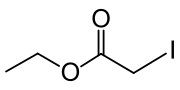
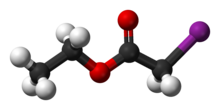
Ethyl iodoacetate
Appearance
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Ethyl iodoacetate | |
| Other names
Ethyl 2-iodoacetate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.816 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| ICH2CO2CH2CH3 | |
| Molar mass | 214.002 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Clear, light yellow to orange liquid |
| Density | 1.808 g/mL |
| Boiling point | 179 to 180 °C (354 to 356 °F; 452 to 453 K) |
| −97.6·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H300, H314 | |
| P280, P301+P310+P330, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P305+P351+P338+P310 | |
| Related compounds | |
Related esters
|
|
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Ethyl iodoacetate is an organic compound with the chemical formula ICH2CO2CH2CH3. It is a derivative of ethyl acetate.[2][3] Under normal conditions, the compound is a clear, light yellow to orange liquid.
Applications
[edit]Used by the British during World War I, it was codenamed SK gas, for the initials of South Kensington, where it was developed.[4]
Like many alkyl iodides, ethyl iodoacetate is an alkylating agent, which makes it useful in organic synthesis, yet toxic. Ethyl iodoacetate is also a lachrymatory agent.
References
[edit]- ^ GHS: Sigma-Aldrich 242934
- ^ "242934 ALDRICH Ethyl iodoacetate". Sigma Aldrich. sigmaaldrich.com. Retrieved 1 June 2017.
- ^ "Ethyl iodoacetate". chemicalbook.com. Retrieved 1 June 2017.
- ^ Timothy T. Marrs; Robert L. Maynard; Frederick Sidell (4 April 2007). Chemical Warfare Agents: Toxicology and Treatment. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 682–. ISBN 978-0-470-06002-5.
