Ewaso Ng'iro
| Ewaso Ng'iro Uaso Nyiro or Lagh Dera | |
|---|---|
 Ewaso Ng'iro in Shaba National Reserve, Kenya | |
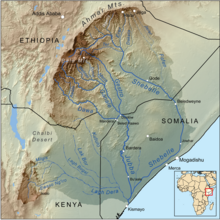 Map of the Jubba/Shebelle drainage basin. The Ewaso Ng'iro-Lagh Dera is located in the south. | |
| Location | |
| Country | Kenya |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Mount Kenya |
| Mouth | |
• elevation | 600 m (2,000 ft) |
| Length | 700 km |
| Basin size | 231.000 km² |

Ewaso Ng'iro, also called Ewaso Nyiro, is a river in Kenya which rises on the west side of Mount Kenya and flows north, then east and finally south-east, passing through Somalia where it joins the Jubba River.[1] The river's name is derived from the local community's language, and means river of brown or muddy water. Downstream, the intermittent stream in Somalia is also called Lagh Dera.
The upper basin of the Ewaso Ng'iro River is 15,200-square-kilometre (5,900 sq mi).[2] The river has a continuous water supply due to the glaciers on Mount Kenya. Ewaso Ng'iro feeds into Lake Ol Bolossat, the only lake in Nyandarua County and the larger Central Kenya,[3][4][5] and crosses seven arid to semi-arid landscapes. It is characterized by vastly different physiographic features and species and has become a fundamental component to the survival of the wildlife, as well as the expansion of the human population and socio-economic developments. Water, the limited land resource provided by the Ewaso Ng’iro watershed, is unevenly distributed throughout the higher and lower regions of the catchment due to the large percentage necessary to maintain agricultural practices and climatic changes (Mutiga, Su, and Woldai 3).

In the arid north of Kenya, water means life. The waters of this great river draw wildlife in great numbers to its banks, creating an oasis of green. Samburu, Shaba and Buffalo Springs National Reserves in Northern Kenya teem with wildlife in an otherwise arid land, because of the water of the river. Below Saricho, the river expands into the Lorian Swamp, a large area of wetlands.[6] The ecological diversity throughout the catchment is unique to the Ewaso Ng’iro watershed specifically, as it originates from the high agriculturally potent lands of Mount Kenya, right at Thome Area of Nanyuki-Laikipia County, that means the exact start point of this river is at the Thome village where it is formed out of convergence of Naromoru River, sourcing water from Mt. Kenya, and Ngarinyiru River sourcing water from Aberdares and it flows over the following seven arid to semi-arid land districts of Meru, Laikipia, Samburu, Isiolo, Wajir, Marsabit, and Garissa (Said et al. 14). Following the independence of Kenya, the stretches of land covered by the Ewaso Ng’iro watershed shifted ownership from the colonial farmers to small-scale farmers (Thenya et al. 2). The catchment became a main resource for the small-scale farmers to support their agropastorial practices and developing livelihoods (Thenya et al. 2).
Ewaso Narok River is one of its tributaries. Thomson's Falls near Nyahururu town is located along Ewaso Narok.
Resource availability
[edit]“Kenya’s renewable supply of fresh water is less than 650 cubic meters per capita per year, making it one of the most water-scarce countries in the world” states the African Development Fund (African Development Fund 6). Although the Ewaso Ng’iro is the largest of five water catchments in Kenya, a shortage in natural resource availability has become prevalent ever so increasingly in the past few years (Said et al. 5).
Climate Change
The tributaries that drain into the catchment have progressively began to dry up, particularly throughout the dry seasons of the year (Mutiga, Su, and Woldai 102). Other changes such as “unreliable rainfall patterns and quantities and decreasing discharge during the low flow periods” also have significant impacts on all aspects of the Ewaso Ng’iro watershed (Aeschbacher, Liniger and Weingartner 155,156). The water catchment lies predominantly through arid to semi arid landscapes where the annual levels of rainfall and precipitation have seemingly decreased over the years (Mutiga, Su, and Woldai 102). As uneven water distribution has become a complex issue, the ability to support the ecosystem's vegetation and wildlife will decrease, and human populations and developments will be faced with ongoing sustainability challenges.
Evapotranspiration
Such phenomenon as mentioned above may be interconnected to the evapotranspiration levels in the catchment, however, obtaining a direct measurement of such energy exchanges has proven to be difficult and complex process (Mutiga, Su, and Woldai 100).
Environmental sustainability
[edit]The Ewaso Ng’iro watershed stretches over a diverse variety of ecosystems from the high regions of Mount Kenya to the lower arid to semi arid regions of land. Each ecosystem delivers a unique contribution to the land and people of Kenya as they interact with one another to achieve a sustainable equilibrium.
Wetland
The wetland ecosystems which are located in the higher regions of Mount Kenya provide a natural water filtration system, a variety of plant and animal species, and nutrients for all other species and ecosystems (Said et al. 8). Due to the recent population influx, Kenya's wetlands have deteriorated, and establishments have become a major hindrance to the ecosystem services (Thenya et al. 6).
Agro-ecosystem
Agro-ecosystems are common in developments in the higher regions of the Ewaso Ng’iro watershed and contribute the forage necessary to sustain wildlife, livestock, as well as human populations (Said et al. 8). By supporting and sustaining all the different ecosystems throughout the Ewaso Ng’iro watershed, it will allow for the environment to flourish as naturally as possible. Disturbances in the ecosystems will impact the growth and sustainability of other species.
Developmental sustainability
[edit]The importance of sustaining the ecosystems that are supported by the Ewaso Ng’iro watershed are crucial for the established populations on both a personal and developmental level. Since 2009, the population that resides in the Ewaso Ng’iro catchment has increased by slightly over 1.5 million in the past 42 years (Said et al. 14). This increase has been seen in particularly the middle to upper regions of the catchment mainly for agropastorial settlements. (Kiteme and Gikonyo 333). A large percentage of water is used by the upper regions of the catchment for irrigation of crops that contributes to the sustainability of “current and future degradation of ecosystems that affect the livelihoods and sustainability […] and long term efforts to reduce poverty (Payet and Obura 24). Human populations rely heavily on the environment and ecosystems as a means of support in terms of “provisioning services, regulating services, cultural services, and supporting services” as briefly outlined by The Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (Said et al. 9). In the more densely populated areas around the Ewaso Ng’iro catchment, market establishments have begun forming with the small scale farmers as a major contributor (Said et al. 27). The over exploitation of natural resource in the upper regions of the catchment are increasingly making development process and agricultural practices more difficult for those situated near the lower regions (Mutiga, Su, and Woldai 102). Humans have increased their livelihood and developments through the utilization of the ecosystems in the Ewaso Ng’iro catchment however, severe consequences may arise due to the exploitation and climatic changes that strongly influence the availability to access water.
Conflicts
[edit]Due to the arid to semi arid landscapes which surround the Ewaso Ng’iro watershed, levels of availability to access and utilize the water decrease as the demand for human consumption and agricultural systems increase (Said et al. 14). Populations situated near the higher regions of the catchment have much greater availability to the natural resource, and have utilized them for agropastorial purposes. However, when these practices are paired up with Kenya's arid to semi arid landscape climatic changes, the downstream population's access to the natural resource has become much more limited (Weismann et al. 12). Those situated in the lower regions of the Ewaso Ng’iro watershed have faced unremitting pressure to access the natural resource to continue to sustain their growing human population and developments (Kiteme and Gikonyo 332). According to the Mountain and Research Development team, “these transboundary problems add to the cultural, religious and political tensions existing in most societies which today are being increasingly integrated into the world economy” (Hurni 386).
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Rough Guide Map Kenya (Map) (9 ed.). 1:900,000. Rough Guide Map. Cartography by World Mapping Project. Rough Guide. 2006. ISBN 1-84353-359-6.
- ^ Makali, Samuel; Boniface Kiteme (September 2005). "The Upper Ewaso Ng'iro Basin, Kenya". Network for Water and Sanitation. Archived from the original on 2007-05-24. Retrieved 2007-06-21.
- ^ Mulli, Thorn. "Discovering Central Kenya's only natural lake". The Standard. Retrieved 2019-02-23.
- ^ "A wreath for Ewaso Ng'iro". Daily Nation. Archived from the original on 2019-02-23. Retrieved 2019-02-23.
- ^ "Why lake that feeds Ewaso was declared protected area". The Star, Kenya. Retrieved 2019-02-23.
- ^ R. H. Hughes, J. S. Hughes (1992). A directory of African wetlands. IUCN. ISBN 2-88032-949-3.
