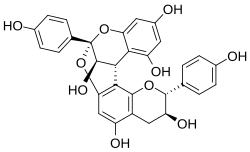
Geranin A
Appearance
(Redirected from Epi-afzelechin-(4β→8, 2β→O→7)-afzelechin)
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(1S,5R,6S,13R,21S)-5,13-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4,12,14-trioxapentacyclo[11.7.1.02,11.03,8.015,20]henicosa-2(11),3(8),9,15,17,19-hexaene-6,9,17,19,21-pentol
| |
| Other names
Epi-afzelechin-(4β→8, 2β→O→7)-afzelechin
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H24O10 | |
| Molar mass | 544.50 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Geranin A is an A type proanthocyanidin of the propelargonidin sub type. Its structure is epi-afzelechin-(4β→8, 2β→O→7)-afzelechin.
Geranins A and B can be found in Geranium niveum and show antiprotozoal activity.[1]
References
[edit]- ^ Calzada, F; Cerda-García-Rojas, CM; Meckes, M; Cedillo-Rivera, R; Bye, R; Mata, R (1999). "Geranins a and B, new antiprotozoal A-type proanthocyanidins from Geranium niveum". Journal of Natural Products. 62 (5): 705–9. doi:10.1021/np980467b. PMID 10346950.
