged away. He is hit from all sides; he staggers, pale, disheveled. Ten soldiers manage to carry him out of the chamber." |

The publication of the decrees was promptly subjected to legal scrutiny, with concerns raised about their legality. In the Chamber of Deputies and the Senate, interpellations and interventions from right-wing and center-left members multiplied. The most notable speech was delivered by the Duke of Audiffret-Pasquier, a center-right deputy, on June 25, 1880, in the upper chamber.[36] Speaking on behalf of Catholics, he denounced the arbitrary nature of the government's measures and proposed a vote on a law to regularize the existence of unauthorized congregations by recognizing the right of association.[N 4][37] However, this proposal was rejected by the Republican parliamentary majority.[38]
The most noteworthy occurrence resulting from the actions of the Union des droites's deputies transpired on November 10 and 11, 1880. It involved Count Léon de Baudry d'Asson, a prominent and restless deputy from Vendée.[39]
On November 10, during the ministerial crisis related to the vote on the judiciary law, he requested the floor and began his speech with the following remarks: "During this brief session, we may observe the struggles of the Republic..." He was promptly called to order by Léon Gambetta, who then demanded that an interpellation session be held every Wednesday to hold the government accountable for its actions. This was a clear reference to the break-ins at convents.[40] While Gambetta had the censure and temporary exclusion for fifteen sessions voted against him,[39] the right-wing deputy continued to rail against the "infamous executions carried out by the men I see before me."[40]
Notwithstanding the prohibition, the right-wing deputy was able to gain access to the chamber during the subsequent session and resumed his position on the bench. Following a reminder of the rules by the president of the Chamber, the latter requested the session's adjournment and dispatched the Chamber's questors to Baudry d'Asson. The Vendée deputy declined to vacate the premises, emboldened by the actions of his right-wing colleagues. Consequently, a detachment of twenty soldiers, under the command of Colonel Riu, apprehended him amidst a violent altercation and following an exchange of blows between the soldiers and the right-wing deputies. Following his incarceration in the legislative palace's detention room, designated as "the small room," Count Baudry d'Asson was released the following day as a result of the intervention of Olivier Le Gonidec de Traissan and Camille Mathéi de Valfons. Baudry d'Asson initiated legal proceedings against the president and questors before the criminal court, which subsequently declared itself incompetent.[39]
- The incident of November 11, 1880
-
Baudry d'Asson apprehended by Colonel Riu, military commander of the Palais-Bourbon, and the chasseurs of the guard post.
-
Baudry d'Asson's expulsion as seen by Le Monde illustré.
-
Baudry d'Asson locked up in the arrest chamber of the Palais Bourbon. Drawing from L'Illustration.
Division of Catholics and failure of monarchist opposition
[edit]

The schism within the Catholic Church between those who were unyielding and those who were more moderate in their views resulted in a partial failure of the protests against the expulsions of congregations. Despite the influence of the resignations of magistrates and officials and the crowds that gathered to honor the religious, the government remained unresponsive to Catholic demonstrations.[41]
This internal dissension can be explained by Pope Leo XIII's conciliatory approach, which sought a resolution through negotiation and only raised protests in a measured manner once a breach had occurred. This approach aimed to maintain concord between Catholics and the Republic, foreshadowing the Ralliement policy. The Roman authorities were already wary of the royalists, who attempted to exploit the demonstrations by taking the forefront in defending Catholicism. Monarchist parliamentarians and activists were thus present during numerous expulsions, such as those of the Jesuits from Rue de Sèvres, the Trappists from Bellefontaine, or the Premonstratensians from Frigolet. They took advantage of the unrest to destabilize the Republic.[41]
Nevertheless, this considerable effort by the monarchists was ultimately unsuccessful in dislodging the Republicans from their position.[41] The Republican newspaper Le National accused the royalists of "engaging in a series of itinerant activities, traveling to various locations across France and engaging in significant events at four or five convents in different provinces or the capital," and stated, "Clericalism was a primary factor in the May 16th crisis, and it ultimately led to its demise. May 16th is now seeking retribution and compromising religion."[42] The protests against the expulsions, being associated with the legitimist movement, failed to sway public opinion.[43] Consequently, the Catholic rally on June 29 at the Cirque d'Hiver was accompanied by a strong popular counter-demonstration chanting "Long live the Republic! Down with the Jesuits! To the border, the Jesuits!" Furthermore, the partial renewal of the general councils on August 1, 1880, saw a surge of the left.[41]
Legal criticism
[edit]Consultation with Edmond Rousse
[edit]
Jules Dufaure, a former Minister of Justice and one of the Republican senators who distinguished himself by opposing Article 7, commissioned the renowned jurist Edmond Rousse, the former President of the Paris Bar Association, to draft a comprehensive legal consultation on the decrees issued in March 1880.[44] The document, published on June 14,[45] had a significant impact, rapidly securing the signatures of 140 Paris Bar Association lawyers (including the Bar President Jules Nicolet) and 1,478 provincial lawyers. It also garnered the support of Charles Demolombe, Dean of the Faculty of Law at Caen and "the foremost jurist in France,"[45] along with approximately ten lawyers at the Court of Cassation.[44]
Rousse demonstrated that the legislative acts on which the government[N 5] had based its arguments had been effectively repealed by subsequent provisions. He proceeded to dismiss, one by one, the legal texts that had been cited by the authors of the decrees. He concluded that the only applicable texts to congregations were the articles of the Penal Code on the right of association. These articles prohibited associations of more than twenty people, except for those residing in the house where the association met. This protected congregations from the law.[47] His conclusions were as follows: no current legislation prohibits the communal life of congregations, even those that are not officially recognized; the dissolution of these congregations cannot be carried out by an administrative authority, but only following a judicial decision; even if administrative dissolution were chosen, it would be impractical and ineffective.[45]
The publication of this consultation, along with the support it received from legal doctrine, served to reinforce the judiciary's stance and intensify the resolve of the congregations to challenge the government's actions.[45]
Mass resignations in the judiciary
[edit]In a ministerial circular dated June 24, 1880, the public prosecutors were charged with the responsibility of carrying out the expulsions. The implementation of the decrees resulted in a significant number of resignations among prosecutors who opposed the anti-religious measures.[48] In total, 556 magistrates declined to comply with the government's directives and instead opted for resignation, emulating the example set by the Attorney General of Douai. Among them were Victor de Marolles and Jean de Boysson. The unrest was pervasive across all levels of the judicial hierarchy, encompassing both the seated judiciary (judges) and the standing judiciary (prosecutors). This included 56 members of the courts of appeal, 63 public prosecutors, 139 deputies prosecutors, 66 justices of the peace, 188 of their deputies, 32 judges,[21] and numerous others.
Catholic newspapers played a pivotal role in inciting unrest by publishing the resignation letters of magistrates and officials daily, citing their refusal to comply. There were also resignations from officers, police commissioners, and police officers. The prosecutors who recused themselves were predominantly Catholic, but there were also Protestants, such as Pelleran, the public prosecutor of Le Havre, who wrote in his resignation letter on October 31, 1880: "As the son of persecuted people, I will never become a persecutor."[21]
Magistrates were not the only officials to resign. Similarly, members of the prefectural corps, such as Gustave Pradelle, Prefect of Oise, and Olivier d'Ormesson, Prefect of Pyrénées-Atlantiques, also vacated their posts during the period when the decrees were being enforced.[49] Some army officers were similarly reluctant to comply with the requisitions of the prefects. For instance, Lieutenant Marchesné, a recently graduated Saint-Cyrien, tendered his resignation and was subsequently brought before a court-martial by General Farre.[50] In other instances, officers were compelled to resign as a result of their conduct during the unrest. This was the case for Henri de la Ferronnays, a future deputy who had supported the Trappists of the Notre-Dame de Melleray Abbey.[51]
Orders from civil courts
[edit]
Many court presidents voiced opposition to the enforcement of the March 1880 decrees by extending a favorable reception to the requests of expelled religious individuals and issuing orders for their expeditious reinstatement to their properties. This action served to counter the administrative authority.[48] The courts of Aix-en-Provence, Angers, Avignon, Béthune, Bordeaux, Bourges, Clermont, Douai, Grenoble, La Flèche, Le Puy-en-Velay, Lille, Limoges, Lyon, Marseille, Nancy, Nantes, Paris, Périgueux, Quimper, Rouen, and Toulouse deemed themselves to possess the requisite competence.[52][53] Of the 138 judicial decisions rendered, 128 were in favor of the congregations.[54] Some of these rulings pertained to the reinstatement of properties, while others concerned damages owed by the prefects and law enforcement personnel for the material damage caused by the expulsions.[55]
To illustrate, on July 1, 1880, Félix Le Roy, then serving as President of the Lille Tribunal, issued the following order: "Even assuming there are current laws prohibiting the existence of unauthorized religious congregations, no constitutional or legal provision grants administrative or governmental authority the power to enforce these laws through high policing measures before any judicial decision." This ruling was based on a legally acceptable foundation;the 1880 decrees specified the application of the decree-law of 3 Messidor, Year XII (June 22, 1804), which stipulated that "our attorneys general and our imperial prosecutors are obliged to [...] "Prosecute and have prosecuted, even by extraordinary means, as the cases require, persons of any sex who would directly or indirectly violate this decree," thus placing the prohibition of congregations under the sanction of judicial authority and not explicitly excluding the intervention of the judicial judge to guarantee the fundamental rights of the individual.[55] President Le Roy was supported by Judge Marion, who had been dismissed from his investigative duties in April 1880 due to his anti-Republican opinions, in his defense of the Jesuits. This prompted the immediate issuance of a conflict order by the Prefect of the Nord department, which referred the matter to the Tribunal des Conflits.[56]
A comparable incident transpired within the purview of the Béthune Tribunal. President Leroux de Bretagne, portraying himself as a champion of individual liberties, declared the decrees invalid and issued a reinstatement order in early July 1880, thereby annulling the expulsion of the Christian Brothers congregation. In haste, he proceeded to the site to enforce his order before the Prefect of Pas-de-Calais could issue a conflicting order to halt the process. As he had feared, this order was filed. Leroux de Bretagne's action was condemned by L'Avenir, the local Republican newspaper, and celebrated by the Catholics of L'Indépendant du Pas-de-Calais.[56]
On September 27, 1880, Jules Le Fizelier, the President of the La Flèche Tribunal, ruled in favor of the Benedictines against the Prefect.[34] On September 30, 1880, the Poitiers Tribunal considered itself competent to hear the case, a position that was subsequently adopted by the Court of Appeal and its president, Merveilleux du Vignaux.[54]
Decision of the Tribunal des Conflits
[edit]| The following is an excerpt from the plea presented by Me Sabatier before the Tribunal des Conflits:[57]
"A new and unprecedented spectacle! French citizens, masters of their civil and political rights; voters, eligible, paying taxes, who have not been incapacitated by any law, who have not been affected by any judgment in their freedom or honor, and who have been reproached only for having gathered without the approval of the authorities, to live and pray together under a religious rule, have been besieged, forced, and seized in their homes by public force, and instead of being brought before magistrates, thrown into the street, under the mere threat that a similar execution would follow any new gathering. Confident in the justice of their country, having heard that ordinary courts are the natural protectors of all rights infringed in their person, property, individual freedom, religious freedom, and the inviolability of the home, these citizens turned to the courts [...]. Everywhere or almost everywhere, they found judges; everywhere too, the government closed the courts that had opened. The administrative execution is consummated and will escape all jurisdiction. There will be no judges, neither ordinary nor extraordinary, to hear the grievances and recognize the rights. Conflicts raised everywhere claim for the government alone the absolute, indefinite, sovereign, uncontrollable right to dispose of the property, freedom, and homes of citizens, as necessary for the dispersal of unauthorized congregations! And today, while even at the very hour I speak, the public force may still be continuing its sad task, while the government sits in person within this tribunal, you are asked, not to give judges, but to suppress them! I ask if this is the public law of modern France—not of monarchical, imperial, authoritarian France, but of democratic France, born from the Revolution, and today constituted under this republican form that so many doctors praise as the natural, necessary, integral expression of civil and political freedom." |

On November 4 and 5, 1880, the Tribunal des Conflits was convened to determine the appropriate scope of judicial and administrative jurisdiction.[56] Maurice Sabatier presented the case of the Jesuits of Lille,[58] while Me Bosviel represented the Jesuits of Avignon. Paul Jozon acted as counsel for Prefect Jules Cambon,[57] and government commissioner Abel-Antoine Ronjat represented the Ferry cabinet.[58] At the commencement of the session, the counsel for the congregations petitioned for the recusal of Jules Cazot. The latter presided over the Tribunal as Minister of Justice, yet Me Bosviel questioned his impartiality due to Cazot's role as one of the authors of the March 1880 decrees and his repeated declaration of himself as "the worst enemy" of the congregations. Me Bosviel advanced the argument that even if the Tribunal does not condemn individuals, it still renders judgments—in a manner analogous to the Court of Cassation. Consequently, he asserted that the members of the Tribunal should be subject to recusal.[57] Following a period of deliberation, the court concluded that "the Tribunal des Conflits, established to ensure the application of the principle of the separation of administrative and judicial powers, is not called upon to rule on any private interest dispute." Therefore, the court determined that the members of the Tribunal were not subject to possible recusal.[59]
At the commencement of the hearing, Me Sabatier presented a petition in support of the competence of,[57] which the press collectively characterized as "vibrant."[60] Paul Jozon, in contrast, advanced the position that this was an administrative act alone and that even if it were illegal, it did not fall within the purview of judicial jurisdiction.[57][61]
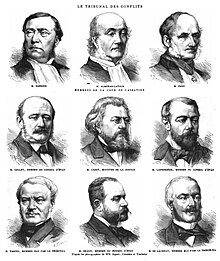
On November 5, the Tribunal issued a ruling in the case of Marquigny v. Prefect of Nord, determining that the judicial system was not the appropriate venue for addressing the matter at hand. The Tribunal's rationale for this decision is as follows:[58]
Considering that it cannot be the role of the judiciary to annul the effects and prevent the execution of this administrative act; that, certainly, as a formal exception to the principle of the separation of powers, this authority can assess the legality of police actions when it is called upon to impose a penalty against offenders, but that this exception does not apply to the present case; — Considering that if Mr. Marquigny and others believed they were justified in arguing that the measure taken against them was not authorized by any law and that, consequently, the decree of March 29, 1880, and the aforementioned order were tainted with excess of power, it was to the administrative authority that they should have turned to seek the annulment of these acts; — Considering that the president of the Lille Tribunal, in declaring himself competent, misunderstood the principle of the separation of powers, [...]
Subsequently, the Tribunal rendered a similar decision in favor of the Prefect of Vaucluse.[54] It appears that the decision was reached following the replacement of certain members of the Tribunal before November 4.[56] The ruling was not unanimous. On November 6, 1880, judges Lavenay (former chamber president of the Council of State under the Second Empire) and Tardif (former counselor at the Court of Cassation)—members elected by their peers from the seated judiciary, excluding the Court of Cassation—resigned. In his letter to the Minister of Justice, Tardif stated,[53] "I am compelled to resign from the Tribunal des Conflits to avoid any association with decisions that I consider to conflict with my conscience as a magistrate. Furthermore, I am unwilling to endorse measures that I believe to be illegal, or to have my signature appear at the bottom of any decisions that I am obliged to report."
Nevertheless, the judicial escalation persists, with civil courts persisting in their assertion of competence, ruling in favor of the religious, and openly disregarding the conflict resolutions issued by the prefects.[62] On November 8, 1880, in Limoges, the Tribunal des Conflits was deemed powerless to act in the face of the "rigorous duty of a magistrate to hear the complaints of citizens violently thrown out of their homes." In his investigation, Judge Rogues de Fursac invoked the decree of September 8, 1870, to challenge the immunity of high-ranking officials and justify the lawsuit filed by the Oblates of Mary Immaculate and the Franciscans. The prefect was compelled to once again involve the Tribunal des Conflits to circumvent the trial.[54] On December 9, 1880, the Criminal Chamber of the Court of Cassation concurred with the Tribunal des Conflits. The Tribunal des Conflits ruled that the prefectural closure order constituted an administrative act and could not be contested or controlled by the judicial authority, as the decree-law of 3 Messidor, Year XII (June 22, 1804) had not excluded the administration's right to intervene in expulsions.[55] The resistance of the Court of Appeal of Poitiers, one of the last to continue fighting against the decrees, was finally overcome by a ruling of the Tribunal des Conflits on December 22, 1880.[54]
In response, the Republican Party took action to remove from office all judges who had opposed the anti-religious decrees. This included the judges Le Roy and Leroux de Bretagne, who were dismissed despite their considerable legal expertise. This action was taken as a retaliatory measure following the lifting of the rule of immovability for judges in 1883.[55]
Outcome of the expulsions
[edit]Expulsion of the Jesuits
[edit]
The initial expulsion, which occurred on June 30, 1880, at the direction of the Charles de Freycinet government, affected solely the Society of Jesus. Concurrently,[63] in the 31 French departments where they were present,[18] the Jesuits were expelled from their residences. Incidents of a similar nature occurred in all locations, with doors being forced open, locks picked, and peaceful protests from demonstrators. Some dramatic events were reported by the press, including the case of Father Fristot, who recalled that the Germans had already expelled him from Strasbourg in 1872. In Toulouse, the gendarmes presented arms to an expelled military chaplain.[63]
The issue of the educational institutions was addressed in a separate section. The deadline for the Jesuits to evacuate their 28 colleges expired on August 31,[63] thereby confirming their expulsion from these institutions. The refusal to secularize to retain the management of the institutions—as Pope Leo XIII would have wanted, but the superiors of the Society renounced it out of honor—led to the transfer of the institutions to laypeople and seculars. As a result of the expulsions, 496 of them withdrew, leaving 701 managing the colleges at the time. However, the remaining members settled outside the schools and attempted to continue teaching as staff members.[43]
The Minister of Public Instruction, Jules Ferry, who was opposed to the continued existence of these institutions, ordered their closure through academic councils under the pretext of "reconstitution de congrégation." This was the case for the Sainte-Marie du Caousou school in Toulouse and the Notre-Dame de Mont-Roland college in Dôle.[63] However, the prestigious Sainte-Geneviève institution in Paris, which had come under lay control, was exempted from this decision.[64]
As a consequence of the expulsions, the Jesuits were also obliged to relinquish their responsibility for seven major seminaries.[43]
Second wave of expulsions
[edit]
The second decree, which was rigorously enforced by Council President Jules Ferry between October 16 and November 9,[28] targeted other unauthorized male congregations.[4] The same expulsion scenes occurred once more, this time with the addition of violent incidents. In some instances, the army was called upon by certain prefects. The military's objective was to occupy the surrounding areas of the religious houses, prevent the crowd from approaching, and prevent any clashes between Catholic and anti-Catholic demonstrators. Troops were rarely directly involved in the expulsion process itself. However, public opinion viewed the army's intervention—this "holy ark"[N 6]—with "strong emotion," and the civil authorities had to intensify their efforts to assuage the officers' concerns.[66]
The two expulsions resulted in the closure of 261 establishments[4] and the dispersal of thousands of religious individuals. On November 7, Ferry announced 5,643 exiles, and this number reached 6,589 in December 1880.[28] This figure represented 88% of the exiles recorded in 1876.
To circumvent expulsion, some congregations opted to relinquish their habits and pursue a process of secularization. This was the decision of the Dominicans of the Saint-Elme School in Arcachon, who sought to safeguard their pioneering preparatory college for the Naval School. The college was notable for its training ship, the three-masted Saint-Elme, which was used to prepare future officers. However, due to the toxic political climate, the ship did not sail after July 15, and the college shifted its focus to more traditional forms of education.[67] In rare cases, certain male congregations managed to avoid expulsion without secularizing. For instance, in the Nord department, where the decrees were particularly unpopular, the Trappists of the Mont des Cats Abbey were able to evade expulsion by being classified as an agricultural society.[68]
Female congregations were spared from the actions of opportunistic Republicans,[30] as the popular piety surrounding them would have caused more serious incidents and endangered the government.[38] However, some anti-clerical municipalities exceeded their orders and expelled the nurse nuns from communal hospitals.[13]
The expulsions of 1880 can be largely traced through the book Expulseurs et expulsés by Gustave de Fleurance.[69]
Outstanding expulsions
[edit]In Paris
[edit]Jesuits on Rue de Sèvres (June 30)
[edit]
The sole establishment in Paris affected by the implementation of the initial decree was the motherhouse of the Society of Jesus,[70] situated at 33 Rue de Sèvres.[38] Consequently, the event was extensively documented by contemporary press outlets,[70] including some foreign journalists.[71]
On June 29, 1880, at nine o'clock, Commissioners Clément and Dulac arrived to seal the door of the chapel, observed by a considerable gathering of onlookers.[63] The following morning, at dawn, a considerable number of devout Catholics and supporters of the Jesuits assembled in front of the establishment.[72] According to L'Illustration, each individual placed a note of gratitude into the mailbox. The silent vigil persisted until 4:30 a.m., when the commissioners returned, accompanied by a hundred police officers and several officers.[70] Also present was Louis Andrieux, the prefect of police.[63] The commissioners proceeded to enter the establishment, where they were met with a hostile reception. The crowd shouted "Long live the Jesuits! Long live freedom! Down with the decrees!" The commissioners were then confronted by Deputy Léon de Baudry d'Asson and Senators Hippolyte-Louis de Lorgeril and Hervé de Saisy. The situation was further complicated by the presence of 500 demonstrators,[70] who were attempting to express their opposition to the commissioners' actions.[33]
With the inner door secured, Clément perused the document containing the expulsion decree. Father Pitol, the superior of the community, and Senator Lacroix de Ravignan from Landes—the president of the civil society owning the building—responded through the door that the Jesuits would only yield to force. A locksmith was called to the scene to break the lock. As the crowd once again threatened to overwhelm the police, two additional brigades of police officers were required to push the demonstrators back to the two ends of the Bon Marché square.[70] Blows were exchanged, and Senator Léon d'Andigné, having torn a policeman's uniform, was arrested.[38]
Upon entering the establishment, Clément and Dulac encountered approximately thirty right-wing parliamentarians at the top of the grand staircase. Meanwhile, the fathers had withdrawn to their cells. Among the elected officials who had spent the night in the convent were former Minister Jean Ernoul, Senators Charles Chesnelong, Joseph de Carayon-Latour, Vincent Audren de Kerdrel, Adrien Tailhand, and Raymond de La Croix de Ravignan, and Deputies Émile Keller, Émile de Kermenguy, Édouard de La Bassetière, Adolphe de Partz, François-Marie Villiers, and Charles du Bodan.[70]
Notwithstanding the objections raised by the parliamentarians, the commissioners proceeded to unlock the cells[38] and forcibly remove their occupants. Each expelled Jesuit was accompanied by a different parliamentarian, and thus they appeared on Rue de Sèvres,[72] with Father Marin and Carayon-Latour at the vanguard. As they proceeded, women attired in black knelt and kissed the hands or cassocks of the fathers, making the sign of the cross. The religious, except for two guards and an infirm man, were then conveyed to vehicles chartered by the parliamentarians.[70]
The chapel being sealed, Commissioner Clément declined to permit the removal of the Blessed Sacrament from the tabernacle by the religious. The following day, Archbishop Richard de La Vergne, the coadjutor of the Archbishop of Paris, arrived and temporarily lifted the seals, thus enabling the retrieval of the consecrated hosts. His return to Saint-Sulpice Church in Paris was followed by a procession of 10,000 Parisian Catholics, and a solemn mass was celebrated in honor of the expelled Jesuits.[73]
- Expulsion of the Society of Jesus as seen by Le Monde illustré
-
The rue de Sèvres at six o'clock in the morning: a Jesuit on the arm of a right-wing member of parliament walks through the cheering and praying crowd.
-
Police commissioners lock up a cell, while a Jesuit prepares to leave on the arm of a member of parliament.
-
Jesuit fathers apprehended in their cells.
Dominicans of Rue Jean-de-Beauvais (November 5)
[edit]

In an account provided to Le Monde illustré, journalist Dick de Lonlay offers a detailed description of the circumstances surrounding the expulsion of the Dominicans from their residence on Rue Jean-de-Beauvais:[74]
At ten minutes to six, Mr. Dulac, accompanied by the police commissioner of the Sorbonne district, Mr. Cotton d'Englesqueville, rings the bell at the Dominican convent. 'Open! In the name of the law!' says Mr. Cotton. 'In the name of what law?' The gate closes abruptly in the commissioners' faces.
Mr. Dulac, irritated, calls the firefighters. Following his orders, these soldiers raise their axes and strike repeatedly at the convent door. It takes five minutes. The door shatters.
Messrs. Dulac and Cotton then see Fathers Mercier and Jouin. These two Fathers, in their white robes, wear the red ribbon and cross of the Legion of Honor. Oh! That's nothing. Just a memento from the 1870 war. Up in the North, with Faidherbe, near Bapaume, these two priests were decorated for their heroic conduct on the battlefield. Brother Bernard is there too. The Crimean and Italian medals shine on his chest. He’s an old Zouave, one of those who took Malakoff.
'Gentlemen,' says Brother Bernard to the commissioners who are trying to read the decrees, 'ten years ago, you defended us against the Communards; today you follow in their footsteps.'
The agents then enter the parlor, separated from the cloister by a glass door. Panels have been placed over the glass. The axes hit the door and the glass shatters. The firefighters hesitate for a moment under this new bombardment. The door finally gives way. The cells are successively invaded, and the religious are expelled.
Fathers Jouin, Mercier, Monjardet, and Bernard remain as guards of the convent.
Le Soleil also notes that Senator Louis Buffet and other laypeople assisted the fathers and that four of them were arrested, including Henry Cochin, poet Lucien Augé de Lassus, and Louis Teste, journalist for Le Gaulois.[75]
Capuchins of Rue de la Santé (November 5)
[edit]
By October 1880, the Capuchin Friars on Rue de la Santé anticipated their imminent expulsion. Each evening, over a hundred Catholics would take up residence in the friars' spacious study hall, which had been converted for the occasion into a dormitory. Among the laypeople who came to support the Capuchins were several prominent figures, including Senator Raymond de Malherbe, Catholic activist Charles Ozanam, journalist Georges de Fourcy (son of Eugène de Fourcy), diplomat Léon-Édouard Amelot de Chaillou, General Charles Camô, engineer Gustave de Ponton d'Amécourt, and royalist Jacques Libman.[74]

On the night of November 5, 1880, at five in the morning, the convent was subjected to a sudden and violent assault by 200 municipal police officers and 20 firefighters. At 6:35 a.m., Commissioner Clément and Commissioner Fehninger, accompanied by ten police officers, entered the chapel while Father Clément was officiating the Mass. Once the Mass had concluded, the Blessed Sacrament was being stored away and the congregation was singing the Magnificat when Clément gave the order for the chapel to be evacuated. The faithful refused to comply and retreated to the rear of the hall, where they were forcibly removed by the police, who dragged them away from the gates separating the attendees from the choir where the Capuchins were located.[74]
Once the evacuation of the chapel is complete, Clément proceeds to seal off the convent and engages in discourse with the provincial superior via the gate. Subsequently, he provides a detailed account of the prefect's decree, which mandates the dissolution of the community. He then demands that the door be opened, but is met with refusal. Subsequently, three firefighters forcibly enter the premises while the religious community sounded the alarm. A second door was then forced open to gain access to the cloister, where Father Provincial Arsène, the other religious, and thirty laypeople, including Libman, Ozanam, Ponton d'Amécourt, and de Fourcy, were located. The latter group greeted the authorities with enthusiastic cries of "Long live the Capuchins! Long live freedom!"[74]
Father Arsène approaches Clément and addresses him with the following words: "You should be aware that, as a result of your actions, you and all those who have participated in this unfortunate undertaking are now excommunicated." In response, the commissioner states: "You are offending a magistrate in office; in the name of the law, I arrest you!" Father Arsène is taken to the Santé prison, as are Libman and Ozanam, who intervened. After this incident, Clément orders the doors of the cells on the first floor to be broken open, resulting in the expulsion of twelve religious individuals. The remaining laypeople present are also detained and taken to the Santé, where they are released at nine in the evening.[74]
- Expulsion of the Capuchins of Rue de la Santé as seen by Le Monde illustré.
-
Father Arsène blessing the friends of the Capuchins, October 30, 1880, in the convent courtyard.
-
Defenders of the religious in the Capuchin study room, November 4, 1880 evening.
-
Father Arsène announces his excommunication to Commissaire Clément, November 5, 1880.
In the rest of France
[edit]'Siege of Frigolet' (November 5-8)
[edit]
On November 5, the Premonstratensians were to be forcibly removed from the Abbey of Saint-Michel de Frigolet, located in Tarascon within a fortified enclosure, by the police. The police, with the assistance of the gendarmerie, were unable to execute the decrees due to the fact that approximately sixty religious figures had barricaded themselves within the abbey with three thousand laypeople,[76] including Frédéric Mistral,[77] Joseph de Cadillan (former deputy and mayor of Tarascon), Hyacinthe Chauffard (former master of requests and publicist Count Hélion de Barrème, and Count Pierre Terray (future mayor of Barbentane).[78]
Faced with this unexpected resistance, Eugène Poubelle, prefect of Bouches-du-Rhône, requisitions General Guyon-Vernier, at the request of General Farre, Minister of War, and places him at the head of the 26th regiment of dragoons with the objective of dislodging the Premonstratensians. With three squadrons—comprising 240 cavalrymen—General Guyon-Vernier established a blockade of the fortress, preventing any ingress but allowing those already within to depart. This enabled the evacuation of women from the premises.[79] Cannons were also positioned and aimed at the abbey.[77]
While the Catholic inhabitants of the abbey engage in musical activities and the preparation of bulletins, the military forces continue to maintain the blockade. Guyon-Vernier relieves two cavalry squadrons comprising 500 infantrymen[79] from the 141st Line[77] and maintains 80 dragoons to continue patrolling the area. With a significant number of laypeople having evacuated the fortress, only 800 men remain with the religious personnel, while a crowd of 2,000 Catholics is gathered in the vicinity and kept at a distance by the troops.[79]
At this juncture, Guyon-Vernier elects to commence the assault. The civil authorities proceed with the legal summons, but when the Premonstratensians decline to comply, the fortress doors are forcibly broken down[79] and the grille is pried open. At the moment of his arrest, the Reverend Father declares, "We are in the painful duty of informing you that you and your accomplices are subject to the major excommunication reserved for the Pope."[77] Consequently, 68 religious in habit are detained and escorted to Tarascon by the dragoons, while two sick religious are allowed to stay on site.[79]
- The siege of Frigolet as seen by the Illustrated Press
-
Location of General Guyon-Vernier's troops, November 8, 1880. Drawing from Le Monde illustré.
-
The Prémontrés convent surrounded by troops positioned on the ridges. Drawing from L'Illustration.
-
The Abbey administrators who reported the siege to the Aix-en-Provence Court of Appeal.
Solesmes (November 5), Bellefontaine (November 6), and Tamié (November 7)
[edit]The expulsion of the religious from the Abbey of Notre-Dame de Bellefontaine and the Abbey of Saint-Pierre de Solesmes also resulted in violent confrontations.[28] At Bellefontaine, near Angers, a considerable number of individuals congregated around the abbey for three days to safeguard it from the authorities.[80] Ultimately, the 70 Trappists were expelled by 500 men from the 135th Line and six gendarmerie brigades.[38] Bishop Freppel, deputy and bishop of Angers, and Henri de Durfort-Civrac, vice-president of the Chamber of Deputies, provided accompaniment and support to the religious during the evacuation. At Solesmes, near Sablé-sur-Sarthe, the expulsion of the Benedictines[81] necessitated the presence of 200 to 300 soldiers,[78] while a crowd demonstrated respect for the soldiers and protested the forced exile of the Benedictines.[78]
On November 7, 1880, the Trappists of the Abbey of Notre-Dame de Tamié were forcibly removed from their premises by seven brigades of gendarmerie and 50 line soldiers. The operation, which commenced at 7 a.m., continued until 2 p.m. due to the necessity of removing the thick planks that were serving as supports for the abbey's iron doors. Furthermore, the authorities were obliged to forcibly open each cell within the abbey to expel the 25 religious figures.[82][78]
Tourcoing Riot (November 8)
[edit]
On November 8, rumors began to circulate that the Marist Fathers of Tourcoing would be expelled. In the early afternoon, a thousand Catholics assembled around the Marists' convent, shouting "Long live the Fathers!" and "Down with the decrees!" In response, pro-expulsion rioters gathered and fights broke out. Initially repelled by the Catholic militants, the crowd returned despite the efforts of the central commissioner.[79]
Subsequently, the rioters assaulted the convent with bricks, smashed the windows, attempted to topple the statue of the Virgin overlooking the entrance door, and endeavored to gain entry to the building through the windows. Law enforcement personnel dispatched from Lille were ultimately responsible for restoring order; in the evening, several mounted charges were necessary to clear the convent. Among the rioters, 80 sustained injuries (including two that were life-threatening), and two gendarmes were also injured.[79]
On November 9, the Marists were forcibly removed from the premises by the police, who gained entry through the windows in the early morning hours.[83]
Consequences
[edit]A relative exile of the congregations
[edit]The ultimate fate of the expelled congregations was markedly disparate. Baron de Mackau's committee of legal experts advised the religious to identify alternative premises and resume their communal life less conspicuously. This entailed reducing the size of the groups, selecting less isolated locations, and avoiding modifications to the premises that would facilitate communal life. Since forming a congregation is not a criminal act, religious individuals are free to relocate to continue their communal life.[9] The government can then effectively disperse the congregation, but no additional sanctions are applicable. Consequently, some communities elect to reside for a few months to a few years in nearby houses provided by laypeople before returning to their convent.[43]
In response to the precariousness of their situation and the possibility of further expulsion, other congregations have opted to relocate to other countries. Spain, Belgium, Italy, the United Kingdom, and Quebec have emerged as prominent destinations.[84] Some communities have even migrated to the United States, Oceania, or China.[9]
Installations in Spain
[edit]
In May 1880, the French ambassador, Benjamin Jaurès, secured from the Spanish President of the Council of Ministers, Antonio Cánovas, an edict banning the establishment of exiled congregations in the Spanish border regions, with all other establishments requiring the approval of the Spanish government. This was done in response to concerns from the French government that such actions might lead to the formation of counter-revolutionary strongholds along the border.[85]
Notwithstanding this concession[N 7] and a few isolated instances,[N 8] Spain proved to be a hospitable refuge for French clergy. The Marquis of Molins, the Spanish ambassador, observed that the actions of the opportunist republicans "enact[ed] the most severe measures against clergy, while a broad amnesty is proclaimed towards the murderers and arsonists of the Commune." He was thus concerned about the fate of Spanish congregants established in France. Consequently, he responded favorably to the requests of the French clergy, providing numerous letters of recommendation to the Spanish government.[85] Moreover, the Spanish monarchical Restoration period was conducive to the establishment of religious congregations, marking a reversal of the anti-clerical climate that had characterized the dynastic crisis of the 1830s.[87] Despite the lack of governmental subsidies,[88] the newcomers were able to secure financial assistance from various sources, including the Spanish clergy,[89] the local population,[88] long-established French clergy,[87] and funds collected by the Denier des Exilés, which, under the management of the Count of Beaurepaire, managed to raise 600,000 francs.[89]
Of the 6,589 clergy members who were expelled, Spain received approximately 840[90] (or 13%), the majority of whom were from congregations based in southwestern France.[9] The primary congregations that relocated to Spain to a certain extent are the Jesuits (at the monastery of San Salvador de Oña and the monastery of Uclés), the Benedictines (at the Priory of Saint-Dominic de Silos), the Capuchins (at the convent of Santo Domingo and in Manresa), and the Assumptionists (in El Burgo de Osma), the Discalced Carmelites (dispersed throughout the country and then gathered from 1883 in Calahorra), the Dominicans (in Salamanca and Belmonte) and the Franciscans (at the convent of Nuestra Señora de Loreto)[10] were among the expelled clergy who sought refuge in Spain. In addition, authorized French congregations (of both sexes) established refuge houses and other establishments in Spain, motivated by concerns about the potential for anti-clerical measures to intensify under the Republic.[91]
Installations in North America
[edit]Several expelled congregations from Europe settled in the northern United States. For example, the Congregation of Holy Cross relocated its headquarters to Notre Dame, Indiana, while the Dominicans founded a convent in Lewiston, Maine, in 1881 to accommodate French exiles.[84] The Eudists, too, settled in Troy, New York.[92]
Nevertheless, the majority of French clergy who migrated to North America established themselves in Quebec, which offered the dual advantage of being both Francophone and Catholic. Among the congregations that settled in Quebec were the Trappists, who established the Abbey of Oka, and the Montfortians,[80] who founded the village of Monfort. The latter were followed by the Daughters of Wisdom.[93] The origin of these pioneering clergy is the Vendée blanche, known for its counter-revolutionary traditions, which partly explains their distrust of the Republic and their exile.[94]
Return of the congregations
[edit]A significant number of congregations were able to resume their activities in their original locations in the subsequent years. The case of the Abbey of Notre-Dame de Bellefontaine is noteworthy. Following the expulsion of the Trappists, a contingent of soldiers was mobilized to guard the abbey's cattle. This allowed the monks to re-enter their abbey a mere five weeks after their initial expulsion.[80] It should be noted, however, that the circumstances were highly variable, with some communities being dispersed for a period exceeding fifteen years. Consequently, the Benedictines of the Abbey of Saint-Pierre de Solesmes, having resided in proximate houses and manors, endeavored to re-establish themselves in the abbey in March 1882. However, they were once again expelled by a substantial detachment of gendarmes. Abbot Dom Delatte initiated efforts to recover the abbey in 1890.[95] He secured the support of the Spanish ambassador, Fernando León y Castillo, at the request of Marie-Christine of Austria, regent queen of Spain.[96] After five years of negotiations, he successfully achieved the re-integration of the abbey on August 23, 1895.[95]
As early as 1882, clergy who had been exiled from their dioceses returned from abroad to re-form their congregations. The rapprochement between the Holy See and the French government commenced in 1885 and reached its zenith with the Ralliement that Leo XIII requested in 1892. This was met with opposition from Eugène Spuller's New Spirit, which in turn accelerated the movement for the return of congregations to France. The Jesuits of Uclés were the last to leave Spain, in 1897.[96]
Towards the end of congregational teaching
[edit]
For Jules Ferry and the Republican Left, the expulsion of the congregations represented merely a preliminary step in their broader campaign against clericalism and in favor of secularizing education. Consequently, on December 21, 1880, shortly after the implementation of the decrees, Deputy Camille Sée, a close associate of Jules Ferry, proposed a legislative measure to establish public secondary education for girls, wherein catechism would be replaced by courses in secular morality. Subsequently, Jules Ferry facilitated the establishment of the École Normale Supérieure de Sèvres, which was designed to train female teachers for the newly created girls' lycées. This development represented a significant achievement for the moderate Republicans, as it marked the end of the Catholic Church's monopoly on secondary education for girls.[13]
With regard to the education of girls and boys in the primary grades, the Ferry Law of June 16, 1881, established its gratuitous nature, which was further reinforced by the Ferry Law of March 29, 1882, which made it secular and compulsory. As a result, primary education became a cornerstone of the Third Republic's triumph over clericalism. The "black hussars," as they were known, were responsible for educating students to become free citizens and ardent patriots.[13] The conflict then intensified around the issue of secular schooling, which Catholics accused of portraying the Church in a negative light and espousing anti-religious sentiments under the guise of neutrality. This led to the First War of the Textbooks, a period of unrest in French communes between 1882 and 1883.[97] In 1886, the Goblet Law further reinforced the Ferry laws by requiring the secularization of the teaching staff in secular schools, effectively barring clergy from teaching in these institutions.[98]
The final eviction of educational establishments run by congregations — whether they were female and thus escaped expulsion, or male and having reconstituted themselves after 1880 — was carried out by the radicals with the expulsion of congregations in 1903, following the implementation of the 1901 law, which was perceived as derogatory by many. In 1904, the struggle ended with the outright prohibition of teaching congregations.[99]
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ This is not the case for female congregations, which are all placed under the authority of bishops or superiors residing in France.[1]
- ^ In 1878, 83 out of 115 male congregations did not have legal authorization.[6]
- ^ Freycinet is, in fact, a devotee of the Abbey of Solesmes where he has made several retreats.[6]
- ^ This right will eventually be recognized by the 1901 law on associations but will be subject to a special regime of severity for religious congregations.
- ^ These include: Article 1 of the law of February 13-19, 1790; Article 1, Title 1, of the law of August 18, 1792; Article 11 of the Concordat; Article 11 of the law of April 8, 1802 (18 germinal year X); the decree-law of June 22, 1804 (3 Messidor year XII); Articles 291 and 292 of the Penal Code; the law of April 10, 1834; the decree-law of January 31, 1852.[46]
- ^ A French expression of the time used to refer to the military institution, which was supposed to be above the parties.[65]
- ^ This diplomatic gesture is notably due to France's help in repressing republican and Carlist subversion between 1878 and 1879.[85]
- ^ On November 12, Catalans attacked about ten Capuchins who had come from Narbonne. Some congregations located in the prohibited zone also had to move.[86]
References
[edit]- ^ a b Laperrière 1996, p. 52
- ^ a b Laperrière 1996, p. 53
- ^ Mayeur, François (1971). "Les évêques français et Victor Duruy : les cours secondaires de jeunes filles". Revue d'histoire de l'Église de France (in French). 57 (159): 267–304. doi:10.3406/rhef.1971.1872. Archived from the original on July 30, 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Mayeur 1980, Contre la milice romaine
- ^ a b c d e Laperrière 1996, p. 54
- ^ a b c Lecomte 2001, p. 138
- ^ a b c Lecomte 2001, p. 139
- ^ Catta 1930, p. 401
- ^ a b c d e Delaunay 1981, p. 296
- ^ a b Delaunay 1981, pp. 313–315
- ^ a b c "Dossier d'histoire : Les lois scolaires de Jules Ferry". www.senat.fr (in French). Archived from the original on April 8, 2022. Retrieved May 27, 2020.
- ^ a b Wright, Vincent (1972). "L'épuration du Conseil d'État en juillet 1879". Revue d'histoire moderne et contemporaine (in French). 19 (4): 621–653. doi:10.3406/rhmc.1972.2239. Archived from the original on August 30, 2024.
- ^ a b c d "29 mars 1880 - Jules Ferry expulse les religieux de l'enseignement - Herodote.net". www.herodote.net (in French). Retrieved May 31, 2020.
- ^ a b "Les lois scolaires de Jules Ferry : la loi du 18 mars 1880 relative à la liberté de l'enseignement supérieur". www.senat.fr (in French). Archived from the original on June 2, 2020. Retrieved May 27, 2020.
- ^ "Loi du 18 mars 1880 relative à la liberté de l'enseignement supérieur : les débats". www.senat.fr (in French). Archived from the original on June 2, 2020. Retrieved May 27, 2020.
- ^ a b c d Delaunay 1981, p. 272
- ^ a b c Catta 1930, p. 389
- ^ a b c d e f g Laperrière 1996, p. 55
- ^ Catta 1930, p. 387
- ^ Hayward 1937, § 15
- ^ a b c Debré, Jean-Louis (1981). La justice au XIXe siècle : Les magistrats (in French). Perrin. ISBN 978-2-262-08478-3. Archived from the original on April 9, 2024.
- ^ Marchasson 1974, p. 355
- ^ Marchasson 1974, p. 370
- ^ Marchasson 1974, p. 358
- ^ Marchasson 1974, p. 363
- ^ a b c Hayward 1937, § 18
- ^ Hayward 1937, § 14
- ^ a b c d e f g h Laperrière 1996, p. 56
- ^ a b c d e f Delaunay 1981, p. 295
- ^ a b c Mayeur 1980, L'échec du compromis
- ^ Renault 1989, p. 397
- ^ Lecomte 2001, p. 149
- ^ a b Lecomte 2001, p. 141
- ^ a b Lecomte 2001, p. 145
- ^ "Paris, 11 novembre 1880, à la Chambre". Le Soleil (in French). November 12, 1880. p. 1. Archived from the original on January 20, 2021.
- ^ "Edme, Armand, Gaston d'Audiffret-Pasquier". Dictionnaire des parlementaires français (in French). Edgar Bourloton. 1889–1891.
- ^ Collectif (2005). Le Grand Exil des congrégations religieuses françaises (1901-1914). Histoire (in French). Paris: Cerf. pp. 59–87. ISBN 2-204-07469-1.
- ^ a b c d e f Sévillia, Jean (2013). Quand les catholiques étaient hors la loi (in French). Place des éditeurs. ISBN 978-2-262-03875-5. Archived from the original on February 9, 2022.
- ^ a b c "Léon, Armand, Charles de Baudry d'Asson". Dictionnaire des parlementaires français (in French). Edgar Bourloton. 1889–1891.
- ^ a b "La Chambre des députés". Le Gaulois (in French). November 10, 1880. p. 1. Archived from the original on September 1, 2023.
- ^ a b c d Mayeur 1980, « Les jésuites à la frontière ! »
- ^ Bauzon, Louis (November 8, 1880). "Nos amis civils". Le National (in French). Archived from the original on September 28, 2022.
- ^ a b c d Laperrière 1996, p. 57
- ^ a b Catta 1930, p. 397
- ^ a b c d Marchasson 1974, p. 374
- ^ Catta 1930, p. 396
- ^ Catta 1930, pp. 398–399
- ^ a b Martinage 1986, p. 673
- ^ "Évènements et bruits du jour". Le Soleil (in French). November 8, 1880. Archived from the original on April 24, 2021.
- ^ "Presse politique de Paris". Le Soleil (in French). November 8, 1880. Archived from the original on April 24, 2021.
- ^ "Henri Ferron de La Ferronnays". Dictionnaire des parlementaires français (in French). Edgar Bourloton. 1889–1891.
- ^ Institut d'histoire du droit et Institut des droits de l'homme (1996). Les Déclarations de l'an I : Colloque de Poitiers (2 et 3 décembre 1993) (in French). note 609. Presses Universitaires de France. ISBN 978-2-13-068047-5. Archived from the original on August 30, 2024.
- ^ a b "Condamné par le Tribunal des conflits". Le Gaulois (in French). November 7, 1880. p. 1. Archived from the original on August 30, 2024.
- ^ a b c d e Lecomte 2001, p. 146
- ^ a b c d Martinage 1986, p. 675
- ^ a b c d Martinage 1986, p. 674
- ^ a b c d e "Au Tribunal des conflits". Le Gaulois (in French). November 5, 1880. Archived from the original on February 3, 2023.
- ^ a b c Hauriou, Maurice (January 7, 2015). "Compétence du tribunal judiciaire pour interpréter le sens d'un règlement administratif, mais non pas pour en apprécier la légalité". Revue générale du droit (in French). Archived from the original on August 30, 2024. Retrieved May 26, 2020.
- ^ Brochard, Adrien (2017). Une histoire du Tribunal des conflits : le Tribunal des conflits et la protection de l'administration (PDF) (in French). Université Paris II - Panthéon-Assas. p. 368. Archived from the original on August 30, 2024.
- ^ "Le Tribunal des conflits". Le Monde illustré. November 20, 1880. Archived from the original on April 24, 2021.
- ^ "Le Tribunal des conflits". Le National (in French). November 6, 1880. Archived from the original on July 11, 2022.
- ^ Dalloz, Édouard (1881). Jurisprudence générale du royaume en matière civile, commerciale et criminelle. Journal des audiences de la Cour de cassation et des Cours royales (in French). Paris: Désiré Dalloz. p. 21. Archived from the original on August 30, 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f Mayeur 1980, Introduction
- ^ "Un peu d'histoire — Lycée Privé Sainte Geneviève". www.bginette.com (in French). Archived from the original on July 30, 2022. Retrieved May 30, 2020.
- ^ Boniface, Xavier (2018). "L'« arche sainte » et ses limites : L'armée, la société et la République". Histoire militaire de la France, vol. 2 : De 1870 à nos jours (in French). Paris: Perrin. pp. 133–151. ISBN 9782262065133. Archived from the original on September 28, 2022.
- ^ Boniface, Xavier (2003). "L'armée et les inventaires dans le Nord de la France (1906)". Revue du Nord (in French) (350): 393–408. doi:10.3917/rdn.350.0393. Archived from the original on August 30, 2024.
- ^ Traizet, Jacques (1977). Le premier navire-école : Une école centrale maritime commerciale, l'École Saint-Elme d'Arcachon (1872-1880) (in French). FeniXX réédition numérique. ISBN 978-2-402-22803-9. Archived from the original on August 30, 2024.
- ^ "Décret du 29 mars 1880 | Mont des Cats" (in French). Archived from the original on July 11, 2022. Retrieved June 4, 2020.
- ^ de Fleurance, Gustave (1888). Expulseurs et expulsés (in French). Paris: Letouzey et Ané. Archived from the original on August 30, 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f g "L'application des décrets du 29 mars". L'Illustration (in French). July 10, 1880. Archived from the original on April 20, 2020.
- ^ "París : expulsión de los jesuitas". La Ilustración Española y Americana (in Spanish). July 15, 1880. Archived from the original on July 11, 2022.
- ^ a b Hayward 1937, § 16
- ^ Catta 1930, p. 404
- ^ a b c d e "L'exécution des décrets à Paris". Le Monde illustré (in French). November 13, 1880. Archived from the original on April 24, 2021.
- ^ "Les expulsions à Paris". Le Soleil (in French). November 6, 1880. Archived from the original on April 24, 2021.
- ^ "Les expulsions en province - Tarascon". Le Soleil (in French). November 6, 1880. Archived from the original on April 24, 2021.
- ^ a b c d Sévillia, Jean (2013). Quand les catholiques étaient hors la loi (in French). Place des éditeurs. ISBN 978-2-262-03875-5. Archived from the original on February 9, 2022.
- ^ a b c d "Départements, Algérie et colonies". Le Soleil (in French). November 8, 1880. Archived from the original on April 24, 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Les expulsions en province". Le Monde illustré (in French). November 20, 1880. Archived from the original on April 24, 2021.
- ^ a b c Laperrière 1996, p. 60
- ^ Hayward 1937, § 19
- ^ "Exécution des décrets". Le National (in French). November 8, 1880. Archived from the original on September 28, 2022.
- ^ "Départements, Algérie et Colonies". Le Soleil (in French). November 12, 1880. Archived from the original on January 20, 2021.
- ^ a b Laperrière 1996, p. 58
- ^ a b c Delaunay 1981, p. 293
- ^ Delaunay 1981, p. 297
- ^ a b Delaunay 1981, p. 298
- ^ a b Delaunay 1981, p. 303
- ^ a b Delaunay 1981, p. 302
- ^ Delaunay 1981, p. 308
- ^ Delaunay 1981, pp. 317–318
- ^ Laperrière 1996, p. 59
- ^ Laperrière 1996, p. 69
- ^ Laperrière 1996, p. 70
- ^ a b Soltner, Dom Louis (2005). L'Abbaye de Solesmes au temps des expulsions (1880-1901) (in French). Editions de Solesmes. ISBN 978-2-85274-292-5.
- ^ a b Delaunay 1981, p. 309
- ^ Déloye, Yves (1994). "Chapitre 5 : Les guerres scolaires". École et citoyenneté : l'individualisme républicain de Jules Ferry à Vichy : controverses (in French). Paris: Presses de la Fondation nationale des sciences politiques. pp. 199–286. ISBN 2-7246-0655-8. OCLC 32818865. Archived from the original on May 20, 2020.
- ^ Ménager, Bernard (2018). "Tensions et conflits entre l'État et les communes du département du Nord lors des laïcisations d'écoles primaires publiques (1886-1900)". Éducation, Religion, Laïcité (XVIe-XXe s.). Continuités, tensions et ruptures dans la formation des élèves et des enseignants. Histoire et littérature du Septentrion (IRHiS) (in French). Publications de l’Institut de recherches historiques du Septentrion. pp. 391–406. ISBN 978-2-490296-17-0. Archived from the original on June 2, 2022.
- ^ Lanfrey, André (2003). Sécularisation, séparation et guerre scolaire : les catholiques français et l'école, 1901-1914 (in French). Éditions du CERF. ISBN 978-2-204-07196-3. Archived from the original on August 1, 2023.
Bibliography
[edit]Beginnings of the Third Republic
[edit]- Capéran, Louis (1957). Histoire contemporaine de la laïcité française (in French). Vol. 1 : La Crise du 16 mai et la revanche républicaine. Marcel Rivière.
- Machelon, Jean-Pierre (1976). La République contre les libertés ? Les restrictions aux libertés publiques de 1879 à 1914 (in French). Presses de la Fondation nationale des sciences politiques. ISBN 978-2-7246-0361-3.
Decrees of March 1880
[edit]- Chambre des députés (1880). L'Etat et les congrégations religieuses : étude d'histoire et de droit sur les décrets du 29 mars 1880 et les lois existantes (in French). A. Quantin. pp. 78 et. seq. Archived from the original on August 30, 2024.
- Bernaudeau, Vincent (2003). "La Magistrature dans la balance au temps de la République combattante : l'affaire des décrets, prélude à la "révolution judiciaire" dans l'ouest de la France (1879-1880)". Histoire de la justice (in French) (15): 199–218.
- Catta, Tony (1930). "Le cinquantenaire d'un coup de force : Les décrets du 29 mars 1880 et l'épuration de la magistrature". Revue catholique des institutions et du droit (in French). 68 « LVIIIe année ». Paris ; Lyon ; Grenoble ; Bruxelles ; Poitiers: 385–414. Archived from the original on June 29, 2021.
- Lecomte, Catherine (2001). "Le préfet et les congrégations religieuses (1880-1883)". La loi du 28 pluviôse an VIII deux cents ans après, le préfet et les libertés : XIXe et XXe siècles (actes du colloque du 1er et 2 décembre 2000 (in French). Limoges: PULIM. pp. 135–149. ISBN 2-8428-7195-2.
- Errors in dates on pages 145 and 146, refer to Dalloz.
- Martinage, Renée (1986). "L'épuration des Magistrats du Nord en 1883". Revue du Nord (in French). 68 (270): 663–676. doi:10.3406/rnord.1986.4241. Archived from the original on February 3, 2023.
Expulsion of congregations
[edit]- Delaunay, Jean-Marc (1981). "Des réfugiés en Espagne : les religieux français et les décrets du 29 mars 1880". Mélanges de la Casa de Velázquez (in French). 17 (1): 291–319. doi:10.3406/casa.1981.2350. Archived from the original on August 30, 2024.
- Laperrière, Guy (1996). Les congrégations religieuses, de la France au Québec (1880-1914) (in French). Vol. 1 : Premières bourrasques (1880-1900). Presses Université Laval. ISBN 978-2-7637-7442-8. Archived from the original on February 6, 2024.
- Mayeur, Jean-Marie (1980). "Il y a cent ans : la République contre les Jésuites". L'Histoire (in French) (24): 85–87. Archived from the original on March 30, 2023.
Vatican diplomacy
[edit]- Hayward, Fernand (1937). "5: « Léon XIII et la France »". Léon XIII (in French). Éditions Grasset. ISBN 978-2-7062-8016-0. Archived from the original on February 23, 2024.
- Marchasson, Yves (1974). La diplomatie romaine et la République française : à la recherche d'une conciliation (1879-1880) (in French). Paris: Beauchesne.
- Renault, François (1989). "Aux origines du Ralliement : Léon XIII et Lavigerie (1880 - 1890)". Revue Historique (in French). 281 (2 (570)): 381–432. ISSN 0035-3264. JSTOR 40954873. Archived from the original on August 30, 2024.
Local evictions
[edit]- Bouju, Paul (1955). "L'expulsion des Trappistes de Bellefontaine". Anjou Historique (in French). 54: 84–99.
- de Fleurance, Gustave (1888). Expulseurs et expulsés (in French). Paris: Letouzey et Ané. Archived from the original on August 30, 2024.
- Lanfrey, André (2004). "Les Frères enseignants face à la sécularisation (1880-1914) : Division, redéploiement, résistance, crispation". Les Congrégations religieuses et la société française d'un siècle à l'autre : Actes du colloque des 17-18 octobre 2003 à la Maison de la chimie (in French). Paris: Éditions Don Bosco.
- Soltner, Dom Louis (2005). L'Abbaye de Solesmes au temps des expulsions (1880-1901) (in French). Éditions de Solesmes. ISBN 978-2-85274-292-5.
Further reading
[edit]Contemporary publications
[edit]- Keller, Émile (1880). Les Congrégations religieuses en France : leurs œuvres et leurs services (in French).
- Pingault, Émile (1880). Expulsion des congrégations dans l'Ouest (in French). Angers: Lachèse et Dolbeau.
- Barcilon, Gustave (1880–1881). Les Magistrats et les Décrets du 29 mars 1880 (in French). Vol. 2. Avignon: Séguin.
- Auffray, Jules; de Crousaz-Crétet, Léon (1881). Les Expulsés devant les tribunaux : recueil des décisions judiciaires relatives à l'exécution des décrets du 29 mars 1880 (in French). Paris: Palmé.
- Legey, Henri (1881). Cinq semaines en exil, Bellefontaine, arrondissement de Cholet (Maine-et-Loire) : expulsion des Trappistes, occupation du monastère (6 novembre : 10 décembre) (in French).
- Duparc, Henry; Cochin, Henry (1881). Expulsion des congrégations religieuses : récits et témoignages (in French). Paris: E. Dentu.
- Marie-Antoine (1881). Le Livre d'or des proscrits (in French). Paris: Éditions Privat.
- Cartier, Eugène (1882). Les Moines de Solesmes : expulsions du 6 novembre 1880 et du 22 mars 1882 (in French). Solesmes.


![Legitimist Senator Charles Chesnelong, one of the leaders of the Catholic opposition to the Higher Education Act.[17]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/ac/Charles_Chesnelong_%281820-1899%29.png/72px-Charles_Chesnelong_%281820-1899%29.png)
![Louis Buffet,[17] senator for life and former head of government.](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/8f/Monchablon-Buffet.jpg/92px-Monchablon-Buffet.jpg)
![Jules Dufaure, former Minister of Justice, who gave a speech on March 8 arguing that unauthorized congregations were not illegal.[17]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/36/Jules_Armand_Dufaure.jpg/96px-Jules_Armand_Dufaure.jpg)
![Baudry d'Asson apprehended by Colonel Riu [fr], military commander of the Palais-Bourbon, and the chasseurs of the guard post.](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Baudry_d%27Asson_1880.jpg/97px-Baudry_d%27Asson_1880.jpg)


![The rue de Sèvres [fr] at six o'clock in the morning: a Jesuit on the arm of a right-wing member of parliament walks through the cheering and praying crowd.](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/83/Expulsion_J%C3%A9suites_1880_0.jpg/96px-Expulsion_J%C3%A9suites_1880_0.jpg)







![The Abbey administrators who reported the siege to the Aix-en-Provence Court of Appeal [fr].](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/94/Siege_de_Frigolet_2.jpg/89px-Siege_de_Frigolet_2.jpg)